Previous Year Questions (PYQs): Indian Polity - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2025:Polity |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2024:Polity |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2023:Polity |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2022:Polity |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2021:Polity |

|
| UPSC Prelims 2020:Polity |

|
UPSC Prelims 2025:Polity
Q1: Consider the following statements about Lokpal:
I. The power of Lokpal applies to public servants of India, but not to the Indian public servants posted outside India.
II. The Chairperson or a Member shall not be a Member of the Parliament or a Member of the Legislature of any State or Union Territory, and only the Chief Justice of India, whether incumbent or retired, has to be its Chairperson.
III. The Chairperson or a Member shall not be a person of less than forty-five years of age on the date of assuming office as the Chairperson or Member, as the case may be.
IV. Lokpal cannot inquire into the allegations of corruption against a sitting Prime Minister of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) III only
(b) II and III
(c) I and IV
(d) None of the above statements is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Only Statement III is correct: The minimum age for a Lokpal Chairperson or Member is 45 years.
Clarifications:
- Statement I is incorrect: Lokpal’s jurisdiction covers Indian public servants, but not those posted abroad.
- Statement II is incorrect: The Chairperson can be a former judge or eminent person with 25+ years of expertise, not necessarily the CJI.
- Statement IV is incorrect: Lokpal can investigate a sitting PM, but with restrictions in sensitive areas.
Q2: With reference to India, consider the following:
I. The Inter-State Council
II. The National Security Council
III. Zonal Councils
How many of the above were established as per the provisions of the Constitution of India?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Among the listed bodies, only the Inter-State Council is constitutionally established. The others are created through statutory or executive measures.
I. Inter-State Council – Correct
Constituted under Article 263 of the Indian Constitution to promote coordination between the Centre and States.
II. National Security Council – Incorrect
Set up in 1998 via an executive order, not enshrined in the Constitution.
III. Zonal Councils – Incorrect
Formed under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, making them statutory but not constitutional bodies.
Q3: With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements:
I. An Ordinance can amend any Central Act.
II. An Ordinance can abridge a Fundamental Right.
III. An Ordinance can come into effect from a back date.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
An Ordinance is a temporary law enacted by the President (under Article 123) or Governor (under Article 213) when the legislature is not in session. It carries the same legal weight as a regular law but is subject to constitutional constraints.
Statement I: Correct
An Ordinance can amend any Central Act, similar to a law passed by Parliament, provided it complies with constitutional provisions.
Statement II: Incorrect
Ordinances cannot violate Fundamental Rights, as per Article 13(2) of the Constitution. Any provision that does so is void.
Statement III: Correct
Ordinances can be applied retrospectively, meaning they may take effect from a prior date.
Q4: With reference to the Indian polity, consider the following statements:
I. The Governor of a State is not answerable to any court for the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of his/her office.
II. No criminal proceedings shall be instituted or continued against the Governor during his/her term of office.
III. Members of a State Legislature are not liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said within the House.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Indian Constitution grants legal immunities and privileges to ensure the independent functioning of constitutional offices and legislative bodies.
Statement I: Correct
Under Article 361(1), the Governor is not accountable to any court for actions performed in their official capacity.
Statement II: Correct
Article 361(2) prohibits the initiation or continuation of criminal proceedings against a Governor during their term of office.
Statement III: Correct
Article 194(2) provides immunity to State Legislators for statements made or votes cast in the State Legislature or its committees.
Q5: Consider the following statements:
I. If any question arises as to whether a Member of the House of the People has become subject to disqualification under the Tenth Schedule, the President’s decision in accordance with the opinion of the Council of Union Ministers shall be final.
II. There is no mention of the word 'political party' in the Constitution of India.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Neither of the statements regarding the Tenth Schedule of the Indian Constitution is correct.
Statement I: Incorrect
The authority to decide on disqualification under the Tenth Schedule lies with the Speaker or Chairman of the respective House, not the President or the Union Council of Ministers.
Statement II: Incorrect
The term ‘political party’ is explicitly referenced in the Tenth Schedule, which governs the disqualification of members on grounds of defection.
Q6: Consider the following statements:
Statement I: In India, State Governments have no power for making rules for grant of concessions in respect of extraction of minor minerals even though such minerals are located in their territories.
Statement II: In India, the Central Government has the power to notify minor minerals under the relevant law.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II explains Statement I
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II does not explain Statement I
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is not correct
(d) Statement I is not correct but Statement II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Regarding the regulation of minerals under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act):
Statement I: Incorrect
The regulation of minor minerals primarily falls under the jurisdiction of State Governments, as per the MMDR Act, 1957. States are empowered to frame rules for granting extraction concessions for minor minerals.
Statement II: Correct
The Central Government has the authority to designate and notify which minerals are classified as 'minor minerals' under the MMDR Act, 1957.
Thus, Statement I is incorrect, while Statement II is correct.
Q7: Consider the following statements:
I. On the dissolution of the House of the People, the Speaker shall not vacate his/her office until immediately before the first meeting of the House of the People after the dissolution.
II. According to the provisions of the Constitution of India, a Member of the House of the People on being elected as Speaker shall resign from his/her political party immediately.
III. The Speaker of the House of the People may be removed from his/her office by a resolution of the House of the People passed by a majority of all the then Members of the House, provided that no resolution shall be moved unless at least fourteen days' notice has been given of the intention to move the resolution.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Statement I: Correct
Under Article 94 of the Indian Constitution, the Speaker of the Lok Sabha remains in office even after the House is dissolved, continuing until immediately before the first meeting of the newly constituted House to ensure continuity.
Statement II: Incorrect
There is no constitutional requirement for the Speaker to resign from their political party. Resigning from the party is a convention, not a mandate, to maintain impartiality in their role.
Statement III: Correct
As per Article 94, the Speaker can be removed from office by a resolution passed by a majority of the members of the Lok Sabha, with a minimum of 14 days' prior notice.
Thus, Statements I and III are correct, while Statement II is incorrect.
Q8: Consider the following pairs: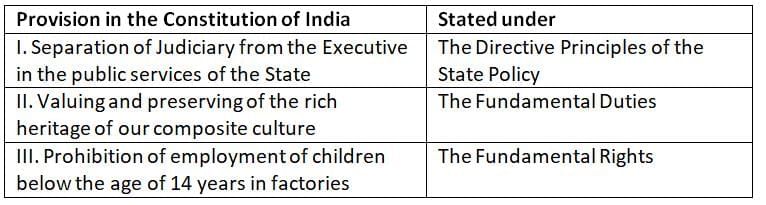
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Each of the following pairs accurately links a constitutional provision to its respective part in the Constitution of India.
Statement I: Directive Principles of State Policy – Correct
Article 50, under the Directive Principles of State Policy, mandates the separation of the judiciary from the executive in the public services of the State to ensure judicial independence.
Statement II: Fundamental Duties – Correct
Article 51A(f), part of the Fundamental Duties, requires citizens to value and preserve the rich heritage of India's composite culture.
Statement III: Fundamental Rights – Correct
Article 24, within the Fundamental Rights, prohibits the employment of children below the age of 14 years in hazardous occupations, such as factories or mines, to safeguard their well-being.
Thus, all three pairs are correctly matched with their respective constitutional provisions.
Q9: With reference to the Government of India, consider the following information: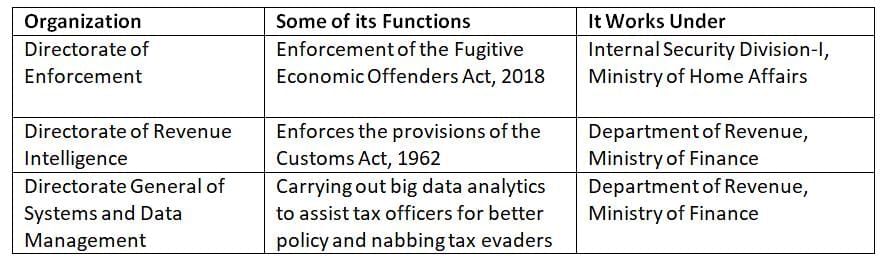
In how many of the above rows is the information correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All the three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The following evaluates the accuracy of mappings between investigative bodies, their functions, and their parent ministries or departments.
Row I: Incorrect
The Directorate of Enforcement (ED) implements the Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018, but it operates under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, not the Ministry of Home Affairs as incorrectly stated.
Row II: Correct
The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) is responsible for enforcing the Customs Act, 1962, and functions under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
Row III: Correct
The Directorate General of Systems and Data Management supports big data analytics for tax enforcement and operates under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
Thus, Rows II and III are correctly mapped, while Row I is incorrect due to the wrong attribution of the parent ministry.
Q10: Consider the following statements:
I. Panchayats at the intermediate level exist in all States.
II. To be eligible to be a Member of a Panchayat at the intermediate level, a person should attain the age of thirty years.
III. The Chief Minister of a State constitutes a commission to review the financial position of Panchayats at the intermediate levels and to make recommendations regarding the distribution of net proceeds of taxes and duties, leviable by the State, between the State and Panchayats at the intermediate level.
Which of the statements given above are not correct?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Statement I: Incorrect
The Constitution of India does not mandate the establishment of intermediate-level Panchayats (Panchayat Samitis) in all states. States with a population below 20 lakh are exempt from creating this tier, as per the 73rd Constitutional Amendment. This allows smaller states flexibility in their Panchayati Raj structure.
Statement II: Incorrect
The minimum age for eligibility to become a member of a Panchayat is 21 years, as specified under the Panchayati Raj Acts of various states, aligning with the Representation of the People Act. The claim of a 30-year minimum age is inaccurate.
Statement III: Incorrect
The State Finance Commission is appointed by the Governor of the state, not the Chief Minister, as per Article 243-I of the Indian Constitution. The Governor is responsible for constituting the commission to review the financial position of Panchayats and make recommendations.
Q11: Consider the following statements:
I. The Constitution of India explicitly mentions that in certain spheres the Governor of a State acts in his/her own discretion.
II. The President of India can, of his/her own, reserve a bill passed by a State Legislature for his/her consideration without it being forwarded by the Governor of the State concerned.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The Constitution grants the Governor discretionary powers in specific situations, such as reserving a state bill for the President’s consideration under Article 200 or appointing a Chief Minister in a hung assembly. These discretionary actions are final, as per Article 163(2). However, the President cannot independently intervene in state legislation without the Governor’s involvement, as only the Governor has the authority to reserve a bill for the President under Article 200.
Evaluation:
- Statement I: Correct – The Governor can exercise discretion in cases like reserving bills or appointing a Chief Minister in a hung assembly, and Article 163(2) upholds the finality of such decisions.
- Statement II: Incorrect – The President cannot unilaterally reserve a state bill for consideration; this power lies solely with the Governor under Article 200.
Q12: Consider the following subjects under the Constitution of India:
I. List I–Union List, in the Seventh Schedule
II. Extent of the executive power of a State
III. Conditions of the Governor’s office
For a constitutional amendment with respect to which of the above, ratification by the Legislatures of not less than one-half of the States is required before presenting the bill to the President of India for assent?
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Under Article 368(2) of the Constitution, amendments that affect the federal structure require ratification by at least half of the State Legislatures. This includes changes to the Union List in the Seventh Schedule, as it alters the federal balance of power, and modifications to the extent of a state’s executive power, which impacts the distribution of authority between the Centre and States. However, amendments concerning the conditions of the Governor’s office do not require state ratification.
Evaluation:
- Statement I: Correct – Amending the Union List in the Seventh Schedule affects the federal structure, necessitating ratification by at least half of the State Legislatures.
- Statement II: Correct – Changes to the extent of a state’s executive power impact the Centre-State power distribution, requiring state ratification.
- Statement III: Incorrect – Alterations to the conditions of the Governor’s office do not affect the federal structure and thus do not require state ratification.
Q13: Consider the following statements:
With reference to the Constitution of India, if an area in a State is declared as Scheduled Area under the Fifth Schedule,
I. the State Government loses its executive power in such areas and a local body assumes total administration.
II. the Union Government can take over the total administration of such areas under certain circumstances on the recommendations of the Governor.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
When an area is declared a Scheduled Area under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution, it remains under the administration of the State Government, but the Governor is granted special powers to promote tribal welfare.
Evaluation:
- Statement I: Incorrect – The State Government retains its executive powers in Scheduled Areas, and there is no provision for a local body to assume full administrative control.
- Statement II: Incorrect – The Union Government cannot take over the complete administration of Scheduled Areas under the Fifth Schedule, even with the Governor’s recommendation.
Q14: Consider the following statements with regard to pardoning power of the President of India:
I. The exercise of this power by the President can be subjected to limited judicial review.
II. The President can exercise this power without the advice of the Central Government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Statement I is correct because the President's pardoning power, while significant, is not absolute and can be subject to judicial review on limited grounds, such as if the decision is made with mala fide intent (bad faith) or is arbitrary.
Statement II is incorrect because the President is not strictly bound to act solely on the advice of the Council of Ministers when exercising the pardoning power. The President can exercise this power with some discretion, as it is a constitutional prerogative under Article 72 of the Indian Constitution, and not entirely dependent on the Council's advice.
Thus, only Statement I is correct.
UPSC Prelims 2024:Polity
Q1: How many Delimitation Commissions have been constituted by the Government of India till December 2023?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Four
Delimitation Commissions are constituted to redraw the boundaries of parliamentary and assembly constituencies based on population changes. As of December 2023, four Delimitation Commissions have been constituted by the Government of India:
- First Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1952 under the Delimitation Commission Act, 1952.
- Second Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1963 under the Delimitation Commission Act, 1962.
- Third Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 1973 under the Delimitation Act, 1972.
- Fourth Delimitation Commission: Constituted in 2002 under the Delimitation Act, 2002.
Each commission has been tasked with the responsibility of readjusting constituencies to reflect changes in population, ensuring fair representation in legislative bodies. Thus, the correct answer to the question is (d) Four.
Q2: The Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992 amends the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution to include which of the following languages?
1. Konkani
2. Manipuri
3. Nepali
4. Maithili
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1,2 and 3
The Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992, brought significant changes to the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India by adding three languages:
- Konkani: Spoken predominantly in the Konkan region of Goa, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
- Manipuri (Meitei): The official language of Manipur, spoken by the Meitei community.
- Nepali: Widely spoken in Nepal and also by a significant population in India, particularly in the northeastern states.
These languages were included to promote their recognition and usage in official capacities throughout India. This amendment reflected India's commitment to linguistic diversity and cultural inclusivity. Therefore, the correct answer is (a) 1, 2 and 3, as these three languages were added by the Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992.
Q3: Consider the following pairs:
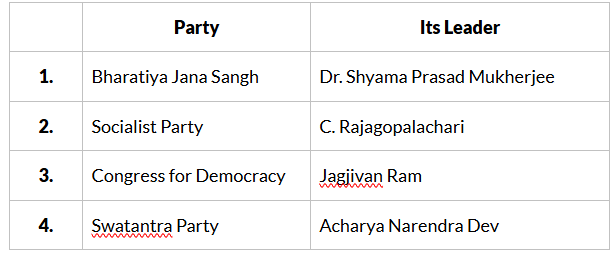
How many of the above are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Only two.
Bharatiya Jana Sangh - Dr. Shyama Prasad Mukherjee: This pair is correctly matched. Dr. Shyama Prasad Mukherjee was indeed associated with the Bharatiya Jana Sangh.
Socialist Party - C. Rajagopalachari: This pair is incorrect. C. Rajagopalachari was not associated with the Socialist Party. He was a prominent leader of the Indian National Congress and later founded the Swatantra Party.
Congress for Democracy - Jagjivan Ram: This pair is correct. Jagjivan Ram was associated with the Congress .
Swatantra Party - Acharya Narendra Dev: This pair is incorrect. Acharya Narendra Dev was not associated with the Swatantra Party. He was a prominent socialist leader.
Q4: Which of the following statements are correct about the Constitution of India?
1. Powers of the Municipalities are given in Part IX A of the Constitution.
2. Emergency provisions are given in fu Part XVIII of the Constitution.
3. Provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution are given in Part XX of the Constitution.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) 1, 2 and 3.
Powers of the Municipalities are given in Part IX A of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part IX A of the Constitution deals with municipalities, providing for their establishment, composition, powers, and responsibilities.
Emergency provisions are given in Part XVIII of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part XVIII of the Constitution (Articles 352 to 360) contains provisions related to emergencies, including national emergency, state emergency (previously termed as President's rule), and financial emergency.
Provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution are given in Part XX of the Constitution: This statement is correct. Part XX of the Constitution (Articles 368) deals with the procedure for amending the Constitution of India.
Therefore, all three statements are correct, and the correct answer is (d) 1, 2 and 3.
Q5: Which one of the following statements is correct as per the Constitution of India?
(a) Inter-State trade and commerce is a State subject under the State List.
(b) Inter-State migration is a State subject under the State List.
(c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List.
(d) Corporation tax is a State subject under the State List.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List.
Inter-State trade and commerce: This falls under the Union List, not the State List. It is regulated by the Central Government under Article 301-307 of the Constitution.
Inter-State migration: This is not explicitly mentioned as a subject under either the Union List or the State List. Migration, especially in terms of rights and restrictions, generally falls under laws related to citizenship, which is a Union subject.
Inter-State quarantine: This is indeed a Union subject under the Union List. It relates to public health and is regulated by the Central Government to prevent the spread of diseases between states.
Corporation tax: This is a Union subject under the Union List (specifically under "Taxes on income other than agricultural income"). It is exclusively within the jurisdiction of the Central Government.
Therefore, among the options given, (c) Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List is the correct statement as per the Constitution of India.
Q6: Under which of the following Articles of the Constitution of India, has the Supreme Court of India placed the Right to Privacy?(a) Article 15
(b) Article 16
(c) Article 19
(d) Article 21
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Article 21
- Article 15: Prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth.
- Article 16: Provides for equality of opportunity in matters of public employment.
- Article 19: Guarantees certain fundamental rights regarding freedom of speech, assembly, association, etc.
- Article 21: Ensures the protection of life and personal liberty. Over the years, the Supreme Court has interpreted Article 21 expansively to include the Right to Privacy as a fundamental right implicit within the right to life and personal liberty.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Article 21.
Q7: Which of the following statements about the Ethics Committee in the Lok Sabha are correct?
1. Initially it was an ad-hoc Committee.
2. Only a Member of the Lok Sabha can make a complaint relating to unethical conduct of a member of the Lok Sabha.
3. This Committee cannot take up any matter which is sub-judice.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 1 and 3 only
Initially it was an ad-hoc Committee: This statement is correct. The Ethics Committee in the Lok Sabha was initially constituted as an ad-hoc committee to examine matters related to the ethical conduct of members of the Lok Sabha.
Only a Member of the Lok Sabha can make a complaint relating to unethical conduct of a member of the Lok Sabha: This statement is incorrect. While members of the Lok Sabha can certainly raise concerns about unethical conduct, complaints can also be made by citizens or other individuals. It's not limited to only members of the Lok Sabha.
This Committee cannot take up any matter which is sub-judice: This statement is correct. The Ethics Committee generally avoids taking up matters that are already under judicial consideration (sub-judice matters).
Therefore, the correct answer, based on the statements provided, is (c) 1 and 3 only.
Q8: Who was the Provisional President of the Constituent Assembly before Dr. Rajendra Prasad took over?
(a) C. Rajagopalachari
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) T.T. Krishnamachari
(d) Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha
Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha served as the first temporary or provisional President of the Constituent Assembly from 9 December 1946 to 11 December 1946. He was succeeded by Dr. Rajendra Prasad, who then became the President of the Constituent Assembly until its completion and adoption of the Constitution.
Q9: As per Article 368 of the Constitution of India, the Parliament may amend any provision of the Constitution by way of:
1. Addition
2. Variation
3. Repeal
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) 1,2 and 3
According to Article 368 of the Constitution of India, Parliament has the authority to amend any provision of the Constitution by way of:
Addition: Parliament can introduce new provisions into the Constitution.
Variation: Parliament can modify or alter existing provisions of the Constitution.
Repeal: Parliament can remove or annul existing provisions of the Constitution.
These three methods provide Parliament with flexibility in amending the Constitution to adapt to changing circumstances or to correct deficiencies in the legal framework. This constitutional provision underscores the dynamic nature of India's governance structure while maintaining the core principles and framework of the Constitution.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 1, 2 and 3, as all these methods are permissible under Article 368 for amending the Constitution of India.
Q10: Which of the following statements are correct in respect of a Money Bill in the Parliament?
1. Article 109 mentions special procedure in respect of Money Bills.
2. A Money Bill shall not be introduced in the Council of States.
3. The Rajya Sabha can either approve the Bill or suggest changes but cannot reject it.
4. Amendments to a Money Bill suggested by the Rajya Sabha have to be accepted by the Lok Sabha.
Select the answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 1,2 and 3
Article 109 mentions special procedure in respect of Money Bills: This statement is correct. Article 109 of the Constitution of India specifies the special procedure that must be followed for the introduction and passage of Money Bills in Parliament.
A Money Bill shall not be introduced in the Council of States: This statement is correct. According to Article 110 of the Constitution, a Money Bill can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha (House of the People), and not in the Rajya Sabha (Council of States).
The Rajya Sabha can either approve the Bill or suggest changes but cannot reject it: This statement is correct. The Rajya Sabha does not have the power to reject a Money Bill. It can only make recommendations for amendments, which the Lok Sabha may or may not accept.
Amendments to a Money Bill suggested by the Rajya Sabha have to be accepted by the Lok Sabha: This statement is incorrect. The Lok Sabha has the discretion to accept or reject any amendments suggested by the Rajya Sabha. However, the Rajya Sabha cannot amend a Money Bill directly; it can only suggest amendments.
Therefore, the correct statements, based on the options provided, are (c) 1, 2 and 3.
Q11. The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. Subsequent to the amendment of NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises which of the following members?
1. Governor of the Constituent State
2. Chief Minister of the Constituent State
3. Three Members to be nominated by the President of India
4. The Home Minister of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1,2 and 3 only
The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. According to the amended provisions of the NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises the following members:
Governor of the Constituent State: The Governors of the North Eastern states are members of the NEC.
Chief Minister of the Constituent State: The Chief Ministers of the North Eastern states are also members of the NEC.
Three Members to be nominated by the President of India: The President of India nominates three members to the NEC.
The Home Minister of India: The Home Minister of India is not a member of the NEC.
Therefore, based on the options provided, the correct answer is (a) 1, 2 and 3 only.
Q12: Consider the following statements regarding ‘Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam’:
1. Provisions will come into effect from the 18th Lok Sabha.
2. This will be in force for 15 years after becoming an Act.
3. There are provisions for the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes Women within the quota reserved for the Scheduled Castes.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Option c is the correct answer.
In September 2023, history was made with Parliament passing the Women’s Reservation Bill called the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam. The bill seeks to reserve one-third of the total number of seats for women in Lok Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies, and Delhi Assembly. The allocation of reserved seats shall be determined by such authority as prescribed by Parliament.
Statement 1 is incorrect. According to the provisions of the Bill, the reservation is set to be enforced following the publication of a new census and the completion of the delimitation exercise. Furthermore, it’s important to note that for the bill to be fully ratified, it necessitates approval from a minimum of 50% of the states.
Statement 2 is correct. Reservation of seats for women shall cease to exist 15 years after the commencement of this Amendment Act.
Statement 3 is correct. The Bill provides that One-third of the total number of seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes shall be reserved for women of those groups in the Lok Sabha and the legislative assemblies.
Q13: A Writ of Prohibition is an order issued by the Supreme Court or High Courts to:
(a) a government officer prohibiting him from taking a particular action.
(b) the Parliament/Legislative Assembly to pass a law on Prohibition.
(c) the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
(d) the Government prohibiting it from following an unconstitutional policy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
A Writ of Prohibition is a legal remedy issued by a higher court (such as the Supreme Court or High Court) to a lower court or tribunal, instructing them to stop or prohibit further proceedings in a particular case. This writ is typically issued when the lower court is acting beyond its jurisdiction or is conducting proceedings that are legally improper or unlawful.
Key points to remember:
- It is not issued to government officers (option a).
- It does not instruct Parliament or Legislative Assembly to pass a law (option b).
- It is not issued to the government to prohibit unconstitutional policies (option d).
Therefore, option (c) is correct because it accurately describes the purpose and scope of a Writ of Prohibition as it pertains to judicial proceedings in lower courts or tribunals.
Q14: Consider the following statements:
1. It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
2. A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 2 only
It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
- This statement is incorrect. The recognition and declaration of any community as a Scheduled Tribe in a State is not done by the Governor alone. It is actually done by the President of India after consultation with the Governor of the concerned State, as per Article 342(1) of the Constitution of India.
A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
- This statement is correct. The list of Scheduled Tribes varies from State to State. A community recognized as a Scheduled Tribe in one State may not necessarily be recognized as such in another State. Each State has its own list of Scheduled Tribes based on their specific social and demographic considerations.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 2 only.
Q15: With reference to Union Budget, consider the following statements:
1. The Union Finance Minister on behalf of the Prime Minister lays the Annual Financial Statement before both the Houses of Parliament.
2.At the Union level, no demand for a grant be made except on the recommendation of the President of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 2 only
The Union Finance Minister on behalf of the Prime Minister lays the Annual Financial Statement before both the Houses of Parliament.
- This statement is incorrect. It is not the Annual Financial Statement, but rather the Union Budget that is presented by the Union Finance Minister on behalf of the President of India. The Budget includes the Annual Financial Statement, but it is formally presented on behalf of the President, not the Prime Minister.
At the Union level, no demand for a grant can be made except on the recommendation of the President of India.
- This statement is correct. As per Article 113 of the Constitution of India, no demand for a grant can be made except on the recommendation of the President. This ensures that all expenditures from the Consolidated Fund of India are approved through a formal recommendation process.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 2 only.
Q16: With reference to the Speaker of the Lok Sabha, consider the following statements:
While any resolution for the removal of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha is under consideration.
1. He/she shall not preside.
2. He/She shall not have the right to speak.
3. He/She shall not be entitled to vote on the resolution in the first instance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) 1only
- Statement 1 is correct. The Speaker shall not preside while a resolution for his/her removal is under consideration.
- Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect. The Speaker can speak and vote in the first instance as a member, but not as the presiding officer.
Q17: With reference to the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements:
1. A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses on its dissolution.
2. A bill passed by the Lok Sabha and pending in the Rajya Sabha lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
3. A bill in regard to which the President of India notified his/her intention to summon the Houses to a joint sitting lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 1 and 2
A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses on its dissolution.
- This statement is correct. When the Lok Sabha is dissolved, all bills pending in it (whether introduced or not) lapse and do not carry over to the next Lok Sabha.
A bill passed by the Lok Sabha and pending in the Rajya Sabha lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- This statement is correct. If a bill has been passed by the Lok Sabha but is pending in the Rajya Sabha at the time of dissolution, it lapses and needs to be reintroduced in the new Lok Sabha.
A bill in regard to which the President of India notified his/her intention to summon the Houses to a joint sitting lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- This statement is incorrect. If the President has notified their intention to summon a joint sitting of both Houses for consideration of a bill, the bill does not lapse on dissolution. It can still be taken up in the joint sitting convened after the new Lok Sabha is constituted.
Therefore, the correct answer is (b) 1 and 2.
Q18: With reference to the Parliament of India, consider the following statements:
1. Prorogation of a House by the President of India does not require the advice of the Council of Ministers.
2. Prorogation of a House is generally done after the House is adjourned sine die but there is no bar to the President of India prorogating the House which is in session.
3. Dissolution of the Lok Sabha is done by the President of India who, save in exceptional circumstances, does so on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) 2 and 3
Prorogation of a House by the President of India does not require the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Incorrect. The President acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers in all matters, including prorogation, as per Article 74 of the Constitution.Prorogation of a House is generally done after the House is adjourned sine die, but there is no bar to the President of India prorogating the House which is in session.
Correct. Prorogation usually occurs after adjournment sine die, but the President can prorogue the House while it is in session.Dissolution of the Lok Sabha is done by the President of India who, save in exceptional circumstances, does so on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Correct. The President dissolves the Lok Sabha based on the advice of the Council of Ministers, except in extraordinary situations, such as when the Council loses the majority and is unable to advise.
UPSC Prelims 2023:Polity
Q1: In essence, what does Due Process of Law' mean?
(a) The principle of natural justice.
(b) The procedure established by law.
(c) Fair application of law.
(d) Equality before law.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The due process of law doctrine examines not only whether a law exists to deprive a person of his or her life and personal liberty, but also whether the legislation is fair, just, and not arbitrary.
- Due process of law is a constitutional guarantee that prevents governments from impacting citizens in an abusive way. In its modern form, due process includes both procedural standards that courts must uphold in order to protect peoples’ personal liberty and a range of liberty interests that statutes and regulations must not infringe.
- It traces its origins to Chapter 39 of King John’s Magna Carta, which provides that no freeman will be seized, dispossessed of his property, or harmed except “by the law of the land,” an expression that referred to customary practices of the court. The phrase “due process of law” first appeared as a substitute for Magna Carta’s “the law of the land” in a 1354 statute of King Edward III that restated Magna Carta’s guarantee of the liberty of the subject.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q2: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: In India, prisons are managed by State Governments with their own rules and regulations for the day-to-day administration of prisons.
Statement-II: In India, prisons are governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 which expressly kept the subject of prisons in the control of Provincial Governments.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Prisons'/'persons detained therein' is a “State-List” subject under Entry 4 of List II of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India.
- Administration and management of prisons and prisoners is the responsibility of respective State Governments who are competent to take appropriate action in this regard. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- However, given the significance of prisons in the Criminal Justice System, the Ministry of Home Affairs has been providing regular guidance and support to the States and UTs on diverse issues relating to prison administration.
- Under Prison act 1894, which governs the prisons, management and administration of prison falls in the domain of state governments. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
Q3: Which one of the following statements best reflects the Chief purpose of the 'Constitution' of a country?
(a) It determines the objective for the making of necessary laws.
(b) It enables the creation of political offices and a government.
(c) It defines and limits the powers of government.
(d) It secures social justice, social equality and social security.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The chief purpose of a constitution is to establish the fundamental principles, structure, and functions of a government and to define the rights and freedoms of individuals within a country. Constitutions serve as the supreme law of the land and provide a framework for governance, ensuring the balance of power, protecting individual rights, and guiding the functioning of the state.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q4: In India, which one of the following Constitutional Amendments was widely believed to be enacted to overcome the judicial interpretations of the Fundamental Rights?
(a) 1st Amendment
(b) 42nd Amendment
(c) 44th Amendment
(d) 86th Amendment
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1st Constitutional Amendment Act, 1951:
- Issues involved in the cases included freedom of speech, acquisition of the Zamindari land, State monopoly of trade, etc.
- Added three more grounds of restrictions on freedom of speech and expression: public order, friendly relations with foreign states and incitement to an offense. Also, it made the restrictions ‘reasonable’ and thus, justiciable in nature.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q5: Consider the following organizations/bodies in India:
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above constitutional bodies?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) was initially constituted by the Central Govt by the National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 and so far the Commission had been reconstituted 7 times up to 2016. The National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 has been repealed through the National Commission for Backward Classes (Repeal) Act, 2018. The Commission has been accorded Constitutional Status and constituted through “The Constitution (One Hundred and Second Amendment) Act, 2018” Act.
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India was established on 12 October, 1993. The statute under which it is established is the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993 as amended by the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006.
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC), is a quasi- judicial commission in India which was set up in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body and is constituted by a notification of the Government of India, Ministry of Law & Justice, Department of Legal Affairs with a definite terms of reference to carry out research in the field of law and the Commission makes recommendations to the Government (in the form of Reports) as per its terms of reference.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q6: Consider the following statements:
- If the election of the President of India is declared voidby the Supreme Court of India, all acts done by him/her in the performance of duties of his/her office of President before the date of decision become invalid.
- Election for the post of the President of India can be postponed on the ground that some Legislative Assemblies have been dissolved and elections are yet to take place.
- When a Bill is presented to the President of India, the Constitution prescribes time limits within which he/she has to declare his/her assent.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- If the election of a person as President or Vice President is declared void by the Supreme court, acts done by him in the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of the office of President or Vice President, as the case may be, on or before the date of the decision of the Supreme Court shall not be invalidated by reason of that declaration. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- When an assembly is dissolved, the members cease to be qualified to vote in the presidential election, even if fresh elections to the dissolved assembly are not held before the presidential election. Thus election to the president will not be postponed on the grounds that some Legislative Assemblies have been dissolved. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Assent to Bills: When a Bill has been passed by the Houses of Parliament, it shall be presented to the President, and the President shall declare either that he assents to the Bill, or that he withholds assent therefrom Provided that the President may, as soon as possible after the presentation to him of a Bill for assent, return the Bill if it is not a Money Bill to the Houses with a message requesting that they will reconsider the Bill or any specified provisions thereof and, in particular, will consider the desirability of introducing any such amendments as he may recommend in his message, and when a Bill is so returned, the Houses shall reconsider the Bill accordingly, and if the Bill is passed again by the Houses with or without amendment and presented to the President for assent, the President shall not withhold assent therefrom Procedures in Financial Matters. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q7: With reference to Finance Bill and Money Bill in the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements:
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Finance Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it can amend or reject the Bill.
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Money Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot amend or reject the Bill, it can only make recommendations.
- In the case of disagreement between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, there is no joint sitting for Money Bill, but a joint sitting becomes necessary for Finance Bill.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Finance Bill is a Money Bill as defined under article 110(a) of the constitution.It is introduced as a part of Annual Financial Statement(Budget) under article 112.
- The Rajya Sabha has limited powers regarding the Money Bill. It cannot reject or amend the money bill after it is passed by the Lok Sabha and transmitted to the Rajya Sabha. It has to return the bill within 14 days with or without recommendations. It is at the discretion of Lok Sabha to accept or reject any or all of the recommendations made by the Rajya Sabha. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Finance bill, being subjected to all the conditions of Money bill, Rajya Sabha can only make recommendations on a finance bill. Rajya Sabha can not amend or reject finance bill(as also the case for Money bill). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The provision of joint sitting is applicable to ordinary bills or financial bills only and not to money bills(including Finance bills) or Constitutional amendment bills. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q8: With reference to Scheduled Areas in India, consider the following statements:
- Within a State, the notification of an area as Scheduled Area takes place through an Order of the President.
- The largest administrative unit forming the Scheduled Area is the District and the lowest is the cluster of villages in the Block.
- The Chief Ministers of the concerned States are required to submit annual reports to the Union Home Ministry on the administration of Scheduled Areas in the States.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The term “Scheduled Areas” are those that are scheduled as such by a Presidential Order under Paragraph 6 (1) of the Fifth Schedule, which states: “In this Constitution, the expression ‘Scheduled Areas’ means such areas as the President may by order declare to be “Scheduled Areas”.
- The specification of “Scheduled Areas” in relation to a State is by a notified order of the President, after consultation with the State Government concerned. The same applies in the case of any alteration, increase, decrease, incorporation of new areas, or rescinding any Orders relating to “Scheduled Areas”. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The largest administrative unit forming the scheduled areas has been the district and the lowest the cluster of villages in the block. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The Governor of each State having Scheduled Areas therein shall annually, or whenever so required by the President, make a report to the President regarding the administration of the Scheduled Areas in that State and the executive power of the Union shall extend to the giving of directions to the State as to the administration of the said areas. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q9: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The Supreme Court of India has held in some judgements that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4) of the Constitution of India would be limited by Article 335 for maintenance of efficiency of administration.
Statement-II: Article 335 of the Constitution of India defines the term 'efficiency of administration'.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-1
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- In the past seven decades of constitutional jurisprudence on reservations, the Supreme Court of India has consistently referred to the notions of “efficiency” and “merit,” while adjudicating the validity of various reservation policies.
- The Court has held in several judgments (Indra Sawhney and others v Union of India and Others 1993; M Nagaraj and Others v Union of India and Others 2006) that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4)1 of the Constitution would be limited by Article 335 (2) which provides for “maintenance of efficiency of administration,”. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, statement 2 is not correct. While considering the claims of the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the making of appointments to public services and posts. This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q10: Consider the following:
- Demographic performance
- Forest and ecology
- Governance reforms
- Stable government
- Tax and fiscal efforts
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used how many of the above as criteria other than population area and income distance?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) All five
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used the following as criteria:
- Population Area
- Forest & ecology Income Distance Tax & fiscal efforts
- Demographic performance
Hence, the correct answer is b.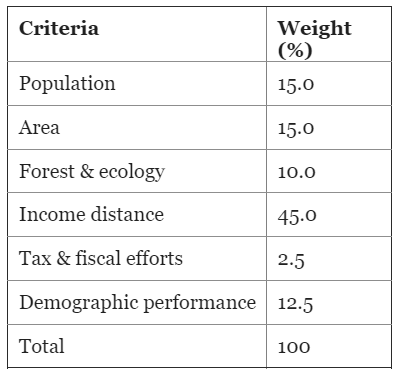
Q11: With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements :
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some States.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- ‘Home Guards’ is a voluntary force, first raised in India in December 1946, to assist the police in controlling civil disturbance and communal riots.
- Subsequently, the concept of the voluntary citizen’s force was adopted by several States. In the wake of Chinese aggression in 1962, the Centre advised the States and Union Territories to merge their existing voluntary organisation into one uniform voluntary force known as Home Guards.
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the States/Union Territories, NOT the Central Government. Hence statement 1 is NOT correct.
- The role of Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary Force to the Police in maintenance of internal security situations, help the community in any kind of emergency such as an air-raid, fire, cyclone, earthquake, epidemic etc., help in maintenance of essential services, promote communal harmony and assist the administration in protecting weaker sections, participate in socio-economic and welfare activities and perform Civil Defence duties. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Fifteen Border Wing Home Guards (BWHG) Battalions have been raised in the border States viz. Punjab (6 Bns.), Rajasthan ( 4 Bns.), Gujarat (2 Bns.) and one each Battalion for Meghalaya, Tripura and West Bengal to serve as an auxiliary to Border Security Force for preventing infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, guarding of VA/VPs and lines of communication in vulnerable area at the time of external aggression. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Q12: With reference to India, consider the following pairs:

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Official Secrets Act was first enacted in 1923 and was retained after Independence. The law, applicable to government servants and citizens, provides the framework for dealing with espionage, sedition, and other potential threats to the integrity of the nation. The law makes spying, sharing ‘secret’ information, unauthorised use of uniforms, (Under Section-6) withholding information, interference with the armed forces in prohibited/ restricted areas, among others, punishable offences. If guilty, a person may get up to 14 years’ imprisonment, a fine, or both. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Under section 7 of Official Secrets Act 1923 No person in the vicinity of any prohibited place shall obstruct, knowingly mislead or otherwise interfere with or impede, any police officer, or any member of 21 [the Armed Forces of the Union] engaged on guard, sentry, patrol or other similar duty in relation to the prohibited place. Hence pair 2 is NOT correctly matched.
- THE ARMS (AMENDMENT) ACT, 2019 says Whoever uses firearm in a rash or negligent manner or in celebratory gunfire so as to endanger human life or personal safety of others shall be punishable with an imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine which may extend to rupees one lakh, or with both. Hence pair 3 is correctly matched.
Q13: Consider the following statements in respect of the National Flag of India According to the Flag Code of India, 2002:
Statement-I: One of the standard sizes the National Flag of India of 600 mm × 400 mm.
Statement-II: The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the Flag shall be 3 : 2.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The standard sizes of national flag shall be as follows:
- Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- The National Flag shall be rectangular in shape. The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the flag shall be 3 : 2. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q14: Consider the following statements in respect of the Constitution Day:
Statement-I: The Constitution Day is celebrated on 26th November every year to promote constitutional values among citizens.
Statement-II: On 26th November, 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution of India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- It is celebrated on 26th November every year. It is also known as National Law Day. On this day in 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India formally adopted the Constitution of India that came into force on 26th January 1950. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- On 29 August, 1947, the Constituent Assembly set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution for India. Hence, statement 2 is incorrect.
- On 13 December 1946, the Constituent Assembly formally commenced its task of framing the Constitution of India. Jawaharlal Nehru moved the Objectives Resolution, which aimed to declare India as an Independent Sovereign Republic and create a Constitution to govern its future. The Resolution established general principles to guide the work of the Constituent Assembly. On January 22, 1947, the Constituent Assembly adopted the Resolution.
Q15: Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana:
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Janani Suraksha Yojana:
- The Yojana, launched on 12th April 2005, is being implemented in all states and UTs with special focus on low performing states.
- It is a safe motherhood intervention under the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- It was implemented with the objective of reducing maternal and neo-natal mortality by promoting institutional delivery among the poor pregnant women. Hence, statements 2 and 3 are correct.
- Providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age is not an objective of the scheme. Hence, statement 4 is not correct.
Q16: Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy:
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Interventions of Anaemia Mukt Bharat:
- Not Prophylactic calcium supplementation but Prophylactic Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation is provided to children, adolescents and women of reproductive age and pregnant women irrespective of anemia. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Appropriate Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) with emphasis on adequate and age-appropriate complementary foods for children 6 months and above. Increase intake of iron-rich, protein-rich and vitamin C-rich foods through dietary diversification/quantity/frequency and food fortification
- Promoting practice of delayed cord clamping (by atleast 3 minutes or until cord pulsations cease) in all health facility deliveries followed by early initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Bi-annual mass deworming for children in the age groups between 1-19 years is carried out every year under National Deworming Day (NDD) programme. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- The Anemia Mukt Bharat, also integrates deworming of women of reproductive age and for pregnant women as part of the NDD strategy.
- Addressing non-nutritional causes of anemia in endemic pockets, with special focus on malaria, haemoglobinopathies and fluorosis. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
Q17: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: India's public sector health care system largely focuses on curative care with limited preventive, promotive and rehabilitative care.
Statement-II: Under India's decentralized approach to health care delivery, the States are primarily responsible for organizing health services.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- The Ayushman Bharat - Health and Wellness Centres (ABHWCs) were launched under the Ayushman Bharat Programme in a bid to move away from selective health care to a more comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care for all ages. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- In AB, HWCs at the Sub Health Centre (SHC) level, Multi-Purpose Workers (male & female) & ASHAs and Primary Health Centre / Urban Primary Health Centre are organized by state govt but in case of tertiary Health services Central govt is also a key stakeholders. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q18: Consider the following statements:
- According to the Constitution of India, the Central Government has a duty to protect States from internal disturbances.
- The Constitution of India exempts the States from providing legal counsel to a person being held for preventive detention.
- According the Prevention of Terrorism Act, 2002, confession of the accused before the police cannot be used as evidence.
How many of the above statement are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- As per Article 355, it shall be the duty of the Union to protect every State against external aggression and internal disturbance and to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution. Hence, Statement 1 is correct.
- Article 22 (1) of the Constitution, for example, guarantees the right to legal counsel, but Article 22 (3) (b) strips this right from persons arrested or detained under preventive detention law. Relying on these provisions, the Supreme Court stated, in A.K. Roy v. Union of India, that detainees do not have the right to legal representation or cross-examination in Advisory Board hearings. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The Terrorist and Disruptive Activities (Prevention) Act, 1987 and the Prevention of Terrorism Act, 2002 (commonly known as TADA and POTA respectively) had made provisions to admit the confessions made by the accused before the police authorities. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- The Indian Evidence Act, 1872 provides that confession made before police authority or under police custody is inadmissible.
Q19: Consider the following statements in respect of election to the President of India:
- The members nominated to either House of the Parliament or the Legislative Assemblies of States are also eligible to be included in the Electoral College.
- Higher the number of elective Assembly seats, higher is the value of vote of each MLA of that State.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Madhya Pradesh is greater than that of Kerala.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The President is elected not directly by the people but by members of electoral college consisting of: 1. the elected members of both the Houses of Parliament; 2. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the states; and 3. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the Union Territories of Delhi and Puducherry1. Thus, the nominated members of both of Houses of Parliament, the nominated members of the state legislative assemblies, the members (both elected and nominated) of the state legislative councils (in case of the bicameral legislature) and the nominated members of the Legislative Assemblies of Delhi and Puducherry do not participate in the election of the President. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Is the value of vote of each elector the same?
- Answer: No. The value of votes of MLAs would differ from State to State as the value of each such vote is calculated by the process explained below. However, the value of votes of all MPs is the same. Statements 2 and 3 are not correct.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry = 471707/30 =
- 15,723.56.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Arunachal Pradesh = 467511/60 = 7,791.85.
The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
UPSC Prelims 2022:Polity
Q1: In India, which one of the following compiles information on industrial disputes, closures, retrenchments and lay-offs in factories employing workers?
(a) Central Statistics Office
(b) Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
(c) Labour Bureau
(d) National Technical Information System Manpower
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Statistics on industrial disputes, closures, retrenchments and lay-offs in India is an annual publication of the Labour Bureau which is an attached office under the Ministry of Labour and Employment. Hence, option (c) is correct.
Labour Bureau:
- Labour Bureau, an attached office under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, was set up on 1st October 1946.
- Labour Bureau collects and publishes statistics and related information on wages, earnings, productivity, absenteeism, labour turnover, industrial relations, working and living conditions and evaluation of working of various labour enactments etc. Besides important economic indicators like Consumer Price Index Numbers for Industrial, Agricultural and Rural Labourers; wage rate indices and data on industrial relations, socio-economic conditions in the organised and unorganised sector of industry etc are also released by the office.
Q2: In India, what is the role of the Coal Controller's Organization (CCO)?
- CCO is the major source of Coal. Statistics in Government of India.
- It monitors progress of development of Captive Coal/Lignite blocks.
- It hears any objection to the Government's notification relating to acquisition of coal- bearing areas.
- It ensures that coal mining companies deliver the coal to end users in the prescribed time.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Coal Controller Organisation: Office of Coal Controller (earlier Coal Commissioner), established in 1916, is one of the oldest offices in Indian Coal sector. Main aim behind setting up this office was to have Government control to adequately meet the coal requirement during First World War.
Functions of Coal Controller’s Organisation are listed as below:
- Inspection of collieries so as to ensure the correctness of the class, grade or size of coal. To issue directives for the purpose of declaration and maintenance of grades of coal of a seam mined in a colliery.
- Assessment and collection of excise duty levied on all raw coal raised and dispatched. Submission of monthly coal data to different ministries of Central and State Government, national and international organization. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Under Coal Bearing Area (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957- Coal Controller is the competent authority under this act to hear any objection to the Central Government’s Notification relating to acquisition of coal bearing land and to furnish his reports to Central Govt. Hence, Statement 3 is correct.
- The Coal Controller’s Organisation monitors progress of development of Captive Coal/Lignite Blocks and their associated end-use projects. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It does not ensure that coal mining company deliver the coal to end user in prescribed time. Hence, statement 4 is not correct.
Q3: If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it?
(a) This would prevent the transfer of land of tribal people to non-tribal people.
(b) This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
(c) This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
(d) The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Land Governance under the fifth Schedule area: Governor can make regulations with regard to the:
- Prohibition and restriction of transfer of land from and between Scheduled Tribes – almost every State in the country, and certainly all States with Scheduled Areas, have enacted legislations relating to prevention/prohibition of land transfer in Scheduled Areas by tribals to non- tribals, and in some cases, even the transfer of land between tribals inter-se is restricted. Hence, option (a) is correct.
- Regulation of allotment of land to tribals in Scheduled Areas.
- Regulation of moneylending in Scheduled Areas to tribals.
Q4: Consider the following statements:
- The India Sanitation Coalition is a platform to promote sustainable sanitation and is funded by the Government of India and the World Health Organization.
- The National Institute of Urban Affairs is an apex body of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in Government of India and provides innovative solutions to address the challenges of Urban India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
India Sanitation Coalition:
- India Sanitation Coalition was formed under the aegis of FICCI.
- The vision of the Coalition is to enable and support an ecosystem for sustainable sanitation through a partnership mode. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
National Institute of Urban Affairs:
- Established in 1976, the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) is India’s leading national think tank on urban planning and development.
- As a hub for the generation and dissemination of cutting-edge research in the urban sector, NIUA seeks to provide innovative solutions to address the challenges of a fast urbanizing India, and pave the way for more inclusive and sustainable cities of the future.
- In 1976, NIUA was appointed as an apex body to support and guide the Government of India in its urban development plans. Since then, it has worked closely with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, alongside other government and civil sectors, to identify key areas of research, and address the lacunae in urban policy and planning. NIUA is associated with MoHUA but not the apex body of MoHUA. Hence, Statement 2 is not correct.
Q5: With reference to the "Tea Board" in India, consider the following statements:
- The Ten Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board's Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices at Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Tea Board is functioning as a statutory body of the Central Government.Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It comes under the Ministry of Commerce. Hence, statement 2 is not correct
- The Board is constituted of 31 members (including Chairman) drawn from Members of Parliament, tea producers, tea traders, tea brokers, consumers, and representatives of Governments from the principal tea producing states, and trade unions. The Board is reconstituted every three years.
- Foreign Offices: Currently Tea Board has two overseas offices located at Dubai, and Moscow. All these foreign offices of the Board are designed to undertake the various promotional measures to boost up export of Indian tea. These offices also act as a liaison office for interaction between importers of Indian tea of the respective regions as well as Indian Exporters. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
- Its headquarters is situated in Kolkata. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q6: Consider the following statements:
- Pursuant to the report of H.N. Sanyal Committee, the Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 was passed.
- The Constitution of India empowers the Supreme Court and the High Courts to punish for contempt of themselves.
- The Constitution of India defines Civil Contempt and Criminal Contempt.
- In India, the Parliament is vested with the powers to make laws on Contempt of Court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The 1963 Bill prepared by the Satyapal Committee was reviewed by a Joint Committee of Parliament (1969-70) (Bhargava Committee). Based on which the Contempt of Court Act, 1971 was enacted. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Article 129 of the Constitution empowered the Supreme Court to punish for contempt of self. Article 215 gave the respective power to the High Courts. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- According to the Contempt of Court Act, 1971, contempt refers to the offence of showing disrespect to the dignity or authority of a court. The expression ‘contempt of court’ has not been defined by the Constitution. However, Article 129 of the Constitution empowers the Supreme Court to punish for contempt of self. Hence statement 3 is not correct.
- The power to punish for contempt is a constitutional power vested in the Supreme Court which cannot be curtailed or abolished even by a legislative act. Article 142(2) states that "subject to the provisions of any law made by Parliament in this behalf" the Supreme Court shall have full power to make any order on the punishment of contempt. Hence statement 4 is correct.
Q7: With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognised as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Government law officers, legal firms and patent jurists are recognized as advocates, while corporate lawyers are outside the recognition of advocates. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
- The Bar Council of India is a statutory body established under Section 4 of the Advocates Act 1961 that regulates legal practice and legal education in India. Its members are elected from amongst lawyers in India and thus represent the Indian Bar. It sets standards of professional conduct, etiquette and exercises disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar.
- It also sets standards for legal education and provides recognition to universities whose law degrees will serve as qualifications for students to enroll as advocates at the undergraduate level. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q8: Consider the following statements:
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Constitution Amendment Bill can be reinstated by a minister or a private member and for this the prior approval of the President is not necessary. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The President is bound to assent to the bill. They can neither keep the bill with themselves nor send it to the Parliament for reconsideration. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It is mandatory to pass the Constitution Amendment Bill separately in each house. In case of disagreement between the two houses, there is no provision to pass the bill in the joint sitting of both the houses. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Q9: Consider the following statements:
- The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
- The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- There are three categories of ministers in the Council of Ministers - Cabinet Ministers, Ministers of State, Deputy Ministers. The difference between them is- their hierarchy, their salary and political importance. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
- The total number of members of the Council of Ministers, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 percent of the total strength of the Lok Sabha. This provision has been included by the 91st Constitutional Amendment Bill, 2003. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Q10: Which of the following is/are the exclusive power(s) of Lok Sabha?
- To ratify the declaration of Emergency
- To pass a motion of no-confidence against the Council of Ministers
- To impeach the President of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- It is the exclusive power of the Lok Sabha to pass a no-confidence motion against the Council of Ministers. When the Lok Sabha passes a no-confidence motion against the Council of Ministers, all the ministers, including the ministers of the Rajya Sabha, have to resign. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The resolution of the proclamation of emergency will be required to be passed by a majority of the total number of members of each House of Parliament and 2/3 majority of the members present and voting. A Declaration of National Emergency is placed before each House of Parliament and if it is not approved within a month, it does not remain in force, but once approved, it can remain in operation for six months. As a result, the Proclamation of Emergency is ratified by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha. It is not the exclusive power of the Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The impeachment motion of the President should be passed by a special majority (two- thirds) in the original house. The motion is then sent to the other house for consideration. The second house acts as an inspector. A Select Committee has been constituted to investigate the allegations against the President. Impeachment of the President of India comes under both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. It is not the exclusive power of Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q11: With reference to anti-defection law in India, consider the following statements?
- The law specifies that a nominated legislator cannot join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House.
- The law does not provide any time-frame within which the presiding officer has to decide a defection case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- A public representative can be disqualified under the Anti-Defection Act if:
- An elected member voluntarily gives up the membership of a political party. An independent elected member joins a political party.
- A member votes against the party in the House.
- A member abstains from voting.
- After the expiry of six months, a nominated member joins a political party.
- Therefore, any nominated MLA can join any political party within six months of being appointed to the House but not after six months. Hence statement 1 is not correct. As per the law, the Speaker of the House has the power to decide the disqualification of the members.
- If any complaint is received regarding the party of the Speaker of the House, any other member elected by the House has the right to take a decision in this regard. Therefore, this law does not prescribe any time period within which the presiding officer has to decide the defection case. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Q12: Consider the following statements:
- Attorney General of India and Solicitor General of India are the only officers of the Government who are allowed to participate in the meetings of the Parliament of India.
- According to the Constitution of India, the Attorney General of India submits his resignation when the Government which appointed him resigns.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- According to the Constitution, only the Attorney General can take part in the proceedings of both the Houses of Parliament or their joint sitting and any committee of the Parliament of which s/he may be named a member, but without a right to vote. In addition to the AG, there are other law officers of the Government of India. They are the solicitor general of India and additional solicitor general of India. They assist the Attorney General in carrying out official duties. The Constitution does not mention the solicitor general and additional solicitor general. Hence statement 1 not correct.
- The procedure and grounds for removal of the Attorney General are not mentioned in the Constitution. He holds office during the pleasure of the President (may be removed by the President at any time). Therefore, the Attorney General of India does not resign on the resignation of the government. Hence statement 2 is not correct.
Q13: With reference to the writs issued by the Courts in India, consider the following statements:
- Mandamus will not lie against a private organisation unless it is entrusted with a public duty.
- Mandamus will not lie against a Company even though it may be a Government Company.
- Any public minded person can be a petitioner to move the Court to obtain the writ of Quo Warranto.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Mandamus is issued to direct a public authority to do its duty. Mandamus is a judicial remedy in the form of an order from a court. It cannot be issued to compel an authority to do something against a statutory provision. Therefore, no mandate will be issued against any private organisation unless it has been entrusted with any public work. Hence option 1 is correct.
- Mandamus is issued by the court to a public official asking him to perform his official duties that he has failed or refused to perform. It can also be issued against any public body, a corporation, an inferior court, a tribunal or government for the same purpose. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Supreme Court or High Court issues this writ to prevent illegal usurpation of public office by any person. Through this writ, the court examines the validity of a person's claim to public office. This writ empowers any person other than the aggrieved person to seek redress. Therefore, any public-prone person can be a petitioner to move the court to obtain a writ of right. Hence option 3 is correct.
Q14: With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements:
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal, health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Ayushman Bharat is a flagship scheme of the country, which was launched as per the recommendation of National Health Policy 2017 to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC). Under Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, citizens will be able to get their Ayushman Bharat health account number, which can be linked to their digital health records.
- Participation in ABDM is voluntary including for citizens. Participation of a healthcare facility or an institution is also voluntary and shall be taken by the respective management (government or private management). However, once the management decides to register the respective healthcare facility/institution in ABDM, it is essential for all the healthcare professionals serving the said facility/institution to register in Healthcare Professionals Registry so that the institution can become fully integrated with the National Digital Health Ecosystem (NDHE). Hence, both statements 1 and 2 are not correct.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission will have a national footprint and will enable seamless portability across the country through a Health ID – Personal Health Identifier, with supporting blocks, including adoption of Health Information Standards will play a pivotal role in national portability. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Q15: With reference to Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, consider the following statements:
- As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as the Speaker may fix.
- There is a mandatory provision that the election of a candidate as Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha shall be from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party.
- The Deputy Speaker has the same power as of the Speaker when presiding over the sitting of the House and no appeal lies against his rulings.
- The well established parliamentary practice regarding the appointment of Deputy Speaker is that the motion is moved by the Speaker and duly seconded by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- According to the rules of procedure and conduct of business in the Lok Sabha, “The election of the Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as may be decided by the Speaker. As per convention, the post of Deputy Speaker is given to the opposition party in India. Hence, option 1 is correct.
- Till the 10th Lok Sabha, both the Speaker and the Deputy Speaker were usually elected from the ruling party. Since the 11th Lok Sabha, it has been a general consensus that the post of Speaker is given to the ruling party/coalition and the post of Deputy Speaker is given to the main opposition party. Hence option 2 is correct.
- He is the final interpreter of the provisions of the Constitution of India, the rules of procedure and conduct of business of the Lok Sabha and parliamentary matters inside the House. In matters of interpretation of these provisions, it often gives decisions which are respected by the members and which are binding in nature. That is, his decision is final. Article 95 provides for the power of the Vice-Chairman or other person to perform the duties of the office of the Speaker or to act as the Speaker. Therefore, while presiding over the sitting of the House by the Deputy Speaker, his power is exactly the same as that of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha and no appeal can lie against his decisions. Hence option 3 is correct.
- The Deputy Speaker is elected by the Lok Sabha from among its members. After the election of the Speaker, the Deputy Speaker is also elected. Hence option 4 is not correct.
UPSC Prelims 2021:Polity
Q1: Under the Indian Constitution, concentration of wealth violates
(a)the Right to Equality
(b)the Directive Principles of State Policy
(c)the Right to Freedom
(d)the Concept of Welfare
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSPs) in Part IV of the Indian Constitution from Articles 36 to 51 are the ideals that are meant for promoting social and economic democracy. According to Articles 39, the State shall in particular, direct its policies towards securing:
- The ownership and control of material resources shall be organised in a manner to serve the common good. The State shall avoid concentration of wealth in a few hands, among others.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q2: What is the position of the Right to Property in India?
(a)Legal right available to citizens only
(b)Legal right available to any person
(c) Fundamental Right available to citizens only
(d)Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Initially, the Right to Property under Articles 31 and Article 19 (1)(f) was given the fundamental status in Indian Constitution. However, with the 44th Amendment Act, 1978, the Right to Property was omitted as a fundamental right and made a legal right under Article 300-A in Part XII of Indian Constitution.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q3: What was the exact constitutional status of India on 26th January, 1950?
(a)A Democratic Republic
(b)A Sovereign Democratic Republic
(c)A Sovereign Secular Democratic Republic
(d) A Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(b)
- The Constitutional status of India on 26th January, 1950 was a Sovereign Democratic Republic as the words- Socialist and Secular were added to the Preamble by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1976.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q4: Constitutional government means
(a)a representative government of a nation with federal structure
(b) a government whose Head enjoys nominal powers
(c) a government whose Head enjoys real powers
(d)a government limited by the terms of the Constitution
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Constitutional government is defined by the existence of a constitution, which may be a legal instrument or merely a set of fixed norms or principles generally accepted as the fundamental law of the polity that effectively controls the exercise of political power.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q5: Consider the following statements in respect of Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards:
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titles under the Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements are not correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c)1 and 3 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(d)
- Article 18(1) prohibits the State to confer titles on anybody whether a citizen or a non- citizen. Military and academic distinctions are, however, exempted from the prohibition. Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are not titles under the Article 18(1). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The Padma Awards were suspended during the years 1978, 1979 and 1993 to 1997. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The recommendations for Bharat Ratna are made by the Prime Minister to the President of India. The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of three in a particular year. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q6: With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b) 2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- In Judicial custody, an accused is in the custody of the concerned Magistrate and lodged in jail. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case may interrogate the suspect but with prior permission from the magistrate. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q7: With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
- State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither I nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Although some criminal statutes carry a right to an eventual parole hearing, typical laws do not absolutely guarantee parole itself. Authorities retain the discretion to deny parole to prisoners they deem dangerous. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The grant of parole is governed by rules made under Prison Act, 1894 and Prison Act, 1900. Many State governments have also formulated guidelines to facilitate decision- making to determine whether parole needs to be granted in a particular case or not. For example, the Rajasthan Prisoners Release on Parole Rules, 1958. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q8: At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006?
(a)Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
(b)Ministry of Panchayati Raj
(c) Ministry of Rural Development
(d) Ministry of Tribal Affairs
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(d)
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, also referred to as the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006, recognizes the rights of the forest-dwelling tribal communities and other traditional forest dwellers to forest resources.
- As per the provisions of the Act and the rules framed thereunder, various schemes and projects are implemented under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q9: A legislation that confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of the application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India?
(a)Article 14
(b)Article 28
(c)Article 32
(d)Article 44
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(a)
Article 14 (‘Equality Before Law’ and Equal Protection of Law)
- No person shall be denied treatment of equality before the law or the equal protection of the laws within the territory of India.
- Therefore, Article 14 acts as a shield against any arbitrary or discriminatory state action and the Court may declare a law ultra vires Article 14.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q10: Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character?
(a)The independence of judiciary is safeguarded.
(b)The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units.
(c) The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties.
(d)The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(a)
- Different sets of government with divided subjects of power and an independent judiciary are vital features of the federal system. Independent judiciary is a core feature of a federal system. The Indian Constitution has ensured the independence of the judiciary through a number of measures.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q11: Which one of the following best defines the term ‘State’?
(a)A community of persons permanently occupying a definite territory independent of external control and possessing an organized government
(b)A politically organized people of a definite territory and possessing an authority to govern them, maintain law and order, protect their natural rights and safeguard their means of sustenance
(c) A number of persons who have been living in a definite territory for a very long time with their own culture, tradition and government
(d)A society permanently living in a definite territory with a central authority, an executive responsible to the central authority and an independent judiciary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- A ‘State’ can be defined as a society of people politically organized within a definite territory, having its own government with the power to enforce obedience and which is free from external control.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q12: With reference to the Indian judiciary, consider the following statements:
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d)Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(c)
As per Article 128 of Indian Constitution, the Chief Justice of India may at any time, with the previous consent of the President, request any person to sit and act as a Judge of the Supreme Court with the following qualifications:
- Who has held the office of a Judge of the Supreme Court. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Being a Court of Record, the High Court can review its own judgments under Article
- 226 of the Constitution of India. Similarly, under Article 137, the Supreme Court shall have the power to review any judgment pronounced or order made by it. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q13: With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- There is only one citizenship and one domicile.
- A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State.
- A foreigner once granted citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)1 and 3
(d) 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The term ‘Domicile’ means a permanent home. A person cannot have more than one domicile. According to the Article 9 of Indian Constitution, if any person voluntarily acquired the citizenship of a foreign State will no longer be a citizen of India. So In India, there is single citizenship and one domicile. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Article 58 signifies nowhere that citizenship should be by birth or naturalization. Similarly, to become a Prime Minister (Head of Government) one has to be: a citizen of India (irrespective of by birth or naturalization) and a member of either Rajya Sabha or Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The Provisions related to the termination of Citizenship are also mentioned in the Indian Citizenship Act, 1955. Under Section (10) of this Act, the Central Government of India may terminate the citizenship of an Indian citizen if;
- The citizen has disrespected the Constitution. Has obtained citizenship by fraud.
- The citizen has unlawfully traded or communicated with the enemy during a war.
- Within 5 years of registration or naturalisation, a citizen has been sentenced to 2 years of imprisonment in any country.
- The citizen has been living outside India for 7 years continuously except for purposes other than educational or in service of a government or international organization of which India is a member or he has not registered annually at an Indian consulate expressing his intention to retain his citizenship. Hence, statement 3 is not correct. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q14: Which one of the following factors constitutes the best safeguard of liberty in a liberal democracy?
(a)A committed judiciary
(b)Centralization of powers
(c)Elected government
(d)Separation of powers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(d)
Liberal democracy is a representative form of government that operates under the following principles:
- Elections between multiple distinct political parties,
- Separation of powers into different branches of government, Rule of law protected by an independent judiciary, and
- Equal protection of human rights, civil rights, civil liberties and political freedoms
- for all people.
- The Separation of powers between the branches of government constitute an important safeguard of liberty in a liberal democracy.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q15: We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model?
- As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the Parliament to legislate is limited.
- In India, matters related to the constitutionality of Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- In India there is no Parliament sovereignty rather there is constitutional sovereignty and the authority and jurisdiction of Parliament are limited. The Judiciary can declare any law or ordinance passed by the legislature void, if any of its provisions violate one or more of the constitutional provisions. Hence, 1 is correct.
- The case involves a substantial question of law pertaining to the interpretation of the Constitution under Article 145(3) of the Constitution, which mandates that such matters be heard by a bench of not less than five judges]. Hence, 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q16: With reference to the Union Government, consider the following statements:
- N. Gopalaswamy Iyengar Committee suggested that a minister and a secretary be designated solely for pursuing the subject of administrative reform and promoting it.
- In 1970, the Department of Personnel was constituted on the recommendation of the Administrative Reforms Commission, 1966, and this was placed under the Prime Minister’s charge.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b)2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d)Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Gopalaswamy Iyengar Committee submitted a ‘Report on Reorganisation of the Machinery of Government’ in 1950. This report has not mentioned setting up a minister and a secretary for administrative reforms. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Constituted in 1966, the first Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) presented a report on Personnel Administration in 1969. The ARC suggested setting up a separate Department of Personnel, to be directly under the control of the Prime Minister. The DoPT was established in 1970 following this report and works under the Ministry Of Personnel, Public Grievances And Pensions. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q17: ‘Right to Privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India?
(a)Article 15
(b) Article 19
(c)Article 21
(d)Article 29
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(c)
- Right to Privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of the Right to Life and Personal Liberty under Article 21 and as a part of the freedoms guaranteed by Part III of the Indian Constitution.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q18: Consider the following statements:
- In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies.
- In the 1991 Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies.
- As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her winning in all the constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)1 and 3
(d)2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:(b)
- In 1996, the Representation of the People Act, 1951 was amended to restrict from ‘three’ to ‘two’ the number of seats one candidate could contest in Lok Sabha and Assembly elections. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- In 1991, Shri Devi Lal contested three Lok Sabha seats, Sikar, Rohtak and Ferozepur seats. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Whenever a candidate contests from more than one seat and wins more than one, the
- candidate has to retain only one, forcing by polls in the rest. It results in an unavoidable financial burden on the public exchequer, government manpower and other resources for holding by-election against the resultant vacancy. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
UPSC Prelims 2020:Polity
Q.1. A parliamentary system of government is one which
(a) All political parties in the parliament are represented in the government
(b) The government is responsible to the Parliament and can be removed by it
(c) The government is elected by the people and can be removed by them
(d) The government is chosen by the parliament but can not be removed by it before completion of a fixed term
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(b)
Solution:This is obvious since people don’t remove the government (option C), it is the Parliament that can remove the government.
Q.2. Which part of the constitution of India declares the ideals of welfare state?
(a) Directive Principles of State policy
(b) Fundamental Rights
(c) Preamble
(d) Seventh schedule
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (a)
Solution: Straightforward.
Q.3.Consider the following statements
1. The constitution of India defines its basic structure in terms of federalism, secularism, fundamental rights, and democracy
2. The constitution of India provides for the ‘judicial review’ to safeguard the citizen’s liberties and to preserve the ideals on which the constitution is based.
Which of the above-given statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (b)
Solution: S1: The Supreme Court has defined the Basic structure, not the Constitution, so S1 is wrong.
S2:Straightforward
Q.4. One common agreement between Gandhism and Marxism is
(a) The final goal of a stateless society
(b) Class struggle
(c) Abolition of private property
(d) Economic determinism
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(a)
Solution:Quoting from the source below, “When Marx spoke of the stateless communist society of the future, he did believe that it was a historical necessity and did not, therefore, depend on the ethical goodness of this individual or that, of this class or that. Somewhat similarly, when Gandhi speaks of Rama Rajya, a social order free from political bindings and consisting of self-governing individuals, he was really convinced that this is a destiny which mankind in its quest for perfection has been aiming at all the time.”
Q.5. In the context of India which one of the following is the characteristic appropriate for Bureaucracy?
(a) An agency for widening the scope for parliamentary democracy
(b) An agency for strengthening the structure of federalism
(c) An agency for facilitating the political stability and economic growth
(d) An agency for the implementation of public policy
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Q.6. The preamble to the constitution of India is
(a) A part of the constitution but has no legal effect
(b) Not a part of the constitution and has no legal effect either
(c) A part of the constitution and has the same legal effect as any other part
(d) A part of the constitution but has no legal effect independently of other parts.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (d)
Solution:It is a part of the Constitution as declared by the SC. It certainly does not have a legal effect independently since it cannot be enforced in a court of law. Although not enforceable in court on its own (option C is wrong), the Preamble states the objects of the Constitution and acts as an aid during the interpretation of Articles when language is found ambiguous. Therefore, it begets some kind of legal effect when read along with the constitution, not independent from it. Option D is more appropriate.
Q.7. With reference to the provisions contained in part IV of the Constitution of India, Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. They shall be enforceable by the courts
2. They shall not be enforceable by any courts
3. The principles laid down in this part are to influence the making of laws by the state.
Select the correct answer using the given code below-
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Q.8.Consider the following statements
1. According to Constitution of India, A person who eligible to vote can be made a minister in a state for six months even if he/she is not a member of the legislature of that state
2. According to the representation of people act, 1951, a person convicted of a criminal offense and sentenced to imprisonment for at least five years is permanently disqualified from contesting an election even after his release from prison.
Which of the above-given statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (a)
Solution: S1: Not quite technically true, since one who is eligible to vote isn’t necessarily eligible to be a Minister (e.g. on grounds of age). But, since UPSC has used the term a voter “can” and not “every voter”, S1 is correct since many voters who meet the eligibility to be a Member of Parliament can be made a Minister.
For e.g. here are few correct and incorrect statements:
Correct: A voter CAN become a minister for six months. CORRECT: A voter eligible to become a Member of Parliament CAN become a minister for six months.
Correct: Every voter that is eligible to become a Member of Parliament CAN become a minister for six months. The first statement is only part of a larger correct statement, still true.
Incorrect: EVERY voter can become a minister for six months.
S2: Specifically, Section 8 of RPA, 1951 states the grounds for disqualification on conviction of certain offences pursuant to Section 8 of RPA, 1951, in case the candidate is convicted of certain offences specified under sub-section (1) (2) (3) of Sec. 8 and sentenced to indicated fine or imprisonment, then such a candidate is disqualified from being a member of either house of Parliament or State Legislature from the date of such conviction till the stated time. This is not permanent, so S2 is wrong.
Q.9. Consider the following statements:
1. The president of India can summon a session of parliament at such a place as he/she thinks fit.
2. The constitution of India provides for three sessions of the parliament in a year but it is not mandatory to conduct all the sessions
3. There is no minimum number of days that the parliament is required to meet in a year
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(c)
Solution: S1 and S2: Article 85(1) of the Constitution empowers the President to summon each House of Parliament to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit, but six months shall not intervene between its last sitting in one session and the date appointed for its first sitting in the next Session.
S3: This is correct, refer to the explanation above.
Q.10. Rajyasabha has equal power with Loksabha in
(a) The matter of creating new all India services
(b) Amending the constitution
(c) The removal of the government
(d) Making cut motions
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (b)
Q.11. Which of the following categories of Fundamental Rights Incorporates protection against untouchability as a form of discrimination?
(a) Right against exploitation
(b) Right to freedom
(c) Right to Constitutional remedies
(d) Right to equality
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Q.12. In India, separation of judiciary from executive is enjoined by
(a) The preamble of the constitution
(b) The directive principles of state policy
(c) The seventh schedule
(d) The conventional practice
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(b)
Q.13. Along with the budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the parliament which include “The Macro-Economic Framework Statement” The aforesaid document is presented because this mandated by
(a) Long-standing parliamentary convention
(b) Article 112 and Article 110(1) of the constitution of India
(c) Article 114 of the Constitution of India
(d) Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Q.14. A constitutional government by definition is a
(a) Government by legislature
(b) Popular government
(c) Multi-party government
(d) Limited government
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Solution:A constitutional government may not have a legislature, could be a bi-party government and need not be a popular government, and can instead be a monarchy. All except D are incorrect.
Q.15.Other than the fundamental rights, Which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflect the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of human rights(1948)?
1. Preamble
2. Directive principles of state policy
3. Fundamental duties
Select the correct answer using the given code below-
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(d)
Solution:If you overread the question, you might exclude S3 from the answer, but this will be incorrect.
S1: e.g. from UDHR: Article 3. Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person.
S2:eg. Article 22 UDHR: Everyone, as a member of society, has the right to social security and is entitled to realization, through national effort and international co-operation and in accordance with the organization and resources of each State, of the economic, social and cultural rights indispensable for his dignity and the free development of his personality. Or, Article 26:
(1) Everyone has the right to education. Education shall be free, at least in the elementary and fundamental stages. Elementary education shall be compulsory. Technical and professional education shall be made generally available and higher education shall be equally accessible to all on the basis of merit.
S3:e.g. Article 27 of UDHR:
(1) Everyone has the right freely to participate in the cultural life of the community, to enjoy the arts, and to share in scientific advancement and its benefits.
(2) Everyone has the right to the protection of the moral and material interests resulting from any scientific, literary, or artistic production of which he is the author.
Q.16. In India, legal service authorities provide free legal services to which of the following type of citizens?
1. Person with an annual income of less than Rs 1,00,000
2. Transgender with an annual income of less than Rs2,00,000
3. Member of other backward classes(OBC) with an annual income of less than Rs 3,00,000
4. All senior citizens
Select the correct answer using the given code below-
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans.(a)
Solution: S1 and S3: The sections of the society as enlisted under Section 12 of the Legal Services Authorities Act are entitled to free legal services, they are :
(a) A member of a Scheduled Caste or Scheduled Tribe;
(b) A victim of trafficking in human beings or begar as referred to in Article 23 of the Constitution;
(c) A woman or a child;
(d) A mentally ill or otherwise disabled person;
(e) A person under circumstances of undeserved want such as being a victim of a mass disaster, ethnic violence, caste atrocity, flood, drought, earthquake or industrial disaster; or (f) An industrial workman; or
(g) In custody, including custody in a protective home within the meaning of clause (g) of Section 2 of the Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956(104 of 1956); or in a juvenile home within the meaning of clause(j) of Section 2 of the Juvenile Justice Act, 1986 (53 of 1986); or in a psychiatric hospital or psychiatric nursing home within the meaning of clause (g) of Section 2 of the Mental Health Act, 1987(14 of 1987); or
(h) a person in receipt of annual income less than the amount mentioned in the following schedule (or any other higher amount as may be prescribed by the State Government), if the case is before a Court other than the Supreme Court, and less than Rs 5 Lakh, if the case is before the Supreme Court.
S2: Limit for Transgender – Rs. 2,00,000
S4:Senior citizens’ eligibility for free legal aid depends on the Rules framed by the respective State Governments in this regard. In Delhi for example, senior citizens are eligible for free legal aid subject to a prescribed ceiling of annual income. Any individual above the age of 60 can apply for free legal aid/services.
FAQs on Previous Year Questions (PYQs): Indian Polity - UPSC
| 1. What are the fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution of India? |  |
| 2. How does the Indian parliamentary system differ from the presidential system? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What is the procedure for amending the Constitution of India? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the President of India in the legislative process? |  |




















