Central Vigilance Commission | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The Indian government introduced the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) in the year 1964. The commission was set up on the recommendation of K. Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption. It was originally introduced through an executive resolution. The Central Vigilance Committee’s role is to advise and guide the Central Government in the field of surveillance.
What is the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC)?
It is an agency constituted to curb corruption in offices of the Indian government. Complaints from whistleblowers (an employee of the firm/public office informing the public about frauds/wrongdoings in the office) under ‘Whistleblower Resolution’ are received by CVC after which the commission can take actions on motivated acts.
CVC is called the apex vigilance institution. It is free of control from any executive authority. Its role is to monitor all vigilance activity under the Central Government and advising various authorities in Central Government organizations in planning, executing, reviewing and reforming their vigilance work.
Facts about the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) for UPSC:
- Since 25 August 1998, CVC is a multi-member commission having a statutory status.
- Central Vigilance Act came into effect in the year 2003 after CVC bill was passed by both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
- First Chief Vigilance Commissioner of India was Nittoor Srinivasa Rau.
- Since 2004, the commission receives complaints under Public Interest Disclosure and Protection of Informers’ Resolution” (PIDPI), also called Whistleblowers’ Resolution.
How many members are there in Central Vigilance Commission?
CVC has three members:
(i) Central Vigilance Commissioner
(ii) Two Vigilance Commissioner (Maximum number of commissioners is 2)
Facts about CVC Members:
- President of India appoints CVC members by warrant under his hand and seal
- The President’s appointment comes after the recommendation by a three-member committee:
(i) Prime Minister
(ii) Minister of Home Affairs (MHA)
(iii) Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha - Term of Office: Four years or if they attain 65 years of age (whichever is earlier)
- After they retire, they are not eligible for reappointment in any central or state government agency.
Can Central Vigilance Members be removed?
Yes, the CVC members can be removed in the following circumstances: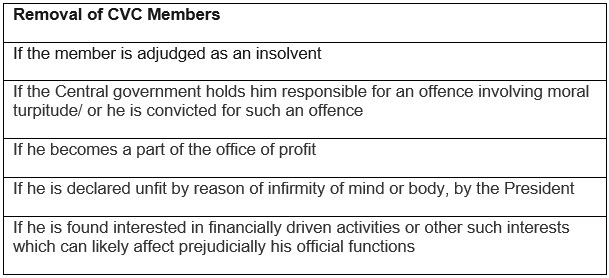
Note: CVC members can also be removed by the President on the grounds of proved misbehaviour. However, the Supreme Court is referred by President only after which CVC member can be removed.
The Organisation of Central Vigilance Commission
There are three departments under the commission, given in the table below: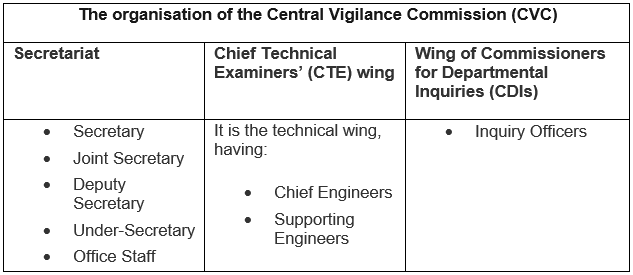
What is the work of the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC)?
The following are the works of CVC members:
- They inquire or investigate whenever a public servant (Central Government employee) commits an offence under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988.
- They inquire or investigate against following officials who commit an offence under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988:
(i) Members of all-India services serving in the Union and Group ‘A’ officers of the Central government
(ii) The specified level of officers of the authorities of the Central government - They superintend the functioning of Delhi Special Police Establishment (CBI) in cases related to Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- They direct Delhi Special Police Establishment in investigative cases related to Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- They review the progress of investigations conducted by the Delhi Special Police Establishment in cases related Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- They review the progress of those applications that are pending with competent authorities for sanction under Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988
- Central Government and its authorities are advised on matters as they refer to CVC members
- They also superintend vigilance departments of government ministries
- They undertake or cause an inquiry into complaints received under Whistleblower Resolution and recommend appropriate action.
- Whenever the central government makes rules and regulations governing the vigilance and disciplinary matters relating to members of Central Services and All-India Services, CVC is consulted.
- CVC members are part of the selection committee which is responsible to recommend the appointment of Director of Enforcement (ED.)
- CVC is a part of the selection committee that recommends officers for appointments to the posts above the level of Deputy Director of Enforcement.
- The Commissions acts as an authority to receive information that is related to suspicious transactions under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
- It recommends to Central Government for the appointment of Director of Prosecution in Central Bureau of Investigation
- CVC members are part of a selection committee that is responsible to recommend the appointment of officers to the posts of the level of SP and above in the CBI except for Director of CBI
- Lokpal refers complaints to CVC who initiate a preliminary inquiry in respect of officers and officials of Groups A, B, C & D
Jurisdiction of Central Vigilance Commission
CVC can extend its jurisdiction to the following: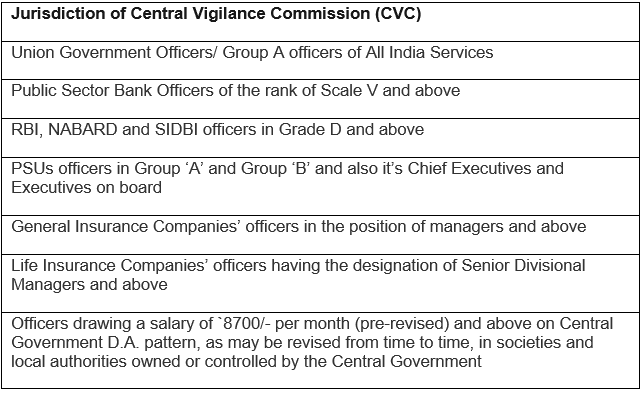
CVC – Vigilance Awareness Week
This awareness week is observed by the Central Vigilance Commission every year in the month of October. The week includes Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel’s birth anniversary which is on October 31.
The motive of Vigilance Awareness Week is to:
- Take an Integrity Pledge by all government ministries and organisations
- Spread the words on prevention of corruption across the nation
- Conduct workshops and campaigns for government employees and other stakeholders on policies/procedures of the organization and preventive vigilance measures
- Establish Integrity Clubs in schools and colleges
Aware Gram Sabhas to sensitize the rural citizens about the ill-effects of corruption
Note: The theme of the 2020 Vigilance Awareness Week is “Satark Bharat, Samriddh Bharat (Vigilant India, Prosperous India)”.
The Whistleblowers Protection Act
The Act came on the heels of “The Public Interest Disclosure and Protection to Persons Making the Disclosure Bill, 2010” in the Lok Sabha on August 26, 2010. The Bill as passed by Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha on 21st February 2014 and received the assent of the President on May 9, 2014.
The act has provided mechanisms to secure the identity of public employees who expose corruption in government ministries and departments. It also aids the intention to expose corruption by public servants, including ministers.
Facts related to the Whistleblowers Protection Act:
- There is a penalty of imprisonment for 2 years or a fine of Rs. 30000 or both, in cases related to false charges
- The Act is not applicable to the state of Jammu and Kashmir, the armed forces and the Special Protection Group mandated to provide security to the Prime Minister and former prime ministers, among others.
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Central Vigilance Commission - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the Central Vigilance Commission? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of the Central Vigilance Commission? |  |
| 3. How does the Central Vigilance Commission promote transparency and accountability? |  |
| 4. Can the Central Vigilance Commission take action against private individuals involved in corruption? |  |
| 5. How can the public report corruption to the Central Vigilance Commission? |  |
















