Laxmikanth Summary: Election Laws | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Representation of the People Act, 1950
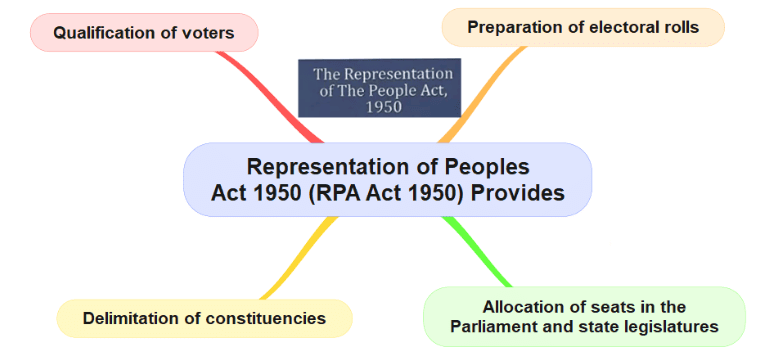
- The Representation of the People Act, 1950, was enacted to provide for the allocation of seats in the House of the People and in the Legislative Assemblies and Legislative Councils of States.
- Articles 81 and 170 of the Indian Constitution set the maximum number of seats in Parliament and State Legislative Assemblies, and outline principles for seat allocation among States in the House of People and State Legislative Assemblies.
- Article 171 specifies the maximum and minimum seats in State Legislative Councils and the methods for filling these seats, leaving the details to be determined by law.
- In allotting seats in the House of the People to different States and in fixingthe total number of seats in the Legislative Assemblies of different States, the population of each State as on 1st March 1950 was taken into account.
- The Act also sought to confer on the President the powers to delimit, afterconsultation with the Election Commission, the various constituencies for the purpose of elections to fill seats in the House of the People and in the Legislative Assemblies and Legislative Councils of States.
- The Act further provided for the registration of electors for Parliamentary Constituencies and for the Assembly and Council Constituencies, and the qualifications and disqualifications for such registration. A special provision has been included for
- Certain action was already taken by the Constituent Assembly Secretariat for the preparation of the electoral rolls for elections to the House of the People and the Legislative Assemblies of the States.
Significance
- The act provides for direct election for every Parliamentary constituency.
- It provides for delimitation of constituencies which ensures the incorporation of changing dynamics of the increasing population making the process more liveable.
- The act strengthened the federal polity of the country by giving due representation to each state in the house of people.
Representation of the People Act, 1951
- The Representation of the People Act, 1950 laid the groundwork for elections in India by addressing the allocation of seats, delimitation of constituencies, voter qualifications, and electoral rolls.
- However, it did not cover all aspects of the electoral process, such as the conduct of elections, qualifications for membership, corrupt practices, and election disputes.
- To fill these gaps, the Representation of the People Act, 1951 was enacted, providing comprehensive guidelines for various electoral matters.
Key Provisions of the Representation of the People Act, 1951
- Qualifications and Disqualifications: The Act outlines the criteria for membership in Parliament and State Legislatures, including qualifications and disqualifications.
- Notification of General Elections: It includes provisions for notifying general elections to ensure a smooth electoral process.
- Administrative Machinery: The Act establishes the administrative framework for conducting elections, ensuring proper oversight and management.
- Registration of Political Parties: It provides guidelines for the registration of political parties, regulating their participation in the electoral process.
- Conduct of Elections: The Act details various aspects of election conduct, including:
(a) Nomination of Candidates: The process for nominating candidates for elections.
(b) Candidates and Their Agents: Regulations concerning candidates and their agents during the electoral process.
(c) General Procedure at Elections: Overall procedures to be followed during elections.
(d) The Poll: Guidelines for the polling process.
(e) Counting of Votes: Procedures for counting votes post-election.
(f) Multiple Elections: Provisions for conducting multiple elections simultaneously.
(g) Publication of Election Results: Guidelines for publishing election results and nominations.
(h) Declaration of Assets and Liabilities: Requirements for candidates to declare their assets and liabilities.
(i) Election Expenses: Regulations regarding election expenses incurred by candidates.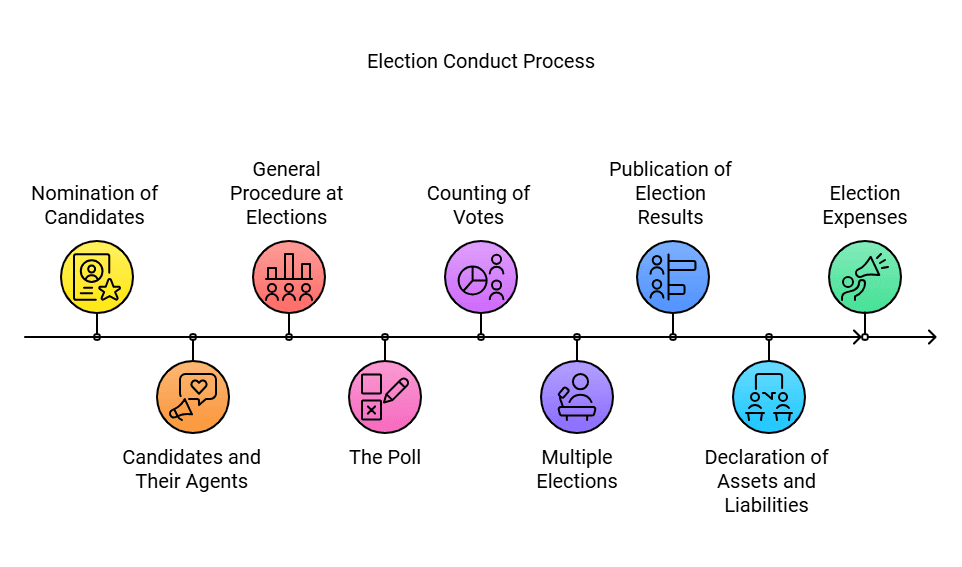
- Free Supply of Materials: The Act allows for the free supply of certain materials to candidates of recognized political parties to ensure a level playing field.
- Disputes Regarding Elections: Provisions related to election disputes include:
(i) Presentation of Election Petitions: Guidelines for presenting election petitions to the High Court.
(ii) Trial of Election Petitions: Procedures for the trial of election petitions.
(iii) Withdrawal and Abatement: Rules regarding the withdrawal and abatement of election petitions.
(iv) Appeals to Supreme Court: Guidelines for appealing election petitions to the Supreme Court.
(v) Costs and Security for Costs: Provisions related to costs and security for costs in election petitions. - Corrupt Practices and Electoral Offences: The Act defines corrupt practices and electoral offences, outlining penalties and measures to ensure fair elections.
- Powers of Election Commission: The Act grants the Election Commission powers to inquire into disqualifications of members, ensuring accountability and transparency.
- Bye-Elections and Filling Vacancies: Provisions for conducting bye-elections and setting time limits for filling vacancies in elected positions.
- Miscellaneous Provisions: Various other provisions related to elections not covered in the above points.
- Barring Jurisdiction of Civil Courts: The Act bars the jurisdiction of civil courts in matters related to elections, ensuring that disputes are resolved within the framework of the law.
Significance
- The act is significant for the smooth functioning of the Indian democracy as it bars the entry of persons with criminal background into representative bodies, thus decriminalizing Indian politics.
- The act requires every candidate to declare his assets and liabilities, and maintain an account of election expenses. This provision ensures the accountability and transparency of the candidate in the use of public funds or misuse of power for personal benefits.
- It prohibits corrupt practices like booth capturing, bribery or promoting enmity etc., which ensures the legitimacy and free & fair conduct of elections which is essential for the success of any democratic setup.
- The Article 326, Representation of the People Act 1950 and Representation of the People Act 1951 cover almost all the essential provision required to make any electoral process efficient and accountable. Thus, making the whole process more accommodative and inclusive along with paving the way for participative democracy.
Delimitation Act, 2002
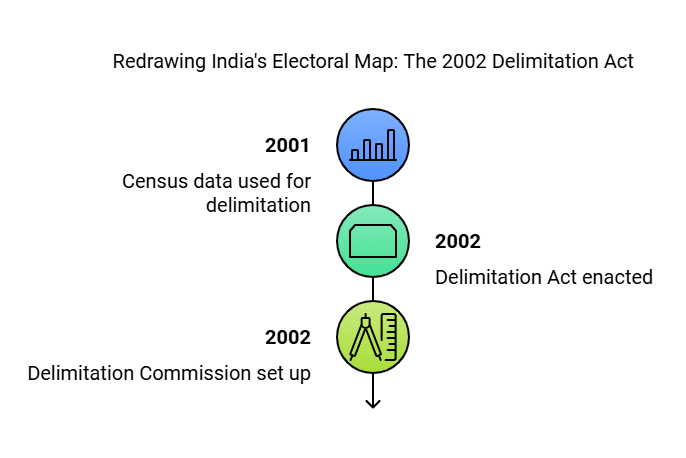
- Articles 82 and 170 of the Constitution of India provide for readjustment and the division of each State into territorial constituencies (Parliamentary constituencies and Assembly constituencies) on the basis of the 2001 census by such authority and in such manner as Parliament may, by law, determine.
- Therefore, the Delimitation Act, 2002, was enacted to set up a Delimitation Commission for the purpose of effecting delimitation on the basis of the 2001 census so as to correct the aforesaid distortion in the sizes of electoral constituencies.
- Articles 330 and 332 provide for re-fixing the number of seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the House of the People and Legislative Assemblies of the States based on the 2001 census.
 Background
Background
- Previous delimitation was based on the 1971 census.
- There has been uneven population growth and continuous migration, leading to significantly different sizes of electoral constituencies, even within the same State.
Purpose of the Delimitation Act, 2002
- To set up a Delimitation Commission to effect delimitation based on the 2001 census.
- To correct the distortions in the sizes of electoral constituencies.
Other Acts Related to Elections
1. Parliament (Prevention of Disqualification) Act, 1959: This Act states that certain offices of profit under the Government will not disqualify the holders from being elected as members of Parliament.
2. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Orders (Amendment) Act, 1976: This Act allows for the inclusion and exclusion of certain castes and tribes from the lists of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes. This is done for the readjustment of representation in parliamentary and assembly constituencies.
3. Government of Union Territories Act, 1963: This Act pertains to the governance of Union Territories in India.
4. Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991: This Act relates to the governance of the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
5. Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Act, 1952: This Act regulates various matters related to elections for the offices of the President and Vice-President of India.
Rules Related to Elections
1. Registration of Electors Rules, 1960. These rules outline the process for creating and publishing electoral rolls
2. Conduct of Elections Rules, 1961. These rules ensure the fair and free conduct of elections for the Parliament and State Legislatures.
3. Prohibition of Simultaneous Membership Rules, 1950. These rules prohibit simultaneous membership in certain bodies.
4. Members of Lok Sabha (Disqualification on Ground of Defection) Rules, 1985. These rules detail the circumstances under which Lok Sabha members can be disqualified due to defection.
5. Members of Rajya Sabha (Disqualification on Ground of Defection) Rules, 1985. Similar to the Lok Sabha rules, these outline disqualification criteria for Rajya Sabha members.
6. Presidential and Vice-Presidential Elections Rules, 1974. These rules govern the elections for the President and Vice-President of India.
7. Members of Lok Sabha (Declaration of Assets and Liabilities) Rules, 2004. These rules require Lok Sabha members to declare their assets and liabilities.
8. Members of Rajya Sabha (Declaration of Assets and Liabilities) Rules, 2004. Similar to the Lok Sabha rules, these require Rajya Sabha members to declare their assets and liabilities.
Orders Related to Elections
1. Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968: This order deals with the specification, reservation, choice, and allotment of symbols used in elections for parliamentary and assembly constituencies. These symbols are crucial for the recognition of political parties during elections.
2. Registration of Political Parties (Furnishing of Additional Particulars) Order, 1992: This order mandates that associations or bodies of individual citizens of India seeking to register as a political party with the Election Commission of India must provide additional particulars. This ensures transparency and clarity in the registration process.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Election Laws - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main objectives of the Representation of the People Act, 1950? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Representation of the People Act, 1951? |  |
| 3. How does the Delimitation Act, 2002 impact electoral constituencies? |  |
| 4. What are the rules related to elections as per the Election Commission of India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the various orders related to elections issued by the Election Commission? |  |

















