El Nino, La Nina , ENSO | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
El Nino and La Niña are opposite phases known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. The ENSO is a recurring climatic pattern involving temperature changes in the eastern and central tropical Pacific Ocean's waters. It changes in the patterns of upper and lower-level winds, sea-level pressure, and tropical rainfall across the Pacific Basin.
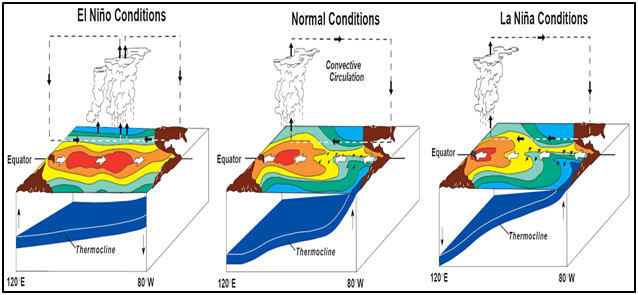
El Nino is often called the warm phase, and La Nina is called the cold phase of ENSO. These deviations from the normal surface temperatures can have a large-scale impact on the global weather conditions and overall climate.
El Nino
The phrase “El Niño” referred to the Christ Child and was coined by fishermen along the coasts of Ecuador and Peru to describe the warming of the central and eastern Pacific.
- El Niño is the name given to the occasional development of warm ocean surface waters and Ecuador and Peru's coast. El Niño events occur irregularly at intervals of 2–7 years, although the average is about once every 3-4 years.
- When this warming occurs the usual upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich deep ocean water is significantly reduced.
- El Niño normally occurs around Christmas and usually lasts for a few weeks to a few months.
- Sometimes an extremely warm event can develop that lasts for much longer time periods. In the 1990s, strong El Niños developed in 1991 and lasted until 1995, and from fall 1997 to spring 1998.
Normal Conditions
- In a normal year, a surface low pressure develops in northern Australia and Indonesia and a high-pressure system over the coast of Peru. As a result, the trade winds over the Pacific Ocean move strongly from east to west.
- The easterly flow of the trade winds carries warm surface waters westward, bringing convective storms (thunderstorms) to Indonesia and coastal Australia. Along the coast of Peru, cold bottom nutrient-rich water wells up to the surface to replace the warm water pulled to the west.
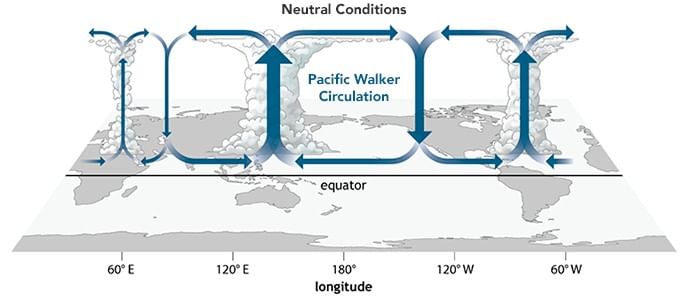
Walker circulation (Occurs during Normal Years)
- The Walker circulation (walker cell) is caused by the pressure gradient force that results from a high-pressure system over the eastern Pacific Ocean, and a low-pressure system over Indonesia.
This cross-section of the Pacific Ocean, along the equator, illustrates atmospheric circulation pattern typically found at the equatorial Pacific. Note the position of the thermocline.
- Thermocline == noun is a temperature gradient in a lake or other water body, separating layers at different temperatures.
- The Walker cell is indirectly related to upwelling off the coasts of Peru and Ecuador. This brings nutrient-rich cold water to the surface, increasing fishing stocks.
During El Nino year
- In an El Niño year, air pressure drops over large areas of the central Pacific and South America.
- The normal low-pressure system is replaced by a weak high in the western Pacific (the southern oscillation). This change in pressure pattern causes the trade winds to be reduced = Weak Walker Cell. Sometimes Walker Cell might even get reversed.
- This reduction allows the equatorial counter-current (current and doldrums) to accumulate warm ocean water and Peru and Ecuador's coastlines.
- This accumulation of warm water causes the thermocline to drop in the eastern part of the Pacific Ocean, which cuts off the upwelling of cold deep ocean water along the coast of Peru.
- Climatically, the development of an El Niño brings drought to the western Pacific, rains to the equatorial coast of South America, and convective storms and hurricanes to the central Pacific.
Effects of El Nino
- The warmer waters had a devastating effect on marine life existing off the coast of Peru and Ecuador.
- Fish catches off South America's coast were lower than in the normal year (Because there is no upwelling).
- Severe droughts occur in Australia, Indonesia, India, and southern Africa.
- Heavy rains in California, Ecuador, and the Gulf of Mexico.
How El Nino impacts monsoon rainfall in India
- El Nino and Indian monsoons are inversely related.
- The most prominent droughts in India – six of them – since 1871 have been El Nino droughts, including the recent ones in 2002 and 2009
- However, not all El Nino years led to a drought in India. For instance, 1997/98 was a strong El Nino year, but there was no drought (Because of IOD).
- On the other hand, a moderate El Nino in 2002 resulted in one of the worst droughts.
- El Nino directly impacts India’s agrarian economy as it tends to lower the production of summer crops such as rice, sugarcane, cotton, and oilseeds.
- The ultimate impact is seen in high inflation, and low gross domestic product growth as agriculture contributes around 14 per cent of the Indian economy.
El Nino Southern Oscillation [ENSO]
- The formation of an El Niño [Circulation of Water] is linked with Pacific Ocean circulation pattern known as the southern oscillation [circulation of atmospheric pressure]
- In oceanography and climatology, Southern Oscillation is a coherent inter-annual fluctuation of atmospheric pressure over the tropical Indo-Pacific region.
- El Nino and Southern Oscillation coincide most of the time; hence, their combination is called ENSO – El Nino Southern Oscillation.
Only El Nino = [Warm water in Eastern Pacific + Coldwater in Western Pacific].
Only SO = [Low Pressure over Eastern Pacific + High Pressure over Western Pacific]
ENSO = [Warm water in Eastern Pacific + Low Pressure over Eastern Pacific] + [Cold water in Western Pacific + High Pressure over Western Pacific].
Southern Oscillation Index and Indian Monsoons
- SO is a see-saw pattern of meteorological changes observed between the Eastern Pacific and Western Pacific.
- When the pressure was high over the equatorial Eastern Pacific, it was low over the equatorial Western Pacific and vice versa.
- The pattern of low and high pressures gives rise to vertical circulation along the equator with its rising limb over the low-pressure area and descending limb over the high-pressure area. This is known as Walker Circulation.
- The location of low pressure and the rising limb over the Western Pacific is considered conducive to good monsoon rainfall in India.
- It’s shifting eastward from its normal position, such as in El Nino years, reduces monsoon rainfall in India.
- Due to the close association between an El Nino (E.N.) and the Southern Oscillation, the two are jointly referred to as an ENSO event.
- The periodicity of SO is not fixed, and its period varies from two to five years.
- Southern Oscillation Index (SOD) is used to measure the intensity of the Southern Oscillation.
- This is the difference in pressure between Tahiti in French Polynesia (Central Pacific), representing the Central Pacific Ocean, and Port Darwin, in northern Australia representing the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- The positive and negative values of the SOI, i.e. Tahiti minus the Port Darwin pressure, point to good or bad rainfall in India.
Indian Ocean Dipole effect (Not every El Nino year is the same in India)
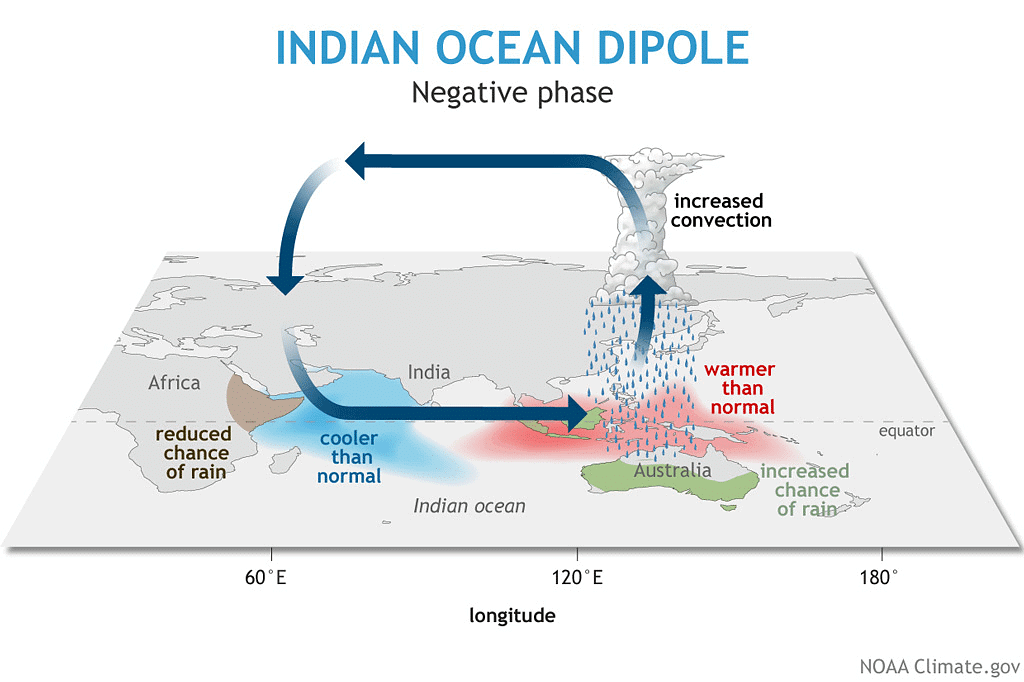
- Although ENSO was statistically effective in explaining several past droughts in India, the ENSO-Monsoon relationship seemed to weaken in the Indian subcontinent in recent decades. In 1997, strong ENSO failed to cause drought in India.
- However, it was later discovered that just like ENSO was an event in the Pacific Ocean, a similar see-saw of the ocean-atmosphere system in the Indian Ocean was also at play. It was discovered in 1999 and named the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD).
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) is defined by the difference in sea surface temperature between two areas (or poles, hence a dipole) – a western pole in the Arabian Sea (western Indian Ocean) and an eastern pole in the eastern Indian Ocean south of Indonesia.
- IOD develops in the equatorial region of the Indian Ocean from April to May peaking in October.
- Positive IOD winds over the Indian Ocean blow from east to west (from the Bay of Bengal towards the Arabian Sea). This results in the Arabian Sea (the western Indian Ocean near the African Coast) being much warmer and the eastern Indian Ocean around Indonesia becoming colder and dry.
- In the negative dipole year (negative IOD), the reverse happens to make Indonesia much warmer and rainier.
- It was demonstrated that a positive IOD index often negated the effect of ENSO, resulting in increased Monsoon rains in several ENSO years like 1983, 1994, and 1997.
- Further, it was shown that the two poles of the IOD – the eastern pole (around Indonesia) and the western pole (off the African coast) were independently and cumulatively affecting the number of rains for the Monsoon in the Indian subcontinent.
Impact of IOD on Cyclonogeneis in the Northern Indian Ocean
- Positive IOD (Arabian Sea warmer than the Bay of Bengal) results in more cyclones than usual in the Arabian Sea.
- Negative IOD results in stronger than usual cyclogenesis (Formation of Tropical Cyclones) in the Bay of Bengal. Cyclogenesis in the Arabian Sea is suppressed.
The El Niño Modoki
- El Niño Modoki is a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon in the tropical Pacific.
- It is different from another coupled phenomenon in the tropical Pacific, namely, El Niño.
- Conventional El Niño is characterized by strong anomalous warming in the eastern equatorial Pacific.
- El Niño Modoki is associated with strong anomalous warming in the central tropical Pacific and cooling in the eastern and western tropical Pacific (see figure below).
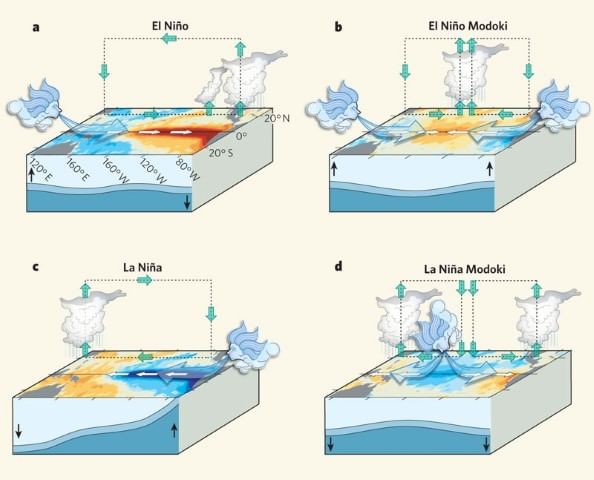
El Niño Modoki Impacts
- The anomalously warm central equatorial Pacific characterizes the El Niño Modoki phenomenon flanked by anomalously cool regions in both the west and east.
- Such zonal gradients result in two-cell Walker Circulation's anomalous over the tropical Pacific, with a wet region in the central Pacific.
La Nina
- After an El Niño event weather conditions usually return to normal.
- However, in some years, the trade winds can become extremely strong, and an abnormal accumulation of cold water can occur in the central and eastern Pacific. This event is called La Niña.
- A strong La Niña occurred in 1988 and scientists believe that it may have been responsible for the summer drought over central North America. During this period, the Atlantic Ocean has seen very active hurricane seasons in 1998 and 1999.
- One of the hurricanes that developed, named Mitch, was the strongest October hurricane ever to develop in about 100 years of record keeping.
Effects of La Nina
Some of the other weather effects of La Niña include
- La Niña is characterized by lower-than-normal air pressure over the western Pacific. These low-pressure zones contribute to increased rainfall.
- In India and Southeast Asia, abnormally heavy monsoons,
- cool and wet winter weather in southeastern Africa, wet weather in eastern Australia,
- cold winter in western Canada and the northwestern United States,
- winter drought in the southern United States.
- Rainfall associated with the summer monsoon in Southeast Asia tends to be greater than normal, especially in northwest India and Bangladesh. This generally benefits the Indian economy, which depends on the monsoon for agriculture and industry.
- Strong La Niña events are associated with catastrophic floods in northern Australia.
- La Niña events are also associated with rainier-than-normal conditions are over southeastern Africa and northern Brazil.
- Drier-than-normal conditions are observed along the west coast of tropical South America, the Gulf Coast of the United States, and southern South America's pampas region.
- La Niña usually has a positive impact on the fishing industry of western South America. Upwelling brings cold, nutrient-rich waters to the surface. Nutrients include plankton eaten by fish and crustaceans.
|
264 videos|875 docs|232 tests
|
FAQs on El Nino, La Nina , ENSO - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is El Nino? |  |
| 2. What is the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO)? |  |
| 3. How does El Nino affect the Indian Monsoons? |  |
| 4. What is the Indian Ocean Dipole effect? |  |
| 5. What is the El Nino Modoki? |  |

















