Ocean Relief Features | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Major and Minor Ocean Relief Features |

|
| Ocean |

|
| Ocean Relief Features |

|
| Continental Shelf |

|
| Significance of the Study of Oceanic Relief |

|
Major and Minor Ocean Relief Features
The Ocean Relief Features are quite different from the continental features because the Oceanic crust is less than 60-70- million years old. In contrast, continental features are of Proterozoic age (Over 1 Billion years old).
Ocean
While there is only one global ocean, the vast body of water, covering 71 percent of the Earth is geographically divided into distinct named regions. The boundaries between these regions have evolved for various historical, cultural, geographical, and scientific reasons.
Historically, there are four named oceans: the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic. However, a new ocean has now been recognized as the Southern (Antarctic) as the fifth ocean. The Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian are known as the three major oceans.
- They are the food source– fish, mammals, reptiles, salt, and other marine foodstuffs.
- The tides can be harnessed to provide power.
- Oceanography is the branch of science that deals with the sea's physical and biological properties and phenomena.
- Earlier echo-sounding techniques were used, now radar soundings and electrical Echo devices are used to find the precise depths of ocean floors and map the relief of oceans.
Ocean Relief Features
Unlike the continents, the oceans merge so naturally into one another that it is hard to demarcate them. The geographers have divided the oceanic part of the earth into five oceans, namely the Pacific, the Atlantic, the Indian, Southern, and the Arctic. The various seas, bays, gulfs, and other inlets are parts of these four large oceans.
A major portion of the ocean floor is found between 3-6 km below the sea level. The ‘land’ under the oceans' waters, that is, the ocean floor exhibits complex and varied features as those observed over the land.
The oceans' floors are rugged with the world’s largest mountain ranges, deepest trenches, and the largest plains. Like those of the continents, these features are formed by the factors of tectonic, volcanic, and depositional processes.
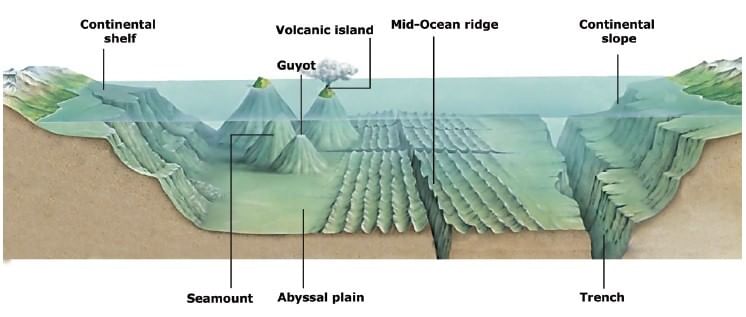
Major Ocean Relief Features
The ocean floors can be divided into four major divisions:
- The Continental Shelf
- The Continental Slope
- The Deep Sea Plain
- The Oceanic Deeps
Besides, these divisions there are also major and minor relief features in the ocean floors like ridges, hills, seamounts, guyots, trenches, canyons, etc.
Continental Shelf
The continental shelf is the extended margin of each continent occupied by relatively shallow seas and gulfs. It is the shallowest part of the ocean showing an average gradient of 1° or even less.
- The shelf typically ends at a very steep slope, called the shelf break.
- The width of the continental shelves varies from one ocean to another. The average width of continental shelves is about 80 km.
- The shelves are almost absent or very narrow along some of the margins like the coasts of Chile, the west coast of Sumatra, etc. On the contrary, the Siberian shelf in the Arctic Ocean, the largest globally, stretches to 1,500 km in width.
- The depth of the shelves also varies. It may be as shallow as 30 m in some areas while it is as deep as 600 m.
- The continental shelves are covered with variable thicknesses of sediments brought down by rivers, glaciers, wind, land, and distributed by waves and currents. Massive sedimentary deposits received over a long time by the continent shelves become the source of fossil fuels.
- There are 3 views on the continental shelf:
- They can be part of the continent submerged due to the rise in sea level.
- Some smaller continental shelves could have been caused by wave erosion.
- They may have been formed by the deposition of lands derived or river-borne materials on the off-shore terrace.
➤ Continental shelf geographical significance
Their shallowness enables sunlight to penetrate through the water, which encourages plants and organisms → now rich in plankton → fishes to thrive on them → . Hence, continental shelves are the richest fishing grounds.
- Example: Grand banks off Newfoundland, the North Sea, and the Sunda shelf.
- Their limited depth and gentle slope keep out cold under-currents and increase the height of the tide. This sometimes hinders shipping and other marine activities since ships can only enter and leave port on the tide.
- Ports like Southampton, London, Hamburg, Rotterdam, Hong Kong, and Singapore are located on continental shelves.
- Marine food comes almost entirely from continental shelves;
- They provide the richest fishing grounds;
- They are potential sites for economic minerals [20% of petroleum and gas production comes from shelves. Polymetallic nodules (manganese nodules; concentric layers of iron and manganese hydroxides) etc. are good sources of various mineral ores like manganese, iron copper, gold, etc.]
Continental Slope
- The continental slope connects the continental shelf and the ocean basins. It begins where the bottom of the continental shelf sharply drops off into a steep slope.
- The gradient of the slope region varies between 2-5°.
- The depth of the slope region varies between 200 and 3,000 m.
- The slope boundary indicates the end of the continents.
- Canyons and trenches are observed in this region.
Continental Rise
- The continental slope gradually loses its steepness with depth.
- When the slope reaches a level of between 0.5° and 1°, it is referred to as the continental rise.
- With increasing depth, the rise becomes virtually flat and merges with the abyssal plain.
Deep-Sea Plain or Abyssal Plain
- An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor.
- Found at depths – between 3,000 meters and 6,000 meters.
- Lying between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface.
- It has extensive submarine plateaus, ridges, trenches, beams, and oceanic islands that rise above sea level in the midst of oceans.
- Example: the Azores, Ascension Island
These plains are covered with fine-grained sediments like clay and silt.
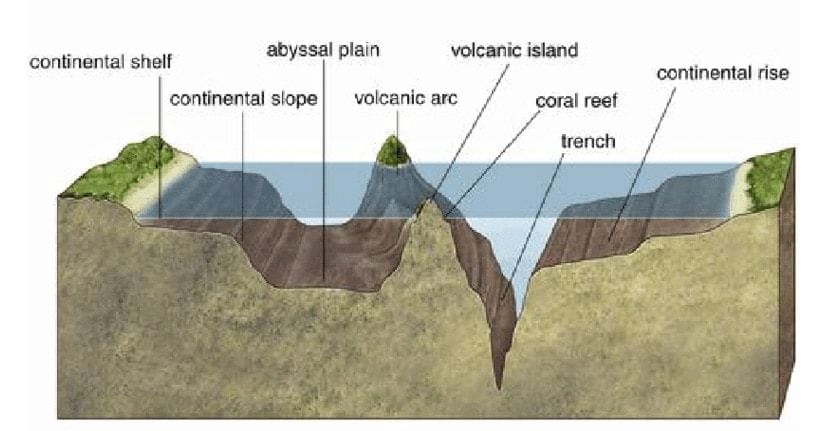
Oceanic Deeps or Trenches
Ocean trenches are steep depressions in the ocean's deepest parts [where old ocean crust from one tectonic plate is pushed beneath another plate, raising mountains, causing earthquakes, and forming volcanoes on the seafloor and land].
- The trenches are relatively steep-sided, narrow basins (Depressions). These areas are the deepest parts of the oceans.
- They are of tectonic origin and are formed during ocean – ocean convergence and ocean-continent convergence.
- They are some 3-5 km deeper than the surrounding ocean floor.
- The trenches lie along the deep-sea plain fringes at the bases of continental slopes and along island arcs.
- The trenches run parallel to the bordering fold mountains or the island chains.
- The trenches are very common in the Pacific Ocean and form an almost continuous ring along the Pacific's western and eastern margins.
- The Mariana Trench off the Guam Islands in the Pacific Ocean is the deepest trench with more than 11 kilometres.
- Other ocean deeps –
- Mindanao deep (35000 feet)
- Tonga trench (31000 feet)
- Japanese trench (28000 feet) (all 3 in the Pacific Ocean)
- They are associated with active volcanoes and strong earthquakes (Deep Focus Earthquakes like in Japan). This makes them very significant in the study of plate movements.
- As many as 57 deeps have been explored so far, 32 are in the Pacific Ocean; 19 in the Atlantic Ocean and 6 in the Indian Ocean.Question for Ocean Relief FeaturesTry yourself:The formation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a typical example of the process of
1. Convergence
2. Divergence
3. Shear
4. Sea floor spreading
Select the correct answer from the following Codes:
View Solution
➤ The Oceanic deposits of the ocean floor
We have read that rivers erode and deposit some materials in flood plains and drop sediments like sand, silt in the sea. Slow sedimentation – in this process, eroded particles are filtered slowly and settled on one another in layers. Oceanic deposits can be classified on a different basis:
Based on Origin:
- Terrigenous deposits: These are the deposits that originated on the terrestrial surfaces and were transported to oceans through wind and water. They contain both organic and inorganic matter. The thickness of terrigenous deposits is highest on the continental shelf and slope.
- Hydrogenous deposits: They originate in water. They include both organic and inorganic particles. Most of the organic materials are derived from dead plants and animals. Inorganic particles contain precipitated salts.
- Cosmic deposits: They are extra-terrestrial. They are less than 1% of total deposits and uniformly distributed on the abyssal plain. Some of them are thin glassy particles called tektites.
The oozes- The biological deposits of oceans are called Oozes.
- Pelagic deposits – fine-grained sediment that accumulates due to the settling of particles to the floor of the open ocean, far from land.
- Made of – shelly and skeletal remains of marine organism
- They have a very fine, flour-like texture and occur as accumulated deposits or float about in suspension.
- They can be of two types –
- Calcareous Oozes – They have a high quantity of calcium. They are found up to the depth of 2500m.
- Silicious Oozes – They have a high quantity of silicon and found beyond 2500 m.
The clays
- They are one of the finest deposits found on the ocean floor.
- Occur as red clay in the deep oceanic basin. (abundant in the Pacific Ocean)
- These are believed as volcanic dust blown out from volcanoes during volcanic eruptions.
Minor Ocean Relief Features
Apart from the above mentioned major relief features of the ocean floor, some minor but significant features predominate in different parts of the oceans.
- Ridges,
- Hills,
- Seamounts,
- Guyots,
- Trenches,
- Canyons,
- Fracture zones,
- Island arcs,
- Atolls,
- Coral reefs,
- Submerged volcanoes and
- Sea-scarps.
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
A mid-oceanic ridge is composed of two chains of mountains separated by a large depression. The mountain ranges can have peaks as high as 2,500 m, and some even reach above the ocean’s surface. Iceland, a part of the Mid- Atlantic Ridge, is an example.
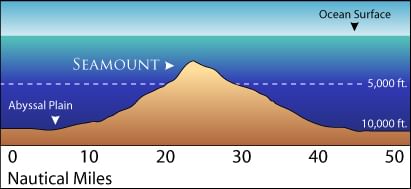
Seamount
It is a mountain with pointed summits, rising from the seafloor that does not reach the ocean's surface. Seamounts are volcanic in origin. These can be 3,000-4,500 m tall. Emperor seamount, an extension of the Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean, is a good example.
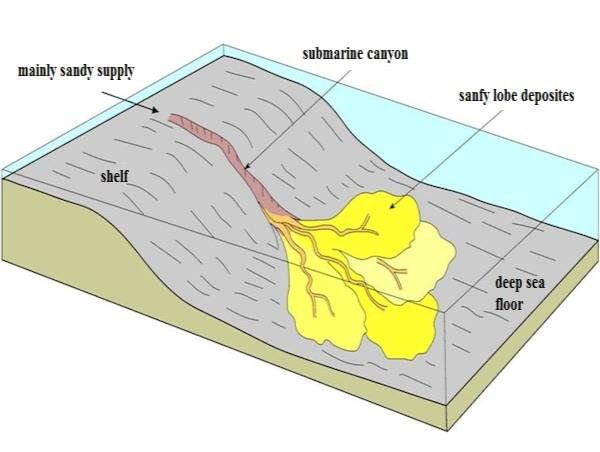
Submarine Canyons
These are deep valleys, some comparable to the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. They are sometimes found cutting across the continental shelves and slopes, often extending from large rivers' mouths. The Hudson Canyon is the best-known submarine canyon in the world.
Guyots
It is a flat-topped seamount. They show evidence of gradual subsidence through stages to become flat-topped submerged mountains. It is estimated that more than 10,000 seamounts and guyots exist in the Pacific Ocean alone.

Atoll
These are low islands found in the tropical oceans consisting of coral reefs surrounding a central depression. It may be a part of the sea (lagoon), or sometimes form enclosing a body of fresh, brackish, or highly saline water.

Bank
- These marine features are formed as’ a result of the erosional and depositional activity.
- A bank is a flat-topped elevation located in the continental margins.
- The depth of water here is shallow but enough for navigational purposes.
- The Dogger Bank in the North Sea and Grand Banks in the north-western Atlantic, Newfoundland are famous examples.
- The banks are sites of some of the most productive fisheries of the world.
Shoal
A shoal is a detached elevation with shallow depths. Since they project out of the water with moderate heights, they are dangerous for navigation.
Reef
- A reef is a predominantly organic deposit made by living or dead organisms that form a mound or rocky elevation like a ridge.
- Coral reefs are a characteristic feature of the Pacific Ocean where they are associated with seamounts and guyots.
- The largest reef in the world is found off the Queensland coast of Australia. [We will study coral reefs in future posts]
- Since the reefs may extend above the surface, they are generally dangerous for navigation.
Significance of the Study of Oceanic Relief
- Ocean relief controls the motion of sea-water.
- The oceanic movement in the form of currents, in turn, causes many variations in both oceans and the atmosphere.
- The bottom relief of oceans also influences navigation and fishing.
|
263 videos|875 docs|232 tests
|
FAQs on Ocean Relief Features - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are some examples of major ocean relief features? |  |
| 2. Can you explain the significance of studying oceanic relief? |  |
| 3. What is the continental shelf? |  |
| 4. How are abyssal plains formed? |  |
| 5. What causes ocean trenches to form? |  |
















