UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location
NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Extent of India |

|
| Standard Meridian |

|
| Indian Subcontinent |

|
| India and its neighbours |

|
| Mind map |

|
Extent of India
- From Kashmir in North to Kanniyakumari in the South and Arunachal Pradesh in the East to Gujarat in the West.
- Territorial limit- 12 nautical miles (21.9 km) from the coast, towards the sea.
- Southern Boundary- 6°45' N latitude in the Bay of Bengal.
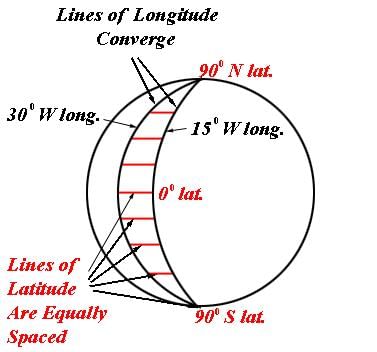
- Latitudinal and Longitudinal Extent of India - roughly 30 degrees.

- Distance between North and South extremity- 3,214 km.
- Distance between East and West extremities - 2,933 km.
- The southern part of the country- lies within the tropics and the Northern part of the country - lies within the subtropical zone or warm temperate zone. This leads to large variations in landforms, climate, soil types, and natural vegetation.
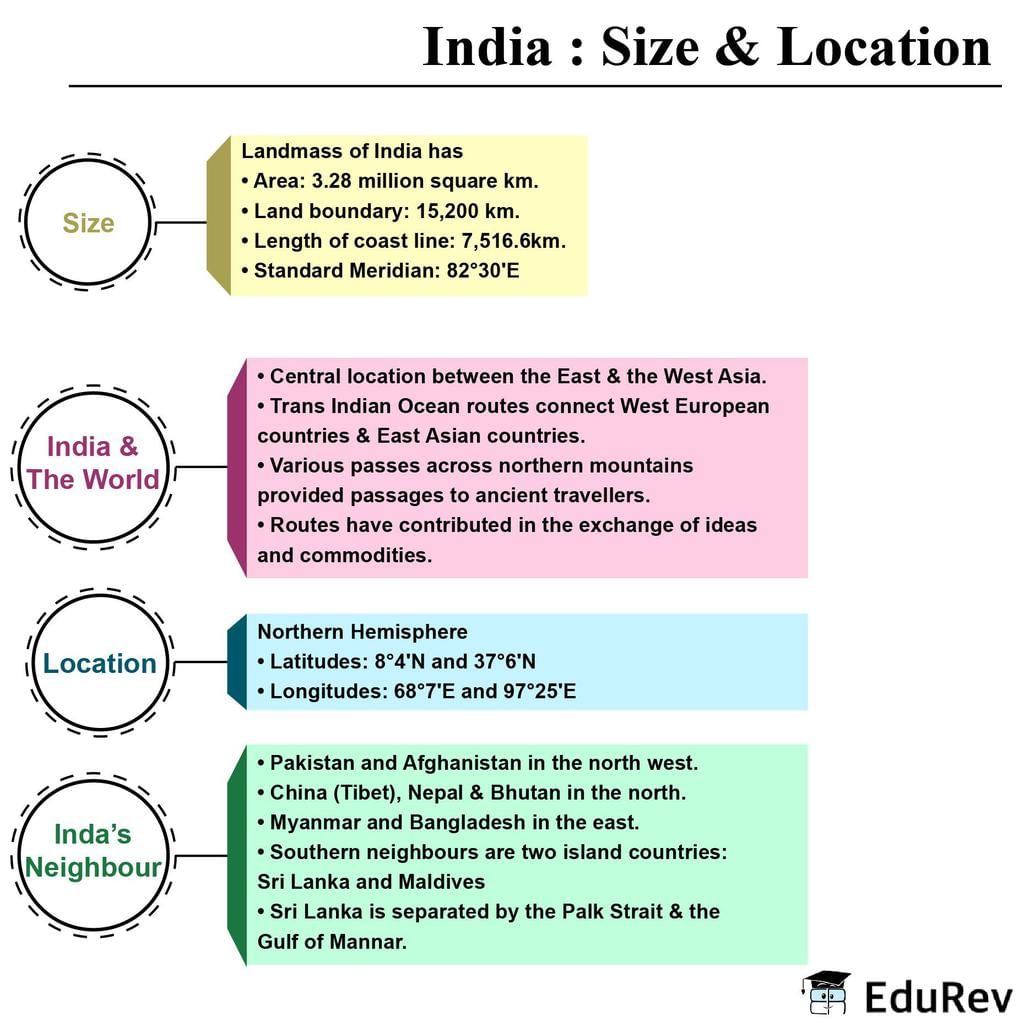
- India has an area of 3.28 million sq km, which accounts for 2.4 percent of the world’s land surface area.
- India is the seventh-largest country in the world, in terms of area.
Standard Meridian
- From the values of longitude - there is a difference of 30 degrees - between the easternmost and the westernmost part of the country- hence a time difference of nearly two hours is caused.
- Countries generally select Standard Meridian as multiples of 7°30' of longitude.
- India selected 82°30' as the ‘Standard Meridian’, which passes through Mirzapur, UP.
- Indian Standard Time - 5hrs and 30 min, ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
- Some countries have more than one Standard Meridian because of the vast East-West extent.
- The USA has seven time zones and Russia has eleven time zones.
Question for NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location
Try yourself:Consider the following statements regarding the Standard Time Zones?
View Solution
Indian Subcontinent
- The subcontinent includes countries - Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and India.
- Himalayas- with other ranges have acted as a formidable barrier in the past.
- Except for a few passes like Khyber, the Bolan, the Shipkila, the Nathula, the Bomdila, etc., it was difficult to cross the Himalayas.
- The Peninsula part of India extends towards the Indian Ocean.
- Provided the country with a coastline of 6,100 km in the mainland and 7,517 km in the entire geographical coast of the mainland plus the island groups.
- Andaman and Nicobar are located in the Bay of Bengal.
- The Lakshadweep islands are located in the Arabian Sea.
 |
Download the notes
NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
India and its neighbours
- India is located in the Southcentral part of Asia, bordering the Indian Ocean and its two arms extend in the form of Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
- Maritime location of Peninsular India helps in linking it to the neighbouring regions through the sea and air routes.
- Indian neighbouring countries located in the Indian Ocean- Maldives and Sri Lanka (both are island countries)
- Sri Lanka is separated from India by - Gulf of Mannar and Palk Strait.
Mind map
The document NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
180 videos|482 docs|193 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: India - Size and Location - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the extent of India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Standard Meridian for India? |  |
Ans. The Standard Meridian of India, which passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, is important because it helps in determining the Indian Standard Time (IST). It serves as the reference point for calculating time zones across the country.
| 3. What countries are part of India's neighbors? |  |
Ans. India shares its borders with several countries. Its neighbors include Pakistan to the northwest, China and Nepal to the north, Bhutan to the northeast, and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east.
| 4. What is the Indian subcontinent? |  |
Ans. The Indian subcontinent refers to the landmass that includes India along with its neighboring countries such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka. It is distinct from the rest of Asia due to its unique geographical and cultural characteristics.
| 5. How does the size and location of India contribute to its diversity? |  |
Ans. The size and location of India play a significant role in its diversity. Its vast size provides a wide range of geographical features, including mountains, plains, plateaus, and coastal areas, which contribute to diverse ecosystems and climates. Additionally, its location in the Indian subcontinent and proximity to other countries has facilitated cultural exchanges, resulting in a rich and diverse cultural heritage.
Related Searches