Nitin Singhania Summary: Indian Literature- 1 | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
- Literature comes from the Latin word "litteratura," meaning writing formed with letters.
- It includes any writing with literary value and is divided into fiction and non-fiction.
- It's further divided into poetry and prose, with various forms like novels, short stories, drama, and novellas.
- Epics were popular in Greco-Roman times and were initially transmitted orally before being written down.
- Print technology in the 18th century made literature more accessible to people.
- Nowadays, electronic literature is widely read by many.
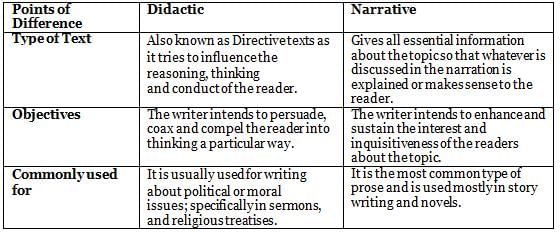
Differences between Didactic and Narrative Text
 In India, four major speech groups are followed, i.e. Austric, Dravidian, Sino-Tibetan and Indo- European.
In India, four major speech groups are followed, i.e. Austric, Dravidian, Sino-Tibetan and Indo- European.Literature in Ancient India
- Ancient Indian literature wasn't just limited to sacred texts like the Vedas and Upanishads; there were also writings in Prakrit that focused on realism and moral values, separate from religious themes.
- The Vedas are the most well-known ancient texts, used both in religious rituals and daily life.
- Epics and lyrical works were also composed in languages like Sanskrit, Prakrit, Pali, and Ardhamagadhi during ancient times.
- Vedic literature is divided into two categories: Shruti and Smriti.
- Shruti includes sacred texts like the Vedas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas, and Upanishads.
- Smriti, meaning 'that which is remembered,' consists of post-Vedic Classical Sanskrit literature, including Vedanga, Smritis Dharmashastras, Shad darshana, Puranas, Itihasa, Upavedas, and Mahakavyas.
Vedas
- The word "Veda" comes from the root 'vid', meaning 'to know', signifying knowledge.
- Vedas aim to provide knowledge for conducting life on earth and beyond.
- They're believed to be Apaurusheya, not created by humans.
- Written in stylized poetic form, using symbolic language and myths.
- Initially transmitted orally by Brahmin families, estimated to be compiled around 1500-1000 BC.
- In Hindu tradition, Vedas are sacred divine revelations guiding humanity eternally.
- They emphasize the unity of the universe and its inhabitants, promoting Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam.
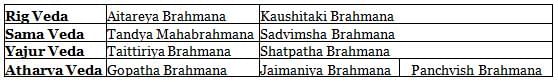
- There are four major Vedas: Rig Veda, Yajur Veda, Sama Veda, and Atharva Veda.
- Written by Vedic seers and poets known as rishis, envisioning cosmic mysteries in Sanskrit poetry.
- All Vedas prioritize yagna (sacrifice).
- Each Veda is accompanied by Brahmanas, Upanishads, and Aranyakas.
(A) Rig Veda
- Oldest Veda with 1028 hymns.
- Focuses on worldly prosperity and natural beauty.
- Organized into 10 books called Mandalas, containing hymns dedicated to various deities.
- Main deities include Lord Indra, Agni, Varuna, and others.
- Hymns recited by Hotri sages.
(B) Yajur Veda
- Concentrates on rituals and sacrifices.
- Two major recensions: Shukla (white) and Krishna (black).
- Acts as a guidebook for priests conducting sacrificial rituals.
- Contains 1875 hymns, with 75 originals.
- Predominantly ritualistic, knows the metal iron.
(C) Sama Veda
- Consists of hymns, detached verses, and 16,000 ragas (musical notes).
- Often called the 'book of chants' due to its lyrical nature.
- Shows the development of Indian music in the Vedic period.
- Hymns recited by Udgatri sages.
- Part of the Trayi Vidya (Triple Science) along with Rig Veda and Yajur Veda.
(D) Atharva Veda
- Also known as Brahma Veda.
- Concerned with peace, prosperity, and daily life aspects, including medical treatments.
- Attributed to rishis Atharvan and Angiras.
- Prescribes treatments for nearly 99 diseases.
- Two major recensions: Paippalada and Saunakiya.
- Deals with healing, magic, speculation on universal changes, and household issues.
1. Didactic text is usually used for story writing and novels.
2. The narrative text is used for writing on political or moral issues.
Which of the above is/are correct?
Brahmanas
- Integral part of Hindu sruti literature, each Veda accompanied by its Brahmana.
- Brahmanas comprise commentaries, legends, facts, and philosophical insights into Vedic rituals.
- They offer guidance on ritual performance and elucidate the symbolic meanings of sacred words.
- Historically estimated to have been composed between 900 and 700 BC.
Aranyakas
- Texts closely associated with the Vedas, delving into the philosophical underpinnings of Vedic rituals and sacrifices.
- Aranyakas expound on topics such as rituals, the cycles of birth and death, and the intricacies of the soul.
- Tradition suggests they were imparted by sages known as Munis, who chose to dwell in forest retreats.
- Each Veda is paired with its respective Aranyaka, serving as a bridge between the ritualistic approach (Karma Marga) advocated by the Brahmanas and the path of knowledge (Gyan Marga) espoused by the Upanishads.
Upanishads
- A collection of over 200 treatises transmitted orally from teacher to student.
- Written in Sanskrit, the Upanishads delve into monastic and mystical themes.
- Often referred to as Vedanta or the 'end of the Veda', they explore human salvation and abstract philosophical questions.
- Prominent Upanishads include Brihadaranyaka and Chandogya Upanishads, with the phrase "Satyameva Jayate" derived from Mundaka Upanishad.
- Foundational to Hindu philosophical thought, they elucidate the interconnectedness of human existence with cosmic realities.
- Difference between Upanishads and Aravankas:
| Upanishad | Jnana-kanda | Knowledge/spirituality section |
| Arayanka | Karma-kanda | Ritualistic actions/sacrifice section |
The Epics: the Mahabharata and the Ramayana
- The two Sanskrit epics are known as Mahakavya because they are deeply ingrained in the collective memory of Hinduism's followers.
- Over time, both texts have been compiled and expanded upon by various sages, bards, and storytellers.
- What we have today is a result of numerous transmissions and additions made throughout the ages.
- They have evolved into rich amalgamations of narratives and wisdom passed down through generations.
(A) Ramayana
- Written by the sage Valmiki, known as Adikavi or the 'first amongst the poets'.
- Estimated to have been compiled around 1500 BC.
- Portrays Rama as the ideal man and provides guidance on achieving Purushartha: Dharma, Artha, Kama, and Moksha.
- Contains 24,000 verses divided into seven books (Khandas).
- Depicts the war between Rama and Ravana over the kidnapping of Sita, with major characters like Hanuman and Lakshmana.
- Various versions exist in Indian languages, with adaptations like 'Ram Charita Manas' by Tulasi Das.
- The Ramayana's influence extends to South-East Asian countries like Cambodia, Thailand, and Indonesia.
(B) Mahabharata
- Penned by Ved Vyas and initially had 8,800 verses known as 'Jaya'.
- Expanded over time to 24,000 verses, then to 100,000 verses during the Gupta period.
- Divided into 18 parvas (chapters), making it the longest epic ever written.
- Central conflict revolves around the Kauravas and Pandavas vying for the throne of Hastinapur.
- Lord Krishna serves as the sutradhar (narrator) of the story.
- Contains the Bhagavad Gita, a didactic text addressing philosophical dilemmas and guiding righteous living.
- Explores themes of duty, violence versus non-violence, and the concept of dharma.
- Referred to as the fifth Veda in Indian tradition.
The Puranas
- Puranas, meaning 'that which renews the old', are ancient Indian mythological texts.
- They narrate stories about the creation of the universe and its history until its supposed destruction.
- Cover diverse subjects like folk tales, pilgrimages, astronomy, grammar, and theology.
- Focus mainly on the Hindu trinity of Brahma, Vishnu, and Mahesh.
- There are 18 major Puranas (Mahapuranas), each highlighting a particular deity and exploring related philosophical and religious concepts.
- Prominent Puranas include Bhagavata, Brahma, Vayu, Agni, Garuda, Padma, Vishnu, and Matsya.
- They offer insights into post-Vedic India's social, cultural, and religious life, as well as geographical, historical, and dynastic details.
- Skanda Purana is the longest, while Markandeya Purana is the shortest.
- Written in story form, blending myths, legends, and sermons about deities.
- Popular among the masses due to their accessible storytelling compared to the complex Vedas.
- Puranas were translated into vernacular languages and spread their message through parables and fables.

Upavedas
- Upavedas are traditional literature associated with technical subjects in Hinduism.
- They include:
(i) Dhanurveda: Science of warfare, linked with the Yajurveda.
(ii) Gandharvaveda: Covers aesthetics, including music, dance, poetry, sculpture, and erotica, associated with the Samaveda.
(iii) Ayurveda: Science of health and life, linked with the Atharvaveda.
(iv) Arthasastra: Deals with public administration, governance, economy, and polity, associated with the Atharvaveda.
(v) Sthapatyaveda: Relates to engineering and architecture, associated with the Yajur Veda.
Upapuranas
- Upapuranas, or minor Puranas, emerged from the popularity of the Puranas among the masses.
- There are approximately 19 minor Puranas.
- They focus on five major subjects as outlined by the Sanskrit lexicographer Amarasimha from the Gupta period.
 Classical Sanskrit Literature
Classical Sanskrit Literature
- The Classical Sanskrit Literature period in India spans from the 4th century AD to the 12th century AD.
- Sanskrit literature is broadly categorized into Vedic and Classical, with notable exceptions like the Mahabharata and Ramayana discussed separately due to their religious significance.
- These epics are considered precursors to Sanskrit epic poetry (kavya), classical drama (nataka), and various treatises on subjects such as medicine, statecraft, grammar, astronomy, and mathematics.
- Panini's Ashtadhyayi serves as a cornerstone for Sanskrit grammar, providing rigid rules that govern the language.
- Other significant works on Sanskrit grammar include Patanjali's Mahabhashya (250 BC) and Katyayana's Varttika-sutra.
- Katyayana's Varttikas on Panini's Sutras, comprising 1500 verses, are only available through references in Patanjali's work.
(A) Sanskrit Drama
- Sudraka composed "Mrichchhakatika" (The Little Clay Cart) around the 5th century CE, featuring a love story between Charudatta, a young Brahmin, and Vasantasena, a wealthy courtesan.
- Vishakhadatta wrote "Mudrarakshasa" and "Devi-Chandraguptam," focusing on King Chandragupta Maurya's ascension and Uttaramacarita depicting Rama's later life.
- Bhasa, predating Kalidasa, authored plays like "Svapnavasavadattam," with his works rediscovered by scholar T. Ganapati Sastri in 1912.
- Harshavardhana authored plays like "Ratnavali," "Nagananda," and "Priyadarsika," each highlighting different aspects of romance and sacrifice.
(B) Sanskrit Poetry
- Kalidasa, a renowned poet, wrote works like "Kumarasambhavam," "Malavikagnimitram," "Raghuvamsa," and "Vikramorvashiyam," renowned for their literary excellence.
- Jayadeva's "Gita Govinda" explores Lord Krishna's life and love for Radha, blending devotion with nature's beauty.
- Other notable poets include Dandin, Magha, Bharavi, and Nayachandra Suri, each contributing to Sanskrit literature with their unique themes and styles.
(C) Other Major Sanskrit Texts
- Kautilya's "Arthasastra" from the Mauryan period delves into economic, social, and military strategies of the empire, often attributed to Chanakya.
- Scientific texts like "Charaka Samhita," "Sushruta Samhita," and "Aryabhatiya" cover fields such as medicine, surgery, mathematics, and astronomy, showcasing ancient Indian knowledge and expertise.
- Scientific texts of this period:
| Charak | Charak Samhita (Book on Medicine) |
| Sushruta | Sushruta Samhita (Book on surgery) |
| Madhava | Madhava Nidana (Book on pathology) |
| Varamihira | Pancha-Siddhantika (Book on astrology) |
| Varamihira | Brihat Samhita (book on wide ranging subjects like planetary movements, geology, architecture,etc. |
| Aryabhatta | Aryabhatiya (Book on astronomy and mathematics) |
| Lagdhacharya | Book on astrology |
| Pingala | Book on Mathematics |
| Bhaskara | Siddhanta Shiromani |
Literature in Pali and Prakrit
- Post-Vedic period saw the rise of Prakrit and Pali literature alongside Sanskrit.
- Prakrit is a term used loosely for languages derived from Sanskrit but not standardized.
- Pali is an archaic form of Prakrit, amalgamating various existing dialects.
- Prakrit gained importance with the composition of Buddhist and Jain religious texts.
- Pali was utilized by Lord Buddha himself for his teachings.
- Canonical works are divided into Tripitakas or "baskets" of knowledge.
(i) Vinaya Pitaka: Rules and regulations for Buddhist monks.
(ii) Sutta Pitaka: Dialogues and speeches of Buddha focusing on morality and righteous dharma.
(iii) Abhidhamma Pitaka: Concentrates on philosophy, metaphysics, ethics, theory of knowledge, and psychology. - Jatakas are non-canonical Buddhist texts depicting stories from Buddha's previous births and the journeys of Bodhisattvas.
- They encompass popular tales, ancient mythology, and socio-political conditions in North India from 600 BC to 200 BC.
- "Buddhacharita" by Aswaghosha (78 A.D.) is a notable Sanskrit Buddhist text.
- Jainism contributed texts in Prakrit forming the basis of Jain canonical literature.
- Notable Sanskrit Jain texts include "Upamitibhava Prapancha Katha" by Siddharasi (906 A.D.).
- Prakrit Jain texts include Angas, Upangas, Parikramas, Chhedab Sutra, and Malasutra.
- Writers like Hemachandra and Haribhadra Suri provided treatises on lexicography, grammar, and socio-political history of Jain communities.
- Prakrit poetry, like "Gathasaptashati" by Hala (300 A.D.), incorporates elements of erotica and features contributions from various female poetesses like Pahai, Roha, Sasippaha, Mahavi, and Reva.
Other Buddhist literary texts
(i) Dipavamsa: written in 3rd-4th centuries BCE in Anuradhapur (Sri Lanka), during the reign of King Dhatusena. Literally means “Chronicle of the Island” & mentions about visit of Buddha to Sri Lanka & relics of Buddha.
(ii) Milinda Panha: dialogue between King Meander (or Milinda) & Buddhist monk Nagasena- it means “Questions of Milinda”- one of the highest philosophical enquiries.
(iii) Mahavamsa: epic poem in Pali language around 3rd-4th centuries BCE during the reign of King Vijaya- historical account of various kingdoms of South Asia.
(iv) Mahavastu: Contains Jakata & Avadana tales- written in mixed Sanskrit, Pali and Prakrit between 2nd century BC- 4th century AD.
(v) Lalitavistara Sutra: meaning “The play in full”- important Mahayana text- contains various stories on life of Buddha till his first sermon at Samath.
(vi) Udana: one of the oldest Theravada (Old School) Buddhist text- contains famous story of “Blind Men & the Elephant”.
(vii) Bodhi Vamv : prose-poem- written in 10th century in Sri Lanka- translated from Sinhalese version-written by Upatissa in Pali.
(viii) Udanavarga: compilation which contains utterances of Buddha & his disciples- written in Sanskrit.
(ix) Mahavibhasa Shastra: written around 150CE- contains discussions about other non-Buddhist philosophies- a Mahayan text.
(x) Abhidharmamoksha: written by Vasubandhu, in Sanskrit - widely respected text & contains discussion on Abhidharma.
(xi) Visuddhimagga: written by Buddhagosha in 5th century- text of Theravada doctrine- contains discussions on various teachings of Buddha.
Jain Texts
- Jain monks wrote in various languages based on the era, region, and patronage.
- During the Sangam Age in South India, they wrote in Tamil.
- They also authored works in languages like Sanskrit, Shauraseni, Gujarati, Kannada, and Marathi.
- Their writings can be broadly categorized into two groups:
(i) Canonical or religious texts known as Jain Agamas or Agam.
(ii) Non-canonical literary works, including texts like Niryuktis and Samhitas. - Bhadrabahu, the last acharya before the Jain Sangha split, authored several non-canonical texts.
Jain Agamas
- Sacred texts contain teachings of Jain tirthankars.
- Originally compiled by Gandharas, immediate disciples of Mahavira.
- Important for Svetambaras.
- Present Angas re-compiled in Vallabhi council in mid-5th century AD.
- Digambaras don't accept authority of Agamas, believing original teachings lost.
- Agamas comprise 46 texts in Ardha-Magadhi Prakrit.
- Teach reverence for all life forms, vegetarianism, asceticism, compassion, and non-violence.
- 12 Angas include Acharanga Sutra, Sutrakritanga, Sthananga Sutra, etc.
- Digambaras attribute sacred status to Karmaprabhrita and Kashayaprabhrita.
- Other important works by Bhadrabahu, Acharya Kundkund, Samanta Bhadra, Ilango Adigal, etc.
- Jain monks used Kannada from 9th-12th centuries.
- Pampa, Ponna, and Ranna are notable Jain-related writers in Kannada literature.
- Lingayat spread in Karnataka reduced Jainism's popularity and literary output after 12th-13th centuries.
Zoroastrian Literature
- Zoroastrianism originated from teachings of Persian prophet Zoroaster.
- Influential on Persian history, culture, and art.
- First religion to believe in angels, day of judgment, demonic figure, and battle between good and evil.
- Under Sassanid Empire, went through reforms and extensive text writing.
- Avesta, the most important text, written in Avestan language.
- Finalized during Sasanian rule in 4th century CE.
- Yasna, a key collection in Avesta, contains 72 chapters, including the revered "Gathas" authored by Zoroaster.
- Yasna is central to faith ceremonies.
- Other Avesta parts include Visperad, Yashts, Siroza, and Nyayeshes.
- Additional texts like Denkard, Bundahishn, Mainog-i-Khirad, and Book of Arda Viraf are significant.
(i) Denkard, written in the 10th century, serves as an encyclopedia.
(ii) Bundahishn elaborates on the theory of creation and includes astronomical ideas.
(iii) Mainog-i-Khirad and Sad-Dar are notable texts.
(iv) Book of Arda Viraf narrates the story of a devotee during the Sassanian era.
Sikh Literature
- Sikh literature refers to writings within the Sikh faith tradition.
- It encompasses texts that hold spiritual significance for Sikhs.
- The central scripture of Sikhism is the Guru Granth Sahib, also known as the Adi Granth.
- Guru Granth Sahib contains the teachings of Sikh Gurus and other saints.
- It is considered the eternal Guru by Sikhs.
- Alongside the Guru Granth Sahib, Sikh literature includes writings by Sikh scholars and poets.
- These writings cover various aspects of Sikh philosophy, history, and spirituality.
- Sikh literature plays a vital role in guiding the Sikh community and preserving its cultural heritage.
- It is written in languages such as Punjabi, Braj, and Persian.
- Sikh literature promotes values of equality, justice, and compassion.
- It inspires Sikhs to lead righteous and virtuous lives.
Dravidian Literature
- Comprises literature in four major Dravidian languages: Tamil, Kannada, Telugu & Malayalam.
- Tamil is the oldest & very close to Sanskrit, especially in terms of the grammar and borrowing of words.
- Most famous literature in Tamil- classical works or Sangam literature.
 |
Download the notes
Nitin Singhania Summary: Indian Literature- 1
|
Download as PDF |
Tamil (Sangam) Literature
- Sangam' literature refers to a collection of approximately 2381 poems attributed to 473 known poets, with an additional corpus from 102 anonymous poets.
- This literature emerged during the Sangam period, spanning from 300 BC to 300 AD, making it the earliest known literature of South India.
- The Sangam period saw the gathering of poets, bards, and writers from various parts of South India in assemblies called 'Sangamas', organized by the Pandya Kingdom.
- Two major schools of Sangam literature exist:
(i) 'Aham/Agam' or 'inner field', focusing on abstract human aspects like love and relationships.
(ii) 'Puram' or 'outer field', discussing social life, ethics, valor, and customs. - Though historical records of the first two Sangams are lacking, they are considered legendary by many scholars.
- The first Sangam was reportedly organized in Madurai by Agastya or Shiva, while the second Sangam took place in Kapatapuram, chaired initially by Agastya and later by his disciple Tolkappiyar.
- Tolkappiyam, a textbook on Tamil grammar and literature, was compiled during the second Sangam.
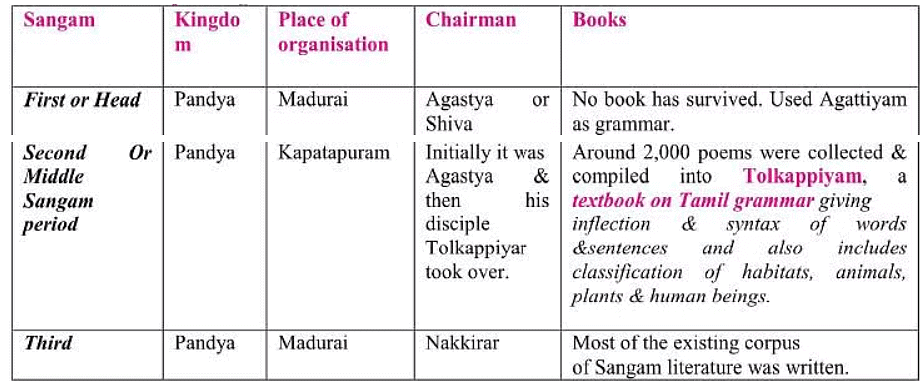 Three Major Sangams
Three Major Sangams - Notably, a significant portion of Sangam literature, around 30,000 lines of poetry, is known as 'Ettuthokai'.
- Tiruvalluvar contributed the Tirukkural to Sangam literature, divided into three parts discussing ethics, governance, and love.
- Avvaiyar, along with other female poets like Nachchellaiyar and Kakkaipadiniyar, made significant contributions to Tamil literature during the Sangam period.
- Besides Sangam literature, other well-known Tamil texts include the Tolkappiyam, elaborating on Tamil grammar and poetry, and literary works like Silappadikaram and Manimekalai, which offer insights into Tamil society's dynamics during the 5th-6th centuries AD.
Malayalam Literature
- Usually spoken in Kerala and surrounding areas, this literature originated in 11th century.
- Two major Malayalam works of medieval period- Kokasandisan & Bhasa Kautilya, commentary on Arthashastra.
- Major literary work in Malayalam was Ramacharitam, an epic poem by Cheeraman in 13th century.
- Ezhuthachan was a strong proponent of Bhakti movement and was the father of Malayalam literature.
- Champu - It is a literacy style and refers to the combination of poetry and prose. This style or genre has been used in Telugu, Odia, Kannada as well as Sanskrit literature.
Bhakti Literature
- During the early Medieval period, Tamil literature began to reflect Vaishnava Bhakti sentiments, characterized by profound devotion to Vishnu or his avatar Krishna.
- Between the 7th and 12th centuries, Tamil texts became highly devotional in nature, influenced by Bhakti sentiments.
- The 12 Alvars, or saint poets, were prominent figures in Tamil literature, expressing devotion to Vishnu through their writings. Among them, Andal, a female saint, is noteworthy.
- Another significant Bhakti group was the Nayanars, who extolled the virtues of Shaivism.
- Two major literary works, Periya Puranam and Kamba Ramayanam (also known as Ramavataram), gained popularity during the Chola period in Tamil Nadu.
- Periya Puranam, authored by Sekkizhar in the 12th century AD under the rule of Kulottunga II, provides poetic accounts of the lives of 63 Nayanars, making it a celebrated masterpiece of Tamil literature often regarded as the fifth Veda in Tamil.
Telugu Literature
- Nannaya (11th century) was the first poet in Telugu.
- Telugu reached its zenith during Vijayanagara period (golden age of Telugu literature).
- Most successful works were Uttaraharivamsam, by Nachana Somanatha, well-known court poet of King Bukka I.
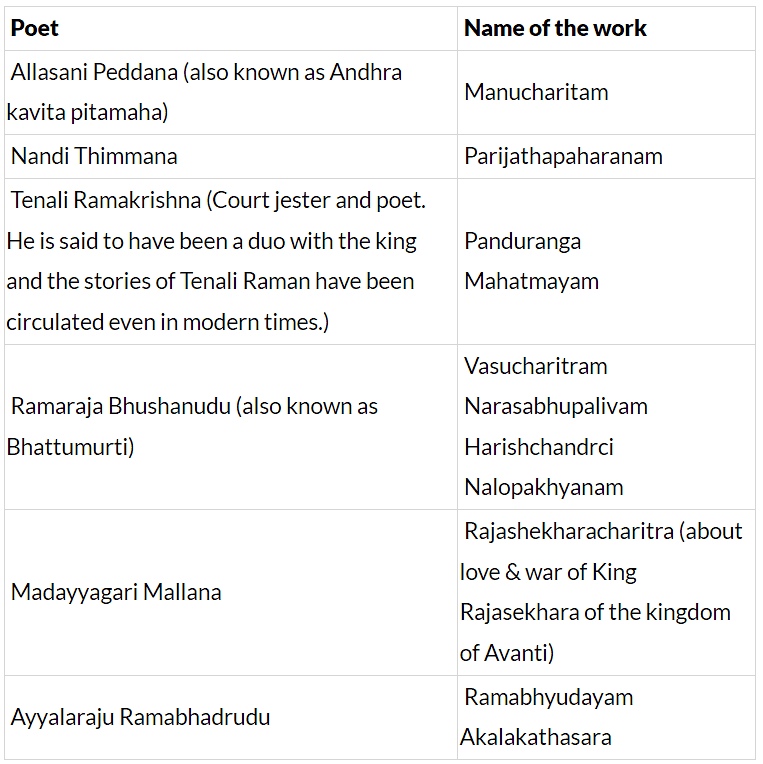
- Kings like Krishnadevaraya (1509-1529)- composed exceptional poetry titled Amuktamalyada(treatise stating instance of Lord Vishnu in his dream). Also eight learned literary personages, called ashtadiggajas were attached to his court, during his reign.
- Some of them are listed below:
1. A parable is a compilation of short stories which usually feature animals, in animal objects, mythical creatures, plants, etc who are given human life qualities.
2. Fables are the short stories which usually features a human character.
Which of the above statement/statements is/are correct?
Krishna Deva Raya - Great Scholar & Patron Of Literature
(i) Scholar & patron of many languages including Telugu, Kannada, Tamil & Sanskrit.
(ii) Reign of Krishna Deva Raya (1509-1529) in Vijayanagara Empire- age of Telugu literature.
(iii) Most important ashtadiggajas- Allasani Peddana.
(iv) Patronised Kannada poets Mallanarya, Chatu Vittalanatha, Timmanna Kavi. Vyasatirtha, a kannada saint was his Rajaguru.
(v) Krishna Deva Rayana Dinachari- another Kannada work on him.
(vi) Also wrote treatise in Sanskrit which includes Madalasa Charita, Satyavadu Parinaya and Rasamanjari & Jambavati Kalyana.
(vii) Patronised Tamil poet Haridasa.
Kannada Literature
- Jain scholars played a significant role in the development of Kannada literature, with the earliest known Jain-influenced text being Dharmanathapurana by Madhava, focusing on the life of the 15th tirthankara.
- The oldest Kannada inscription, known as the Halmidi inscription, dates back to the 5th century AD, indicating the antiquity of Kannada as a language.
- Notable Jain scholars, including Vilasa and Uritta Vilasa, contributed to Kannada literature with works such as Dharma Parikshe and Kavirajamarga.
- The "three gems" or Ratnatraya of Kannada literature were Pampa, Ponna, and Ranna, renowned poets from the 9th to 11th centuries AD.
- Pampa, often referred to as the "Father of Kannada," authored Adipurana and Vikramarjuna Vijaya, showcasing his poetic mastery and association with the Chalukya court.
- Ponna wrote the Shanti Purana, a biography of the 16th Jain Tirthankar Shantinath, while Ranna authored Ajitha Purana, based on the life of the 2nd Jain Tirthankar Ajitanatha, and Sahasa Bhima Vijaya.
- The growth of Kannada literature in the 10th century was supported by the patronage of the Vijayanagara Empire, leading to the creation of works like Shabdamanidarpana by Keshiraja, clarifying the language's grammar.
- Quasi-religious texts, such as Narahari's Torave Ramayana and Lakshmisha's Jaimini Bharata, also contributed to Kannada literature, reflecting its close association with the people.
- The literary style known as Champu, a blend of poetry and prose, gained prominence in Kannada literature, demonstrated by the writing of Madana Vijaya or Kabbigara Kava by Andayya, the first pure Kannada text without any Sanskrit influence.
- Honnamma, the first notable poetess in Kannada literature, authored Hadibadeya Dharma, emphasizing the duties of a devout wife.
- Other major texts in Kannada literature:
| Poets | Texts |
| Harishvara | Harishchandra Kavya Somanatha Charita |
| Bandhuvarma | Harivamshabhyudaya Jiva Sambodhana |
| Rudra Bhata | Jagannathavijaya |
| Andayya | Madana Vijaya or Kabbigara Kava (celebrated text as it was first pure Kannada text which did not have any Sanskrit word) |
1. Sushruta Samita deals with medicine.
2. Madhava Nidana deals with Pathology.
Which of the above statement/statements is/are correct?
Medieval Literature
- Major change- emergence of Persian as writing of Delhi Sultanate & Mughal courts.
- This period also sees development of Hindi from ancient upubhrumsu language
Persian
- Introduced to India during the 12th century by Turks and Mongols.
- Became the primary language of communication in courts during their rule.
- Notable Persian poets like Amir Khusrau Dehlavi emerged, known for works like Diwan and Masnavi Duwal Rani Khizr Khan.
- Delhi Sultanate saw the creation of numerous Persian texts.
- Historians like Zia-ud din Barani and Ibn Batuta contributed significantly.
- Flourished during the Mughal period with works like Tuzuk-I-Babari and Ain-e Akbari.
- Akbar commissioned translations of Sanskrit texts into Persian.
- Saw the creation of illustrated works like aamzanama and Padrnavat.
- Notable writers include Badauni and Faizi.
- Records of Shah Jahan's reign found in Shah Jahan-nama and Padshahnama.
- Aurangzeb's era saw the composition of Kulliyat by Mir Jafar Zatalli.
Urdu
- Developed from interactions between Persian and Hindi.
- Amir Khusrau contributed to early Urdu literature.
- Follows the grammar of Hindi with the form and script of Persian.
- Initially referred to as Dakkani.
- Mirza Ghalib emerged as a prominent Urdu poet.
- Other notable poets include Sauda, Dard, and Mir Taqi Mir.
- Influential figures like Iqbal and Sir Sayyid Ahmad Khan contributed to its modernization.
Hindi and its Dialects
- Evolved from Apabhramsa between the 7th and 14th centuries.
- Received a significant boost from the Bhakti movement.
- Regional languages like Bengali, Marathi, and Gujarati also experienced growth.
- Initially overshadowed by Sanskrit literature.
- Early Hindi literature includes works like Prithviraj Raso.
- Bhakti poets like Kabir and Tulsidas made notable contributions.
- Mirabai gained fame for her devotion to Krishna.
- Bihari's Satsai is renowned in Hindi literature.
Modern Literature
- The period of modern literature is referred to as Adhunik kaal.
- Hindi emerged as a major language in Northern India, alongside other languages like Bengali.
Hindi
- Hindi prose underwent significant changes with the arrival of the British.
- Bharatendu Harishchandra's famous drama "Andher Nagari" became a notable play in the 1850s.
- Notable works include "Bharat Durdasha" by Mahavir Prasad Dwivedi.
- The modern period of Hindi literature can be categorized into four subsections: Bhartendu Yug, Dwivedi Yug, Chhayavad Yug, and the contemporary period.
- Swami Dayanand spearheaded a movement to establish Hindi as a national language, with his notable work "Satyartha Prakash."
- Prominent Hindi authors include Munshi Prem Chand, Surya Kant Tripathi 'Nirala,' and Maithili Sharan Gupt.
- Munshi Prem Chand, known for works like "Godan" and "Bade Bhaiya," contributed to both Hindi and Urdu literature.
- Other significant writers include Sumitranandan Pant, Ramdhari Singh 'Dinkar,' and Harivansha Rai Bachchan.
- Mahadevi Verma, a Padma Vibhushan recipient, is among the most famous female Hindi writers of the 20th century.
Bengali, Odia, and Assamese Literature
- Bengali literature witnessed significant development in the 20th century, rivalling Urdu and Hindi.
- Distribution of Bengali literature was facilitated by the Baptist Mission Press at Serampore, Bengal, established by William Carey in 1800.
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy was among the pioneers of Bengali literature, along with Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar and Akshay Kumar Dutta.
- Bankim Chandra Chatterjee elevated Bengali literature with works like "Anand Math," which provided inspiration for "Vande Mataram."
- Rabindranath Tagore became the first Indian to win the Nobel Prize for Literature with his Bengali masterpiece "Geetanjali" in 1913.
- Assamese literature during the medieval period was dominated by court chronicles known as buranjis.
- Modern Assamese literature saw contributions from scholars like Padmanaba Gohain Barua and Lakshmi Nath Bezbaroa.
- Odia literature boasts a substantial corpus, with Sarala Das's work considered among the earliest.
- Upendra Bhanja was a notable writer in medieval Odia literature.
- In the modern period, Radha Nath Ray and Fakirmohan Senapati introduced a nationalistic tone in Odia literature.
Gujarati, Rajasthani, and Sindhi Literature
- The Bhakti movement had a profound impact on Gujarati literature.
- Narsinh Mehta combined devotional songs of Krishna with local folk traditions.
- Gujarati literature reached its pinnacle with works like Dr. K.M. Munshi's "Prithvi Vallabha."
- Medieval Rajasthani literature featured two main forms of fictional writing called Dingal and Pingal.
- Sindhi literature was influenced by regions like Rajasthan and Gujarat, with a lyrical style of poetry.
Kashmiri Literature
- Kashmiri literature traces back to Kalhan's "Rajatarangini" in Sanskrit.
- The Bhakti movement influenced early Kashmiri literature, with figures like Lai Ded emerging.
- Post-Islam and Sufism, writers like Sufi Ghulam Muhammad and Mahjoor made significant contributions.
Punjabi Literature
- Punjab's literature reflects regional and geographical influences.
- It is composed in two major scripts: Persian and Gurmukhi.
- Sufi poetry by Baba Farid and Bulley Shah gained popularity.
- Modern Punjabi literature was influenced by nationalistic writing and legends like Bhagat Singh.
Marathi Literature
- Saint Jnaneshwar's work in the 13th century marked the beginning of Marathi literature.
- Saints like Namdev, Sena, and Gora contributed significantly.
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak's newspaper "Kesari" criticized British policies in Marathi.
Nationalist Literature of India
- Bankim Chandra Chatterjee initiated the journal Bangadarshan to educate and inspire Bengalis towards nationalism, with his novel Anand Math playing a significant role.
- Rabindranath Tagore expressed nationalism through humanity in works like Gora and Ghare Baire, with his composition Jana Gana Mana becoming the national anthem.
- Bharatendu Harischandra used poetry and plays like Andher Nagari to highlight British oppression.
- Dadabhai Naoroji's Poverty and Un-British Rule in India exposed economic exploitation by the British, marking the start of economic critique.
- R.C. Dutt contributed to economic nationalism with The Economic History of India and patriotic historical novels.
- Bhagat Singh's essay, Why I am an Atheist, propagated nationalist ideas during his incarceration.
- Books like The Indian Struggle by Subhas Chandra Bose, The Discovery of India by Jawaharlal Nehru, and The Indian War of Independence by V.D. Savarkar fostered patriotism.
- Mahatma Gandhi's Songs from Prison translated Sanskrit hymns, nurturing nationalist sentiments.
Indian English Literature
- Emerged from exposure to British education during British rule.
- Early examples include travel narratives like The Travels of Dean Mahomet and novels like Rajmohan’s Wife by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay and Bianca by Toru Dutt.
- Notable early poets in English include Derozio, Michael Madhusudan Dutt, and Sarojini Naidu.
- Speeches of prominent figures like Swami Vivekananda, Rabindranath Tagore, and Mahatma Gandhi shaped both modern India and the development of English literature.
- Later Indian English writers include Salman Rushdie, Anita Desai, Arundhati Roy, and Vikram Seth, among others.
|
113 videos|550 docs|173 tests
|
FAQs on Nitin Singhania Summary: Indian Literature- 1 - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of Indian literature? |  |
| 2. What are the major themes explored in Indian literature? |  |
| 3. Who are some prominent Indian authors and their notable works? |  |
| 4. How has Indian literature evolved over time? |  |
| 5. How can one appreciate and understand Indian literature better? |  |