NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Ecosystem | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
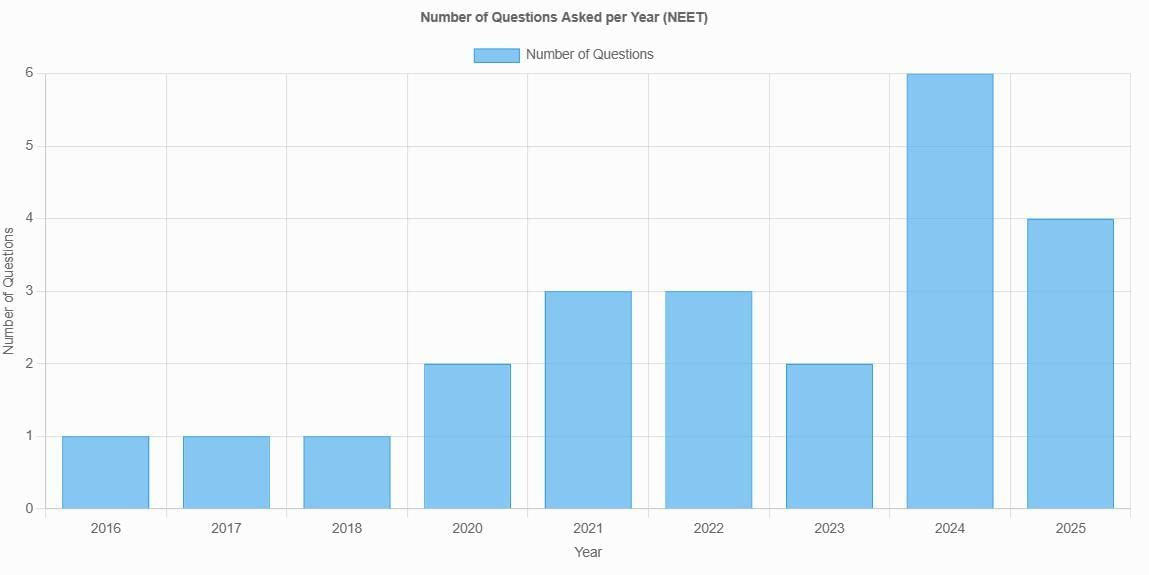
From 2016 to 2025, the number of questions on ecosystem topics in NEET exams showed a general upward trend, starting with 1 question each in 2016, 2017, and 2018, increasing to 2 in 2020, 3 in 2021 and 2022, dropping slightly to 2 in 2023, and peaking at 6 in 2024 before settling at 4 in 2025. This distribution indicates a growing emphasis on ecosystem concepts in recent years, with a total of 24 questions across these years. The questions were primarily focused on primary productivity (GPP vs. NPP), energy flow and pyramids, decomposition processes, and basic ecological principles, with no specific difficulty distribution provided in the data. Key focus areas included the unidirectional energy flow, limitations of ecological pyramids, nutrient cycling, and productivity units.
2025
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: The primary source of energy in an ecosystem is solar energy.
Statement II: The rate of production of organic matter photosynthesis in an ecosystem is called net primary productivity (NPP).
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from this options given below.
(a) Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
(c) Both statement I and statement II are correct
(d) Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
Ans: (a)
Statement I: The primary source of energy in an ecosystem is solar energy.
- This statement is correct. Solar energy is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems. Producers (like plants) capture this energy and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
Statement II: The rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis in an ecosystem is called net primary productivity (NPP).
- This statement is incorrect. The rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed gross primary productivity (GPP), not NPP.
- Net primary productivity (NPP) is the energy remaining after subtracting the energy used by producers for their own respiration from the gross primary productivity.
- Mathematically, NPP = GPP - Respiration (R).
Q2: Who is known as the father of Ecology in India? (NEET 2025)
(a) Ram Udar
(b) Birbal Sahni
(c) S. R. Kashyap
(d) Ramdeo Misra
Ans: (d)
- Ramdeo Misra is revered as the Father of Ecology in India. Born on 26 August 1908, Ramdeo Misra obtained Ph.D in Ecology (1937) under Prof. W. H. Pearsall, FRS, from Leeds University in UK.
- He established teaching and research in ecology at the Department of Botany of the Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi.
- His research laid the foundations for understanding of tropical communities and their succession, environmental responses of plant populations and productivity and nutrient cycling in tropical forest and grassland ecosystems.
- Due to his efforts, the Government of India established the National Committee for Environmental Planning and Coordination (1972) which, in later years, paved the way for the establishment of the Ministry of Environment and Forests (1984).
Other Options:
- S. R. Kashyap - Known for his work in bryology (study of mosses).
- Ram Udar - His contributions are mainly in the field of plant sciences.
- Birbal Sahni - A renowned paleobotanist known for his research on the fossils of the Indian subcontinent.
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: In ecosystem, there is unidirectional flow of energy of sun from producers to consumers.
Statement II: Ecosystems are exempted from 2nd law of thermodynamics.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
(c) Both statement I and statement II are correct
(d) Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
Ans: (a)
Statement I (Correct):
- Energy flow in an ecosystem is unidirectional. It originates from the sun, is captured by producers (plants) during photosynthesis, and then moves to consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores) and decomposers.
- Producers convert solar energy into chemical energy (e.g., glucose), which is then transferred to consumers when they eat plants or other consumers. Decomposers break down dead matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment but do not reverse the flow of energy.
- This unidirectional flow ensures energy is consistently passed through trophic levels but is never recycled back to the sun, adhering to the principle of energy flow in ecosystems.
Statement II (Incorrect):
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics applies to ecosystems. This law states that energy transformations lead to an increase in entropy (disorder), and some energy is always lost as heat during these processes.
- Ecosystems are not exempt from the Second Law of thermodynamics. They need a constant supply of energy to synthesise the molecules they require, to counteract the universal tendency toward increasing disorderliness.
- For example, when energy moves through trophic levels, a significant portion is lost as heat during respiration or metabolic activities. Only about 10% of the energy is transferred to the next trophic level, following the "10% law."
Q4: Which of the following is the unit of productivity of an Ecosystem? (NEET 2025)
(a) K Cal m−3
(b) (KCalm−2) yr−1
(c) gm−2
(d) KCalm−2
Ans: (b)
Productivity
- The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants, by the process of photosynthesis is called primary production.
- It is expressed in units of weight (g per m2) or energy (Kcal per m2).
- The rate of biomass production is called productivity and it is expressed as g m-2 yr-1 or (Kcal m-2) yr-1.
Primary productivity is further divided into two categories:
- Gross Primary Productivity (GPP): The rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is called gross primary productivity. A large amount of GPP is lost by plants during respiration.
- Net Primary Productivity (NPP):It is defined as the difference between gross primary productivity and the respiration losses (R) by plants.
- NPP = GPP - R;
- It is the measure of net available biomass for heterotrophs (herbivores and decomposers).
- Since net primary productivity is obtained after subtracting respiration losses from gross primary productivity; it is always less than gross primary productivity.
2024
Q1: In an ecosystem if the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of first trophic level is 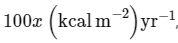 what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (NEET 2024)
what would be the GPP (Gross Primary Productivity) of the third trophic level of the same ecosystem? (NEET 2024)
(a) 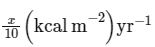
(b) 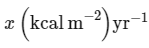
(c) 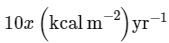
(d) 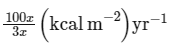
Ans: (c)
NPP at first trophic level would be the GPP for second trophic level. NPP at second trophic level would be GPP for third trophic level. Therefore, 100x (kcal/m2 /yr) would be GPP at second trophic level and 100x × 10% (kcal/m2 /yr) i.e., 10x (kcal/m2 /yr) energy would be GPP at third trophic level.
Q2: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
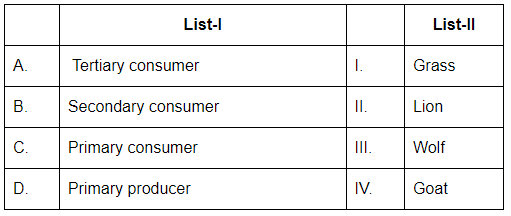
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(c) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
Ans: (d)
- A. Tertiary consumer: A tertiary consumer is typically a predator that is at the top of the food chain. Lions (II) are apex predators, meaning they are tertiary consumers in the food web.
- B. Secondary consumer: A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers (herbivores). Wolves (III) are secondary consumers because they prey on primary consumers like deer and other herbivores.
- C. Primary consumer: A primary consumer is an herbivore that feeds on plants. Goats (IV) are primary consumers, as they feed on grasses and other plants.
- D. Primary producer: A primary producer is an organism that makes its own food through photosynthesis, such as grass (I), which is at the base of the food chain.
Thus, the correct matching is A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I.
Q3: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is not related to the chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors.
Statement II: In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is faster if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
(c) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(d) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
Ans: (b)
Statement I: The rate of decomposition is indeed related to both the chemical composition of detritus (e.g., the presence of lignin, cellulose, and other compounds) and climatic factors (e.g., temperature, moisture, and humidity). So, Statement I is false because it incorrectly states that the rate of decomposition is not related to these factors.
Statement II: In fact, lignin and chitin are compounds that are known to be more resistant to decomposition, meaning that when detritus is rich in these substances, the decomposition rate is typically slower, not faster. Thus, Statement II is false.
Therefore, both statements are incorrect.
Q4: What is incorrect about an ecosystem? (NEET 2024)
(a) It can vary from a small-sized pond to a large-sized sea
(b) It may be anthropogenic in origin
(c) It may be temporary or permanent
(d) It involves the function of the flow of energy but not the recycling of nutrients
Ans: (d)
An ecosystem includes both the flow of energy and the cycling of nutrients. Energy flows through the ecosystem in one direction (from producers to consumers and decomposers), but nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and water are recycled within the ecosystem. Nutrient cycling is a crucial component of ecosystem function, alongside energy flow.
The other statements are correct:
- Statement 1: Ecosystems can indeed vary in size, from small environments like a pond to large ecosystems like the sea.
- Statement 2: Ecosystems can be anthropogenic (human-made), such as urban environments or agricultural landscapes.
- Statement 3: Ecosystems can be temporary (such as a temporary pond or a seasonal wetland) or permanent (like forests or oceans).
Thus, Statement 4 is incorrect because ecosystems involve both the flow of energy and the recycling of nutrients.
Q5: Consider the pyramid of energy of an ecosystem given below : (NEET 2024)
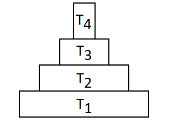 If T4 is equivalent to 1000 J, what is the value of T1?
If T4 is equivalent to 1000 J, what is the value of T1?
(a) 1000/10 J
(b) 1000/10 x 4 J
(c) 10,000 J
(d) 10, 00, 000 J
Ans: (d
In a pyramid of energy, the energy decreases as you move up the trophic levels. The amount of energy decreases typically by a factor of 10 for each successive level.
If T₄ = 1000 J, then:
- T₃ = 1000 × 10 = 10,000 J
- T₂ = 10,000 × 10 = 100,000 J
- T₁ = 100,000 × 10 = 1,000,000 J (or 10,00,000 J)
Thus, the value of T₁ is 10,00,000 J, which matches with option (d).
Q6: Which one of the following is not a limitation of ecological pyramids? (NEET 2024)
(a) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids
(b) It assumes a simple food chain that almost never exists in nature
(c) It accommodates a food web
(d) It does not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels
Ans: (c)
Ecological pyramids are a graphical representation of the trophic structure in an ecosystem. The limitations of ecological pyramids are as follows:
- (a) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids: This is true. Ecological pyramids do not account for decomposers (saprophytes), who play an essential role in nutrient cycling.
- (b) It assumes a simple food chain that almost never exists in nature: This is also true. Ecological pyramids typically represent a simple food chain, while in reality, ecosystems have complex food webs.
- (c) It accommodates a food web: This is incorrect. Ecological pyramids typically represent simple food chains, not food webs. A food web consists of multiple interconnected food chains, and ecological pyramids don't directly accommodate this complexity.
- (d) It does not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels: This is true. In nature, some species can occupy different trophic levels, but ecological pyramids do not account for this overlap.
Thus, (c) is the correct answer, as ecological pyramids do not accommodate a food web directly.
2023
Q1: Identify the correct statements: (NEET 2023)
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
C. Water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, D only
(b) C, D, E only
(c) D, E, A only
(d) A, B, C only
Ans: (d)
Let's evaluate each statement:
A. Detrivores perform fragmentation.
This statement is true. Detrivores, such as earthworms and beetles, break down detritus (dead organic material) into smaller pieces in a process called fragmentation.
B. The humus is further degraded by some microbes during mineralization.
This statement is true. Microbes, including bacteria and fungi, break down humus into inorganic nutrients in a process called mineralization.
C. Water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil and get precipitated by a process called leaching.
This statement is true. Leaching refers to the process where nutrients are washed away from the soil into lower layers or into bodies of water.
D. The detritus food chain begins with living organisms.
This statement is false. The detritus food chain begins with dead organic material or detritus, not living organisms.
E. Earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles by a process called catabolism.
This statement is false. The process by which earthworms break down detritus into smaller particles is called fragmentation, not catabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones, along with the release of energy.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Option D: A, B, C only.
Q2: In the equation GPP − R= NPP (NEET 2023)
GPP is Gross Primary Productivity
NPP is Net Primary Productivity
R here is ________.
(a) Photosynthetically active radiation
(b) Respiratory quotient
(c) Respiratory loss
(d) Reproductive allocation
Ans: (c)
In the equation GPP - R = NPP,
GPP stands for Gross Primary Productivity, NPP stands for Net Primary Productivity, and R represents the energy used by plants for their own metabolic processes, which is also known as Respiratory loss.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Statement I: Decomposition is a process in which the detritus is degraded into simpler substances by microbes.
Statement II: Decomposition is faster if the detritus is rich in lignin and chitin
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(b) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(c) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Ans: (b)
- Decomposition is the process by which decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances.
- The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. Decomposition is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars.
Q2: Detritivores break down detritus into smaller particles. This process is called: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Fragmentation
(b) Humification
(c) Decomposition
(d) Catabolism
Ans: (a)
(Detritivores break down detritus into smaller particles) e.g. earthworm. This process is called fragmentation.
Q3: The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called
(a) Net primary production
(b) Secondary production
(c) Primary production
(d) Gross primary production (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
- Productivity is the total amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area. Over a period of time by plants. This is also called Primary production.
- Productivity of consumer is called Secondary production.
2021
Q1: The amount of nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, etc. present in the soil at any given time, is referred to as the - (NEET 2021)
(a) Nutrient status of soil
(b) Standing state
(c) Standing crop
(d) Mineral state.
Ans: (b)
- Amount of all the inorganic substances or nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium present in soil at any given time, is referred as standing state.
- Amount of living material present in different trophic levels at a given time, is referred standing crop.
- Climax community is the last community in biotic succession which is relatively stable and is in near equilibrium with the environment of that area.
Q2: In the equation GPP - R = NPP (2021)
R represents:
(a) Environment factor
(b) Respiration losses
(c) Radiant energy
(d) Retardation factor
Ans: (b)
In the equation,
GPP - R = NPP
R refers to respiratory loss
GPP is gross primary productivity
NPP is net primary productivity
Q3: Which of the following statements is not correct? (2021)
(a) Pyramid of energy is always upright.
(b) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem is upright.
(c) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted.
(d) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally upright.
Ans: (d)
- Pyramid of biomass in a sea is generally inverted because the primary producers (phytoplanktons) have a lower biomass than that of succeeding zooplanktons, which further have a lower biomass than that of succeeding small fishes and so on.
- Pyramid of energy is the only pyramid that can never be inverted and is always upright. This is because some amount of energy in the form of heat is always lost to the environment at every trophic level of the food chain.
- In a grassland ecosystem, the number of producers is always maximum, followed by reducing number of organisms at second trophic level, third trophic level and other higher level (if present). Thus, the pyramid of number in grassland is upright.
2020
Q1: In relation to Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity of an ecosystem. Which one of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2020)
(a) Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity are one and same.
(b) There is no relationship between Gross primary productivity and Net primary productivity
(c) Gross primary productivity is always less than Net primary productivity.
(d) Gross primary productivity is always more than Net primary productivity.
Ans: (d)
Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Net primary productivity is GPP-respiration. Hence, gross primary productivity is always more than NPP.
Q2: Match the trophic levels with their correct species examples in grassland ecosystem. (NEET 2020)
(A) Fourth trophic level (i) Crow
(B) Second trophic level (ii) Vulture
(C) First trophic level (iii) Rabbit
(D) Third trophic level (iv) Grass
Select the correct option
(a) (A) → (iv), (B) → (iii), (C) → (ii), (D) → (i)
(b) (A) → (ii), (B) → (iii), (C) → (iv), (D) → (i)
(c) (A) → (i), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
(d) (A) → (iii), (B) → (ii), (C) → (i), (D) → (iv)
Ans: (b)
Grassland ecosystem is a terrestrial ecosystem. It includes various trophic levels. First trophic level (T1) – Grass Second trophic level (T2) – Rabbit Third trophic level (T3) – Crow Fourth trophic level (T4) – Vulture.
2018
Q1: What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data? (NEET 2018)
Secondary consumer : 120 g
Primary consumer : 60 g
Primary producer : 10 g
(a) Inverted pyramid of biomass
(b) Pyramid of energy
(c) Upright pyramid of numbers
(d) Upright pyramid of biomass
Ans: (a)
The given data depicts the inverted pyramid of biomass, usually present in aquatic ecosystem. Upright pyramid of biomass and numbers are not possible, as the data depicts primary producer is less than primary consumer and this is less than secondary consumers. Pyramid of energy is always upright.
2017
Q1: Which ecosystem has the maximum biomass? (2017)
(a) Grassland ecosystem
(b) Pond ecosystem
(c) Lake ecosystem
(d) Forest ecosystem
Ans: (d)
Forest ecosystem has the maximum biomass.
Some very high productive ecosystem are
– Tropical rain forest
– Coral reef
– Estuaries
– Sugarcane fields
2016
Q1: The term ecosystem was coined by (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) E. Haeckel
(b) E.Warming
(c) E.P. Odum
(d) A.G. Tansley
Ans: (d)
Sir Arthur George Tansley was an English botanist and a pioneer in the science of ecology who coined the term ecosystem.
|
78 videos|386 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Ecosystem - Biology Class 12
| 1. What is an ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How do biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biodiversity in an ecosystem? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact ecosystems? |  |
| 5. What are some ways to protect and conserve ecosystems? |  |

















