NCERT Summary: An Introduction- 1 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
- Economics as a word comes from the Greek: oikos means ‘family, household, or estate’, and nomos stands for ‘custom, law’ etc. Thus, “house hold management” or management of scarce resources is the essential meaning of economics. Economics encompasses production, distribution, trade and consumption of goods and services. Economic logic is applied to any problem that involves choice under scarcity.
- Initially, economics focused on “wealth” and later “welfare”. Still later, in recent years, it has given sufficient attention to the study of trade offs- giving up one to gain another. The focus on trade offs arises from the traditional assumption that resources are scarce and that it is necessary to choose between competing alternatives. Choosing one benefit implies for going another alternative the opportunity cost (cost of foregoing an Opportunity).
- Adam Smith, generally regarded as the Father of Economics, author of ‘An Inquiry into the Nature’ and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (generally known as The Wealth of Nations) defines economics as “The science of wealth.” Smith offered another definition, “ The Science relating to the laws of production, distribution and exchange.”
- Definitions in terms of wealth emphasize production and consumption, and do not deal with the economic activities of those not significantly involved in these two processes, for example, children and old people. The belief is that non-productive activity is a cost on society. It meant that man was relegated to the secondary position and wealth was placed above life.
- Thus arose the shift in the focus to welfare economics study of man and of human welfare, not of money alone. Economics involves social action connected with the attainment of human well being.
- (i) Types of Economics
Economics is usually divided into two main branches: - Microeconomics which examines the economic behavior of individual actors such as consumers, businesses, households etc. to understand how decisions are made in the face of scarcity and what effects they have.
- Macroeconomics, which studies the economy as a whole and its features like national income, employment, poverty, balance of payments and inflation.
- The two are linked closely as the behavior of a firm or consumer or household depends upon the state of the national and global economy.
(ii) Mesoeconomics
‘Mesoeconomics’ studies the intermediate level of economic organization in between the micro and the macro economics like institutional arrangements etc.
DIVISION OF ECONOMICS FOCUS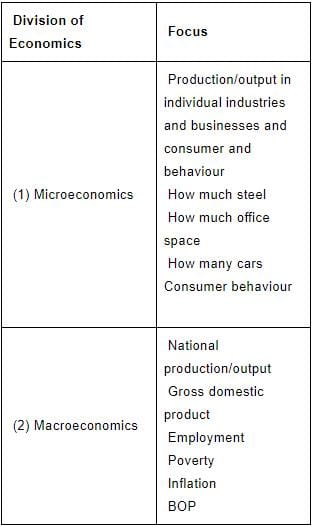
There are broadly the following approaches in the mainstream economics. The basis of all the streams is the same: resources are scarce while wants are unlimited (often mentioned as the economic problem).
(i) Keynesian theory of Macro Economics
- Keynesian macroeconomics based on the theories of twentieth - century British economist John Maynard Keynes. It says that the state can stimulate economic growth and restore stability in the economy through expansionary policies. For example- through massive programme of spending on infrastructure when the demand is low and growth is negative.
- In the recessionary phase that the economies of the western world in particular and rest of the world in general, went through (some are still undergoing the recession) due to 2008 financial crisis, the relevance of Keynes is growing.
- The intervention by State is only when the economic cycle turns down and growth slows down or is negative. In normal times, it is the market that drives growth through the force of supply and demand.
- Indian government stepped up expenditure with three fiscal stimuli since December 2008 to revive growth. With growth spurting, the gradual and calibrated exit from the stimulus was begun in the 2010-11 Union Budget.
- The theories of Keynesian economics were first presented in ‘The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money’ (1936).
(ii) Neo-liberalism
Neo-liberalism refers to advocacy of policies such as individual liberty, free markets, and free trade. Neo- liberalism “proposes that human well being can best be advanced by liberating individual entrepreneurial freedoms and skills within an institutional framework characterized by strong private property rights, free markets and free trade”.
(iii) Socialist theory of Economics
In distinction to the above, there is the school of socialist economics based on public (State) ownership of means of production to achieve greater equality and give the workers greater control of the means of production. It establishes fully centrally planned economy which is also called command economy -economy is at the command of the State. Private ownership of assets is not allowed. For example, erstwhile USSR, Cuba etc.
(iv) Development Economics
Development economics is a branch of economics which deals with economic aspects of the development process, mainly in low income countries. Its focus is not only promoting economic grow thand structural change but also improving the well being of the population as a whole through health and education and work place Conditions, whether through public or private channels. The most prominent contemporary development economists are Nobel laureates Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz.
(v) Structural Change
Structural change of an economy refers to along - term wide spread change of a fundamental structure, rather than micro-scale or short - term change. For example a subsistence economy is transformed into a manufacturing economy, or a regulated mixed economy is liberalized. An insulated and protectionist economy becomes open and globalized. A current structural change in the world economy is globalization.
(vi) Green Economics
Green economics focuses on and supports the harmonious interaction between humans and nature and attempts to reconcile the two.
(vii) Economic Growth and its Measument Methods
Economic growth is the change- increase or decrease, in the value of goods and services produced by an economy. If it is positive, it means an increase in the output and the income of a country. It is generally shown as the increase in percentage terms of real gross domestic product (GDP adjusted to inflation) or real GDP.
(viii) Measuring Growth
Measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate the value of goods and services produced in an economy. They use a system of national accounts or national accounting. Some of the common measures are Gross National Product (GNP) and Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
(ix) National Income Accounting
- National income accounting refers to a set of rules and techniques that are used to measure the national income of a country.
- GDP is defined as the total market value of all final goods and services produced within the country in a given period of time usually a calendar year or financial year.
- GDP can be real or nominal. Nominal GDP refers to the current year production of final goods and services valued at current year prices. Real GDP refers to the current year production of goods and service valued all base year prices. Base year prices are Constant prices.
- In estimating GDP, only final marketable goods and services are considered. Only their values are added up and they pertain to a given period. When it is compared to the base year figure, the growth levels are Seen.
- To explain further, gains from resale are excluded bu t the services provided by the agents are counted. Similarly, transfer payments (pensions, scholarships etc) are excluded as there is income received but no good or service produced in return. However, not all goods and services from productive activities enter in to market transactions. Hence, imputations are made for these non-marketed but productive activities: for example, imputed rental for owner-occupied housing.
(x) Market Price and Factor Cost
- Market price refers to the actual transacted price and it includes indirect taxes custom duty, excise duty, sales tax, service tax etc.
- Factor cost refers to the actual cost of the Various factors of production includes government grants and subsidies but it excludes indirect taxes.
- Relationship between market price and factor cost.
- GNP at factor cost = GNP at market price - indirect taxes + subsidies
- GDP at factor cost = GDP at market price - indirect taxes + subsidies
(xi) Factor Costs
Factor costs are the actual production costs at which goods and services are produced by the firms and industries in an economy. They are really the costs of all the factors of production such as land, labour, capital, energy, raw materials like steel etc. that are used to produce & given quantity of output in an economy. They are also called factor gate costs (farm gate, firm gate and factory gate) since all the costs that are incurred to produce a given quantity of goods and services take place behind the factory gate i.e. within the walls of the firms, plants etc in an economy.
(xii) Transfer Payments
Transfer payment refers to payments made by government to individuals for which there no economic activity is produced in return by these individuals. Examples of transfer are scholarship, pension.
GDP/GNP
(i) Three Approaches
- There are three different ways of calculating GDP. The expenditure approach adds consumption, investment, government expenditure and net exports (exports minus imports).
- On the other hand, the income approach adds what factors earn: wages, profits, rents etc.
- Output approach adds the market value of final goods and services.
- The three methods must yield the same results because the total expenditures on goods and services must by definition be equal to the value of the goods and services produced (GNP) which must be equal to the total income paid to the factors that produced these goods and services.
- In reality, there will be minor differences in the results obtained from the various methods due to changes in inventory levels. This is because goods in inventory have been produced (and therefore included in GDP), but not yet sold. Similar timing is sues can also cause as light discrepancy between the value of goods produced (GDP) and the payments to the factors that produced the goods, particularly if inputs are purchased on credit.
(ii) Final Goods
- Final goods are goods that are ultimately consumed rather than used in the production of another good. For example, a car sold to a Consumer is a final good; the components such as tyres sold to the car manufacturer are not; they are intermediate goods used to make the final goods. The same tyres, if sold to a consumer, would be a final goods. Only final goods are included when measuring national income. If intermediate goods were included too, this would lead to double counting; for example, the value of tyres would be counted once when they are sold to the car manufacturer, and again when the car is sold to the consumer.
- Only newly produced goods are counted. Transactions in existing goods, such as second-hand cars, are not included, as these do not involve the production of new goods.
(iii) GDP
- GDP considers only marketed goods. If a cleaner is hired, their pay is included in GDP. If one does the work himself, it does not add to the GDP. Thus much of the work done by women at home- taking care of the children, aged; chores etc which is called ‘care economy’ is outside the GDP.
- Gross means depreciation (wear and tear of machinery in their use) of capital stock is not subtracted. If depreciation is subtracted, it becomes net domestic product.
- Calculating the real GDP growth-inflation adjusted GDP growth- allows us to determine if production increased or decreased, regardless of changes in the-inflation and purchasing power of the currency.
(iv) Differences between GDP and GNP
- The two are related. The difference is that GNP includes net foreign income. GNP adds net foreign investment income compared to GDP. GDP shows how much is produced with in the boundaries of the country by both the citizens and the foreigners. It is the market value of all the output produced in the territory of a nation in one year. GDP focuses on where the output is produced rather than who produced it. GDP measures all domestic production, disregarding the producing entities nationalities.
- In contrast, GNP is a measure of the value of the output produced by the “nationals” of a country- both with in the geographical boundaries and outside. That is, all the output that the Indian citizens produce in a given year - both within India and all other countries.
- For example, there are Indian and foreign firms operating in India. Together what they produce with in the Indian geography is the GDP of India. The profits of foreign firms earned with in India are included in India’s GDP, but not in India’s GNP.
- In other words, in come is counted as part of GNP according to who owns the factors of production rather than where the production takes place. For example, in the case of a German- owned car factory operating in the US, the profits from the factory would be counted as part of German GNP rather than US GNP because the capital used in production (the factory, machinery, etc .) is German owned. The wages of the American workers would be part of US GDP, while the wages of any German workers on the site would be part of German GNP.
- GDP is essentially about where production takes place. GNP is about who produces. If it is an open economy with great levels of foreign investment (FD1) and lesser levels of outbound FDI, its GDP is likely to be larger than GNP.
- If it is an open economy but more of its nationals tend to move economic activity a broad or earn more from investing abroad compared with non-nationals doing business and earning incomes within its borders, its GNP will be larger than GDP.
- If it is a closed economy where nobody leaves its shores, nobody in vests abroad, nobody comes in and nobody invests in the country, its GDP will be equal to GNP.
- Japan used to belong in the last category. Until the mid-1990s, the difference between Japan’s GDP and GNP amounted to less than one percentage point of GDP. With only limited numbers of people doing business abroad, the GDP and GNP were essentially the same thing.
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: An Introduction- 1 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is GDP? |  |
| 2. What is GNP? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between GDP and GNP? |  |
| 4. How is GDP/GNP calculated? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of GDP/GNP as economic indicators? |  |

















