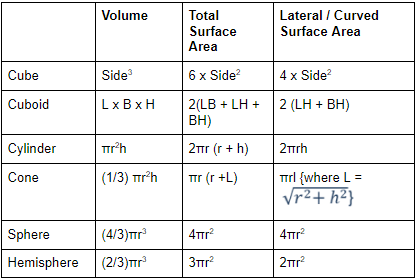
Important Formulas for CAT Geometry & Mensuration
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Lines and Angles |

|
| 2. Triangles |

|
| 3. Polygons |

|
| 4. Quadrilaterals |

|
| 5. Hexagon (Regular) |

|
| 6. Circles |

|
Geometry & Mensuration hold significant weight in competitive exams, making it a crucial topic for aspirants. This document serves as a valuable resource by providing essential formulas for Geometry & Mensuration. It is designed to facilitate quick and effective revision, ensuring that candidates can reinforce their understanding of key concepts in preparation for competitive exams.
1. Lines and Angles
- The sum of the angles in a straight line is 180°
- Vertically opposite angles are congruent (equal).
- If any point is equidistant from the endpoints of a segment, then it must lie on the perpendicular bisector.
When two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal:
- Corresponding angles are equal.
- Alternate interior angles are equal.
- Co-interior angles are supplementary.
(All acute angles formed are equal to each other, and all obtuse angles are equal to each other.)
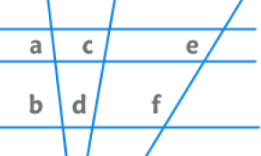
EduRev Tip: The ratio of intercepts formed by a transversal intersecting three parallel lines is equal to the ratio of corresponding intercepts formed by any other transversal.
⇒ a/b = c/d = e/f
2. Triangles
- The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°, and the sum of the exterior angles is 360°.
- Exterior Angle = Sum of remote interior angles.
- The sum of two sides is always greater than the third side, and the difference of two sides is always less than the third side.
- The side opposite to the biggest angle is the longest, and the side opposite to the smallest angle is the shortest.
Area of a triangle:
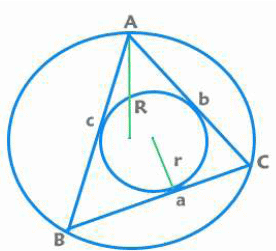
= ½ x Base x Height
= ½ x Product of sides x Sine of included angle
= 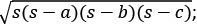 here s is the semi perimeter [s = (a+b+c)/2 ]
here s is the semi perimeter [s = (a+b+c)/2 ]
= r x s [r is radius of incircle]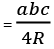 [R is radius of circumcircle]
[R is radius of circumcircle]
- Median of a triangle is a line segment joining a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. The three medians intersect at the Centroid, which divides each median in the ratio 2:1.
- The altitude is a perpendicular line drawn from a vertex to the opposite side or its extension. The three altitudes meet at the Orthocenter of the triangle.
- A Perpendicular Bisector of a side is a line perpendicular to that side at its midpoint. The three perpendicular bisectors meet at the Circumcenter, the centre of the circumcircle passing through all vertices.
- An Angle Bisector divides an angle into two equal parts. The three angle bisectors meet at the Incenter, the centre of the incircle touching all sides.
EduRev Tips:
- Centroid and Incenter always lie inside the triangle.
- For an acute-angled triangle, Circumcenter and Orthocenter lie inside the triangle.
(i) For an obtuse-angled triangle, Circumcenter and Orthocenter lie outside the triangle.
(ii) For a right-angled triangle, Circumcenter lies at the midpoint of the hypotenuse
(iii) Orthocenter lies at the right-angled vertex.- The Orthocenter, Centroid, and Circumcenter lie on a line called the Euler Line.
(i) The Orthocenter is twice as far from the Centroid as the Circumcenter is.
(ii) In an isosceles triangle, the Incenter also lies on the Euler line.
(iii) In an equilateral triangle, all four points coincide.
Theorems
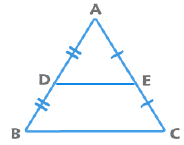
1. Mid Point Theorem: The line joining the midpoint of any two sides is parallel to the third side and is half the length of the third side.
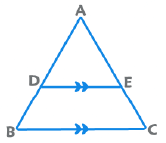
2. Basic Proportionality Theorem: If DE || BC, then AD/DB = AE/EC
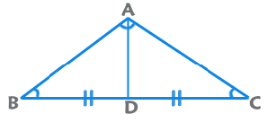
3. Apollonius’ Theorem: AB2 + AC2 = 2 (AD2 + BD2)
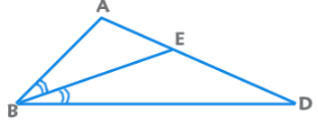
4. Interior Angle Bisector Theorem: AE/ED = BA/BD
Special Triangles
1. Right Angled Triangle:
∆ABC ≈ ∆ ADB ≈ ∆ BDC
BD2 = AD x DC and AB x BC = BD X DC
2. Equilateral Triangle: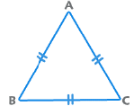
All angles are equal to 60°. All sides are equal also.
Height = 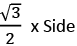
Area = 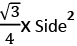
Inradius = 1/3 Height
Circumradius = 2/3 Height.
3. Isosceles Triangle: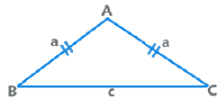
Angles equal to opposite sides are equal.
Area 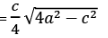
(i) 30°-60°-90° Triangle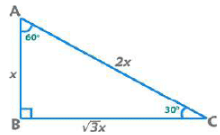
Area 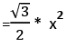
(ii) 45°-45°-90° Triangle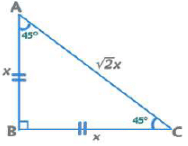
Area = x2/2
(iii) 30°-30°-120° Triangle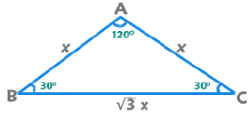
Area =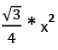
Similarity of Triangles
Two triangles are similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are in proportion.
Tests of similarity: Angle-Angle (AA), Side-Side-Side (SSS), Side-Angle-Side (SAS)
- For similar triangles, if corresponding sides are in the ratio a:b, then corresponding heights, medians, circumradii, inradii, and perimeters are also in the ratio a:b.
- However, the areas are in the ratio a² : b².
Congruency of Triangles
Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are congruent.
Tests of congruence: (SSS / SAS / AAS / ASA)
All ratios mentioned in similar triangles are now 1:1
3. Polygons
- Sum of interior angles = (n-2) x 180° = (2n-4) x 90°
- Sum of exterior angles = 360°
- Number of diagonals =
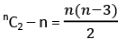
- Number of triangles which can be formed by the vertices = nC3
Regular Polygon:
If all sides and angles are equal, the polygon is called regular. All regular polygons can be inscribed in a circle or circumscribed about a circle.
Area = ½ × Perimeter × Inradius (the perpendicular distance from the centre to any side)
Each interior angle = 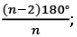 Exterior angle = 360°/n
Exterior angle = 360°/n
4. Quadrilaterals
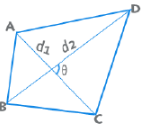
- Sum of the interior angles = Sum of the exterior angles = 360°
- Area for a quadrilateral is given by ½ d1 d2 Sinθ.
Cyclic Quadrilateral
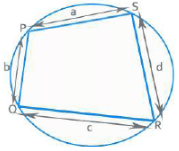
If all vertices of a quadrilateral lie on the circumference of a circle, it is known as a cyclic quadrilateral.
Opposite angles are supplementary
Area = 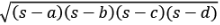 where s is the semi-perimeter
where s is the semi-perimeter 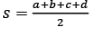
EduRev Tips:
- Sum or product of opposite sides = Product of diagonals
- If a circle can be inscribed in a quadrilateral, its area is given by = √abcd
Different types of Quadrilaterals
(a) Parallelogram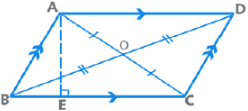
- Opposite sides are parallel and congruent.
- Opposite angles are congruent, and consecutive angles are supplementary.
- Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
- Perimeter = 2(Sum of adjacent sides);
- Area = Base x Height = AD x BE
EduRev Tips:
- A parallelogram inscribed in a circle is always a rectangle. A parallelogram circumscribed about a circle is always a rhombus.
- Each diagonal divides a parallelogram in two triangles of equal area.
- Sum of squares of diagonals = Sum of squares of four sides
⇒ AC2 + BD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2- A rectangle is formed by intersection of the four angle bisectors of a parallelogram.
(b) Rhombus
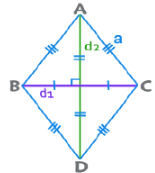
- A parallelogram with all sides equal is a Rhombus. Its diagonals bisect at 90°.
- Perimeter = 4a
- Area = ½ × d1 × d2
- Area = d1 ×
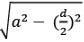
(c) Rectangle
- A parallelogram with all angles equal to 90° is a rectangle. Its diagonals are equal in length.
- Perimeter = 2(l + b)
- Area = length × breadth
(d) Square
- A parallelogram with all sides equal and all angles equal is a square. Its diagonals are equal and bisect each other at 90°.
- Perimeter = 4a
- Area = a2
- Diagonals = a√2
EduRev Tip: From all quadrilaterals with a given area, the square has the least perimeter. For all quadrilaterals with a given perimeter, the square has the greatest area.
(e) Kite
- Two pairs of adjacent sides are congruent.
- The longer diagonal bisects the shorter diagonal at 90°.
- Area = Product of Diagonals / 2
(f) Trapezium / Trapezoid
- A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides is known as a Trapezoid. The parallel sides are known as bases, and the non-parallel sides are known as lateral sides.
- Area = ½ x (Sum of parallel sides) x Height
- The median, the line joining the midpoints of the lateral sides, equals half the sum of the parallel sides.
EduRev Tip: Sum of the squares of the length of the diagonals = Sum of squares of lateral sides + 2 Product of bases.
⇒ AC2 + BD2 = AD2 + BC2 + 2 x AB x CD
Isosceles Trapezium
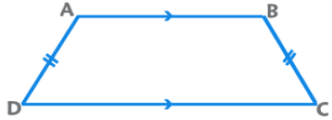
The non-parallel sides (lateral sides) are equal in length. The angles made by each parallel side with the lateral sides are equal.
EduRev Tip: A trapezium can be inscribed in a circle only if it is isosceles. If a circle can be inscribed in a trapezium, the sum of the lengths of the parallel sides equals the sum of the lengths of the lateral sides.
5. Hexagon (Regular)
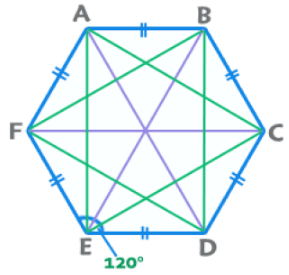
- Perimeter = 6a; Area =
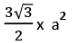
- Sum of Interior angles = 720°.
- Each Interior Angle = 120°. Exterior = 60°
- Number of diagonals = 9 {3 big and 6 small}
- Length of big diagonals (3) = 2a
- Length of small diagonals (6) = √3a
EduRev Tips: A regular hexagon can be considered as a combination of six equilateral triangles. All regular polygons can be considered as a combination of ‘n’ isosceles triangles.
Area of a Pentagon = 1.72 a2
Area of an Octagon = 2(√2 + 1) a2
6. Circles
- Diameter = 2r; Circumference = 2πr; Area = πr2
- Chords equidistant from the centre of a circle are equal.
- A line from the centre, perpendicular to a chord, bisects the chord.
- Equal chords subtend equal angles at the centre.
- The diameter is the longest chord of a circle.
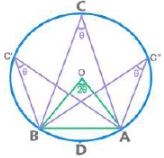
- A chord /arc subtends an equal angle at any point on the circumference and double that angle at the centre.
- Chords / Arcs of equal lengths subtend equal angles.
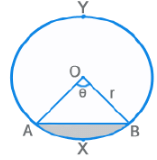
- Chord AB divides the circle into two parts: Minor Arc AXB and Major Arc AYB.
- Measure of arc AXB = ∠AOB = θ
- Length (arc AXB) =
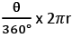
- Area (sector OAXB) =
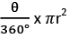
- Area of Minor Segment = Shaded Area in the above figure
⇒ Area of Sector OAXB - Area of ∆ OAB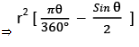
Properties of Tangents, Secants and Chords
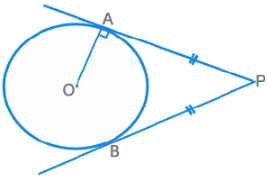
- The radius and tangent are perpendicular to each other.
- There can only be two tangents from an external point, which are equal in length PA = PB
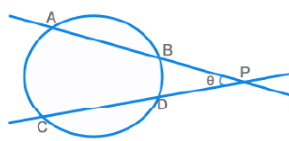
PA x PB = PC x PD
θ = ½ [ m(Arc AC) – m(Arc BD) ]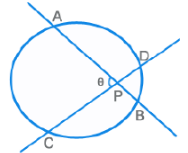
PA x PB = PC x PD
θ = ½ [ m(Arc AC) + m(Arc BD) ]
Properties (contd.)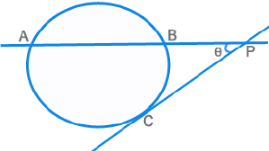
PA x PB = PC2
θ = ½ [ m(Arc AC) - m(Arc BC) ]
Alternate Segment Theorem
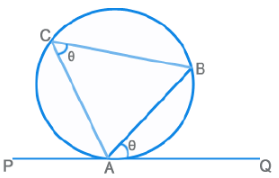
The angle made by the chord AB with the tangent at A (PQ) is equal to the angle that it subtends on the opposite side of the circumference.
⇒ ∠BAQ = ∠ACB
Common Tangents
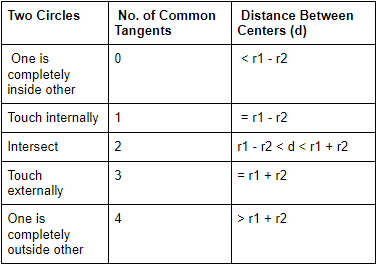
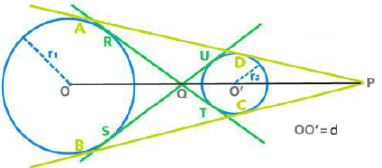
⇒ AD = BC = 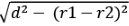
Length of the Transverse Common Tangent (TCT)
⇒ RT = SU = 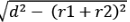
EduRev Tips:
- The two centers(O and O’), point of intersection of DCTs (P)and point of intersection of TCTs (Q) are collinear. Q divides OO’ in the ratio r1 : r2 internally whearea P divides OO’ in the ratio r1 : r2 externally.
- There are 4 body diagonals in a cube / cuboid of length (√3 x side) and
respectively.
|
205 videos|264 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas for CAT Geometry & Mensuration
| 1. What are the basic properties of triangles in geometry? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the area of a rectangle? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? |  |
| 4. How can I find the volume of a cube? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between perimeter and area in geometry? |  |