Governor: Power, Tenure, Qualifications, Appointment- 2 | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
What is the Constitutional Position of Governor?
The Constitutional Position of the governor can be understood by the following articles: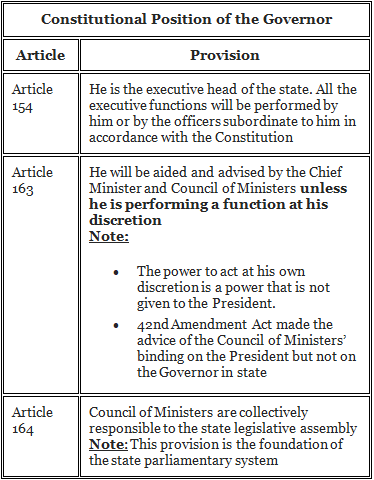
The Constitution has mentioned the authority of the governor to decide the validity of his actions taken in his own discretion in circumstances where his actions are called into action.
Governor’s Discretionary Powers
The Governor of state, unlike the President of India, is conferred with power to act at his own discretion. There are two categories of discretion for the governor. One is Constitutional Discretion and the other is Situational Discretion. Read more about the Constitutional Discretion of Governor in the linked article.
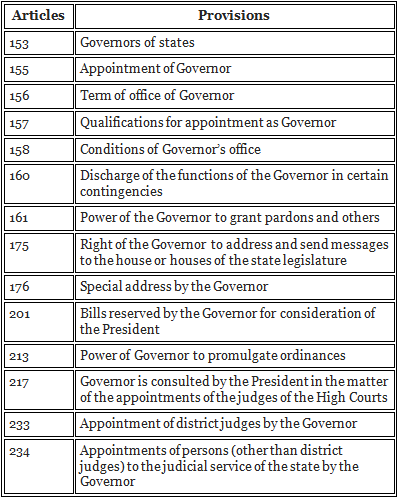
Important Constitutional Articles related to the Governor
IAS aspirants should know the articles in the constitution that are related to the governor:
Difference between President and Governor Veto Power in India
Comparison of Veto Power with regard to Ordinary Bill
⇒ President - Every ordinary bill, after being passed by Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha is presented to the President for his assent and he can take three steps-
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act(Absolute Veto).
- He may return the bill for reconsideration of the Houses. If the bill is passed by both the Houses again with or without amendments and presented to the President for his assent, the president must give his assent to the bill. Thus the president enjoys only a ‘suspensive veto’.
⇒ Governor - Every ordinary bill, after it is passed by the legislative assembly in case of a unicameral legislature or by both the Legislative Assembly and Legislative Council in case of a bicameral legislature, is presented to the governor for his assent. In this case Governor has four alternatives-
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act(Absolute Veto).
- He may return the bill for reconsideration of the House or Houses. If the bill is passed by the House or Houses again with or without amendments and presented to the governor for his assent, the governor must give his assent to the bill. Thus, the governor enjoys only a ‘suspensive veto’.
- He may reserve the bill for the consideration of the President.
⇒ President - When a state bill is reserved by the governor for the consideration of the President, the President has three options-
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an Act.
- He may return the bill for reconsideration of the House or Houses of the state legislature. When a bill is so returned, the House or Houses have to reconsider it within six months. If the bill is passed by LA or LA&LC again with or without amendments and presented to the president for his assent, the president is not bound to give his assent to the bill. He may give his assent to such a bill or withhold his assent.
⇒ Governor - When the governor reserves a bill for the consideration of the President, he will not have any further role in the enactment of the bill and now the power of consideration of the Bill rests solely with the President and Governor has nothing to do with it. Even if President sends it for the reconsideration of the SLA, after being reconsidered the Bill will directly be placed in front of the President and not the Governor.
Comparison of Veto Power with regard to Money Bill
# President - Every money bill after it is passed by the Parliament, is presented to the President for his assent.
In this case he has 2 options -
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act.
# Governor - Every money bill, after it is passed by the state legislature (SLA or SLA&SLC), is presented to the governor for his assent.
In this case Governor has three options -
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act.
- He may reserve the bill for the consideration of the president.
# President - The President cannot return a money bill for the reconsideration of the Parliament.
In regular terms, the president gives his assent to a money bill as it is introduced in the Parliament with his previous permission.
When a Money Bill is reserved by the Governor for the consideration of the President, the President has two options -
- He may give his assent to the bill, the bill then becomes an Act.
- He may withhold his assent to the bill, the bill then ends and does not become an act. Thus, the President cannot return a money bill for the reconsideration of the state legislature similar to what happens in the case of Parliament.
Governor - He cannot send the Bill back to the SLA for reconsideration and he normally accords his assent to the Money Bill as it is introduced with his prior consent.
If the Governor reserves the Money Bill for the consideration of the President his role ends.
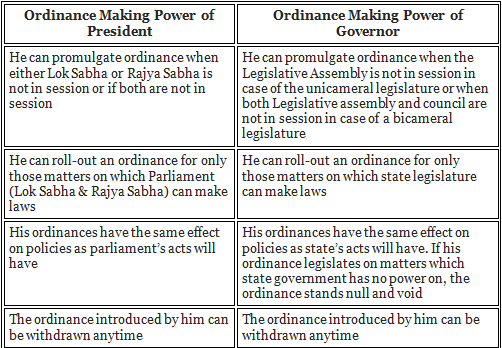
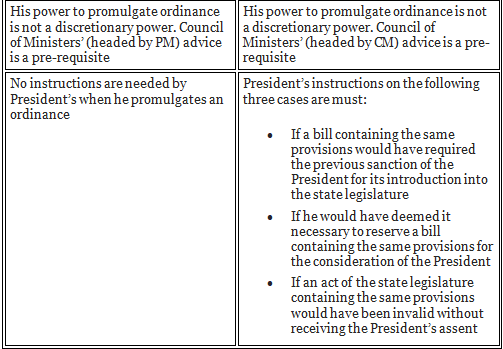
Comparison between Ordinance Making Power of President and Governor
Article 213 deals with the power of Governor to legislate through ordinances. His power of ordinance making is quite similar to the President’s power. The comparisons between these two w.r.t. Ordinance making is given below:
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Governor: Power, Tenure, Qualifications, Appointment- 2 - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the powers of a governor? |  |
| 2. How long does a governor's tenure last? |  |
| 3. What are the qualifications to become a governor? |  |
| 4. How is a governor appointed? |  |
| 5. Can a governor be impeached or removed from office? |  |
















