Metals and Non-Metals - 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
Q1: Which one of the following metals does not react with cold water?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Mg
(d) Fe
Ans: (d)
Iron does not react with cold water and reacts very slowly with hot water or steam to form iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃) and hydrogen gas (H₂).
Reaction with steam: 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
Q2: Study the given table and answer the following questions:
A student took the samples of four metals A, B, C and D and added the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows:
(a) Which is the most reactive metal? (1 Marks)
(b) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of
(i) Copper
(ii) Sulphate? (1 Marks)
(c) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity? (1 Marks)
(d) Which gas is produced when dilute HCl is added to a reactive metal? (1 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Metal B displaces iron from iron (II) sulphate, indicating that B is more reactive than iron. Displacing iron from its salt solution is a clear sign that B is highly reactive.
(b) Since B is more reactive than iron (and iron is more reactive than copper), B will also displace copper from copper (II) sulphate solution.
(c) B > A > C > D
- B is more reactive than iron and copper, but not reactive with zinc.
- A displaces copper but does not react with iron.
- C and D show very little reactivity. Therefore, B is the most reactive, followed by A, C, and then D.
(d) Hydrogen gas is produced when dilute HCl is added to a reactive metal. This is a standard reaction where a reactive metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas and a salt.
Q3: What is meant by metallurgy? (1 Marks)
Ans: 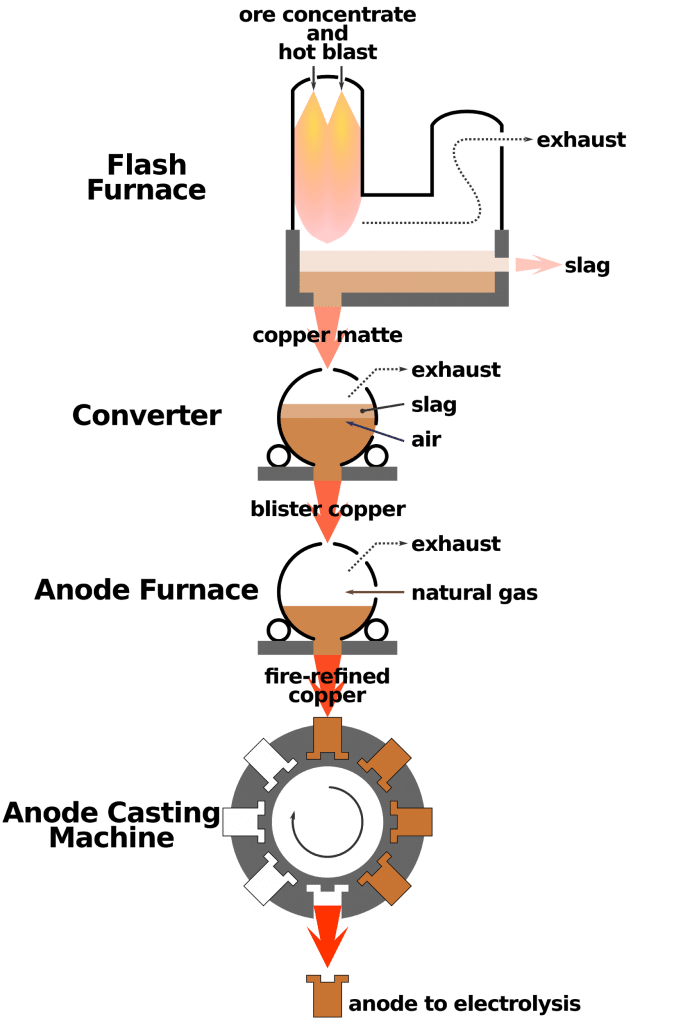 MetallurgyThe extraction of metals from their ores and then refining them for use is known as metallurgy. Metallurgy involves all the processes used to obtain metals in their pure form from naturally occurring materials.
MetallurgyThe extraction of metals from their ores and then refining them for use is known as metallurgy. Metallurgy involves all the processes used to obtain metals in their pure form from naturally occurring materials.
Q4: (a) Write chemical equations for the following reactions : (5 Marks)
(i) Calcium metal reacts with water.
(ii) Cinnabar is heated in the presence of air.
(iii) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
(b) What are alloys? List two properties of alloys.
Ans: (a) (i) Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
(ii)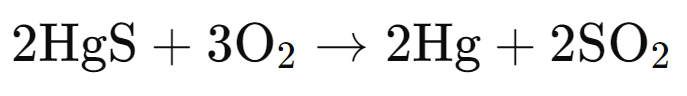
(iii) 3MnO2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 3Mn
(b) Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal. Alloys are formed to improve the properties of the base metal.
Properties:
1. Increased Strength and Hardness: Alloys are generally stronger and harder than their constituent pure metals. For example, steel (an alloy of iron and carbon) is much stronger than pure iron.
2. Corrosion Resistance: Alloys often have greater resistance to corrosion compared to pure metals. For example, stainless steel (an alloy of iron, chromium, and nickel) resists rusting and corrosion better than pure iron.
Q5: Describe electrolytic refining of copper with chemical equations. Draw a well-labelled diagram for it. (3 Marks)
Ans: Electrolytic Refining: This method is widely used as purification of metals like zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), aluminium (Al), chromium (Cr), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni) and gold (Au). In this process, impure metal is used as anode, a strip of pure metal is used as cathode, and soluble salt of metal is used as electrolyte. On passing electric current through the electrolyte, cations move towards the cathode, gain electrons, and pure metal gets deposited on the cathode. In electrolytic refining of copper, the impurities left behind at anode called anode mud contain valuable metals such as gold and silver, which can be recovered in the native state.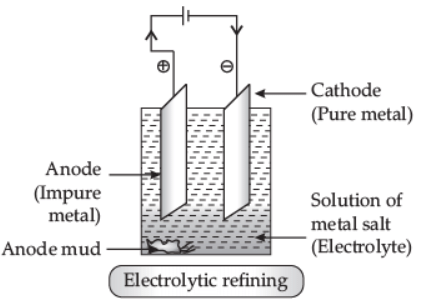 Q6: Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous. (1 Marks)
Q6: Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous. (1 Marks)
Ans: Non-metal (lustrous) = Iodine (I)
Metal (non-lustrous) = Sodium (Na)
Q7: Assertion and Reason :
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion ( A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion ( A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(i) Assertion (A): Zinc oxide is amphoteric in nature.
Reason (R): Zinc oxide reacts with both acids and bases.
Ans: (a)
Zinc oxide is considered amphoteric because it has the ability to react with both acids and bases. This dual reactivity confirms its amphoteric nature, making the reason a correct explanation for the assertion.
(ii) Assertion (A): Metals are sonorous.
Reason (R): They are generally brittle in the solid-state; they break into pieces when hammered. (1 Marks)
Ans: (c)
The assertion that "Metals are sonorous" is true. Metals produce a ringing sound when struck, which is why they are described as sonorous. However, the reason provided is false. Metals are generally not brittle; instead, they are malleable and ductile, meaning they can be hammered into thin sheets or drawn into wires without breaking. Brittle materials break or shatter when hammered, which is characteristic of non-metals, not metals.
(iii) Assertion (A): Gas bubbles are observed when sodium carbonate is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide is given off in the reaction. (1 Marks)
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and the reason are true. When sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) is added to dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl), a chemical reaction occurs, producing carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas, water, and sodium chloride (NaCl). The formation of CO₂ gas leads to the observation of gas bubbles. Therefore, the reason correctly explains the assertion.
Q8: What happens when zinc granules are treated with dilute solutions of H2SO4, HCl, HNO3, NaCl and NaOH? Also, write the chemical equation. (5 Marks)
Ans: (i) With dilute H2SO4: H2 gas is evolved.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 ↑
(ii) With dilute HCl: H2 gas is evolved.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
(iii) With dilute HNO3: Zinc nitrate, nitrous oxide and water are formed.
Here, HNO3, is an oxidising agent which oxidises H2 gas to H2O.
4Zn + 10HNO3 → 4Zn(NO3)2 + 5H2O + N2O↑
(iv) With dilute NaCl: No chemical reaction takes place.
(v) With dilute NaOH: Sodium Zincate is formed and H2 gas is evolved.
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2 ↑
Q9: Explain the following. (3 Marks)
(a) Sodium chloride is an ionic compound which does not conduct electricity in solid state, whereas it conducts electricity in molten state as well as in its aqueous solution.
(b) Reactivity of aluminium decreases if it is dipped in nitric acid.
(c) Metals like calcium and magnesium are never found in their free state in nature.
Ans:
(a) Sodium chloride is an ionic compound formed by ions of sodium (Na+) and chlorine (Cl–). In solid-state, ions are fixed in position, so no free electrons are available to conduct electricity. Whereas in molten state and aqueous solution of sodium chloride, free electrons are available to conduct electricity.
(b) On dipping aluminium in nitric acid, a layer of aluminium oxide is formed as nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. The layer of aluminium oxide prevents further reaction of aluminium due to which the reactivity of aluminium decreases.
(c) Because these metals are highly reactive and readily react with atmospheric oxygen and other gas.
Q10: Define alloys. List the properties of alloys that make them useful over pure metals? Explain this fact with suitable examples. (3 Marks)
Ans: Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal that cannot be separated into their components by physical methods.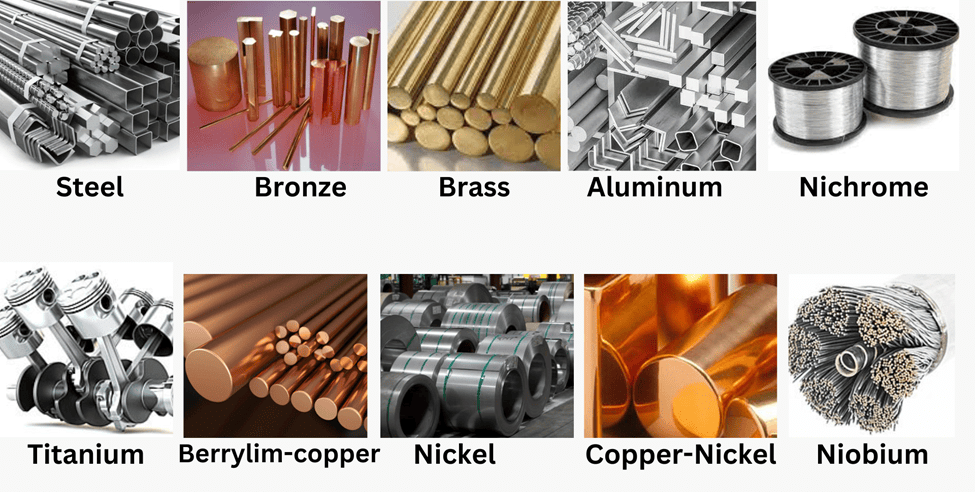 Alloys(i) The electrical conductivity.
Alloys(i) The electrical conductivity.
(ii) Melting point of an alloy is less than that of a pure metal.
Example: Brass and Bronze are not good conductors of electricity whereas copper is used in making electrical circuits.
Example: Solder has a low melting point.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Metals and Non-Metals - 1 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the physical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. How do metals and non-metals react with acids? |  |
| 3. Can you give examples of common metals and non-metals? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between the chemical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |

















