Resistance of Pure Metals
(i) We know that
For a given conductor, l, A and n are constant, hence R is directly proportional to (1/τ)
If λ represents the mean free path (Average distance covered between two successive collisions) of the electron and vrms, the root-mean-square speed, then
Hence R is directly proportional to
Now,
(a) λ decreases with rise in temperature because the amplitude of vibrations of the +ve ions of the metal increases and they create more hindrance in the movement of electrons and,
(b) (i) vrms increases because vrms is directly proportional to under root T. Therefore, Resistance of the metallic wire increases with rise in temperature. As ρ is directly proportional to R and σ is directly proportional to (1/ρ), hence resistivity increases and conductivity decreases with rise in temperature of the metallic of the metallic wires.
(ii) If R0 and Rτ represent the resistances of metallic wire at 0°C and t°C respectively then Rt is given by the following formula :
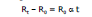
where α is called as the Temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of the wire.
α depends on material and temperature but generally it is taken as a constant for a particular material for small change.
Rt - R0 = R0 α t
for very small change in temperature dR = R0 α dt
(c) Resistance of semiconductors
(i) There are certain substances whose conductivity lies in between that of insulators and conductors, higher than that of insulators but lower than that of conductors. These are called as semiconductors, e.g., silicon, germanium, carbon etc.
(ii) The resistivity of semiconductors decreases with increase in temperature i.e., a for semiconductors is -ve and high.
(iii) Though at ordinary temperature the value of n (no. of free electrons per unit volume) for these materials is very small as compared to metals, but increases very rapidly with rise in temperature (this happens due to breaking of covalent bonds). Though τ decreases but factor of n dominates. Therefore, the resistance
goes on decreasing with increase in temperature.
Specific Resistance or Resistivity
- R of a conductor is directly proportional to its length (l).
- R of a conductor is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section (A).
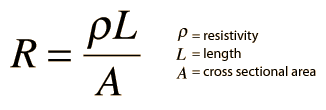
Resistivity depends only upon the material of which the conductor is made. It is defined as the resistance of the conductor made of a given material having length of 1 meter and area of cross-section 1 m2
If P1 and P2 are resistivities of a material at temperatures T1
and T2 respectively, then :
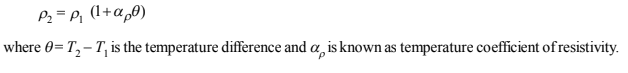
FAQs on Effect of Temperature on Resistance & Resistivity - JEE
| 1. How does temperature affect the resistance of an object? |  |
| 2. What is the relationship between temperature and resistivity? |  |
| 3. How does temperature affect the conductivity of a material? |  |
| 4. Why does the resistance of a conductor increase with temperature? |  |
| 5. Can the resistance of all materials be affected by temperature? |  |














