Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Metals and Non-metals
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: The metals obtained from their molten chlorides by the process of electrolytic reduction are: (1 Mark)
(a) Gold and silver
(b) Calcium and magnesium
(c) Aluminium and silver
(d) Sodium and iron
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Calcium and magnesium
Highly reactive metals (like sodium, magnesium, calcium) are obtained by electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides — the chapter gives magnesium and calcium as examples of metals produced this way.
Q2: The most common method of extraction of metals from their oxide ores is: (1 Mark)
(a) Reduction with carbon
(b) Reduction with hydrogen
(c) Reduction with aluminium
(d) Electrolytic reduction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Reduction with carbon
Metals that are moderately reactive are usually extracted from their oxide ores by reducing them with carbon.
Example:
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Here, carbon acts as a reducing agent and converts zinc oxide into metallic zinc.
Q3: Reaction between two elements A and B, forms a compound C. A loses electrons and B gains electrons. Which one of the following properties will not be shown by compound C? (1 Mark)
(a) It has high melting point.
(b) It is highly soluble in water.
(c) It has weak electrostatic forces of attraction between its oppositely charged ions.
(d) It conducts electricity in its molten state or aqueous solution.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) It has weak electrostatic forces of attraction between its oppositely charged ions.
When element A loses electrons and element B gains electrons, an ionic compound is formed. Ionic compounds have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions, giving them high melting points, solubility in water, and electrical conductivity in molten or solution form. Hence, statement (c) is incorrect.
Q4: Aluminium powder is used in thermit welding because: (1 Mark)
(a) Its reaction with iron is highly exothermic.
(b) When it is heated with iron (III) oxide, molten iron is obtained.
(c) When it is heated with iron (III) oxide, molten aluminium oxide is obtained to join railway tracks.
(d) Its melting point is low as compared to iron and a molten alloy of iron and aluminium is formed on heating which is used to join railway tracks.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) When it is heated with iron (III) oxide, molten iron is obtained.
Aluminium reacts with iron(III) oxide in a highly exothermic thermit reaction, producing molten iron used for welding railway tracks.
Fe₂O₃ + 2Al → 2Fe(l) + Al₂O₃ + Heat
Q5: The products formed when Aluminium and Magnesium are burnt in the presence of air respectively are: (1 Mark)
(a) Al₃O₄ and MgO₂
(b) Al₂O₃ and MgO
(c) Al₃O₄ and MgO
(d) Al₂O₃ and MgO₂
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Al₂O₃ and MgO
When aluminium and magnesium burn in air, they react with oxygen to form their respective metal oxides.
4Al + 3O₂ → 2Al₂O₃
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
Q6: A metal, M, displaces iron from aqueous solution of ferrous sulphate but fails to do so in case of aqueous solution of aluminium sulphate. The metal M is: (1 Mark)
(a) Magnesium
(b) Copper
(c) Lead
(d) Zinc
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Zinc
Zinc is more reactive than iron and can displace it from ferrous sulphate solution:
Zn + FeSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Fe
However, zinc is less reactive than aluminium, so it cannot displace aluminium from aluminium sulphate solution.
Q7: The colour of the solution observed after about 1 hour of placing iron nails in copper sulphate solution is: (1 Mark)
(a) Blue
(b) Pale green
(c) Yellow
(d) Reddish brown
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Pale green
When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution, a displacement reaction occurs where iron displaces copper:
Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu
Copper gets deposited as a reddish-brown layer, and the solution turns pale green due to the formation of iron(II) sulphate.
Q8: Assertion (a): Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid.
Reason (R): Nitric acid is a strong reducing agent and reduces the hydrogen produced in the reaction to water. (1 Mark)
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
When metals react with nitric acid, hydrogen gas is not evolved because nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent and it oxidises the hydrogen formed to water, while itself getting reduced to nitrogen oxides (N₂O, NO, or NO₂).
Q9: Assertion (A): The metals high up in the reactivity series cannot be obtained from their compounds by heating with carbon.
Reason (R): Displacement reactions can also be used to obtain metal. (1 Mark)
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Metals high up in the reactivity series (like sodium, calcium, and aluminium) cannot be obtained by heating with carbon because they have a stronger affinity for oxygen than carbon does. They are extracted by electrolytic reduction, not by displacement reactions.
Q10: Assertion (A): Ductility is that property of metals which enables copper to be used in making cooking utensils.
Reason (R): Copper is a metal which is ductile as well as malleable. (1 Mark)
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Copper is used for making cooking utensils because it is malleable and a good conductor of heat, not because of its ductility. Ductility allows a metal to be drawn into wires, while malleability allows it to be beaten into thin sheets.
Q11: Assertion (a): Brass is prepared by first melting copper and then dissolving tin into it in a definite proportion.
Reason (R): The primary metal of brass is copper. (1 Mark)
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Assertion (a) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, not copper and tin. Therefore, the statement about tin is false. However, the reason is true because copper is indeed the primary metal in brass.
Q12: Assertion (a): Silver chloride turns grey in sunlight.
Reason (R): Decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine takes place by sunlight. (1 Mark)
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both Assertion (a) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (a).
Silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because it decomposes into silver and chlorine gas when exposed to light:
2AgCl → 2Ag + Cl₂
The grey colour is due to the formation of metallic silver.
Q13: The main observations while performing the experiment of burning magnesium ribbon in air are:
(i) Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.
(ii) A white powder is formed.
(iii) Magnesium ribbon vapourises.
(iv) Aqueous solution of the white powder turns blue litmus to red. (1 Mark)
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) (i) and (ii)
When magnesium ribbon burns in air, it burns with a dazzling white flame and forms a white powder of magnesium oxide (MgO).
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
The oxide formed is basic in nature, so it turns red litmus blue, not the other way around.
Q14: While burning a magnesium ribbon in air, list two safety measures which should be followed. Also state two observations of this activity. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Safety measures:
- Wear protective goggles to avoid harm from the bright white light produced.
- Do not look directly at the burning magnesium ribbon.
Observations:
- Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.

- A white powder of magnesium oxide (MgO) is formed after burning.
Reaction:
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
Q15: (a) In common practice silver is recovered from silver nitrate solution by the use of copper metal. Name the type of reaction that takes place in this process and give the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) Name the method used for refining silver. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) The reaction between copper and silver nitrate is a displacement reaction.
In this process, copper being more reactive than silver displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
As a result, silver metal is deposited and copper nitrate is formed in the solution.
Chemical equation:
Cu + 2AgNO₃ → Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2Ag
(b) The method used for refining silver is electrolytic refining.
In this process, impure silver is made the anode and a thin strip of pure silver is made the cathode.
A solution of silver nitrate is used as the electrolyte. When electric current is passed, pure silver deposits on the cathode, and impurities settle at the bottom as anode mud.
Q16: Cinnabar is an ore of a metal 'X'. When this ore is heated in air, it is first converted into oxide of 'X' (XO) and then reduced to metal 'X' on further heating. Identify metal 'X' and write chemical equations for the reactions that occur in the above processes. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The metal ‘X’ is mercury (Hg). Its ore, cinnabar (HgS), when heated in air, first forms mercuric oxide (HgO), which on further heating is decomposed to produce liquid mercury and oxygen gas.
The reactions involved are:
Reactions:
- 2HgS + 3O₂ → 2HgO + 2SO₂
- 2HgO → 2Hg + O₂
Q17: Name a metal found in the earth's crust
(i) in free state and
(ii) in the form of its compound.
State where each of these metals are placed in the reactivity series of metals. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Gold (Au) is found in the free state in the earth’s crust. It is placed low in the reactivity series, as it is least reactive.
(ii) Zinc (Zn) is found in the form of its compounds, such as zinc oxide (ZnO) or zinc sulphide (ZnS). It is placed in the middle of the reactivity series.
Q18: (a) Show the formation of magnesium chloride by electron transfer. Write the name of the cation and anion present in the compound formed. (Atomic Number of Mg=12, Cl=17) (2 Marks)
OR
(b) How is zinc extracted from its ore? Name the processes involved in the extraction and write chemical equations for the reactions that occur during these processes. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Magnesium has the electronic configuration 2,8,2 and chlorine has 2,8,7.
Magnesium loses its two outermost electrons to form a magnesium ion (Mg²⁺), while each chlorine atom gains one electron to form a chloride ion (Cl⁻).
These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form magnesium chloride (MgCl₂).
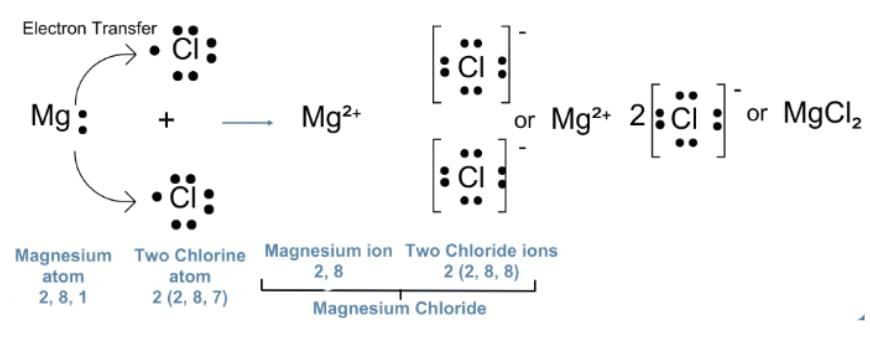 OR
OR
(b) Zinc is extracted from its ore zinc blende (ZnS) by two main steps — roasting and reduction.
- Roasting: The zinc sulphide ore is heated in the presence of excess air to form zinc oxide.
2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂ - Reduction: The zinc oxide formed is then heated with carbon to obtain metallic zinc.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Q19: (a) With the help of an activity, explain the conditions under which iron articles get rusted. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Aim: To find the conditions under which iron articles get rusted.
Activity:
Take three clean iron nails and place them in three separate test tubes labeled A, B, and C.
In test tube A, add ordinary water and cork it.
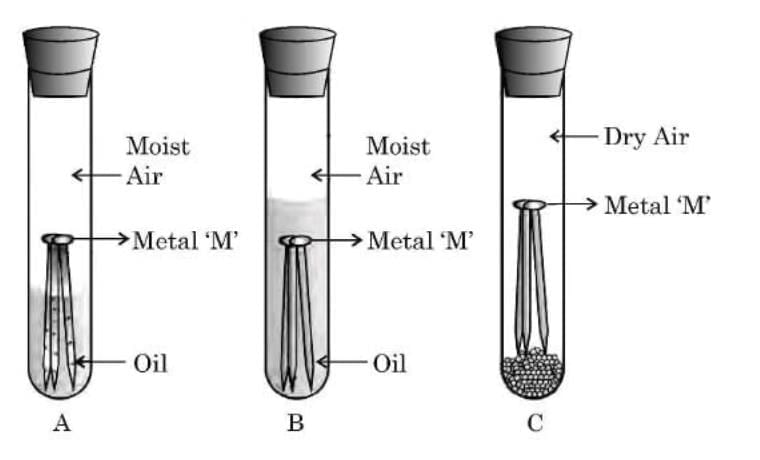
In test tube B, add boiled distilled water (to remove dissolved air), pour a thin layer of oil over it, and cork it.
In test tube C, put some anhydrous calcium chloride and cork it tightly.
Observation:
After a few days, the iron nails in test tube A get rusted.
The nails in test tube B and test tube C do not rust.
Conclusion:
Iron articles rust only when both air (oxygen) and water (moisture) are present together.
The rust formed is hydrated iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O).
OR
(b) (i) Name two metals which react violently with cold water. List any three observations which a student notes when these metals are dropped in a beaker containing water.
(ii) Write a test to identify the gas evolved (if any) during the reaction of these metals with water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) The two metals which react violently with cold water are Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K).
Observations:
- The metals move rapidly on the surface of water due to the evolution of a gas.
- The reaction is highly exothermic — the evolved heat may ignite the metal, producing a flame (potassium gives a lilac flame, sodium gives a golden-yellow flame).
- The gas evolved during the reaction burns with a pop sound, confirming it is hydrogen gas.
Reactions:
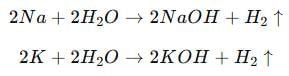
(ii) Test for hydrogen gas:
Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube — the gas burns with a ‘pop’ sound, confirming the presence of hydrogen gas.
Q20: (a) "Displacement reactions also play a key role in extracting metals in the middle of the reactivity series." Justify this statement with two examples.
(b) Why can metals high up in the reactivity series not be obtained by reduction of their oxides by carbon? (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) Metals in the middle of the reactivity series, such as iron, zinc, and lead, can be extracted from their oxides using displacement reactions.
Highly reactive metals like aluminium act as reducing agents and displace less reactive metals from their oxides.
Examples:
- 3MnO₂ + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al₂O₃ + Heat
- Fe₂O₃ + 2Al → 2Fe + Al₂O₃ + Heat
These reactions are highly exothermic and produce the metal in the molten state (as in the thermit reaction).
(b) Metals high up in the reactivity series (like sodium, calcium, aluminium) cannot be obtained by carbon reduction because they have a greater affinity for oxygen than carbon. Therefore, their oxides cannot be reduced by carbon and are instead extracted by electrolytic reduction of their molten compounds.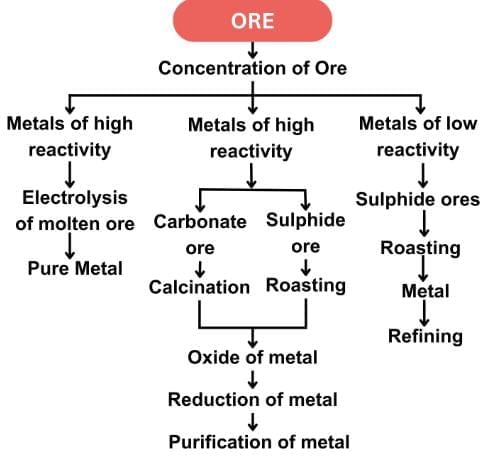
Q21: Name and describe the most widely used method for refining impure metals? (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
The most widely used method for refining impure metals is Electrolytic Refining.
In this process:
- The impure metal is made the anode.
- A thin strip of pure metal is made the cathode.
- A solution of the metal salt (such as copper sulphate for copper) is used as the electrolyte.
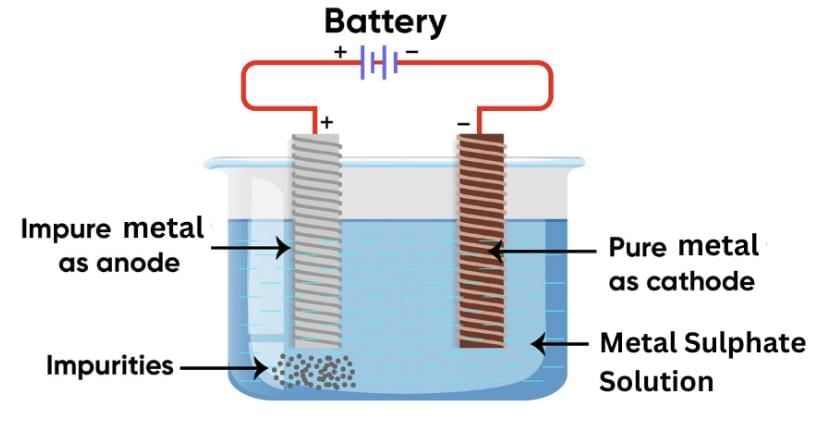
When electric current is passed:
- The pure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte.
- An equal amount of pure metal is deposited on the cathode.
- Insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode as anode mud.
Example:
For copper refining —
Impure copper (anode), pure copper (cathode), and acidified CuSO₄ solution (electrolyte):
Cu (anode) → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu (cathode)
Q22: Design an activity to show that metals are good conductors of heat and have high melting points. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Aim: To show that metals are good conductors of heat and have high melting points.
Materials required:
An aluminium or copper wire, a stand with a clamp, a pin, wax, and a burner or candle.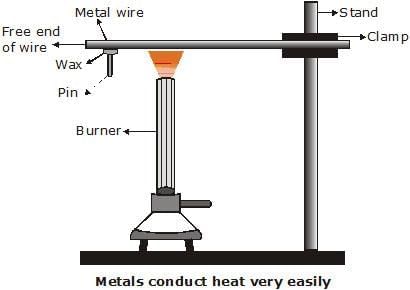
Procedure:
- Clamp one end of the metal wire to the stand and fix a pin to the free end using wax.
- Heat the wire near the clamped end using a spirit lamp or burner.
- Observe what happens after some time.
Observation:
After heating, the pin fixed with wax falls off because the heat travels quickly through the metal wire and melts the wax.
Conclusion:
This shows that metals are good conductors of heat.
Also, the metal wire itself does not melt easily, proving that metals have high melting points.
Q23: Samples of four metals A, B, C, and D were added one by one to the following solutions. The results obtained were tabulated as follows: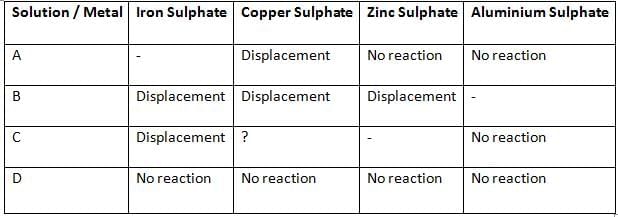
(i) Which is the least reactive metal?
(ii) What would be observed if C is added to a solution of copper sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C, and D in the order of their decreasing reactivity. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) D — it shows no reaction with any of the salt solutions, so it is the least reactive metal.
(ii) Displacement will occur as ‘C’ is able to displace Fe from its solution, indicating that it is more reactive than Fe. However, ‘C’ is not able to displace Al, which means it is less reactive than Al.
Hence, the metal ‘C’ is more reactive than Cu and is placed above Cu in the reactivity series. Therefore, ‘C’ will displace Cu from its salt solution.
When C is added to copper sulphate, C displaces copper from the solution and copper metal gets deposited while a salt of C is formed:
C + CuSO₄ → C-SO₄ (aqueous) + Cu (s)
(iii) Order of decreasing reactivity: B > C > A > D.
Reasoning (brief):
B displaces Fe, Cu and Zn, so B is the most reactive of the four.
C displaces Fe but not Zn, so C is less reactive than Zn but more reactive than Fe (hence above A).
A displaces Cu but not Fe or Zn, so A is less reactive than Fe and Zn but more reactive than Cu.
D shows no displacement with any salt, so it is the least reactive.
Q24: (a) Observe the following diagram showing an experiment to determine the conditions under which a metal ‘M’ corrodes.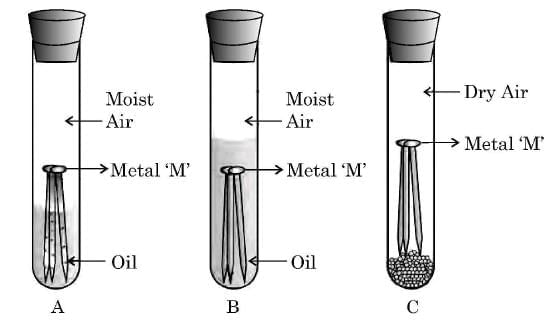
List your observations in each of the three cases A, B and C with reason, if the metal ‘M’ is generally protected against corrosion by the method of galvanisation. (3 Marks)
Ans: ______
OR
(a) Show the formation of Aluminium Nitride (AlN) by the transfer of electrons. [At. no. of Al = 13; N = 7]
(b) "Ionic compounds are solids and are generally brittle and break into pieces when pressure is applied." Give reason to justify the statement.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Observations:
- Test tube A: The metal ‘M’ rusts (corrodes) because both moisture and air are present. Corrosion requires the presence of water and oxygen together.
- Test tube B: The metal ‘M’ does not rust, because oil prevents the entry of air into the water. Hence, even though moisture is present, air is absent.
- Test tube C: The metal ‘M’ does not rust, because the air is dry, and there is no moisture to support corrosion.
Reason:
Metal ‘M’ (such as iron) rusts only in the presence of both air and moisture.
Galvanisation:
In galvanisation, a thin layer of zinc is coated on iron to protect it from corrosion. Zinc acts as a sacrificial metal, preventing rusting even if the coating is damaged.
OR
(a) 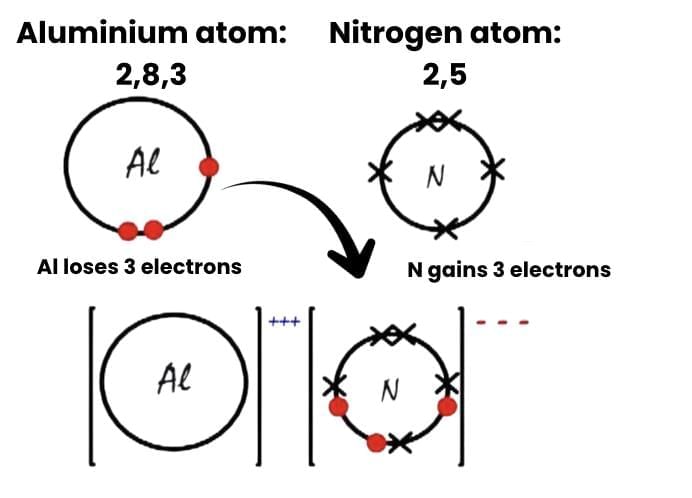 (b) Regarding the properties of ionic compounds, they are typically solid at room temperature due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions, which hold them in a rigid lattice structure. When pressure is applied to an ionic solid, the layers of ions can shift. If like charges are forced together, they repel each other, leading to the compound breaking into pieces. This brittleness is a characteristic feature of ionic compounds.
(b) Regarding the properties of ionic compounds, they are typically solid at room temperature due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions, which hold them in a rigid lattice structure. When pressure is applied to an ionic solid, the layers of ions can shift. If like charges are forced together, they repel each other, leading to the compound breaking into pieces. This brittleness is a characteristic feature of ionic compounds.
Q25: (i) Consider the following metals: K, Ca, Al, Cu, Ag, Fe
Select from the above metals, a metal which:
I. Does not react with oxygen even at high temperature.
II. Reacts with oxygen at ordinary temperature and forms a protective oxide layer which prevents the metal from further oxidation.
III. Catches fire when kept in the open.
IV. Does not burn in oxygen but the hot metal is coated with a black coloured oxide layer.
(ii) What are amphoteric oxides? With the help of balanced chemical equations show that aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide.
(iii) What are alkalis? Give one example. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i)
I. Does not react with oxygen even at high temperature: Ag.
II. Reacts with oxygen at ordinary temperature and forms a protective oxide layer: Al.
III. Catches fire when kept in the open: K.
IV. Does not burn but on heating the hot metal is coated with a black oxide layer: Cu.
(ii) An amphoteric oxide is one that reacts with both acids and bases to give salts and water. Aluminium oxide shows this behaviour:
With acid:
Al₂O₃ + 6HCl → 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂O
With base:
Al₂O₃ + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO₂ + H₂O
(iii) Alkalis are substances produced when certain metal oxides dissolve in water; they are basic (alkaline) in nature. Example: sodium oxide dissolves in water to give sodium hydroxide:
Na₂O + H₂O → 2NaOH — NaOH (sodium hydroxide) is an example of an alkali.
Q26: Many pure metals like copper, iron, and gold are very soft and as such are considered unsuitable for certain uses. Metallic objects around us such as cooking utensils, statues, ornaments, guns, etc., are actually not made up of pure metals. Instead of pure metals, alloys are used in the design of most of the useful objects. Making alloys enhances the basic properties of a metal which is the primary constituent (metal) of an alloy.
(I) How does electrical conductivity and melting point of a metal change when it is converted to its alloy by mixing a small amount of an element in it? (1 Mark)
(II) Name an alloy used for welding two wires together in an electric circuit. Write its major constituents. (1 Mark)
(III) (a) What are alloys?
(b) How is 'Brass' (an alloy) prepared? (2 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(I) When a metal is converted into an alloy, both its electrical conductivity and melting point decrease.
(II) The alloy used for welding electrical wires is Solder, which is made up of lead (Pb) and tin (Sn).
(III) (a) Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or of a metal and a non-metal, prepared by first melting the primary metal and then dissolving the other elements in definite proportions before cooling.
(b) Brass is prepared by mixing copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) — copper is the main constituent and zinc is added to improve hardness and strength.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: A metal and a non-metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature are respectively: (2024)(a) Bromine and Mercury
(b) Mercury and Iodine
(c) Mercury and Bromine
(d) Iodine and Mercury
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Mercury is a metal that is liquid at room temperature.
- Bromine is a non-metal that is also liquid at room temperature.
- Thus, the correct answer is (c) Mercury and Bromine.
Q2: Oxides of aluminum and zinc are: (2024)
(a) acidic
(b) basic
(c) amphoteric
(d) neutral
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Oxides of aluminum and zinc are classified as amphoteric.
This means they can react with both acids and bases, displaying the following characteristics:
- They can act like acids in some reactions.
- They can behave like bases in other reactions.
- This versatility makes them important in various chemical processes.
Q3: The metals which are found in both free state as well as combined state are: (2024)
(a) Gold and platinum
(b) Platinum and silver
(c) Copper and silver
(d) Gold and silver
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The correct answer is (c) Copper and silver. These metals can be found in their pure, uncombined form (free state) in nature, as well as in compounds with other elements (combined state). This means they can exist both as standalone metals and as part of various minerals.
Q4: A metal ‘X’ is used in the thermit process. When ‘X’ is heated with oxygen, it gives an oxide ‘Y’, which is amphoteric in nature. ‘X’ and ‘Y’ respectively are: (2024)
(a) Mn, MnO2
(b) Al, Al2O3
(c) Fe, Fe2O3
(d) Mg, MgO
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Metal ‘X’ is aluminium, used in the thermit process. When aluminium is heated with oxygen, it produces aluminium oxide (Y), which is amphoteric. This means it can react with both acids and bases.
- Metal X: Aluminium (Al)
- Oxide Y: Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Nature: Amphoteric
Q5: Source-based/case-based questions with 2 to 3 short subparts. (2024)
The metals produced by various reduction processes are not very pure. They contain impurities, which must be removed to obtain pure metals. The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
(i) What is the cathode and anode made of in the refining of copper by this process?
(ii) Name the solution used in the above process and write its formula.
(iii) (A) How does copper get refined when electric current is passed in the electrolytic cell?
OR
(iii) (B) You have two beakers ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing copper sulphate solution. What would you observe after about 2 hours if you dip a strip of zinc in beaker ‘A’ and a strip of silver in beaker ‘B’? Give reasons for your observations in each case.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The cathode is made of pure copper and the anode is made of impure copper.
(ii)) The solution used in this process is acidified copper sulphate, with the formula CuSO4.
(iii) (A) When electric current is passed through the electrolytic cell:
- Pure copper from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte.
- An equivalent amount of pure copper is deposited on the cathode.
- Soluble impurities enter the solution.
- Insoluble impurities settle at the bottom of the anode, forming anode mud.
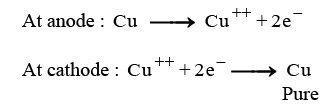
OR
(iii) (B) Observations after 2 hours:
- Beaker A: The blue colour of the solution fades or becomes colourless.
- Reason: Zinc is more reactive than copper, displacing it from the solution.
- Beaker B: No change in colour is observed.
- Reason: Silver is less reactive than copper, so no reaction occurs.
Q6: Assertion - Reason based questions: These questions consist of two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: (2024)
Assertion (A) : Different metals have different reactivities with water and dilute acids.
Reason (R): Extraction of a metal from its ore depends on its position in the reactivity series.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A) is correct because different metals react differently with water and acids. However, while Reason (R) is also true, it explains how we extract metals rather than directly explaining why their reactivities vary.
Q7: State reasons for the following: (2024)
(a) Zinc oxide is an amphoteric oxide.
(b) Sodium metal is stored in bottle filled with kerosene oil.
(c) In the reactions of nitric acid with metals, generally hydrogen gas is not evolved.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Amphoteric oxide (zinc oxide) reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salt and water.
Reaction with acids: Zinc oxide reacts with acids to form a salt and water. For example:
ZnO+2HCl→ZnCl2+H2OReaction with bases: Zinc oxide reacts with strong bases to form a salt (zincate). For example:
ZnO+2NaOH+H2O→Na2[Zn(OH)4]
(b) If kept in open, sodium metal reacts vigorously with air and catches fire / kerosene oil does not allow sodium to come in contact with air and catch fire.
(c) Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the hydrogen produced in the reaction to water. This is due to the strong oxidizing nature of nitric acid, which reduces itself to nitrogen oxides (like NO, NO₂) while oxidizing the hydrogen.
Q8: (a) State giving reason the reduction process to obtain the following metals from their compounds: (2024)
(i) Mercury,
(ii) Copper and
(iii) Sodium
OR
(b) State giving reason for the change in appearance observed when each of the following metal is exposed to atmospheric air for some time:
(i) Silver,
(ii) Copper and
(iii) Iron
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) Reduction Process- Roasting
Reason: Mercury has low reactivity.
(ii) Reduction Process- Roasting
Reason: Copper has low reactivity.
(iii) Reduction Process- Electrolytic Reduction.
Reason: Sodium has high reactivity.
OR
(b) (i) Change in appearance - White to black colour.
Reason: Silver sulphide is formed.
(ii) Change in appearance – Reddish brown to green colour.
Reason: Basic Copper Carbonate is formed.
(iii) Change in appearance- Grey to brown colour.
Reason: Rust (iron oxide) is formed.
Q9: Name the ore of mercury and state the form in which it is found in nature. Write the chemical equations along with the condition required for the reactions involved in the extraction of mercury from its ore. (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ore of mercury: Cinnabar
Form in nature: Sulphide ore
The extraction of mercury from cinnabar involves the following chemical reactions:
- When heated in air, cinnabar (HgS) converts to mercuric oxide (HgO):
- 2HgS(s) 3O2(g) → 2HgO(s) 2SO2(g)
- Further heating of mercuric oxide produces mercury:
- 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l) O2(g)
Q10: Some metals react with acids to produce salt and hydrogen gas. Illustrate it with an example. How will you test the presence of this gas? (2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 (g)
To test for the presence of hydrogen gas:
- Bring a burning matchstick near the gas.
- If hydrogen is present, it will burn with a pop sound.
Q11: Assertion - Reason based questions: These questions consist of two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: (CBSE 2024)
Assertion ( A): A piece of zinc metal gets reddish-brown coating when kept in copper sulphate solution for some time.
Reason (R): Copper is more reactive metal than zinc.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Assertion (A): A piece of zinc metal gets a reddish-brown coating when kept in copper sulfate solution for some time. This is true. When zinc is placed in a copper sulfate solution, a displacement reaction occurs where zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate. The copper then deposits on the zinc surface as a reddish-brown coating.
Reason (R): Copper is more reactive than zinc. This is false. In the reactivity series, zinc is more reactive than copper, which is why zinc can displace copper from copper sulfate.
Since Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false, the correct answer is (c) (A) is true, but (R) is false
Q12: Consider the following compounds: (CBSE 2024)
FeSO4; CuSO4; CaSO4; Na2CO3
The compound having maximum number of water of crystallisation in its crystalline form in one molecule is ______.
(a) FeSO4
(b) CuSO4
(c) CaSO4
(d) Na2CO3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Na2CO3
Na2CO3 ⋅ 10H2O (hydrated sodium carbonate) has the largest concentration of water molecules in its crystalline structure, with 10 molecules per formula unit.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: The following questions are source based/case based questions. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow. The melting points and boiling points of some ionic compounds are given below: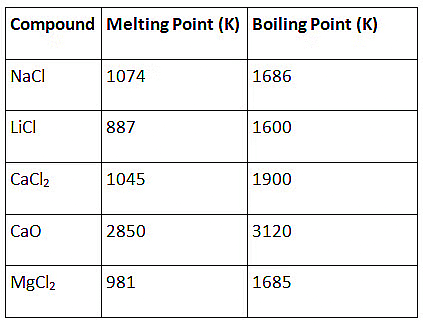
These compounds are termed ionic because they are formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal. The electron transfer in such compounds is controlled by the electronic configuration of the elements involved. Every element tends to attain a completely filled valence shell of its nearest noble gas or a stable octet.
(i) Show the electron transfer in the formation of magnesium chloride.
(ii) List two properties of ionic compounds other than their high melting and boiling points.
(iii) (A) While forming an ionic compound say sodium chloride how does sodium atom attain its stable configuration?
(B) Give reasons:
(i) Why do ionic compounds in the solid state not conduct electricity?
(ii) What happens at the cathode when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Transfer of electrons during the creation of magnesium chloride: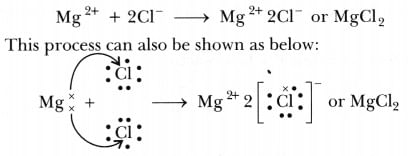 (ii) The two properties of ions Compounds are:
(ii) The two properties of ions Compounds are:
(a) Solubility: Electrovalent compounds are generally soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene, petrol, etc.
(b) Conduction of Electricity:
- The conduction of electricity through a solution involves the movement of charged particles.
- A solution of an ionic compound in water contains ions, which move to the opposite electrodes when electricity is passed through the solution.
- Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure.
- But ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state.
- This is possible in the molten state since the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome due to the heat.
- Thus, the ions move freely and conduct electricity.
- Sodium atom has one electron in its outermost shell.
- If it loses the electron from its M shell then its L shell now becomes the outermost shell and that has a stable octet.
- The nucleus of this atom still has 11 protons but the number of electrons has become 10, so there is a net positive charge giving us a sodium cation Na+.
- On the other hand chlorine has seven electrons in its outermost shell and it requires one more electron to complete its octet.
- If sodium and chlorine were to react, the electron lost by sodium could be taken up by chlorine.
- After gaining an electron, the chlorine atom gets a unit negative charge, because its nucleus has 17 protons and there are 18 electrons in its K, L and M shells.
- This gives us a chloride anion Cl–.
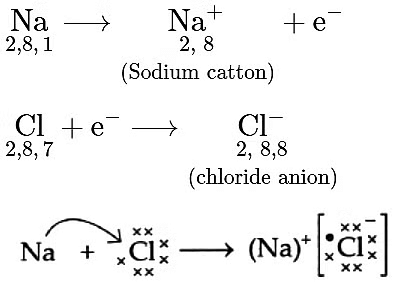
(B) (i)
- The conduction of electricity through a solution involves the movement of charged particles.
- A solution of an ionic compound in water contains ions, which move to the opposite electrodes when electricity is passed through the solution.
- Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because the movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure.
- But ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state.
- This is possible in the molten state since the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome due to the heat.
- Thus, the ions move freely and conduct electricity.
Q2: The following questions are source-based/case-based questions. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow. Metals are required for a variety of purposes. For this, we need their extraction from their ores. Ores mined from the earth are usually contaminated with many impurities which must be removed before the extraction of metals. The extraction of pure metal involves the following steps:
(1) Concentration of ore
(2) Extraction of metal from the concentrated ore
(3) Refining of metal
(a) Name an ore of mercury and state the form in which mercury is present in it.
(b) What happens to zinc carbonate when it is heated strongly in a limited supply of air?
(c) The reaction of a metal A with Fe2O3 is highly exothermic and is used to join railway tracks.
(I) Identify the metal A and name the reaction taking place.
(II) Write the chemical equation or the reaction of metal A with Fe2O3. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) An ore of mercury is cinnabar, and mercury is present in it in the form of mercury sulfide (HgS).
(b) When zinc carbonate (ZnCO3) is heated strongly in a limited supply of air, it undergoes thermal decomposition to produce zinc oxide (ZnO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O):
ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
(c) (I) The metal is aluminium (Al), and the reaction is called the thermite reaction.
(II) The chemical equation for the reaction of iron (A) with iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) is:
2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(s)
This reaction is highly exothermic and is used in various industrial applications, including joining railway tracks due to its high heat generation and the ability to melt and fuse metals.
Q3: A metal ‘X’ is used in thermite process. When X is burnt in air it gives an amphoteric oxide 'Y'. 'X' and 'Y' are respectively:
(a) Fe and Fe2O3
(b) Al and Al2O3
(c) Fe and Fe3O4
(d) Al and Al3O4 (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In the thermite process, aluminum (Al) is used because of its high reactivity and ability to reduce metal oxides, such as iron oxide, to produce molten iron.
When aluminum is burnt in air, it forms aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), which is an amphoteric oxide (meaning it can react with both acids and bases).
Therefore, X is aluminum (Al) and Y is aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), making the correct answer (b) Al and Al₂O₃.
Q4: Almost all metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature. But some metal oxides show both basic as well as acidic behaviour. Different metals show different reactivities towards oxygen. Some react vigorously while some do not react at all.
(A) What happens when copper is heated in air? (Give the equation of the reaction involved).
(B) Why are some metal oxides categorised as amphoteric? Give one example.
(C) Complete the following equations: 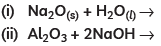
OR
(C) On burning sulphur in oxygen a colourless gas is produced.
(i) Write chemical equation for the reaction.
(ii) Name the gas formed.
(iii) State the nature of the gas.
(iv) What will be the action of this on a dry litmus paper? (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Copper is a reactive element. When it is heated in the air, it forms black copper oxide (CuO).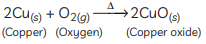 (B) Metal oxides are categorised as amphoteric oxides that react with both acids as well as bases to create salts and water. Amphoteric oxides, among many others, include lead oxide and zinc oxide. These oxides are oxygen compounds that show both acidic and basic characteristics. These undergo a neutralisation reaction to form water and salt.
(B) Metal oxides are categorised as amphoteric oxides that react with both acids as well as bases to create salts and water. Amphoteric oxides, among many others, include lead oxide and zinc oxide. These oxides are oxygen compounds that show both acidic and basic characteristics. These undergo a neutralisation reaction to form water and salt.
Example: 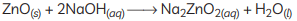
(C) 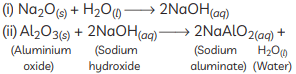
OR
(C) (i) 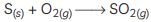
(ii) The gas formed is sulphur dioxide which is colourless and poisonous.
(iii) The nature of the gas is acidic.
(iv) SO2 gas has no effect on dry litmus paper because it shows acidic behavior only in the presence of water
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: A clear solution of slaked lime is made by dissolving Ca(OH)2 in an excess of water. This solution is left exposed to air. The solution slowly goes milky as a faint white precipitate form. Explain why a faint white precipitate forms, and support your response with the help of a chemical equation.Keerti added dilute Hydrochloric acid to four metals and recorded her observations as shown in the table given below: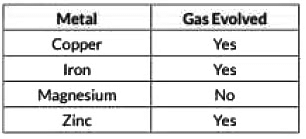 Select the correct observation(s) and give chemical equation(s) of the reaction involved. (2022)
Select the correct observation(s) and give chemical equation(s) of the reaction involved. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When a clear solution of slaked lime (Ca(OH)2) is exposed to air, carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere dissolves into the solution and reacts with the dissolved calcium hydroxide. This reaction produces calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), which is insoluble and appears as a faint white precipitate (“milky” appearance). The chemical equation is: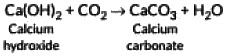 Thus, the “milkiness” arises from the formation of solid calcium carbonate.
Thus, the “milkiness” arises from the formation of solid calcium carbonate.
Copper (below H)
- Does not react with dilute HCl to give hydrogen gas.
- No visible reaction under normal conditions.
Iron (above H)
- Does react to produce hydrogen gas.
- Reaction: Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Magnesium (above H)
- Does react quite vigorously, giving hydrogen gas.
- Reaction: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Zinc (above H)
- Does react, evolving hydrogen gas.
- Reaction: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Therefore, corrected table becomes :

So, the correct observations are for iron and zinc only.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: Why is potassium kept immersed in kerosene? (2021 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Potassium is kept immersed in kerosene because it reacts vigorously with air and water.
- The reaction with air forms a layer of potassium oxide on the surface, while the reaction with water produces potassium hydroxide.
- Both of these reactions release hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable.
- By keeping potassium immersed in kerosene, it is protected from air and water, preventing any unwanted reactions.
Q2: Give a reason why:
(a) gold and silver are used for making jewellery.
(b) a few metals are used for making cooking utensils. (2021 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Gold and silver are highly malleable metals so, they are used for making jewellery.
(b) Metals used to make cooking utensils are chosen not just for their good heat conduction but also for their relatively low reactivity. You generally don’t want a metal that reacts with food or with the conditions (high temperature, presence of water vapor, mild acids in food, etc.). Here’s how it ties to reactivity:
- Metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series (like copper, silver, gold) do not readily react with acids or water under normal cooking conditions.
- Metals that form stable oxide layers (like aluminum, which is higher in the series) are protected from further corrosion by that oxide coating.
- Alloys such as stainless steel (predominantly iron but mixed with chromium/nickel) also resist corrosion because chromium forms a very adherent oxide layer that protects the iron underneath.
Thus, metals like iron (in stainless steel), aluminum, and copper are commonly used for utensils because:
- They do not corrode easily or leach into food.
- They are good conductors of heat.
- They maintain a protective surface layer (oxide or alloy layer), preventing further reaction
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: Compare in tabular form the reactivities of the following metals with cold and hot water: (2020)(a) Sodium
(b) Calcium
(c) Magnesium
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: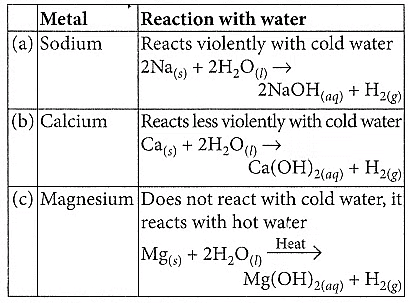
Q2: (a) Write the electron dot structure of Ca (At. No. 20) and O (At. No. 8).
(b) Show the formation of calcium oxide by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in this compound.
(d) List four important characteristics of this compound. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 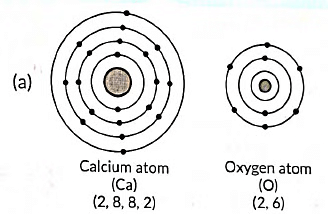
(b) The formation of calcium oxide (CaO) involves the transfer of electrons. Calcium (Ca) donates two electrons to oxygen (O) to form Ca2+ cation and O2- anion. The ionic bond is formed between these ions to create calcium oxide.
(c) In calcium oxide (CaO), the ions present are Ca2+ (calcium cation) and O2- (oxygen anion).
(d) Four important characteristics of calcium oxide (CaO) are:
- It is a white, crystalline solid.
- It has a high melting and boiling point.
- It is an ionic compound.
- It is commonly used as a desiccant and in cement production.
Q3: List three differentiating features between the processes of galvanisation and alloying. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three differentiating features between the processes of galvanisation and alloying are as follows:
- Definition: Galvanisation is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to iron or steel to prevent corrosion, while alloying is the process of combining two or more metals or metals with a non-metal to create a new material with enhanced properties.
- Purpose: Galvanisation is primarily used to protect the base metal from corrosion by providing a sacrificial layer of zinc, whereas alloying is done to improve specific properties of the metal, such as strength, hardness, or resistance to corrosion.
- Procedure: In galvanisation, the metal is coated with zinc through processes like hot-dip galvanisation or electroplating. On the other hand, alloying involves melting and mixing different metals or adding non-metallic elements to create an alloy with the desired properties.
Q4: (a) Complete and balance the following chemical equations: (2020)
(i) AI2O3 + HCI →
(ii) K2O + H2O →
(iii) Fe + H2O →
(b) An element 'X' displaces iron from the aqueous solution of iron sulphate. List your observations if the element 'X’ is treated with the aqueous solutions of copper sulphate, zinc sulphate and silver nitrate. Based on the observations arrange X, Zn, Cu and Ag in increasing order of their reactivities.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(i) AI2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
(ii) K2O + H2O → 2KOH
(iii) Fe + 2H2O → Fe(OH)2 + H2
(b) Observations:
- When element 'X' is treated with copper sulphate solution, no reaction occurs.
- When element 'X' is treated with zinc sulphate solution, 'X' displaces zinc from the solution, resulting in the formation of 'X' sulphate and zinc metal.
- When element 'X' is treated with silver nitrate solution, 'X' displaces silver from the solution, resulting in the formation of 'X' nitrate and silver metal.
Based on the observations, the increasing order of reactivities is:
Ag<Cu<Zn<X
Q5: (i) By the transfer of electrons, illustrate the formation of a bond in magnesium chloride and identify the ions present in this compound.
(ii) Ionic compounds are solids. Give reasons.
(iii) With the help of a labelled diagram show the experimental set-up of steam action on a metal. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 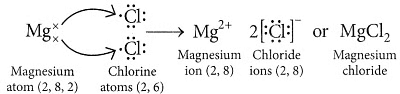
(ii) Ionic compounds are solids because the particles that make up ionic compounds are held together by strong electrostatic bonds.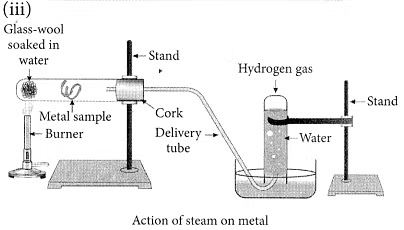
Q6: (a) (i) Write two properties of gold that make it the most suitable metal for ornaments.
(ii) Name two metals which are the best conductors of heat.
(iii) Name two metals that melt when you keep them on your palm.
(b) Explain the formation of the ionic compound CaO with an electron-dot structure. Atomic numbers of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8 respectively. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) The malleability and ductility properties of gold make it suitable for ornaments. Also, beacause of less reactive natureof gold, it's prefered for making jewellery.
(ii) Silver and gold.
(iii) Gallium and caesium have so low melting points that they melt even on keeping them in the palm.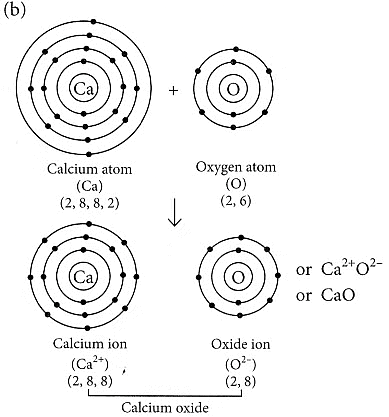
(b) Formation of the ionic compound CaO (calcium oxide) with an electron-dot structure:
Calcium oxide (CaO) is formed through the transfer of electrons between calcium (Ca) and oxygen (O) atoms. Calcium, with an atomic number of 20, loses two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of a noble gas (argon), while oxygen, with an atomic number of 8, gains two electrons to complete its valence shell.
The electron-dot structure of CaO can be represented as follows:
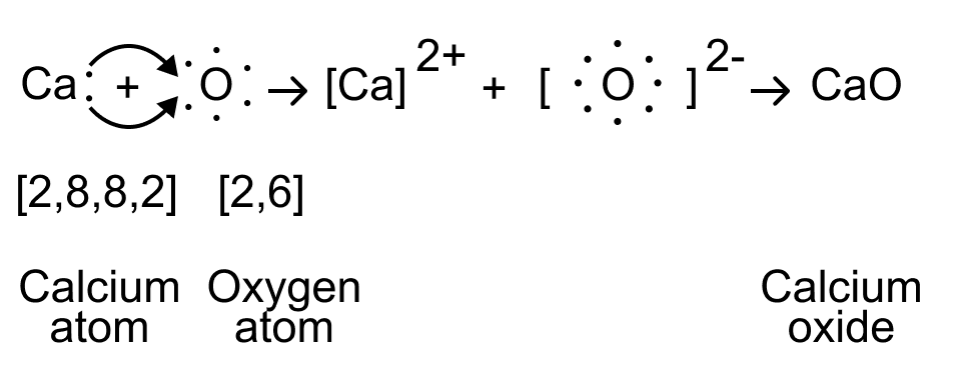
In this structure, the calcium atom loses its two valence electrons to oxygen, resulting in a Ca2+cation and an O2- anion. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms the ionic bond in calcium oxide (CaO).
Q7: Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium to their respective metals. Why? Where are these metals placed in the reactivity series? How are these metals obtained from their ores? Take an example to explain the process of extraction along with chemical equations. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sodium, magnesium and aluminium have a higher affinity towards oxygen than carbon because these are highly reactive metals. Hence, carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium to their respective metals. These metals are placed at the top of the reactivity series. Highly reactive metals like Na, Mg, Al, etc. are extracted by electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides or oxides. Electrolytic reduction is brought about by passing electric current through the molten state. Metal gets deposited at the cathode.
NaCl ⇌ Na+ + Cl–
At cathode : Na+ + e– → Na+
At anode : 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Q8: Write balanced chemical equations to explain what happens, when
(i) Mercuric oxide is heated.
(ii) A mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous sulphide is heated.
(iii) Aluminium is reacted with manganese dioxide.
(iv) Ferric oxide is reduced with aluminium.
(v) Zinc carbonate undergoes calcination. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) On heating, mercuric oxide decomposes to give mercury and oxygen.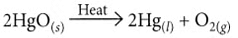
(ii) On heating a mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous sulphide, copper and sulphur dioxide are produced.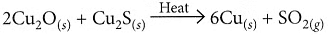
(iii) When aluminium is heated with manganese dioxide, manganese and aluminium oxide are formed.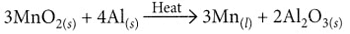
(iv) Ferric oxide reacts with aluminium to produce aluminium oxide and iron.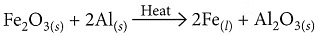
(v) On calcination, zinc carbonate produces zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.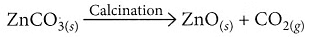
Q9: (a) Name the following: (CBSE 2020)
(i) Metal that can be cut by a knife
(ii) Lustrous non-metal
(iii) Metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature
(iv) Most malleable and ductile metal
(v) Metal that is the best conductor of electricity
(vi) Non-metal that can exist in different forms
(b) How are alloys better than metals? Give the composition of solder and amalgam.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) Sodium
(ii) Iodine
(iii) Mercury
(iv) Gold
(v) Silver
(vi) Carbon
(b) Alloys offer several advantages over pure metals:
- They are generally stronger.
- They resist corrosion better.
- They often have lower melting points.
- They usually have lower electrical conductivity.
The composition of: - Solder: An alloy of lead and tin.
- Amalgam: An alloy of mercury with another metal.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: What would a student report nearly after 30 minutes of placing duly cleaned strips of aluminium, copper, iron and zinc in freshly prepared iron sulphate solution taken in four beakers? (2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: After approximately 30 minutes, the student would observe that the strip of iron would start to show signs of corrosion or rusting. This is because iron is more reactive than copper, aluminium, and zinc and will displace the iron from the iron sulphate solution, forming iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
Explanation: When cleaned metal strips of aluminium (Al), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn) are each placed into separate beakers containing freshly prepared iron(II) sulphate (FeSO₄) solution, here’s what the student would observe after about 30 minutes:
Aluminium strip (Al)
- Above Fe in the reactivity series:
Al+FeSO4⟶Al2(SO4)3+Fe - Expected change: A brownish deposit of iron on the aluminium strip and possible fading of the greenish FeSO₄ solution.
- Above Fe in the reactivity series:
Copper strip (Cu)
- Below Fe in the reactivity series:
- Copper cannot displace iron from its salt.
- Expected change: No reaction; the copper strip remains unchanged, and the solution color stays the same.
- Below Fe in the reactivity series:
Iron strip (Fe)
- Same metal as in the solution:
- No net displacement reaction occurs because the metal and the dissolved ion are both iron.
- Expected change: No reaction; no visible change in the metal strip or the solution.
- Same metal as in the solution:
Zinc strip (Zn)
- Above Fe in the reactivity series:Zn+FeSO4⟶ZnSO4+ Fe
- Expected change: A brownish deposit of iron on the zinc strip and the FeSO₄ solution may lose its greenish color as Fe²⁺ ions are displaced.
- Al in FeSO₄: Brownish deposit (iron) forms on the strip.
- Cu in FeSO₄: No change.
- Fe in FeSO₄: No change.
- Zn in FeSO₄: Brownish deposit (iron) forms on the strip.
Q2: A pale green solution of ferrous sulphate was taken in four separate test tubes marked I, II, III and IV. Pieces of Cu, Zn and Al were dropped in test tubes II, III and IV respectively. In which case(s)
(a) Does the colour of the ferrous sulphate solution match with the colour in test tube (I)? Give reason.
(b) the colour of the ferrous sulphate solution will fade and a black mass will be deposited on the surface of the metal. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The colour of the ferrous sulphate solution in test tube (I) will match the colour of the solution in test tube II when a piece of copper is dropped in it. This is because copper is less reactive than iron and will not displace iron from ferrous sulphate solution, resulting in no change in the colour of the solution.
No reaction: Cu + FeSO4 → CuSO4 + Fe
(b) The colour of the ferrous sulphate solution will fade and a black mass will form on the metal surface in the following cases:
Zinc displacing iron:
Zn+FeSO4 ⟶ ZnSO4+Fe (s)- The FeSO₄ solution fades because Fe²⁺ ions are replaced by Zn²⁺.
- The displaced iron is deposited on the zinc strip, often appearing black or brown in color.
Aluminium displacing iron:
2Al+3FeSO4⟶Al2(SO4)3+3Fe (s)- Similarly, the pale green color of FeSO₄ solution fades as iron ions are displaced.
- The black/brown deposit of iron forms on the aluminium strip.
Q3: An ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence. Name the type of ore with one example. What steps will be required to obtain metal from the enriched ore? Also, write the chemical equations for the reactions involved in the process. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The ore that produces brisk effervescence when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid is a carbonate ore. One example of a carbonate ore is limestone (CaCO3).
Steps to obtain metal from the enriched ore:
- Calcination: The ore is heated strongly in the absence of air to convert it into metal oxide.
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) - Reduction: The metal oxide is then reduced using a suitable reducing agent, such as carbon or hydrogen, to obtain the metal.
CaO(s) + C(s) → Ca(s) + CO(g)
Q4: Silver articles become black when kept in the open for some time, whereas copper vessels lose their shiny brown surfaces and gain a green coat when kept in the open. Name the substances present in the air with which these metals react and write the name of the products formed. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The substances present in the air with which silver reacts are hydrogen sulphide (H2S) and sulphur compounds. Silver reacts with these substances to form a black layer of silver sulphide (Ag2S) on its surface.
- The substances present in the air with which copper reacts are moisture, carbon dioxide (CO2), and oxygen (O2). Copper reacts with these substances to form a green layer of copper carbonate (CuCO3) or copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) on its surface.
Q5: (a) List in tabular form three chemical properties based on which we can differentiate between a metal and a non-metal.
(b) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Most metals conduct electricity well.
(ii) The reaction of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) with heated aluminium is used to join cracked machine parts. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)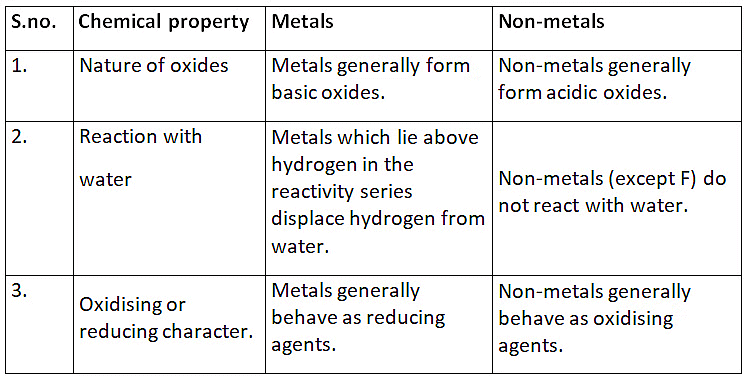
(b) (i) Metals conduct electricity due to the flow of free electrons present in them.
(ii) The reaction of iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3 with aluminium is highly exothermic and the iron produced melts. This molten iron is used to join cracked iron parts of machines and railway tracks.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: (a) What is reactivity series? How does the reactivity series help in predicting the relative activity of various metals?(b) Suggest different chemical processes used for obtaining a metal from its oxides of metals in the middle and top of the reactivity series. Support your answer with one example. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in order of their decreasing reactivity. It helps predict how metals will react with each other and with other substances.
Key points about the reactivity series:
- Metals higher in the series are more reactive.
- For example, if metal A can displace metal B from a solution, A is more reactive than B.
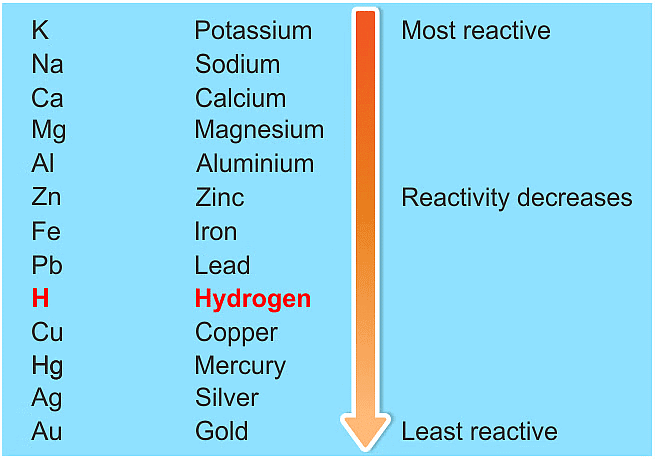 (b) The metals in the middle of the reactivity series are obtained from their ores by chemical reduction with a suitable reducing agent, e.g.
(b) The metals in the middle of the reactivity series are obtained from their ores by chemical reduction with a suitable reducing agent, e.g.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
The metals at the top of the series are obtained by electrolytic reduction of their molten orc.
Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
At cathode: 2Al3+ + 6e- → 2Al
At anode: O2- - 2e- → O
O + O → O2
Q2: (a) Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series from their carbonate ores.
(b) How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations. Draw a labelled diagram for the electrolytic refining of copper. (2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Extraction of metals of medium reactivity:
- The metals in the middle of the reactivity series include zinc, iron, and lead.
- These metals are typically found in the form of carbonates or sulphides.
- To extract the metal, the carbonate ores must first be converted to oxides, as it is easier to obtain metals from their oxides.
(b) Copper glance (Cu2S) when heated in air gets partially oxidised to copper oxide which further reacts with the remaining copper glance to give copper metal.
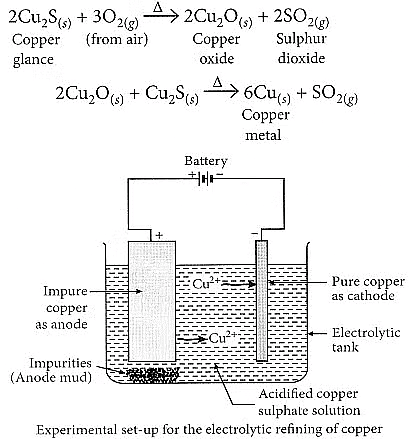
Electrolytic refining of copper:
- The process uses an electrolyte of acidified copper sulphate.
- The anode is made of impure copper, while the cathode is a strip of pure copper.
- When electric current is passed, pure copper is deposited on the cathode.
- Soluble impurities dissolve in the solution, and insoluble impurities settle as anode mud.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: Describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts. (2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: To find out the conditions under which iron rusts, you can perform the following activity:
- Take three test tubes and label them as A, B, and C.
- Fill test tube A with water, test tube B with water and oil, and test tube C with water and salt.
- Place a small piece of iron nail in each test tube and allow them to stand undisturbed for a few days.
- Observe the test tubes regularly and note any changes in the appearance of the iron nails.
- After a few days, check for the presence of rust on the iron nails in each test tube.
- Analyze the results and determine the conditions under which iron rusts.
Q2: A metal 'X' combines with a non-metal 'Y' by the transfer of electrons to form a compound Z.
(i) State the type of bond in compound Z.
(ii) What can you say about the melting point and boiling point of compound Z?
(iii) Will this compound dissolve in kerosene or petrol?
(iv) Will this compound be a good conductor of electricity? (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) The type of bond in compound Z is an ionic bond.
(ii) Ionic compounds generally have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive and negative ions.
(iii) Ionic compounds like compound Z do not dissolve in non-polar solvents like kerosene or petrol. They are only soluble in polar solvents.
(iv) No, compound Z will not be a good conductor of electricity in a solid state because the ions are held in a fixed position and cannot move. However, it may conduct electricity when dissolved in water or molten state as the ions become free to move and carry electric charge.
Q3: Why do some metal surfaces acquire a dull appearance when they are exposed to moist air? Write the colour acquired by the surfaces of copper and silver in such a situation and also write the chemical names of the substances due to which it happens. (Board Term I, 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When metal surfaces are exposed to moist air, they can undergo oxidation. This process results in the formation of metal oxides on the surface. The effects on different metals are as follows:
- Copper: The surface develops a greenish coating known as copper(II) oxide (CuO), which gives it a dull appearance.
- Silver: The surface forms a blackish coating called silver sulfide (Ag2S), also resulting in a dull look.
Q4: (a) Define corrosion.
(b) What is corrosion of iron called?
(c) How will you recognise the corrosion of silver?
(d) Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem?
(e) How can we prevent corrosion of iron? (Board Term I, 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(a) The process of slowly eating up metals due to their conversion into oxides, carbonates, sulphides, etc., by the action of atmospheric gases and moisture is called corrosion.
(b) The corrosion of iron is called rusting.
(c) Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air. This is due to the formation of a coating of black silver sulphide (Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
(d) Corrosion of iron is a serious problem. Every year large amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron articles. Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metals especially those of iron.
(e) Corrosion of iron is prevented by coating it with a layer of oil. The reason is that the layer of oil does not allow air and water to reach the surface of iron. Corrosion of iron can also be prevented by painting, greasing, galvanising, anodising, electroplating or making alloys.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Give a reason for the following: (Board Term I, 2016)(i) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most of the metals react with nitric acid.
(ii) Zinc oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(iii) Metals conduct electricity.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Most metals do not evolve hydrogen gas when they react with nitric acid because nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. It oxidizes hydrogen gas produced during the reaction to water and itself gets reduced to nitrogen oxides. Therefore, instead of hydrogen gas, the products obtained are nitrogen oxides.
(ii) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide because it shows both acidic and basic properties. It reacts with acids to form zinc salts and water, exhibiting basic characteristics. Additionally, it reacts with bases to form zincates and water, showing acidic properties. This ability to react with both acids and bases classifies it as an amphoteric oxide.
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 O
ZnO + 2NaOH + H2 O → Na2 (Zn (OH)4 )
(iii) Metals conduct electricity because they have a large number of free or delocalized electrons. These electrons are not bound to any particular atom and can move freely throughout the metal lattice. When a potential difference is applied across a metal, these free electrons can easily move and carry an electric current.
Q2: Reverse of the following chemical reaction is not possible:
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Justify this statement with reason. (Board Term I, 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The reverse of the given chemical reaction is not possible because it violates the principle of conservation of mass. In the forward reaction, zinc (Zn) displaces copper (Cu) from copper sulfate (CuSO4) to form zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) and copper. However, in the reverse reaction, copper cannot displace zinc from zinc sulfate, as copper is less reactive than zinc. Hence, the reverse of this reaction is not feasible.
Q3: (a) Define corrosion. (CBSE 2016)
(b) What is corrosion of iron called?
(c) How will you recognise the corrosion of silver?
(d) Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem?
(e) How can we prevent corrosion of iron?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) It is a process in which a metal reacts with substances present in the air to form surface compounds.
(b) Rusting.
(c) Black layer on its surface due to formation of Ag2S.
(d) It makes the metal weak and brittle, which is a serious problem.
(e) Oiling, painting, greasing, galvanisation, and alloying can prevent iron from corrosion.
Q4: (a) Define corrosion, what name is given to the corrosion of iron?
(b) Name the colour of the coating formed on silver and copper articles, when exposed to air.
(c) List two damages caused by corrosion and suggest how corrosion can be prevented. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) When a metal is attacked by substances around it, such as moisture, acids, etc., it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion. Corrosion of iron is called rusting.
(b) Coating formed on silver is black and that formed on copper is green.
(c) Damages caused by corrosion:
- It causes damage to car bodies and bridges.
- It damages iron railings and ships.
Prevention of corrosion:
- Corrosion can be prevented by oiling, painting, greasing and galvanising.
- Corrosion can be prevented by galvanising and alloying.
Q5: Give reasons for the following: (CBSE 2016)
(i) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction of metals.
(ii) Ionic compounds have generally high melting points.
(iii) Hydrogen is not a metal, but it has been assigned a place in the reactivity series of metals.
(iv) The galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken.
(v) The wires carrying current in homes have a coating of PVC.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) It is easier to convert metal oxides to metals as compared to carbonates and sulphides. Therefore carbonates are calcinated and sulphides are roasted to oxides.
(ii) There are electrostatic forces of attraction between the cations and anions in ionic compounds which are difficult to break. Therefore ionic compounds have high melting points.
(iii) Metals above hydrogen evolve hydrogen gas and metals below hydrogen do not evolve hydrogen when treated with an acid. That is when hydrogen has been assigned a place in the reactivity series of metals.
(iv) Even if the zinc layer is broken, it will preferentially be oxidised because it is more reactive than iron.
(v) The wires carrying current in homes have a coating of PVC. This is because PVC is an insulating substance and protects from electric shock.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: What happens when carbon dioxide is compressed in water at higher pressure? (CBSE 2015) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Carbonic acid is formed.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
Q2: Write the chemical equation for the reaction taking place when steam is passed over hot aluminium. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 2Al(s) + 3H2O (g) → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Q3: (a) Write the electron dot structure for chlorine (At No. 17) and calcium (At No. 20). Show the formation of calcium chloride by the transfer of electrons.
(b) Identify the nature of the above compound and explain the three physical properties of such compounds. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: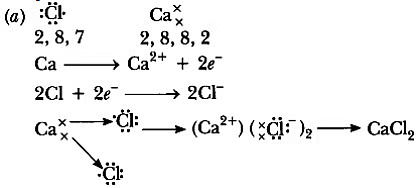
(b) It is an ionic compound.
Physical properties:
(i) It is hard and solid.
(ii) It has a high melting and boiling point.
(iii) It is soluble in water.
Previous Year Questions 2013
Q1: Explain the following:(A) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(B) Iron articles are galvanised.
(C) Metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg are never found in their free state in nature. (CBSE 2013)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Sodium and magnesium have a tendency to react with oxygen rather than carbon because these are highly reactive metals. They have a greater affinity for oxygen than for carbon. Hence, their oxides are stable. The reduction of these metallic oxides with carbon requires very high temperature and at that temperature, metals react with carbon to form their corresponding carbides. Hence, carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(B) Galvanisation is a process of formation of thin layer over metal surface. It prevents further contact of metal surface with atmosphere and reduces the corrosion level. So, iron articles are galvanised with a thin layer of zinc over them. Since zinc is more reactive than iron, it undergoes oxidation more readily than iron. As a result, iron articles remain protected.
(C) Metals such as Na, K, Ca and Mg are highly reactive metals and hence they are not found in their free state in nature. Na, K, Ca and Mg are alkali and alkaline Earth metals. They are the most reactive metals and readily react with atmospheric oxygen and other gases. Therefore, they are found in nature in the form of their compounds.
Previous Year Questions 2012
Q1: In nature, aluminium is found in combined state, whereas silver/gold are found in free state. Give reason. (CBSE 2012, 11, 10) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Silver and gold are least reactive metals and are often found in their native or free state. Aluminium is a very reactive metal and is never found in free state, but in combined state.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Metals and Non-metals
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. How do metals and non-metals react with acids? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of common metals and non-metals found in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What are some physical properties that distinguish metals from non-metals? |  |
| 5. Why are metals considered good conductors of electricity? |  |

















