Accounting Ratios (Part - 5) | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Question:101
Calculate Working Capital Turnover Ratio from the following information:
Revenue from Operations 30,00,000; Current Assets 12,50,000; Total Assets 20,00,000; Non-current Liabilities 10,00,000, Shareholders' Funds 5,00,000.
Solution: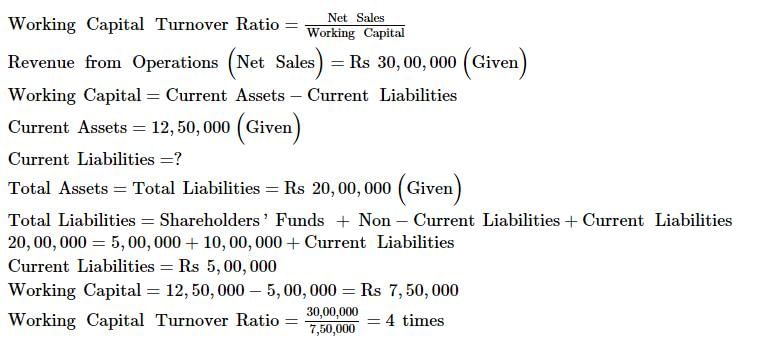 Question:102
Question:102
A company earns Gross Profit of 25% on cost. For the year ended 31st March, 2017 its Gross Profit was 5,00,000; Equity Share Capital of the company was 10,00,000; Reserves and Surplus 2,00,000; Long-term Loan 3,00,000 and Non-current Assets were 10,00,000.
Compute the 'Working Capital Turnover Ratio' of the company.
Working Capital Turnover Ratio= Revenue from Operation/Working Capital
Solution:
Gross Profit = 25% on Cost
Let the Cost of Goods sold be 100.
Gross Profit = 25
Revenue from Operations = 100 + 25 = 125
When Gross profit is 25, revenue from operations is = 125
And, if Gross profit is 5,00,000 then revenue from operations will be = 5,00, 000 × 125/25 = 25,00,000
Capital Employed = Shareholder’s Funds + Non-Current Liabilities
= 10,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 3,00,000
= 15,00,000
Also, Capital Employed = Non Current Assets + Working Capital
Alternatively, Working Capital = Capital Employed – Non-current Assets = 15,00,000– 10,00,000
= 5,00,000
Hence, Working Capital Turnover Ratio= 25,00,000/5,00,000= 5 times
Question:103
Compute Gross Profit Ratio from the following information:
Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold
5,40,000; Revenue from Operations Net Sales
6,00,000.
Solution:
Gross Profit = Revenue from Operations – Cost of Revenue from Operations
= 6,00,000 – 5,40,000
= Rs 60,000 
Question:104
From the following, calculate Gross Profit Ratio:
Gross Profit:50,000; Revenue from Operations 5,00,000; Sales Return: 50,000.
Solution:
Net Sales = Rs 5, 00, 000Gross Profit = Rs 50, 000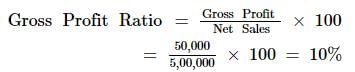
Note: Here we will not deduct the amount of sales return because the amount of net sales has already been provided in the question.
Question:105
Compute Gross Profit Ratio from the following information:
Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales = 4,00,000; Gross Profit 25% on Cost.
Solution: 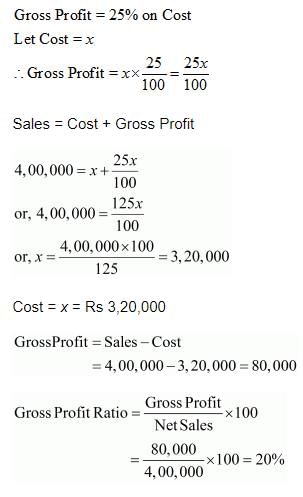
Question:106
Calculate Gross Profit Ratio from the following data:
Cash Sales are 20% of Total Sales; Credit Sales are 5,00,000; Purchases are 4,00,000; Excess of Closing Inventory over Opening Inventory 25,000.
Solution:
Credit Sales = 5,00,000
Cash sales = 20% of Total Sales
Let Total Sales be ‘x’
Therefore, Cash Sales = 20% of x
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales 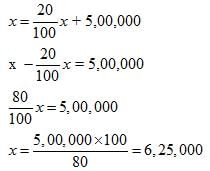
Cost of Goods Sold = Purchases – Excess of Closing Stock over Opening Stock
= Rs 4,00,000 – Rs 25,000 = Rs 3,75,000
Gross Profit = Total Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
= Rs 6,25,000 – 3,75,000 = Rs 2,50,000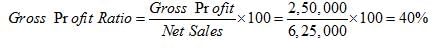
Question:107
From the following information, calculate Gross Profit Ratio:
Credit Sales 5,00,000
Decrease in Inventory 10,000
Purchases 3,00,000
Returns Outward 10,000
Carriage Inwards 10,000
Wages 50,000
Rate of Credit Sale to Cash Sale 4:1
Solution:
Credit Sale = Rs 5,00,000
Rate of Credit Sale to Cash Sale = 4:1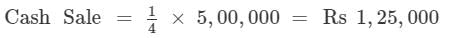
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales = Rs 1,25,000 + Rs 5,00,000 = Rs 6,25,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Purchases – Return Outward + Carriage Inwards + Wages + Decrease in Inventory
= Rs 3,00,000 – Rs 10,000 + Rs 10,000 + Rs 50,000 + Rs 10,000
= Rs 3,60,000
Gross Profit = Total Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
= Rs 6,25,000 – Rs 3,60,000 = Rs 2,65,000 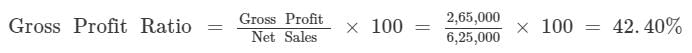
Question: 108
Calculate Gross Profit Ratio from the following data:
Average Inventory 3,20,000; Inventory Turnover Ratio 8 Times; Average Trade Receivables 4,00,000; Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio 6 Times; Cash Sales 25% of Net Sales.
Solution:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = 8 times
Average Inventory = Rs 3,20,000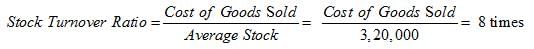
Cost of Goods sold = 25,60,000
Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio = 6 times
Average Trade Receivables = Rs 4,00,000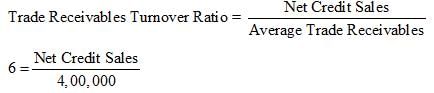
Net Credit Sales = 24,00,000
Total Sales = Cash Sales + Credit Sales
Total Sales = 25% of Total Sales + Credit Sales
75% of Total Sales = 24,00,000 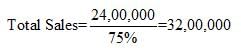
Gross Profit = Total Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
= 32,00,000 – 25,60,000 = 6,40,000 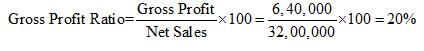
Question:109
i. Revenue from Operations: Cash Sales 4,20,000; Credit Sales 6,00,000; Return 20,000. Cost of Revenue from Operations or Cost of Goods Sold 8,00,000. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio.
ii. Average Inventory 1,60,000; Inventory Turnover Ratio is 6 Times; Selling Price 25% above cost. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio.
iii. Opening Inventory 1,00,000; Closing Inventory 60,000; Inventory Turnover Ratio 8 Times; Selling Price 25% above cost. Calculate Gross Profit Ratio.
Solution: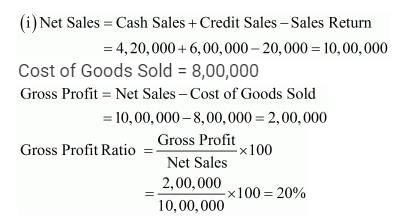
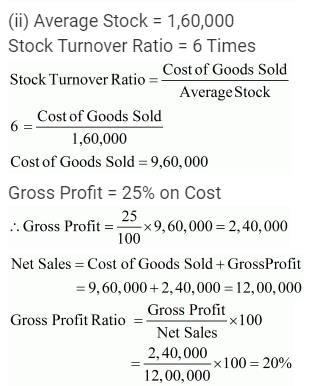
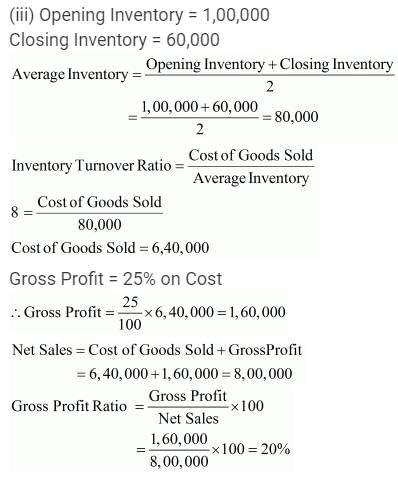
Question:110
Gross Profit Ratio of a company is 25%. State giving reason, which of the following transactions will
a. increase or b. decrease or c. not alter the Gross Profit Ratio.
i. Purchases of Stock-in-Trade 50,000.
ii. Purchases Return 15,000.
iii. Cash Sale of Stock-in-Trade 40,000.
iv. Stock-in-Trade costing 20,000 withdrawn for personal use.
v. Stock-in-Trade costing 15,000 distributed as a free sample.
Solution: 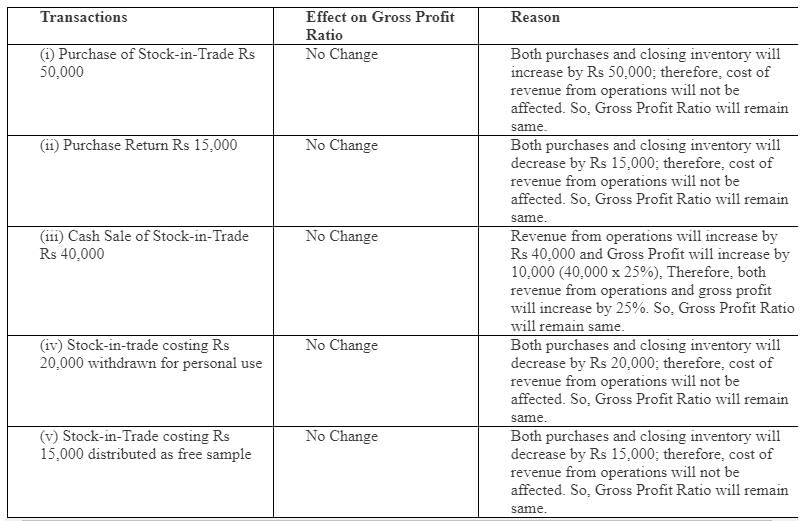 Question:111
Question:111
Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold
3,00,000. Operating Expenses 1,20,000. Revenue from Operations: Cash Sales 5,20,000; Return 20,000. Calculate Operating Ratio.
Solution: 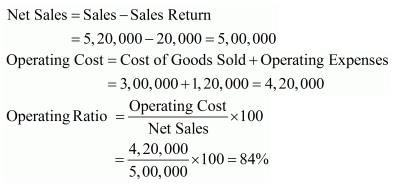
Question:112
Operating Ratio 92%; Operating Expenses 94,000; Revenue from Operations 6,00,000; Sales Return 40,000. Calculate Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold.
Solution: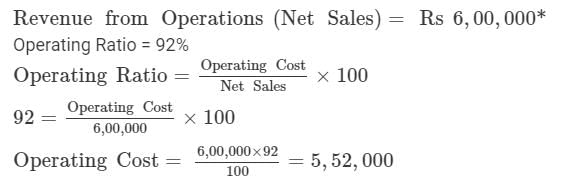
Operating Cost = Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses
5,52,000 = Cost of Goods Sold + 94,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Rs 4,58,000
*Note: Sales Return will not be considered since net sales are given which means sales return have already been adjusted in the sales figure.
Question:113
i. Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold Rs 2,20,000; Revenue from Operations Net Sales Rs 3,20,000; Selling Expenses 12,000; Office Expenses 8,000; Depreciation 6,000. Calculate Operating Ratio.
ii. Revenue from Operations, Cash Sales 4,00,000; Credit Sales 1,00,000; Gross Profit 1,00,000; Office and Selling Expenses 50,000. Calculate Operating Ratio.
Solution: 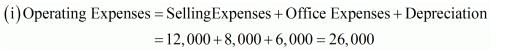
Cost of Goods Sold = 2,20,000
Operating Cost = Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses
Operating Cost = 2,20,000 + 26,000 = 2,46,000
Sales = 3,20,000 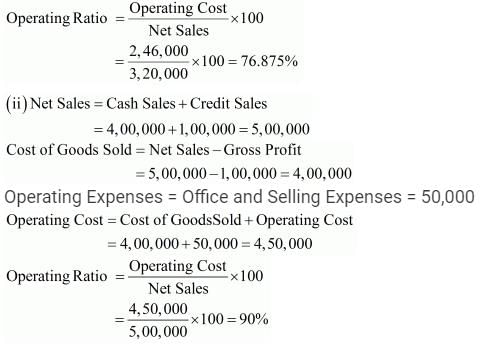
Question:114
From the following information, calculate Operating Ratio:
Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold 52,000
Revenue from Operation Gross Sales 88,000
Operating Expenses 18,000
Sales Return 8,000
Solution:
Net Sales = Gross Sales - Sales Return = 88, 000 - 8, 000 = Rs 80, 000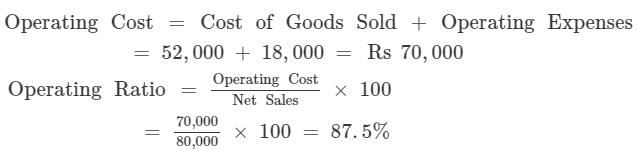
Question:115
Calculate Cost of Revenue from Operations from the following information:
Revenue from Operations 12,00,000; Operating Ratio 75%; Operating Expenses 1,00,000.
Solution:
Revenue from Operations Net Sales = Rs 12, 00, 000
Operating Ratio = 75%
Operating Expenses = Rs 1, 00, 000
Find out: Cost of Revenue from Operations
Operating Ratio = 

Question:116
Calculate Operating Ratio from the following information:
Operating Cost 6,80,000; Gross Profit 25%; Operating Expenses 80,000.
Solution:
Given: Operating Cost = Rs 6, 80, 000
Operating Expenses = Rs 80, 000
Gross Profit Ratio = 25 %
Find out: Operating Ratio
Operating Cost = Cost of Revenue from Operations + Operating Expenses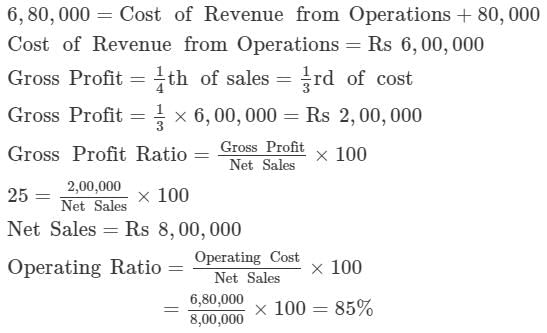
Question:117
Calculate Operating Profit Ratio from the following information:
Opening Inventory 1,00,000
Closing Inventory 1,50,000
Purchases 10,00,000
Loss by fire 20,000
Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales 14,70,000
Dividend Received 30,000
Administrative and Selling Expenses 1,70,000
Solution:
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Inventory + Purchases – Closing Inventory
= 1,00,000 + 10,00,000 – 1,50,000 = 9,50,000
Operating Expenses = Administrative and Selling Expenses = 1,70,000
Operating Cost = Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses
= 9,50,000 + 1,70,000 = 11,20,000
Net Sales = 14,70,000 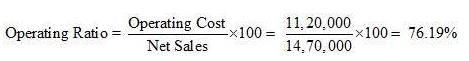
Operating Profit Ratio = 100 – Operating Ratio = 100 – 76.19 = 23.81%
Question:118
Calculate Operating Profit Ratio from the Following:
Revenue from Operations Net Sales 5,00,000
Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold 2,00,000
Wages 1,00,000
Office and Administrative Expenses 50,000
Interest on Borrowings 5,000
Solution:
Cost of Goods Sold = 2,00,000
Operating Expenses = Office and Administrative Expenses = 50,000
Operating Cost = Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses
= 2,00,000 + 50,000 = 2,50,000
Net Sales = 5,00,000 
Operating Profit Ratio = 100 – Operating Ratio = 100 – 50 = 50%
Question:119
What will be the Operating Profit Ratio, if the Operating Ratio is 82.59%?
Solution:
Operating Ratio = 82.59%
Operating Ratio + Operating Profit Ratio = 100%
Operating Profit Ratio = 100% − 82.59% = 17.41%
Question:120
Calculate Operating Profit Ratio,in each of the following alternative cases:
Case 1: Revenue from Operations Net Sales 10,00,000; Operating Profit 1,50,000.
Case 2: Revenue from Operations Net Sales 6,00,000; Operating Cost 5,10,000.
Case 3: Revenue from Operations Net Sales 3,60,000; Gross Profit 20% on Sales; Operating Expenses 18,000
Case 4: Revenue from Operations Net Sales 4,50,000; Cost of Revenue from Operations 3,60,000; Operating Expenses 22,500.
Case 5: Cost of Goods Sold, i.e., Cost of Revenue from Operations 8,00,000; Gross Profit 20% on Sales; Operating Expenses 50,000.
Solution: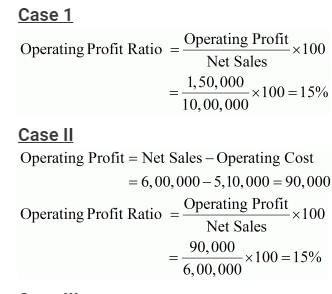
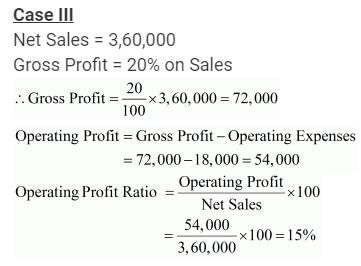
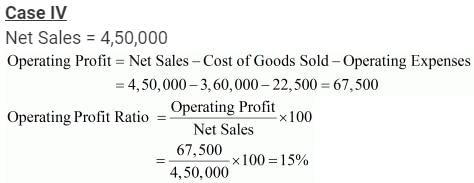
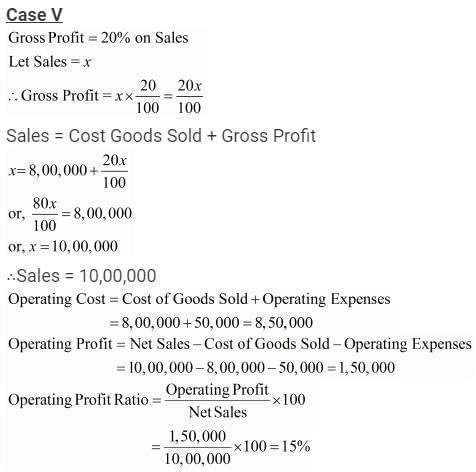
Question:121
Revenue from Operations 9,00,000; Gross Profit 25% on Cost; Operating Expenses 45,000. Calculate Operating Profit Ratio.
Solution: 
Question:122
Operating Cost 3,40,000; Gross Profit Ratio 20%; Operating Expenses 20,000. Calculate Operating Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Cost of Revenue from Operations = Operating Cost - Operating Expenses = 3,40,000 - 20,000 = Rs 3,20,000 3,20,000 × 20
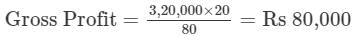
Revenue from Operations = Cost of Revenue from Operations + Gross Profit
=3,20,000+80,000 = Rs 4,00,000
Operating Profit = Revenue from Operations - Operating Cost
= 4, 00, 000 − 3, 40, 000 = Rs 60,000
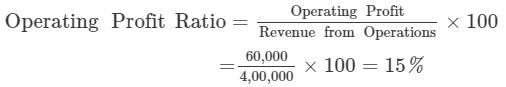
Question:123
Cash Sales 2,20,000; Credit Sales 3,00,000; Sales Return 20,000; Gross Profit 1,00,000; Operating Expenses 25,000; Non-operating incomes 30,000; Non-operating Expenses 5,000. Calculate Net Profit Ratio.
Solution: 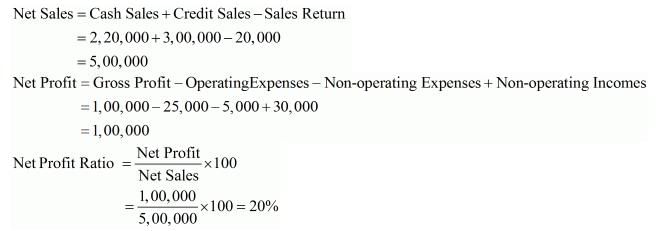
Question:124
Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales 6,00,000. Calculate Net Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Net Sales = 6,00,000
Net profit = 60,000 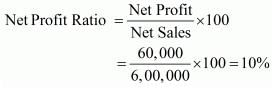
Question:125
Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales 8,20,000; Return 10,000; Cost of Revenue from Operations Cost of Goods Sold 5,20,000; Operating Expenses 2,09,000; Interest on Debentures 40,500; Gain Profit on Sale of a Fixed Asset 81,000. Calculate Net Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Net Sales = Rs 8, 20, 000
Gross Profit = Net Sales - Cost of Goods Sold
= 8, 20, 000 - 5, 20, 000
= Rs 3, 00, 000
Net Profit = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses - Interest on Debentures + Profit on Sale of Fixed Asset
= 3, 00, 000 - 2, 09, 000 - 40, 500 + 81, 000
= Rs 1, 31, 500 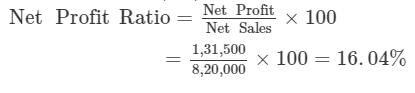
Question:126
Revenue from Operations 4,00,000; Gross Profit Ratio 25%; Operating Ratio 90%. Non-operating Expenses 2,000; Non-operating Income 22,000. Calculate Net Profit Ratio.
Solution:
Net Profit = Operating Profit + Non Operating Incomes - Non Operating Expenses
= 40,000+22,000- 2,000 = Rs 60,000
Operating Profit Ratio = 100 − Operating Ratio =100-90 =10%
Operating Profit = 4, 00, 000 × 10% = Rs 40,000 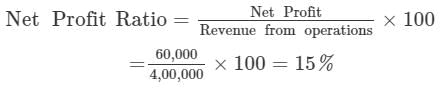
Question:127
Calculate Return on Investment ROI
from the following details: Net Profit after Tax 6,50,000; Rate of Income Tax 50%; 10% Debentures of 100 each 10,00,000; Fixed Assets at cost 22,50,000; Accumulated Depreciation on Fixed Assets up to date 2,50,000; Current Assets 12,00,000; Current Liabilities 4,00,000.
Solution:
Net Fixed Assets = Fixed Assets at cost
− Accumulated Depreciation
= 22,50,000 − 2,50,000 = 20,00,000
Capital Employed = Net Fixed Assets + Current Assets − Current Liabilities
= 20,00,000 + 12,00,000 − 4,00,000
= 28,00,000
Interest on 10% Debentures = 10% of 10,00,000 = 1,00,000
Let Profit before Tax be = x
Profit after Tax = Profit Before Tax − Tax
Tax Rate = 50%
∴ Tax = 0.5 x
x − 0.5 x = 6,50,000
x = 13,00,000
Net Profit before Tax = x = 13,00,000
Profit before Interest and Tax = Profit before Tax + Interest on Long-term Debt
= 13,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 14,00,000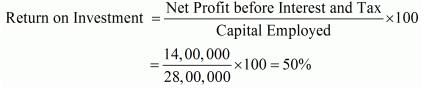
Question:128
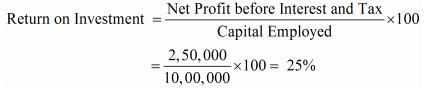
Net Profit before Interest and Tax 2,50,000; Capital Employed 10,00,000. Calculate Return on Investment.
Solution:
Net Profit before Interest and Tax = 2,50,000
Capital Employed = 10,00,000
Question:129
Net Profit before Interest and Tax 6,00,000; Net Fixed Assets 20,00,000; Net Working Capital 10,00,000; Current Assets 11,00,000. Calculate Return on Investment.
Solution:
Net Profit before Interest and Tax = 6,00,000
Capital Employed = Net Fixed Assets + Net Working Capital
= 20,00,000 + 10,00,000 = 30,00,000 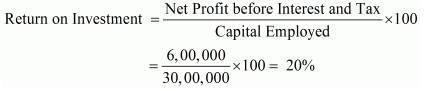
Question:130
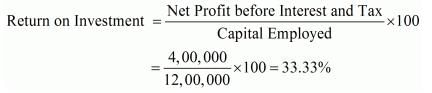
Net Profit before Interest and Tax 4,00,000; 15% Long-term Debt 8,00,000; Shareholders' Funds 4,00,000. Calculate Return on Investment.
Solution:
Net Profit before Interest and Tax = 4,00,000
Capital Employed = 15% long-term Debt + Shareholders’ Funds
= 8,00,000 + 4,00,000 = 12,00,000
Question:131
y Ltd.'s profit after interest and tax was 1,00,000. Its Current Assets were 4,00,000; Current Liabilities 2,00,000; Fixed Assets 6,00,000 and 10% Long-term Debt 4,00,000. The rate of tax was 20%. Calculate 'Return on Investment' of Y Ltd.
Solution:
Return on Investment = Net Profit before Interest, Tax and Dividend/Capital Employed × 100
Let Profit before tax be Rs 100
Tax = Rs 20
Profit after tax = 100 – 20 = 80
If Profit after tax is Rs 80 then profit before tax is = Rs 100
If Profit after tax is Rs 1,00,000 then profit before tax is = Rs 1, 00, 000 × 100/80 = 1,25,000
Interest on long-term borrowings = Rs 4, 00, 000 × 10/100 = Rs 40,000
Profit after interest and Tax = Rs 1,25,000 + 40,000 = Rs 1,65,000
Capital Employed = Fixed Assets + Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 6,00,000 + 4,00,000 – 2,00,000
= 8,00,000
Return on Investment = 1,65,000/8,00,000 × 100 = 20.625% or 20.63%
approx.
Question:132
From the following Balance Sheet of Global Ltd., you are required to calculate Return on Investment for the year 2018-19: 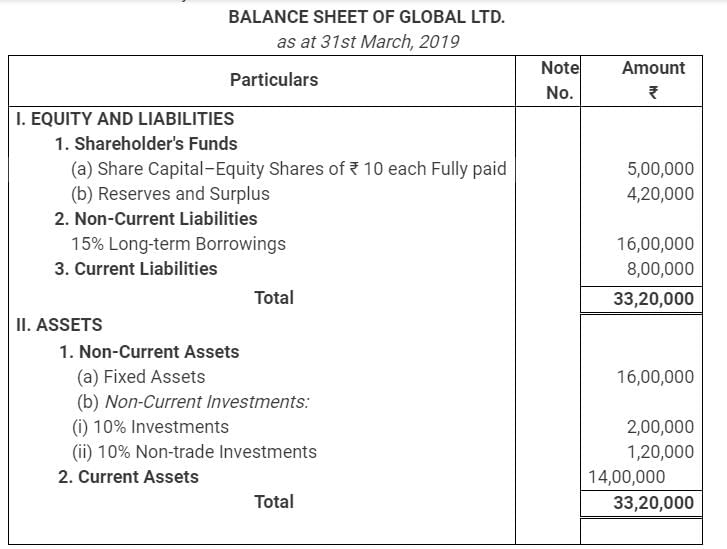
Solution:
Return on Investment = (Net Profit before Interest, Tax and Dividend/ Capital Employed × 100)
Interest on borrowings = ₹ (16,00,000 × 15/100)= ₹ 2,40,000
Net Profit before Tax = ₹ 9,72,000
Net Profit before Interest and Tax = ₹ (9,72,000 + 2,40,000) = ₹ 12,12,000
Net Profit before Interest and Tax (excluding interest on Non-trade investments) = ₹ (12,12,000 – 12,000) = ₹ 12,00,000
Capital Employed = Shareholder’s Funds + Non-Current Liabilities – Non-Trade Investment
= ₹ (5,00,000 + 4,20,000 + 16,00,000 – 1,20,000) = ₹ 24,00,000
Return on Investment = (12,00,000/24,00,000 × 100) = 50%
Question:133
Following is the Balance Sheet of the Bharati Ltd. as at 31st March, 2019: 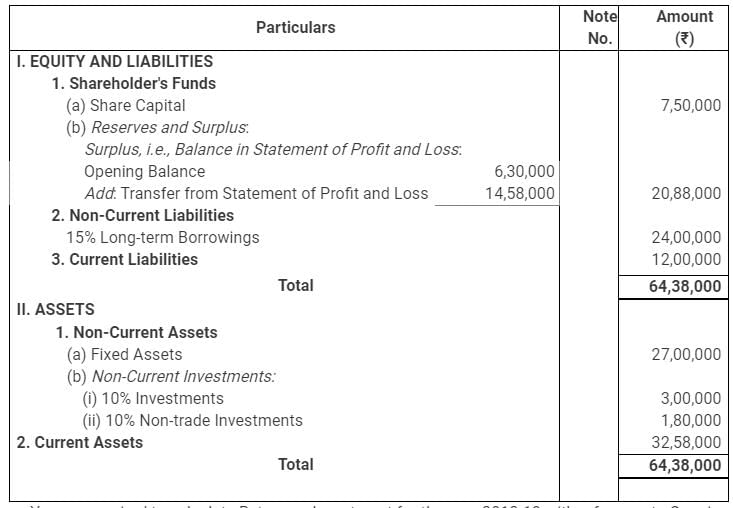
You are required to calculate Return on Investment for the year 2018-19 with reference to Opening Capital Employed.
Solution:
Return on Investment = (Net Profit before Interest, Tax and Dividend/ Capital Employed × 100)
Interest on borrowings = ₹ (24,00,000 × 15/100) = ₹3,60,000
Net Profit before Interest and Tax = Net Profit after tax + Interest on borrowings – Interest received on Non-trade Investments
= ₹ (14,58,000 + 3,60,000 – 18,000) = ₹ 18,00,000
Opening Capital Employed = Shareholder’s Funds (Opening) + Non-Current Liabilities (Opening) – Non-Trade Investment
= ₹(7,50,000 + 6,30,000 + 24,00,000 – 1,80,000) = ₹36,00,000
Return on Investment = (18,00,000/36,00,000 × 100) = 50%
Question:134
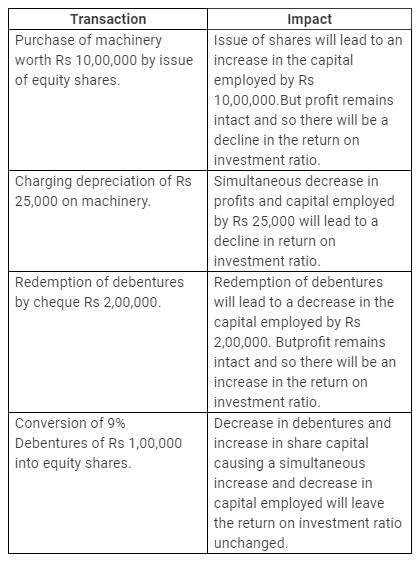
State with reason whether the following transactions will increase, decrease or not change the 'Return on Investment' Ratio:
(i) Purchase of machinery worth ₹10,00,000 by issue of equity shares.
(ii) Charging depreciation of ₹25,000 on machinery.
(iii) Redemption of debentures by cheque ₹2,00,000.
(iv) Conversion of 9% Debentures of ₹1,00,000 into equity shares.
Solution:
Question:135
Opening Inventory ₹80,000; Purchases ₹4,30,900; Direct Expenses ₹4,000; Closing Inventory ₹1,60,000; Administrative Expenses ₹21,100; Selling and Distribution Expenses ₹40,000; Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales ₹10,00,000. Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio; Gross Profit Ratio; and Opening Ratio.
Solution:
(i) Opening Inventory = 80,000
Closing Inventory = 1,60,000
Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Inventory + Purchases + Direct Expenses − Closing Inventory
= 80,000 + 4,30,900 + 4,000 − 1,60,000
= 3,54,900
(ii) Sales = 10,00,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales − Cost of Goods Sold
= 10,00,000 − 3,54,900 = 6,45,100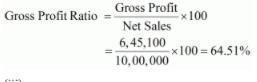
(iii) Operating Expenses = Administration Expenses + Selling and Distribution Expenses
= 21,100 + 40,000 = 61,100
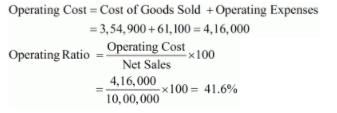
Question:136
Following information is given about a company: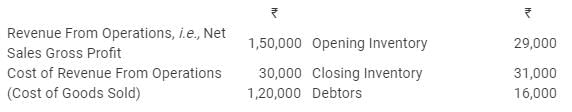
From the above information, calculate following ratios:
(i) Gross Profit Ratio,
(ii) Inventory Turnover Ratio, and
(iii) Trade Receivables Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
(i) Sales = 1,50,000
Gross Profit = 30,000
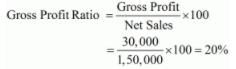
(ii) Opening Inventory = 29,000
Closing Inventory = 31,000
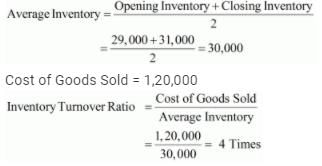
(iii)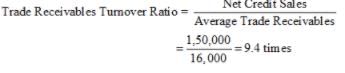
Question:137
From the following information, calculate any two of the following ratios:
(i) Current Ratio;
(ii) Debt to Equity Ratio; and
(iii) Operating Ratio.
Revenue from Operations (Net Sales) ₹ 1,00,000; cost of Revenue from Operations (Cost of Goods Sold) was 80% of sales; Equity Share Capital ₹ 7,00,000; General Reserve ₹ 3,00,000; Operating Expenses ₹ 10,000; Quick Assets ₹ 6,00,000; 9% Debentures ₹ 5,00,000; Closing Inventory ₹ 50,000; Prepaid Expenses ₹ 10,000 and Current Liabilities ₹ 4,00,000.
Solution:
(i) Current Assets = Quick Assets + Closing Stock + Prepaid Expenses
= 6,00,000 + 50,000 + 10,000 = 6,60,000
Current Liabilities = 4,00,000
(ii) Long-term Debts = 9% Debentures = 5,00,000
Shareholder’s Funds = Equity Share Capital + General Reserve
= 7,00,000 + 3,00,000 = 10,00,000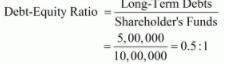
(iii) Sales = 1,00,000
Cost of Goods Sold = 80% of Sales = 80,000
Operating Expenses = 10,000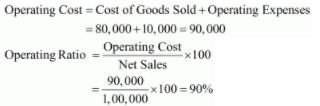
Question:138
From the following information, calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio; Operating Ratio and Working Capital Turnover Ratio:
Opening Inventory ₹ 28,000; Closing Inventory ₹ 22,000; Purchases ₹ 46,000; Revenue from Operations, i.e., Net Sales ₹ 80,000; Return ₹10,000; Carriage Inwards ₹ 4,000; Office Expenses ₹ 4,000; Selling and Distribution Expenses ₹ 2,000; Working Capital ₹ 40,000.
Solution:
(i) Opening Inventory = 28,000
Closing Inventory = 22,000

Cost of Goods Sold = Opening Inventory + Purchases + Carriage Inwards − Closing Inventory
= 28,000 + 46,000 + 4,000 − 22,000 = 56,000
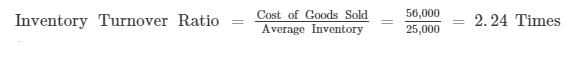
(ii) Operating Expenses = Office Expenses + Selling and Distribution Expenses
= 4,000 + 2,000 = 6,000
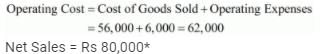
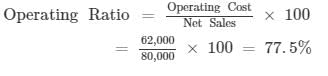
(iii) Working Capital = 40,000
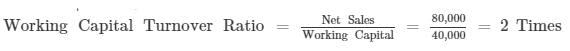
*Note: Sales return will not be considered as the amount of net sales is provided in the question.
Question:139
From the following calculate:
(a) Current Ratio; and
(b) Working Capital Turnover Ratio.
Solution: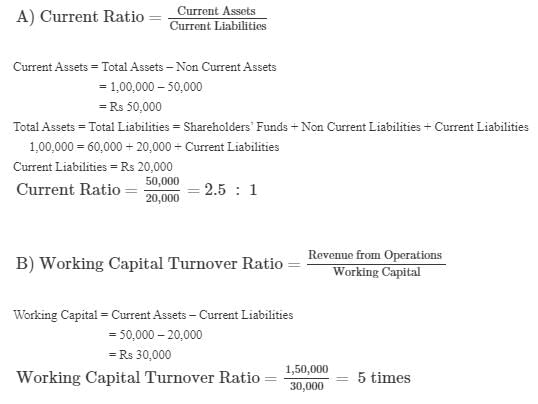
Question:140
Calculate following ratios on the basis of the following information:
(i) Gross Profit Ratio;
(ii) Current Ratio;
(iii) Acid Test Ratio; and
(iv) Inventory Turnover Ratio.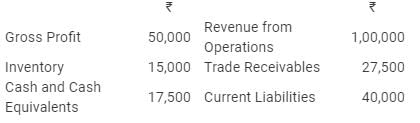
Solution: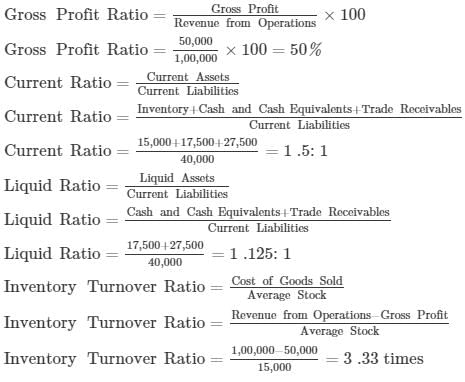
Question:141
Calculate following ratios on the basis of the given information:
(i) Current Ratio;
(ii) Acid Test Ratio;
(iii) Operating Ratio; and
(iv) Gross Profit Ratio.
Solution:
(i) Current Assets = 70,000
Current Liabilities = 35,000
(ii) Liquid Assets = Current Assets − Inventory
= 70,000 − 30,000 = 40,000

(iii) Net Sales = 1,20,000
Operating Cost = Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses
= 60,000 + 40,000 = 1,00,000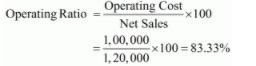
(iv) Gross Profit = Net Sales − Cost of Goods Sold
= 1,20,000 − 60,000 = 60,000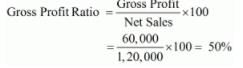
Question:142
From the information given below, calculate any three of the following ratio:
(i) Gross Profit Ratio;
(ii) Working Capital Turnover Ratio:
(iii) Debt to Equity Ratio; and
(iv) Proprietary Ratio.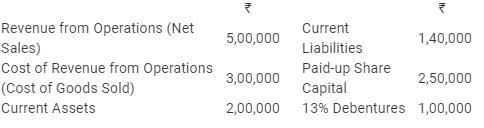
Solution:
(i) Net Sales = 5,00,000
Cost of Goods Sold = 3,00,000
Gross Profit = Net Sales − Cost of Goods Sold
= 5,00,000 − 3,00,000 = 2,00,000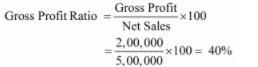
(ii) Current Assets = 2,00,000
Current Liabilities = 1,40,000
Working Capital = Current Assets − Current Liabilities
= 2,00,000 − 1,40,000 = 60,000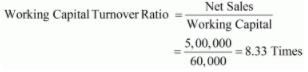
(iii) Long-term Debts = 13% Debentures = 1,00,000
Equity = Paid-up Share Capital = 2,50,000
(iv) Total Assets = Total Liabilities
= Current Liabilities + Paid-up Share Capital + 13% Debentures
= 1,40,000 + 2,50,000 + 1,00,000
= 4,90,000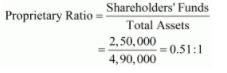
Question:143
On the basis of the following information calculate:
(i) Debt to Equity Ratio; and
(ii) Working Capital Turnover Ratio.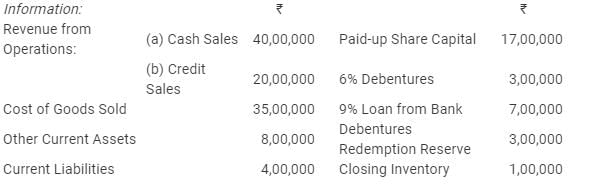
Solution:
(i) Long-term Debts = 6% Debentures + 9% Loan from Bank
= 3,00,000 + 7,00,000 = 10,00,000
Equity = Paid-up Share Capital + Debenture Redemption Reserve
= 17,00,000 + 3,00,000 = 20,00,000
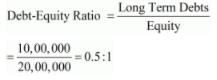
(ii) Current Assets = Other Current Assets + Inventory
= 8,00,000 + 1,00,000
= 9,00,000
Working Capital = Current Assets − Current Liabilities
= 9,00,000 − 4,00,000
= 5,00,000
Net Sales = Cash Sales + Credit sales
= 40,00,000 + 20,00,000
= 60,00,000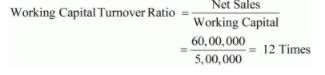
Question:144
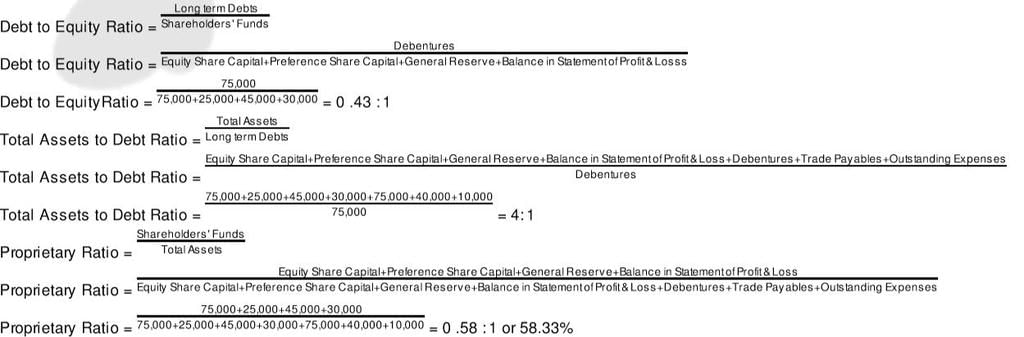
From the following, calculate (a) Debt to Equity Ratio; (b) Total Assets to Debt Ratio; and (c) Proprietary Ratio:
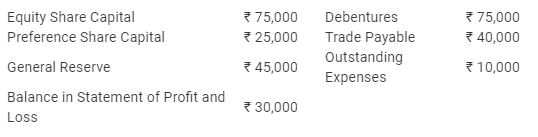
Solution:
Question:145
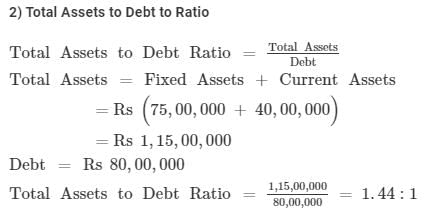
From the following information related to Naveen Ltd., calculate (a) Return on Investment and (b) Total Assets to Debt Ratio:
Information: Fixed Assets ₹ 75,00,000; Current Assets ₹ 40,00,000; Current Liabilities ₹ 27,00,000; 12% Debentures ₹ 80,00,000 and Net Profit before Interest, Tax and Dividend ₹ 14,50,000.
Solution: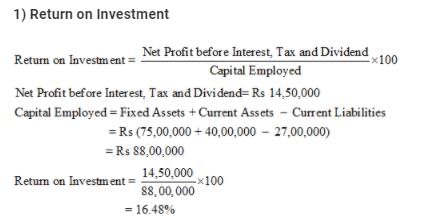
Question:146
Calculate Current Ratio, Quick Ratio and Debt to Equity Ratio from the figures given below: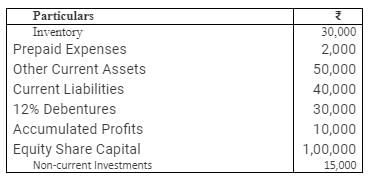
Solution:
(i) Current Assets = Inventory + Prepaid Expenses + Other Current Assets
= 30,000 + 2,000 + 50,000 = 82,000
Current Liabilities = 40,000
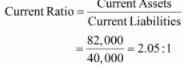
(ii) Liquid Assets = Current Assets − Inventory − Prepaid Expenses
= 82,000 − 30,000 − 2,000 = 50,000
(iii) Long-term Debts = 12% Debentures = 30,000
Equity = Accumulated Profits + Equity Share Capital
= 10,000 + 1,00,000 = 1,10,000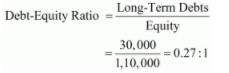
Question:147
From the following informations, calculate Return on Investment (or Return on Capital Employed):
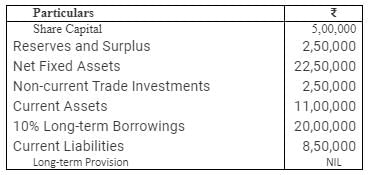
Solution:
Net Profit before tax = 6,00,000
Net Profit before interest, tax and dividend = Net Profit before tax + Interest on long-term borrowings
= 6,00,000 + 10% of 20,00,000 = 6,00,000 + 2,00,000 = 8,00,000
Capital Employed = Share Capital + Reserves and Surplus + Long-term borrowings
= 5,00,000 + 2,50,000 + 20,00,000 = 27,50,000

|
42 videos|199 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Accounting Ratios (Part - 5) - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are accounting ratios and why are they important in commerce? |  |
| 2. How are accounting ratios calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of profitability ratios in accounting? |  |
| 4. How can liquidity ratios help assess a company's financial health? |  |
| 5. What are some common limitations of accounting ratios? |  |





















