Laxmikanth Summary: Governor | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
- Articles 153 to 167 in Part VI of the Constitution deal with the state executive. The state executive consists of the governor, the chief minister, the council of ministers, and the advocate general of the state. Thus, there is no office of vice-governor (in the state) like that of Vice-President at the Centre.
- The governor is the chief executive head of the state. But, like the president, he is a nominal executive head (titular or constitutional head). The governor also acts as an agent of the central government. Therefore, the office of governor has a dual role.

- Usually, there is a governor for each state, but the 7th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1956 facilitated the appointment of the same person as a governor for two or more states.
Appointment of Governor
- The governor is neither directly elected by the people nor indirectly elected by a specially constituted electoral college as is the case with the president.
- He is appointed by the president by warrant under his hand and seal. In a way, he is a nominee of the Central government.
The Draft Constitution provided for the direct election of the governor on the basis of universal adult suffrage.
But the Constituent Assembly opted for the present system of appointment of governor by the president because of the following reason:
- The direct election of the governor is incompatible with the parliamentary system established in the states.
- The mode of direct election is more likely to create conflicts between the governor and the chief minister.
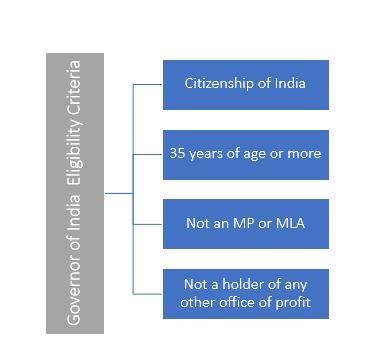
The Constitution lays down only two qualifications for the appointment of a person as a governor. These are:
- He should be a citizen of India.
- He should have completed the age of 35 years.
Qualifications, Oath, and Conditions
The position of Governor in India comes with specific qualifications, an oath, and certain conditions as outlined in the Constitution and recommended by the Sarkaria Commission.
Qualifications
To be appointed as a Governor, a person must fulfill certain constitutional requirements.

Sarkaria Commission Recommendations (1983-88):
- Should be eminent in some field.
- Should be from outside the state.
- Should not be closely tied to local politics.
- Should not have been heavily involved in politics recently.
- Avoid appointing ruling party politicians as governors in states run by other parties.
- Consultation with the state chief minister should be mandatory (amend Article 155).
- Prime Minister may informally consult Vice-President and Lok Sabha Speaker.
Oath or Affirmation
Before Taking Office: The governor must take an oath or affirmation to:
- Carry out the duties of the office honestly.
- Safeguard, uphold, and defend the Constitution and the law.
- Serve and promote the welfare of the state’s citizens.
Administered By: The Chief Justice of the state’s High Court, or the highest-ranking judge if the Chief Justice is not available.
Others: Anyone acting as governor must also take this oath.
Conditions of Governor's Office
The Constitution lays down the following conditions for the governor's office:
- He should not be a member of either House of Parliament or a House of the state legislature.
- He should not hold any other office of profit.
- He is entitled without payment of rent to the use of his official residence (the Raj Bhavan).
- When the same person is appointed as the governor of two or more states, the emoluments and allowances payable to him are shared by the states in such proportion as determined by the president.
Term of governor’s office: Five years
Salary: The salary of governors was increased by Parliament in 2018 to ₹3.50 lakh per month, up from ₹1.10 lakh.
Privileges and Immunities: Governors enjoy certain privileges and immunities, including:
- Immunity from legal liability for actions taken in office.
- Immunity from criminal proceedings during their term, even for personal actions.
- Protection from arrest or imprisonment.
- Civil proceedings for personal actions can occur after two months’ notice.
Term of Governor's Office
Term of Office:
- A governor's term lasts for five years, starting from when they assume office.
- However, this term is subject to the President's discretion, meaning the President can remove the governor at any time.
- Governors also have the option to resign at any time by submitting a resignation letter to the President.
No Security of Tenure:
- The Supreme Court ruled in the Surya Narain case (1981) that governors do not have job security or a guaranteed term, as the President's pleasure is not a valid reason for removal.
The Constitution does not specify grounds for removal, allowing the President to remove governors without stated reasons.
- For instance, in 1989, the V.P. Singh government requested the resignation of governors appointed by the previous Congress government, with some being replaced and others retained.
Similarly, in 1991, the P.V. Narasimha Rao government replaced 14 governors appointed by earlier administrations.
Transfer and Reappointment:
The President can transfer a governor to another state for the remainder of their term.
Additionally, a governor whose term has ended may be reappointed in the same state or in a different state.
Continuity of Office:
- To ensure seamless governance, a governor may continue in office beyond their five-year term until a successor is appointed.
Contingency Provisions:
- In the event of unforeseen circumstances, such as a governor's death, the President can make arrangements for the fulfillment of the governor's duties.
- For example, the chief justice of the state's high court may be appointed temporarily to assume the governor's responsibilities.
Powers and Functions of Governor
The powers and functions of the governor can be studied under the following heads:
1. Executive Powers
The executive powers and functions of the Governor are:
(i) All executive actions of the government of a state are formally taken in his name.
(ii) He can make rules for more convenient transactions of the business of a state government and for the allocation among the ministers of the said business.
(iii) He appoints the chief minister, advocate general of a state, election commissioner, appoints the chairman and members of the state public service commission.
(iv) He can seek any information relating to the administration of the affairs of the state and proposals for legislation from the chief minister.
(v) He can require the chief minister to submit for the consideration of the council of ministers any matter on which a decision has been taken by a minister but which has not been considered by the council.
(vi) He can recommend the imposition of constitutional emergency in a state to the president.
2. Legislative Powers
A governor is an integral part of the state legislature.
In that capacity, he has the following legislative powers and functions:
(i) He can summon or prorogue the state legislature and dissolve the state legislative assembly.
(ii) He can send messages to the house or houses of the state legislature, with respect to a bill pending in the legislature or otherwise.
(iii) He can appoint any member of the State legislative assembly to preside over its proceedings when the offices of both the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker fall vacant. Similarly, he can appoint any member of the state legislature council to preside over its proceedings when the offices of both Chairman and Deputy Chairman fall vacant.
(iv) He nominates one-sixth of the members of the state legislative council from amongst persons having special knowledge or practical experience in literature, science, art, cooperative movement and social service, He can nominate one member to the state legislature assembly from the Anglo-Indian Community.
(v) He decides on the question of disqualification of members of the state legislature in consultation with the Election Commission.
(vi) When a bill is sent to the governor after it is passed by state legislature, he can:
- Give his assent to the bill.
- Withhold his assent to the bill.
- Return the bill (if it is not a money bill) for reconsideration of the state legislature. However, if the bill is passed again by the state.
(vii) He can promulgate ordinances when the state legislature is not in session. These ordinances must be approved by the state legislature within six weeks from its reassembly.
3. Financial Powers
The financial powers and functions of the governor are:
(i) He sees that the Annual Financial Statement (state budget) is laid before the state legislature.
(ii) Money bills can be introduced in the state legislature only with his prior recommendation.
(iii) No demand for a grant can be made except on his recommendation.
(iv) He can make advances out of the Contingency Fund of the state to meet any unforeseen expenditure.
(v) He constitutes a finance commission after every five years to review the financial position of the panchayats and the municipalities.
4. Judicial Powers
The judicial powers and functions of the governor are:
(i) He can grant pardons, reprieves, respites, and remissions of punishment or suspend, remit, and commute the sentence of any person convicted of any offence against any law relating to a matter to which the executive power of the state extends.
(ii) He is consulted by the president while appointing the judges of the concerned state high court.
(iii) He makes appointments, postings, and promotions of the district judges in consultation with the state high court.
(iv) He also appoints persons to the judicial service of the state (other than district judges) in consultation with the state high court and the State Public Service Commission.
5. Discretionary Powers
Article 154 of the Constitution empowers the Governor to act according to their own discretion, without being bound by ministerial advice.
The Governor's discretionary powers include:
(i) Reserving a Bill for the President of India.
(ii) Recommending the imposition of President’s Rule in the State.
(iii) Acting as the administrator of a nearby Union Territory when given additional charge.
(iv) Deciding on payments by State Governments to an Autonomous Tribal District Council for mineral exploration licenses.
(v) Requesting information from the Chief Minister on administrative and legislative matters.
(vi) Appointing the Chief Minister in a hung assembly or when the position becomes vacant unexpectedly.
(vii) Dismissing the Council of Ministers (CoM) if they cannot prove majority support.
(viii) Dismissing the State Legislative Assembly when the CoM has lost its majority.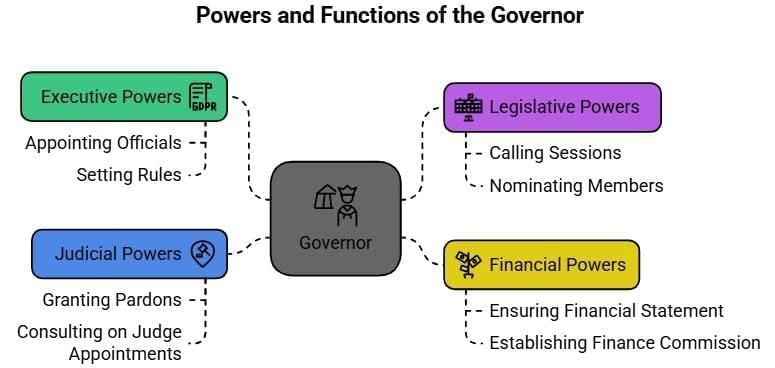
Constitutional Provision of Governor
Constitutional Framework:
- The Indian Constitution establishes a parliamentary system in states, making the governor a nominal executive, with real executive power held by the council of ministers led by the chief minister (Articles 154, 163, 164).
- The governor acts on the advice of the council of ministers, except in cases where the governor has the discretion to act independently.

Differences from the President:
The Constitution allows the governor to act in their discretion in certain cases, unlike the President, where no such provision exists.
After the 42nd Amendment (1976), ministerial advice is binding on the President, but no such binding provision exists for the governor.
Discretionary Powers:
Constitutional Discretion (Explicit in the Constitution):
Reserving a bill for the President’s consideration.
Recommending President’s Rule in the state.
Acting as administrator of an adjoining union territory (if assigned).
Determining royalty payments for tribal councils in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram for mineral exploration licenses.
Situational Discretion (Arising from political circumstances):
Appointing a chief minister when no party has a clear majority or after the sudden death of a chief minister with no clear successor.
Dismissing the council of ministers if it loses the confidence of the state legislative assembly.
Dissolving the state legislative assembly when the council of ministers loses its majority.
The governor’s decision on whether a matter falls under their discretion is final and cannot be challenged.
Special Responsibilities: The governor has specific duties assigned by the President, where they consult the council of ministers but act in their discretion:
Maharashtra: Establishing development boards for Vidarbha and Marathwada.
Gujarat: Establishing development boards for Saurashtra and Kutch.
Nagaland: Maintaining law and order during internal disturbances in the Naga Hills-Tuensang Area.
Assam: Administering tribal areas.
Manipur: Administering hill areas.
Sikkim: Ensuring peace and socio-economic advancement of different population sections.
Arunachal Pradesh: Maintaining law and order.
Karnataka: Establishing a development board for the Hyderabad-Karnataka region.
Dual Role:
The governor serves as both the constitutional head of the state and the representative of the Centre (i.e., the President) in the Indian federal system.
Issues in Governor's Functioning
The Sarkaria Commission (1983-88) highlighted ongoing issues in the functioning of governors, as summarized below:
 Newspaper's Article on Sarkaria Commission
Newspaper's Article on Sarkaria Commission
Choosing a Chief Minister:
- Clear Majority: When a single party or coalition has a clear majority, there is no issue in selecting a Chief Minister.
- No Absolute Majority: In cases where there is no absolute majority, governors must use their judgment to select a Chief Minister, typically choosing the leader with the most support in the assembly.
- Confidence Votes: The assembly conducts confidence votes to minimize claims of bias in the selection process.
- Resigning Ministry: Similar judgment is required when a ministry resigns after losing majority support or a confidence vote.
Testing Majority:
Governors use varied methods to verify majority support, such as reviewing lists of supporters or physically counting heads.
The lack of a consistent approach in testing majority support has raised concerns about fairness and transparency.
Dismissing a Chief Minister:
There are no standardized rules for dismissing a Chief Minister.
A Chief Minister must either resign or demonstrate majority support in the assembly if they lose backing.
Inconsistent practices among governors regarding dismissals have led to criticism and perceptions of bias.
Dissolving the Legislative Assembly:
A chief minister with majority support can advise dissolution, which is usually binding.
In cases where the chief minister lacks majority, some governors refuse dissolution, while others accept it, leading to inconsistent practices.
Recommending President’s Rule:
Governors often recommend President's Rule under Article 356 during periods of political instability.
There are concerns that governors may not fully consider all options for stable government formation, acting in a biased manner.
The lack of a standard approach in recommending President's Rule raises questions about fairness and due process.
Reserving Bills for President’s Consideration:
Governors’ decisions to reserve state bills for the President’s review have sparked controversy, with questions about their discretionary use.
Nominations to Legislative Council:
Governors’ discretionary nominations to the legislative council have been criticized, as many argue they lack discretion in such matters and should follow ministerial advice.
Discretion as University Chancellor:
- Governors, as chancellors of state universities, have powers under university laws, such as nominating council members or officials.
- These actions are questioned, with some arguing that governors should follow the advice of the council of ministers rather than acting on their own discretion.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Governor - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the appointment conditions for a Governor in India? |  |
| 2. What are the executive powers of the Governor? |  |
| 3. What legislative powers does the Governor hold? |  |
| 4. How does the Governor exercise financial powers? |  |
| 5. What are discretionary powers of the Governor? |  |






















