The Hindu Analysis - 30th Sept 2020 | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download
Leuser Ecosystem
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
(i) Recently, Leuser Ecosystem was in the news.
(ii) An investigation by the global watchdog Rainforest Action Network (RAN) has shown that various food, cosmetics and finance companies have links with companies which are responsible for the destruction of the Leuser Ecosystem.
(iii) It is a forest area on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia.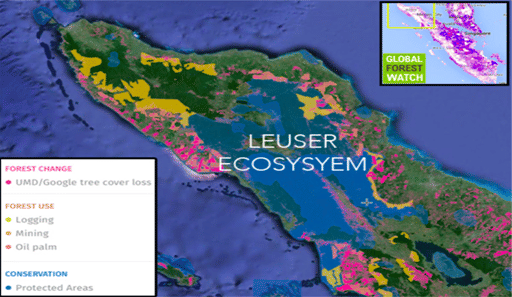
Important value additions
Leuser Ecosystem
(i) It is among the most ancient and life-rich ecosystems ever documented by science.
(ii) It is a world-class hotspot of biodiversity.
(iii) It is widely acknowledged to be among the most important areas of intact rainforest left in all of Southeast Asia.
(iv) It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
(v) The ecosystem stretches across the province of Aceh and North Sumatra, Indonesia. Its diverse landscape includes lowland and montane rainforests and carbon-rich peatlands.
Do you know?
(i) It supports viable populations of rare species like Sumatran tigers, orangutans, rhinos, elephants, clouded leopards and sun bears.
(ii) It plays an important role regulating the global climate by storing massive amounts of carbon in its peatlands and standing forests.
(iii) Threats: (1) Industrial development for palm oil, pulp and paper plantations and mining; (2) The fires from this widespread destruction have caused major haze pollution
Vodafone Case: Perils of State Overreach
Context: The Vodafone Group has just won one of the most high-stakes legal battles involving a foreign investor and the Indian state under international law. For a brief background on the issue:
Do You Know?
(i) 2012 Amendment of Income Tax Act: The income deemed to be accruing to non-residents, directly or indirectly, through the transfer of a capital asset situated in India is taxable retrospectively with effect from April 1, 1962.
(ii) This amendment was carried out to override the Supreme Court ruling in favour of Vodafone.
(iii) The Court held that Vodafone didn’t owe any tax to the Indian state on account of Vodafone acquiring a 67% stake in Hutchison Essar through an offshore transaction.
What was the ruling?
- An Investor-State Dispute Settlement (ISDS) tribunal, constituted under the India-Netherlands bilateral investment treaty (BIT), has ruled that India’s imposition of tax liability amounting to ₹22,000 crore on Vodafone is in breach of India’s BIT obligations.
Can the government challenge the award?
(i) It is likely that the government might challenge the award at the seat of arbitration or resist the enforceability of this award in Indian courts alleging that it violates public policy.
(ii) If the government indeed follows these options, there’s a long, gruelling road ahead for Vodafone.
(iii) The government would be ill-advised to go down this road because it would mean that India does not honour its international law obligation
Key lessons from the case
(i) Against the spirit of Democratic norms: Unleashing tax inspectors to extract money out of foreign investors by constantly changing the rules of the game is not an attribute that a liberal democracy should be proud of.
(ii) Retrospective Amendment termed as Tax Terrorism: The opposition of the day vehemently criticised the retrospective amendment calling it “tax terrorism”.
(iii) Investor Sentiment: India should learn that being a country that values the rule of law is an important quality to win over the confidence of foreign investors and international goodwill.
(iv) Usage of Taxpayer’s Money: The tribunal has ordered India to reimburse legal costs to the tune of more than ₹40 crore incurred by Vodafone in fighting this case, which will come from taxpayer’s money.
(v) Cost of non-compliance: If the order is not complied, it would send a deleterious signal to foreign investors reaffirming the sentiment that doing business in India is indeed excruciating.
(vi) Honouring international law: All the three organs of the Indian state — Parliament, executive, and the judiciary — need to internalise India’s BIT and other international law obligations. These organs need to ensure that they exercise their public powers in a manner consistent with international law.
(vii) Impact on other disputes: This ruling might have an impact on the two other ISDS claims that India is involved in with Cairn Energy and Vedanta on the imposition of taxes retrospectively.
(viii) Restrain from further hardening BITs: India unilaterally terminated almost all its BITs after foreign investors started suing India for breaching BITs. The belief in the Indian establishment is that the ISDS regime unduly intrudes into India’s sovereignty. Hence it is quite possible that India might use this award to further harden its antagonistic stand against ISDS and BITs, which should be resisted.
Conclusion
(i) The case is a reminder that the ISDS regime, notwithstanding its weaknesses, can play an important role in fostering international rule of law
(ii) If the government is serious about wooing foreign investment, India should immediately comply with the decision and repeal the retrospective provision which still remains in statute books.
Defence Acquisition Procedure – 2020 released
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence; Security
In news
(i) Union Defence Minister unveiled the Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) – 2020 recently.
(ii) DAP 2020 will be applicable with effect from 01 October 2020.
(iii) The first Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP) was promulgated in 2002 and has since been revised periodically.
Key takeaways
(i) The New Category of Buy (Global – Manufacture in India) incorporates ‘manufacture of either the entire/part of the equipment or Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) facility for the equipment, through its subsidiary in India.
(ii) The categories of Buy(Indian-IDDM), Make I, Make II, Production Agency in Design & Development, OFB/DPSU and SP model will be exclusively reserved for Indian Vendors meeting the criteria of Ownership and Control by resident Indian Citizens with FDI not more than 49%.
(iii) A simple and practical verification process has been instituted and Indigenous Content (IC) will now be calculated on ‘Base Contract Price’.
(iv) Provision for exploring options for operating base applications like Fire Control System, Radars, Encryption, Communications etc. on indigenous software in Buy (Indian- IDDM) & Buy (Indian) cases has been included.
(v) A separate dedicated chapter has been incorporated in the DAP 2020 for acquisition of systems Designed and Developed by DRDO/DPSUs/OFB.
(vi) The Offset guidelines have been revised, wherein preference will be given to manufacture of complete defence products over components and various multipliers have been added to give incentivisation in discharge of Offsets.
Virgin Hyperloop to do feasibility study
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Achievements of Indians in Sci & Technology
In news
(i) India’s IT hub, Bengaluru may soon get its own hyperloop network as a future mode of mobility.
(ii) Recently, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between Virgin Hyperloop and Bangalore International Airport Limited (BIAL) to conduct a feasibility study for a proposed Hyperloop corridor from Bengaluru Airport.
Key takeaways
(i) The pre-feasibility study, which focuses on technical, economic and route feasibility, is expected to be completed in 2 phases of six months each.
(ii) With speeds of up to 1,080 kmph, hyperloop could transport thousands of passengers per hour from Bengaluru Airport to the city center in under 10 minutes, according to the preliminary analysis.
(iii) This will help the people of Bengaluru to save a lot of the time that goes to travel in one of India’s most congested cities.
(iv) Passengers travelling to the Bengaluru airport could streamline their multimodal trip with seamless check in and security – for both their hyperloop as well as air travel at centrally-located hyperloop portals which will help in reducing the overall travel time.
(v) In addition to the road network, the airport will also be connected with the sub-urban railway soon and will have Metro connectivity in four years.
Tata CRISPR Test
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health & GS-III – Achievements of Indians in Sci & Technology
In news
- India’s first CRISPR Covid-19 test, developed by the Tata Group and CSIR-IGIB, has been approved for use in India.
Key takeaways
(i) The Tata CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) test is powered by CSIR-IGIB (Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology) FELUDA.
(ii) This test uses an indigenously developed, cutting-edge CRISPR technology for detection of the genomic sequence of SARS-CoV-2 virus.
(iii) CRISPR is a genome editing technology for diagnosing diseases.
(iv) It is the world’s first diagnostic test to deploy a specially adapted Cas9 protein to successfully detect the virus causing Covid-19.
(v) It achieves accuracy levels of traditional RT-PCR tests, with quicker turnaround time, less expensive equipment, and better ease of use.
World Bank’s Human Capital Index 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Human Resources
In news
(i) Recently, the World Bank released the Human Capital Index (HCI) report for 2020.
(ii) India has been ranked at the 116th position in the HCI 2020.
(iii) Last year India was ranked 115 out of 157 countries.
(iv) India’s score increased to 0.49 in 2020 from 0.44 in 2018.
Key takeaways
(i) Parameters Used in HCI: Health and education data of children for 174 countries up to March 2020.
(ii) It covers 98% of the world’s population.
(iii) The pandemic puts at risk the decade’s progress in building human capital, including the improvements in health, survival rates, school enrollment, and reduced stunting.
(iv) More than 1 billion children have been out of school and could lose out, on average, half a year of schooling.
(v) It has created significant disruptions to essential health services for women and children, with many children missing out on crucial vaccinations.
(vi) It has increased income inequality, its economic impact has been particularly deep for women and for the most disadvantaged families, leaving many vulnerable to food insecurity and poverty.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Space; Achievements of Indians in Sci & Technology
In news
(i) Recently, the Government of India has created the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe).
(ii) It is an independent nodal agency under the Department of Space.
Key takeaways
(i) IN-SPACE is to be established as a single-window nodal agency, with its own cadre, which will permit and oversee the activities of private companies.
(ii) Functions: (1) Encourage, promote and handhold the private sector for their participation in the Space Sector; (2) Draw up an integrated launch manifest considering the requirements for ISRO, New Space India Limited (NSIL) and private companies; (3) Work out a suitable mechanism to offer sharing of technology, expertise and facilities; (4) Permit establishment of facilities, within ISRO premises, based on safety norms and feasibility assessment.
(iii) The decision of IN-SPACE shall be final and binding on all stakeholders including ISRO and private players will not be required to seek separate permission from ISRO.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. It is an independent nodal agency under the Department of Space.
2. It aims to encourage, promote and handhold the private sector for their participation in the Space Sector.
India based Neutrino Observatory
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Achievements of Indians in Sci & Technology
In news
(i) An India based Neutrino Observatory (INO) is going to be set up in Bodi West Hills, in Theni district, Tamil Nadu.
(ii) Funded by: Dept. of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Dept. of Science and Technology (DST).
Key takeaways
(i) Objective: To observe neutrinos and antineutrinos produced in the atmosphere of the Earth.
(ii) Features: The project includes: (1) Underground laboratory and associated surface facilities at Bodi West Hills; (2) Construction of a magnetized Iron Calorimeter (ICAL) detector for studying neutrinos.
(iii) Advantages: (1) This observation will tell us more about the properties of neutrino particles; (2) This will also help in developing a model of physics beyond the so-called Standard Model of Particle Physics; (3) It would also have a great impact on diverse fields such as nuclear and particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, medical imaging etc.
Do you know?
(i) INO Project is a multi-institutional effort aimed at building a world-class underground laboratory with a rock cover of approx. 1200 m for non-accelerator based high energy and nuclear physics research in India.
(ii) National Neutrino Collaboration group (NNCG) includes more than 50 scientists from about 15 Institutes and Universities in India.
(iii) It is tasked with detailing various aspects related to INO activity and to come up with a proposal for an underground neutrino laboratory.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. It is an underground laboratory.
2. It is located in Tamil Nadu.
Increase in Frequency of Medicanes
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
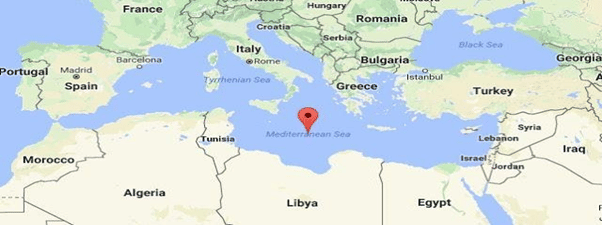
- Recently, scientists have warned that extra-tropical storms in the Mediterranean Sea, known as ‘Medicanes’ or ‘Mediterranean Hurricanes’, could become more frequent due to human-induced climate change.
Important value additions
Medicanes
(i) Medicanes are tropical-like cyclones formed over the Mediterranean Sea.
(ii) With the surrounding dry climate and the relatively shallow waters of the sea, the occurrence of tropical-like cyclones is infrequent.
(iii) They typically form in the fall or winter months and occur once or twice a year.
(iv) On September 18, 2020, a medicane named Lanos made landfall along the coast of Greece and caused heavy rainfall and flooding in Greece and surrounding islands.
India-Sri Lanka Virtual Bilateral Summit held
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
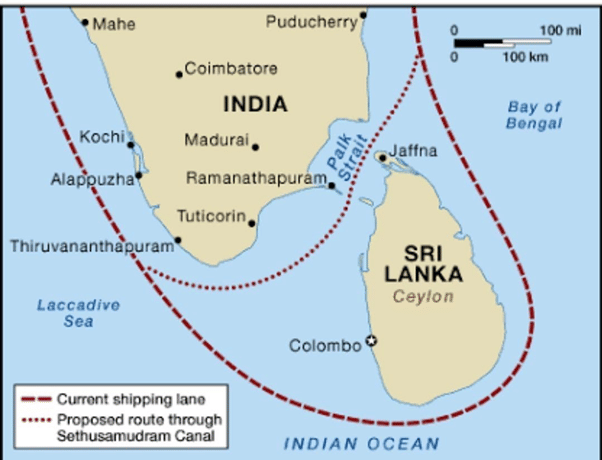
- Recently, Indian Prime Minister and Sri Lankan PM held the first-ever India-Sri Lanka Virtual Bilateral Summit.
Key takeaways
(i) A grant assistance of 15 million dollars shall be provided to Sri Lanka.
(ii) The grant will assist in deepening people-to-people linkages between the two countries in the sphere of Buddhism.
(iii) They agreed that the Indian side would facilitate the visit of a delegation of Buddhist pilgrims from Sri Lanka in the first inaugural flight to Kushinagar.
(iv) Both sides also agreed to explore opportunities in the areas of Ayurveda and Yoga.
(v) India and Sri Lanka have reached an understanding to extend the MoU on High Impact Community Development Projects for a five-year period beginning 2020.
(vi) Both leaders agreed to continue the successful Indian housing project and gave instructions to the relevant officials to fast-track the construction of 10,000 houses in the plantation sector.
(vii) Implementation of the 13th Amendment to the Sri Lankan Constitution was also emphasised as it is essential for carrying forward the process of peace and reconciliation and realizing the expectations of Tamils for equality.
Do you know?
- Kushinagar Airport was designated as an international airport recently recognizing its importance as a Buddhist site.
|
21 videos|562 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Analysis - 30th Sept 2020 - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of The Hindu Analysis for UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 2. How can The Hindu Analysis be beneficial for UPSC exam preparation? |  |
| 3. How frequently should UPSC aspirants refer to The Hindu Analysis? |  |
| 4. Can The Hindu Analysis be used as the sole source of current affairs preparation for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How can UPSC aspirants make the most out of The Hindu Analysis? |  |





















