The Hindu Analysis - 25th Sept 2020 | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download

FRONT PAGE
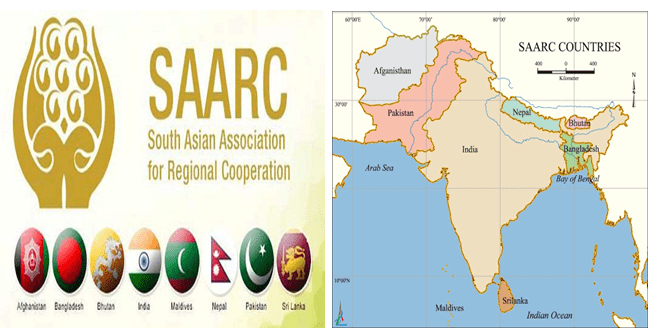
1. News: India, Pak. trade charges at SAARC, CICA meets
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains: GS 2
Sub Topic: India and its Neighbourhood- Relations.Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
Context
India and Pakistan crossed swords over terrorism and Jammu and Kashmir at the Foreign Minister’s meetings of the 8 nation South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and the 27nation Conference on Interaction and ConfidenceBuilding Measures in Asia (CICA).
Key particulars
(i) The SAARC platform to make a detailed statement on the resolution of “longstanding disputes”, a veiled reference to Jammu and Kashmir and New Delhi’s 2019 move to withdraw Article 370.
(ii) A similar statement was made at the CICA Special Ministerial the conference, that brings together Asian nations ranging from Russia and Central Asia to the Gulf and SouthEast Asia.
(iii) All SAARC nations including India and Pakistan, however, built a common stand on the need to cooperate in battling the coronavirus pandemic.
(iv) India has contributed $10 million to ‘COVID19 Information Exchange Platform (COINEX), a SAARC Food Bank mechanism, as well as the SAARC COVID19 Emergency Fund.

1. Bangladesh
2. Myanmar
3. Maldives
4. Nepal
5. Sri Lanka
6. Afghanistan
Which of the above are members of the SAARC group?
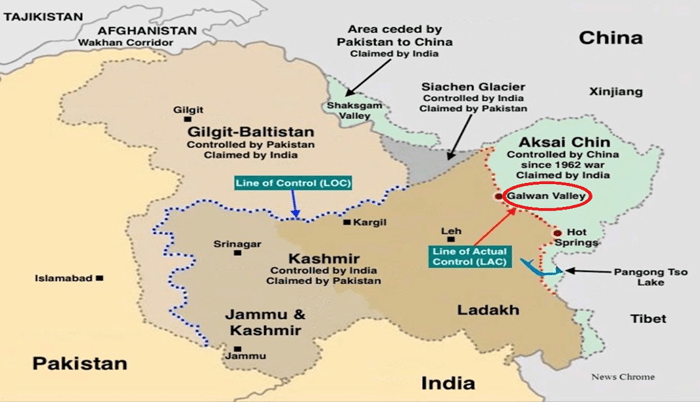
2. News: If PLA comes close, our troops can fire
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains: GS 1
Sub Topic: geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Context
Shots have been fired in the air on multiple occasions on the north and south banks of Pangong Tso in eastern Ladakh recently, and the Chinese have been given a clear message that pushing back Indian soldiers physically will not work any more, a senior government official said on Thursday.
PAGE NUMBER 4
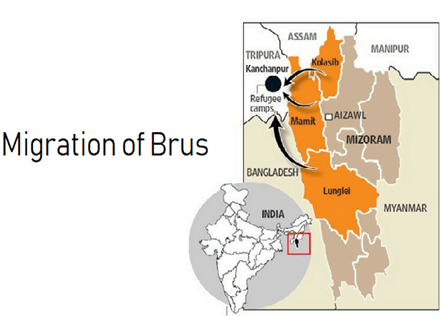
News: More opposition against Tripura Bru resettlement
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains: GS 1
Sub Topic: Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
Context
More local communities in Tripura are up in arms against the resettlement of the Brus displaced from adjoining Mizoram.
Key particulars
(i) Members of the Halam community, a Scheduled Tribe of Tripura, also called Riam, on Thursday prevented surveyors from assessing land in the Churaibari area in Dharmanagar Subdivision of North Tripura district.
(ii) The area borders Assam. People belonging to the Manipuri and Muslim communities in the area too protested the proposed settlement of Bru refugees in the area.
(iii) The sizeable Bengali, Mizo and local Brus – also called Reangs – have been against the settling of the Bru refugees near the areas they inhabit.
Ethnic violence
(i) More than 35,000 Brus displaced due to ethnic violence in Mizoram since 1997 are currently distributed among seven relief camps in these two subdivisions.
(ii) Leaders of the refugees, in January, signed a quadripartite agreement with the Centre and the Mizoram and Tripura governments for rehabilitation in Tripura instead of returning to “uncertainty” in Mizoram.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. The Brus are spread across Tripura and Mizoram only.
2. Brus displaced due to ethnic violence in Mizoram.
PAGE NUMBER 6
1. News: Shadow force apart, India needs a China plan
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Indian and World Geography - Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World
Mains: GS 2
Sub Topic: India and its Neighbourhood- Relations
Context
With a resolution to the standoff far away, New Delhi must study how Beijing has handled its other boundary disputes
Key particulars
(i) It is true that one or two rounds of talks cannot be expected realistically to resolve a situation that is, in many ways, even more complex than the 1986 SumdorongChu stand off and that took six years before the status quo was restored.
(ii) On the night of August29-30, in a surprise move, the Indian Army turned the tables on China by occupying heights that were not only of great tactical importance north and south of the Pangong Tso lake as also dominating the Spangur Gap.
(iii) During the era of the “Great Game”, the British employed natives to patrol their own lands, which included Tibetans.
(iv) The strategic importance of Tibet cannot be overemphasised. It is the roof of the world, with vast mineral and natural resources
(v) The mighty rivers that emanate from its expansive glaciers — such as the Brahmaputra, the Yangtse, the Yellow river, the Mekong, the Salween and the Indus — together with thousands of their tributaries have nurtured civilisations in peripheral countries for centuries.
(vi) The Kailash Mansarovar, which is centered in this region and with its spiritual overtones, tugs at the heart strings of every Indian. In an act of naked aggression, China occupied Tibet in 1959.
(vii) Mao Zedong declared, “Tibet is the palm that we shall occupy and then go after the five fingers,Ladakh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh
What must be done
(i) It would be fallacious to surmise that there will be any resolution to the ongoing stand-off between India and China in the near future.
(ii) Let us assume that both countries wish to avoid a full scale war considering the nuclear backdrop, theCOVID19 pandemic and also the economic downturn.
(iii) The road ahead will have to be evolved and based on a study of the manner in which China has negotiated its boundary disputes with 12 of its neighbours and the results achieved.
Which of the pairs given above is are correct?
Pass - State
Nathu La Pass - Sikkim
Shipki La Pass - Sikkim
Jelep La Pass - Himachal Pradesh
2. News: The foreign hand
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains: GS 2
Sub Topic: Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Context
NGOs fill in for the state; regulations should not stifle their functioning
Key particulars
(i) Amendments to the FCRA( Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010), drafted without consultation with stakeholders and passed with limited discussion in Parliament, further clip the wings of India’s battered civil society.
(ii) New regulations put onerous conditions on civil society organisations, and educational and research institutions that have partnerships, including of a financial nature, with foreign entities.
(iii) Passions overwhelm rationality in conversations on foreign influences, and it could well be true that a portion of such foreign assistance may be reaching the wrong hands.
(iv) Some of the restrictions appear well meaning, but could impact NGOs besides showing up India to be over-regulated.
(v) The International Commission of Jurists has said the new law was incompatible with international obligations and India’s own constitutional provisions on rights.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
1. A person who receives foreign contribution must use it only for the purpose for which the contribution is received
2. Under the act, the election candidates can accept foreign contribution
PAGE NUMBER 9
News: ‘China refused plea for help from northeast insurgents
UPSC Syllabus Heading
Prelims: Indian Polity and Governance - Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc
Mains: GS 1
Sub Topic: Social Empowerment, Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism.
Context
(i) The Assam government has informed a UAPA (Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act) tribunal that major extremist outfits of the northeast had contacted Chinese authorities for assistance in their “fight against India”, but the Chinese had refused to provide assistance directly or indirectly.
Key particulars
(ii) The affidavit, filed by the government before the tribunal in May, said the United National Liberation Front of West of South East Asia (UNLFWSEA), a Myanmar based conglomerate of banned outfits such as the NSCNK, ULFAI, NDFBS and KLO, had taken a resolution “to take assistance from a third nation” to achieve their goal.
(iii) The tribunal was constituted under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) after the Union Home Ministry extended the ban on the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) in November 2019 for five years.
(iv) After the Chinese refused, “as an alternative, UNLFWSEA looked for establishing nexus with Pakistan at any cost at the earliest,” (The Union Home Ministry informed the tribunal)
PAGE NUMBER 13
News: China cautious on G4 push for UNSC reforms
UPSC Syllabus Headings
Prelims: Current events of national and international importance
Mains: GS 2
Sub Topic: Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Context
China on Thursday said there were “enormous divisions” and a lack of consensus on taking forward the stalled reforms of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), a day after the G4 countries — India, Brazil, Japan and Germany — called for an early push for text based negotiations.

Key particulars
The Foreign Ministers of the four countries that are seeking UNSC reforms and permanent membership of the body met virtually on Wednesday, expressing their frustration at the repeated attempts to stall and derail the reforms process.
Text-based negotiations
(i) External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar said the meeting had “called for a decisive push” and was unanimous in backing “text based negotiations in a fixed time frame”.
(ii) India begins a two year term as one of the 10 nonpermanent UNSC members in January and it is pushing for reforms in UNSC.
PAGE NUMBER 14
News Govt. extends IBC pause by 3 months
UPSC Syllabus Headings
Prelims: Economic and Social Development - Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc
Mains: GS 3
Sub Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Context
Corporate India has got three more months of relief from invocation of insolvency and bankruptcy proceedings by lenders, with the government extending the suspension of relevant provisions of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) against firms defaulting on their loans since March 25 this year.
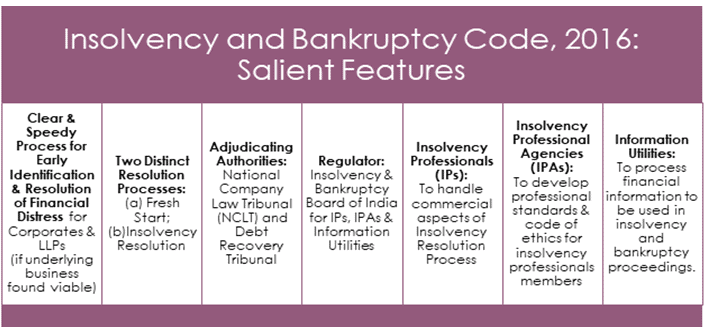
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Key particulars
(i) The IBC’s invocation was first suspended for a period of six months in view of the emergent stress on balance sheets due to the COVID19 pandemic and the national lockdown announced in March
(ii) The suspension of the corporate insolvency resolution process for another three months will help companies stay afloat,
(iii) The current COVID19 situation has had a debilitating effect on the Indian economic situation and the passing of the Bill will give such stressed companies the much–needed cushioning effect.
1. Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code was introduced in 2018.
2. This was enacted for reorganization and insolvency resolution of corporate companies only.
|
21 videos|562 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Analysis - 25th Sept 2020 - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of The Hindu Analysis for UPSC preparation? |  |
| 2. How can The Hindu Analysis help in improving my UPSC answer writing skills? |  |
| 3. Does The Hindu Analysis cover all relevant topics for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. Can The Hindu Analysis be used as the sole study material for UPSC preparation? |  |
| 5. How can I access The Hindu Analysis for UPSC preparation? |  |
















