Sea Floor Spreading | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Seafloor Spreading Theory
- H. Harry Hess put forward the hypothesis of seafloor spreading in 1960. This was a new development that again proved the theory of continental drift.
- In this article series, we learn about the theories that explain the present distribution of oceans and continents. These concepts explain the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes, folds and faults.
- In the previous article, we have learned about the Continental Drift Theory given by Alfred Wegener. Although Wegener is right in stating that the continents drift over time, his assumption that the continents were blocks of rock that slid across the ocean floor was incorrect.
- We know today that the continents and ocean floor are part of the same layer of the earth.
- We will learn about Sea Floor Spreading, which explains continental drift with the help of plate tectonics theory. Before coming directly into the concept of Sea Floor Spreading, we must understand some basic concepts that explain Sea Floor Spreading.
These concepts are Ocean Floor Mapping, Distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes, Convectional Current theory and Paleomagnetism.
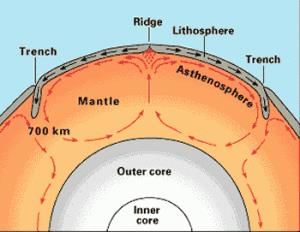
Convection Current Theory
- Convection Current Theory is the soul of the Seafloor Spreading Theory.
- Arthur Holmes in the 1930s discussed the possibility of convection currents in the mantle.
- These currents are generated due to radioactive elements causing thermal differences in the mantle.
- According to this theory, the intense heat generated by radioactive substances in the mantle (100-2900 km below the earth’s surface) seeks a path to escape and gives rise to the formation of convection currents in the mantle.
- Wherever rising limbs of these currents meet, oceanic ridges are formed on the seafloor due to the lithospheric plates' divergence (tectonic plates). Wherever the failing limbs meet, trenches are formed due to the lithospheric plates' convergence (tectonic plates).Question for Sea Floor SpreadingTry yourself:Who proposed the theory of Continental Drift?View Solution
- The movement of the lithospheric plates is caused by the movement of the magma in the mantle.
Palaeomagnetism
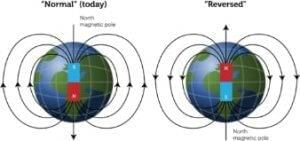
- Palaeomagnetism is studying the record of the earth’s magnetic field with magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archaeological materials.
- The polarity of the Earth’s magnetic field and magnetic field reversals are thus detectable by studying different ages' rocks.
- Rocks formed from underwater volcanic activity are mainly basaltic (low silica, iron-rich), making up most of the ocean floor.
- Basalt contains magnetic minerals, and as the rock is solidifying, these minerals align themselves in the direction of the magnetic field.
- This locks in a record of which way the magnetic field was positioned at the time.
- Paleomagnetic studies of rocks have demonstrated that the earth’s magnetic field's orientation has frequently alternated (geomagnetic reversal) over geologic time.
- Palaeomagnetism led the revival of the continental drift hypothesis and its transformation into Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics theories.
- The regions that hold the unique record of earth’s magnetic field lie along the mid-ocean ridges where the seafloor is spreading.
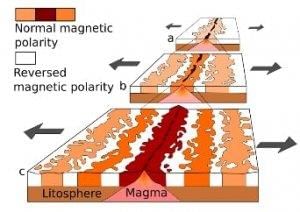
- On studying the paleomagnetic rocks on either side of the oceanic ridges, it is found that alternate magnetic rock stripes were flipped so that one stripe would be of normal polarity and the next, reversed.
- Hence, paleomagnetic rocks (paleo: denoting rocks) on either side of the mid-ocean or submarine ridges provide the most important evidence to the concept of Sea Floor Spreading.
- Magnetic field records also provide information on the past location of tectonic plates.
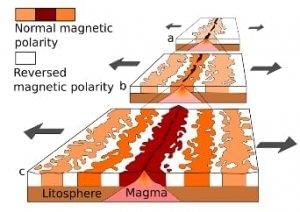
- These oceanic ridges are boundaries where tectonic plates are diverging (moving apart).
- The fissure or vent (in between the ridge) between the plates allowed the magma to rise and harden into a long narrow band of rock on either side of the vent.
- Rising magma assumes the polarity of Earth’s geomagnetic field at the time before it solidifies on the oceanic crust.
- As the conventional currents pull the oceanic plates apart, the solidified rock band moves away from the vent (or ridge), and a new band of rock takes its place a few million years later when the magnetic field was reversed. This results in this magnetic striping where the adjacent rock bands have opposite polarities.
- This process repeatedly repeats, giving rise to a series of narrow parallel rock bands on either side of the ridge and alternating magnetic striping pattern on the seafloor.
Sea Floor Spreading theory
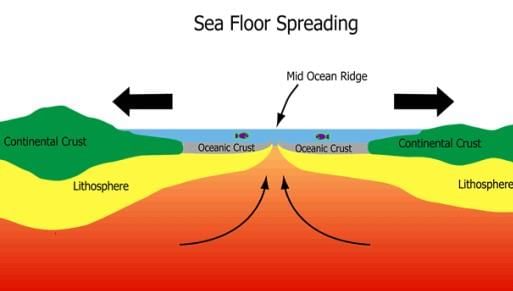
- Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
- The idea that the seafloor itself moves (and carries the continents with it) expands from a central axis proposed by Harry Hess.
- According to this theory, the intense heat generated by radioactive substances in the mantle (100-2900 km below the earth’s surface) seeks a path to escape and gives rise to the formation of convection currents in the mantle.
- Wherever rising limbs of these currents meet, oceanic ridges are formed on the seafloor and, wherever the failing limbs meet, trenches are formed.
- Adds new material to the ocean floor while pushing older rocks away from the ridge.
- New ocean floor forms along cracks in the ocean crust as molten material erupt from the mantle spreading out and pushing older rocks to the sides of the crack.
- The new ocean floor is continually added by the process of sea-floor spreading.
Mid-Ocean Ridge – the longest chain of mountains in the world—these are divergent plate boundaries.
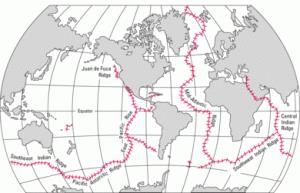
Evidence for Seafloor Spreading
- Evidence from Molten Material
- Evidence from Magnetic Stripes
- Evidence from Drilling Samples
- Subduction
- Deep-Ocean Trench
Evidence from Molten Material – Rocks shaped like pillows(rock pillows) show that molten material has erupted again and again from cracks along the mid-ocean ridge and cooled quickly.
Evidence from Magnetic Stripes – Rocks that make up the ocean floor lies in a pattern of magnetising stripes that hold a record of the reversals in Earth’s magnetic field.
Evidence from Drilling Samples – Core samples from the ocean floor show that older rocks are found farther from the ridge; the youngest rocks are in the ridge's centre.
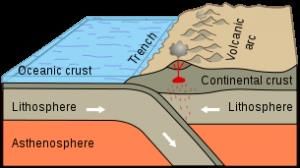
Subduction – Process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle; allows part of the ocean floor to sink back into the mantle.
Deep-Ocean Trench – This occurs at subduction zones. Deep underwater canyons form where oceanic crust bends downward.
Distribution of Earthquakes and Volcanoes along the mid-ocean ridges
- The average temperature gradient on the seafloor is 9.4° C/300 m, but near the ridges, it increases, indicating an upwelling of magmatic material from the mantle.
- Dots in the central parts of the Atlantic Ocean and other oceans are almost parallel to the coastlines. This indicates that the seafloor has widened with time.
- In general, the foci of the earthquake in mid-oceanic ridges are at shallow depths whereas, along the Alpine-Himalayan belt and the rim of the Pacific, the tremors are deep-seated ones.
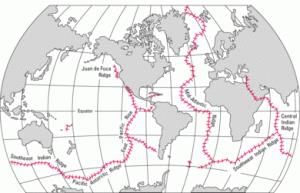
Seafloor spreading solved many of the unsolved problems.
- It solved the younger age crust found at the mid-oceanic ridges and older rocks being discovered as we go away from the middle part of the ridges.
- It also explained why the sediments at the central parts of the oceanic ridges are relatively thin.
- The sea-floor spreading also proved the drifting of continents as propounded by Alfred Wegener and helped develop the theory of plate tectonics.
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Sea Floor Spreading - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the seafloor spreading theory? |  |
| 2. How does the convection current theory relate to seafloor spreading? |  |
| 3. What is paleomagnetism and how does it support the theory of seafloor spreading? |  |
| 4. How does the seafloor spreading theory explain the formation of oceanic trenches? |  |
| 5. Can seafloor spreading occur on land or only in the oceanic realm? |  |






















