Factors affecting Bond Parameters | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Bond Energy |

|
| Bond Length |

|
| Bond angle |

|
| Bond order |

|
| Formal Charge |

|
| Resonance in Chemical Bonding |

|
| London Dispersion Forces |

|
- Covalent bonds can be characterized on the basis of several bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, bond order, and bond energy (also known as bond enthalpy).
- These bond parameters offer insight into the stability of a chemical compound and the strength of the chemical bonds holding its atoms together.
- Various bond parameters and factors affecting them are as follows.
Bond Energy
The amount of energy required to break one mole of bonds of a particular type so as to separate them into gaseous atoms is called bond dissociation enthalpy or simply bond enthalpy.
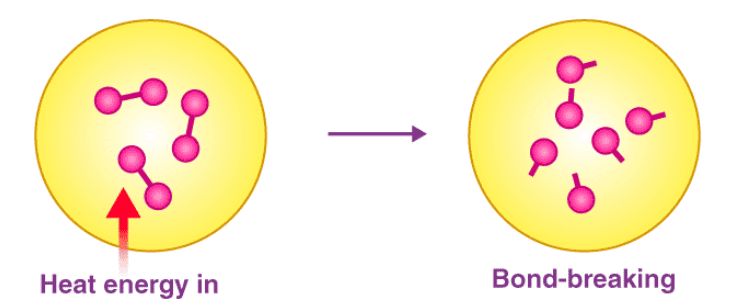
Factors affecting Bond energy
(i) Size of the atoms: Greater the size of the atoms, greater is the bond length and less is the bond dissociation enthalpy, i.e., less is the bond strength.
(ii) Multiplicity of bonds: For the bond between the same two atoms, greater is the multiplicity of the bond, greater is the bond dissociation enthalpy. This is firstly because atoms come closer and secondly, the number of bonds to be broken is more. For example, bond dissociation enthalpies of H2, O2 and N2 are in the order: H–H < O = O < N ≡ N
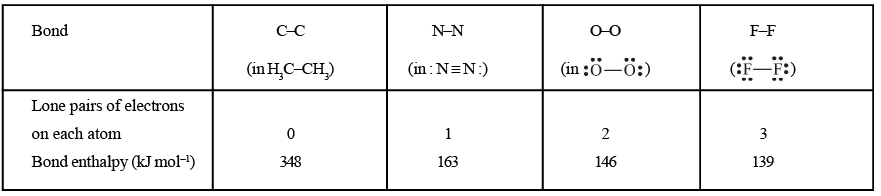
(iii) Number of lone pairs of electrons present: Greater the number of lone pairs of electrons present on the bonded atoms greater is the repulsion between the atoms and hence less is the bond dissociation enthalpy. For example, for a few single bonds, we have
Bond Length
The equilibrium distance between the centres of the nuclei of the two bonded atoms is called its bond length.
Factors affecting the bond length
- Size of the atoms: The bond length increases with increase in the size of the atoms. For example, bond lengths of H–X are in the order:
HI > HBr > HCl > HF - Multiplicity of bond: The bond length decreases with the multiplicity of the bond. Thus, bond length of carbon-carbon bonds are in the order:
C ≡ C < C = C < C – C - Type of hybridisation: As an sorbital is smaller in size, greater the s-character, shorter is the hybrid orbital and hence shorter is the bond length. For example,
Bond lengths : sp3 C–H > sp2 C–H > sp C–H
s-character : (25%) (33%) (50%) - Resonance and delocalisation: C-C bond length is 1.54Å and C = C bond length is 1.34 Å but in benzene, due to resonance, the carbon-carbon bond is neither single nor double but intermediate between single and double and same holds for bond length and is equal to 1.39 Å.
Bond angle
The angle between the lines representing the directions of the bonds, i.e., the orbitals containing the bonding electrons is called the bond angle.
Factors affecting Bond Angle
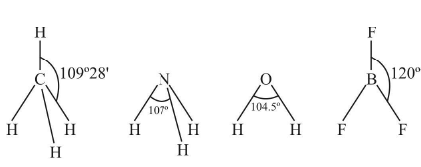
- Hybridization: Bond angle depends on the state of hybridization of the central atom.
Hybridization sp3 sp2 sp
Bond angle 109028' 1200 1800
Example CH4 BCl3 BeCl2
It is observed that as s-character increases in the hybrid bond, the bond angle increases. - Lone pair repulsion: Bond angle is affected by the presence of lone pair of electrons at the central atom. A lone pair of electrons at the central atom always tries torepel the shared pair (bond.edpair) of electrons. Due to this, the bonds are displaced slightly inside resulting in a decrease of bond angle.The bond angle in NH3 is 107° and bond angle in H2O is 105° inspite of the fact that N-atom and O-atom undergo sp3 hybridization.
- Electronegativity: If the electronegativity of the central atom decreases, bond angle decreases. In case the central atom remains the same, bond angle increases with decrease ill the electronegativity of the surrounding atoms.
Bond order
- In the Lewis representation of a molecule or ion, the number of bonds presents between two atoms is called bond order. For example, the bond orders of a few molecules are given below:
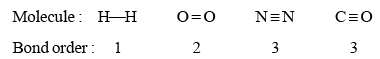
- For odd electron molecules, as the three electron bond is considered as equivalent to half covalent bond, bond order can be fractional also. For example, Lewis structure of NO is
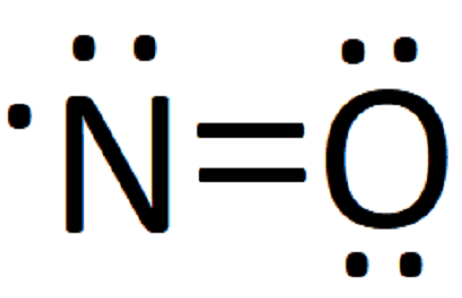
- It is observed that with increase in bond order, bond enthalpy increases while bond length decreases.
Formal Charge
The formal charge on an atom in a molecule or ion is defined as the difference between the number of valence electrons of that atom in the free state and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure, assuming that in each shared pair of electrons, the atom has one electron of its own and the lone pair on it belongs to it completely.
Thus, it can be calculated as follows: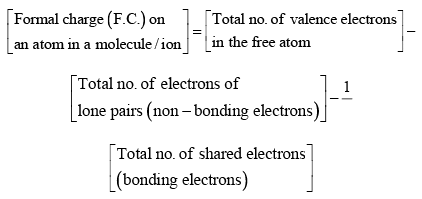
Example:
Calculate formal charge on each O-atom of O3 molecule.
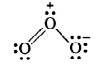
Sol. Lewis structure of O3 is: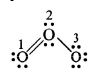
The atoms have been numbered as 1, 2 and 3.
Formal charge on end O-atom numbered 1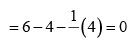
Formal charge on central O-atom numbered 2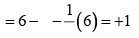
Formal charge on end O-atom numbered 3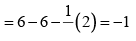
Hence, we represent O3 along with formal charges as:
Example:
Write the formal charges on atoms in (i) carbonate ion (ii) nitrite ion.
Sol. (i) Lewis structure of CO32– ion is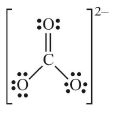
Formal charge on C atom
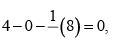
Formal charge on double bonded O atom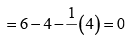
Formal charge on single bonded O atom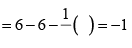
(ii) Lewis structure of NO2– ion is 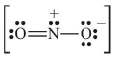
Formal charge on N atom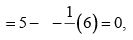
Formal charge on double bonded O atom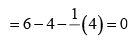
Formal charge on single bonded O atom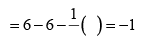
Significance of formal charge:
The main advantage of the calculation of formal charges is that it helps to select the most stable structure, i.e., the one with least energy out of the different possible Lewis structures. The most stable is the one which has the smallest formal charges on the atoms.
Resonance in Chemical Bonding
There are molecules and ions for which drawing a single Lewis structure is not possible. For example, we can write two structures of O3.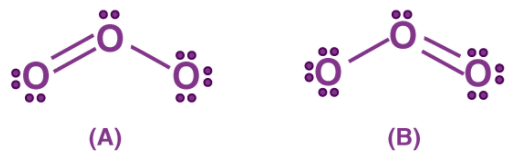
In (A) the oxygen-oxygen bond on the left is a double bond and the oxygen-oxygen bond on the right is a single bond. In B the situation is just the opposite. The experiment shows, however, that the two bonds are identical.
Therefore neither structure A nor B can be correct. One of the bonding pairs in ozone is spread over the region of all three atoms rather than localized on a particular oxygen-oxygen bond. This delocalized bonding is a type of chemical bonding in which bonding pair of electrons are spread over a number of atoms rather than localized between two.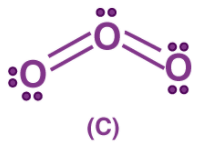
Structures (A) and (B) are called resonating or canonical structures and (C) is the resonance hybrid. This phenomenon is called resonance, a situation in which more than one canonical structure can be written for a species. The chemical activity of an atom is determined by the number of electrons in its valence shell. With the help of the concept of chemical bonding, one can define the structure of a compound and is used in many industries for manufacturing products in which the true structure cannot be written at all.
Some other examples:
- CO32– ion
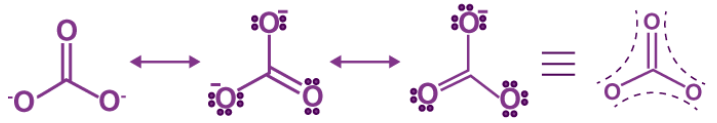
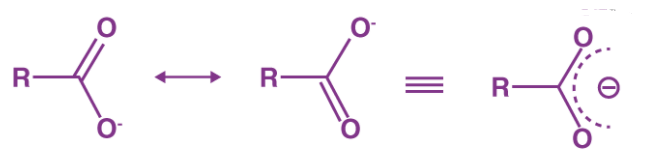
- Carbon-oxygen bond lengths in carboxylate ion are equal due to resonance.
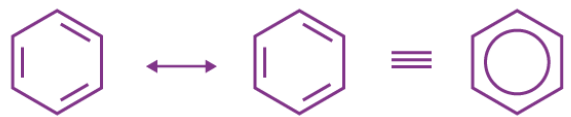
- Benzene
-Vinyl Chloride
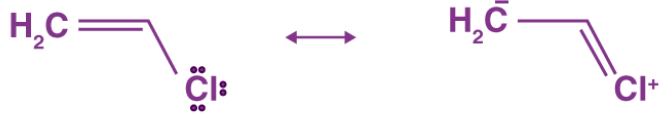
The difference in the energies of the canonical forms and resonance hybrid is called resonance stabilization energy.
London Dispersion Forces
Another form of chemical bonding is caused by London dispersion forces. These forces are weak in magnitude.
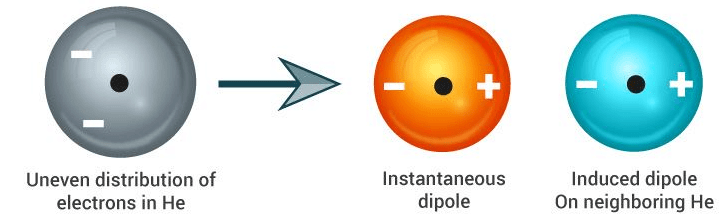 London Dispersion Forces
London Dispersion Forces
These forces occur due to a temporary charge imbalance arising in an atom. This imbalance in the charge of the atom can induce dipoles on neighbouring atoms. For example, the temporary positive charge on one area of an atom can attract the neighbouring negative charge.
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Factors affecting Bond Parameters - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What is bond energy? |  |
| 2. How is bond length defined? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of bond angle? |  |
| 4. How is bond order calculated? |  |
| 5. What is the concept of resonance in chemical bonding? |  |




















