Metals and Non-metals - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science
Q.1. What happens when calcium is treated with water? (1 Marks)
(i) It does not react with water
(ii) It reacts violently with water
(iii) It reacts less violently with water
(iv) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (d)
Solution. Calcium reacts slowly with water. The reaction forms calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2 and hydrogen gas (H2). The calcium metal sinks in water and after an hour or so bubbles of hydrogen are observed, stuck to the surface of the metal.
Q.2. Element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept open in air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element from the following : (1 Marks)
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) P
(d) Ca
Ans. (b)
Solution. Sodium is so soft that it can be cut using a knife. It reacts with oxygen or moisture present in air readily and reacts with water vigorously. Because of this, sodium is stored in kerosene oil to prevent any reaction or accident.
Q.3. Give an example of a metal which is the best conductor of heat. (1 Marks)
Ans. Silver or Copper.
Q.4. An element X forms an oxide which turns red litmus blue. Identify whether X is a metal or non-metal. (1 Marks)
Ans. Metal, because metal oxides are basic in nature.
Q.5. Sohan went door to door, posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him, which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new, but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was sad, but after a futile argument, the man beat a hasty retreat.
(i) Which of the following is used for dissolution of gold? (1 Marks)
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Aqua regia
Ans. (d)
Solution. Aqua Regia is a mixture of concentrated HNO3 and concentrated HCl. It is used for dissolution of gold.
(ii) The composition of aqua-regia is (1 Marks)
(a) Dil. HCl:Conc. HNO3 3:1
(b) Conc. HCl:Dil. HNO3 3:1
(c) Conc. HCl:Conc. HNO3 3:1
(d) Dil. HCl:Dil. HNO3 3:1
Ans. (c)
Solution. Aqua regia is a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, that is 3 part conc. HCl and one part conc. HNO3 (3:1). (iii) Why was the weight of the bangle reduced drastically? (1 Marks)
(iii) Why was the weight of the bangle reduced drastically? (1 Marks)
Ans. As the gold from the bangles was dissolved in Aqua regia, their weight was reduced drastically.
(iv) Aqua regia is a strong oxidizing agent. (True or False) (1 Marks)
Ans. True. Aqua Regia is a strong oxidizing agent due to the formation of NOCl (Nitrosyl chloride) and chlorine produced by reaction of two acids.
Q.6. Given below are the steps for the extraction of copper from its ore. Write the chemical equation of the reactions involved in each case.
(i) Roasting of copper (i) sulphide
(ii) Reduction of copper (i) oxide from copper (i) sulphide
(iii) Electrolytic refining (3 Marks)
Ans.
(i) Roasting of copper (I) sulphide: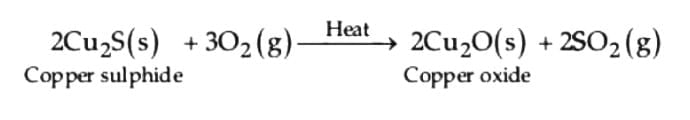 (ii) Reduction of copper (I) oxide from copper (I) sulphide:
(ii) Reduction of copper (I) oxide from copper (I) sulphide: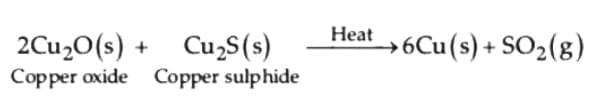 (iii) Electrolytic refining :
(iii) Electrolytic refining :
At anode: Cu(s) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2e−
At cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2e− → Cu(s)
Q.7. Galvanization is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating with a thin layer of (1 Marks)
(a) Gallium
(b) Aluminium
(c) Zinc
(d) Silver
Ans. (c)
Solution. In the process of galvanization, iron is covered by a coat of zinc. This layer of zinc prevents iron from getting rusted.
Q.8. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
During extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals. During the process, the impure metal is made the anode, and a thin strip of pure metal is made the cathode. The solution of the metal salt is used as an electrolyte. On passing the current through the electrolyte, the pure metal from the anode dissolves from the electrolyte. An equivalent of pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited on the cathode.
(i) What is the refining of metals? (1 Marks)
Ans. Refining of metal is the process of purification of the metal obtained after reduction
(ii) Which of the metals are refined by electrolytic refining? (1 Marks)
I. Au
II. Cu
III. Na
IV. K
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and III
(d) II and IV
Ans. (a)
Solution. Metals like Cu, Zn, Ag and Au are refined by electrolytic refining.
(iii) During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets (1 Marks)
(a) deposited on cathode
(b) deposited on anode
(c) deposited on cathode as well as anode
(d) remains in the solution
Ans. (a)
Solution. Ions of zinc are positively charged, thus while electrolytic refining of zinc, zinc is deposited at the cathode (negatively charged pole).
(iv) In electrolytic refining of copper, ________ (anode/cathode) acts as impure copper, while _________ (anode/cathode) is a strip of pure copper. (1 Marks)
Ans. In electrolytic refining of copper, anode acts as impure copper while cathode is a strip of pure copper.
Q.9. State the reason for the following:
(i) Aluminium oxide is called an amphoteric oxide.
(ii) An iron strip dipped in a blue copper sulphate solution turns blue, pale green solution.
(iii) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most metals react with nitric acid.
(iv) Calcium does not occur in a free state in nature.
(v) Sodium and potassium metals are kept immersed under kerosene. (5 Marks)
Ans. (i) As it reacts with both acids as well as bases to form salts.
(ii) Iron being more reactive than copper displaces copper from copper sulphate to form green ferrous sulphate solution.
(iii) Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. Hydrogen gas produced and gets oxidised to H2O.
(iv) Calcium is a very reactive metal. It reacts with the chemicals in the surroundings and occurs in a combined state.
(v) Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals and react vigorously with oxygen in air and may even catch fire. They do not react with kerosene.
Q.10. Why is carbon not used for reducing aluminium from aluminium oxide? (1 Marks)
Ans. Because aluminium has a greater affinity for oxygen than for carbon, therefore carbon cannot reduce alumina (Al2O3) to aluminium.
Q.11. Name the metal which has a very low melting point and can melt with the heat of your palm? (1 Marks)
Ans. Gallium.
Q.12. Generally, non-metals are not lustrous. Which of the following non-metal is lustrous? (1 Marks)
(a) Sulphur
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Iodine
Ans. (d)
Solution. Iodine is a non-metal, but it is lustrous.
Q.13. Make a distinction between metals and non-metals with respect to the nature of their oxide. (1 Marks)
Ans.
- Metallic oxides are basic; few are amphoteric.
- Non-metallic oxides are acidic; few are neutral.
Q.14. (i) Explain the formation of ionic compound CaO with electron dot structure. Atomic numbers of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8, respectively.
(ii) Name the constituent metals of bronze. (3 Marks)
Ans. (i) Calcium (20) – 2, 8, 8, 2
Oxygen (8) – 2, 6
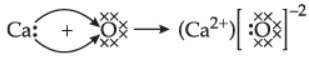
(ii) Constituents metals of bronze – copper, tin.
Q.15. (a) Define the terms ‘alloy’ and ‘amalgam’. Name the alloy used for welding electric wires together. What are its constituents?
(b) Name the constituents of the following alloys :
(i) Brass
(ii) Stainless steel
(iii) Bronze,
State one property in each of these alloys, which is different from its main constituents. (5
Marks)
Ans. (a)
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal, mixed in the molten state. Amalgam is an alloy of a metal with mercury.
Solder is the alloy used for the welding of electric wires. Tin and Lead are their constituents.
(b) (i) Brass – copper and zinc
(ii) Stainless steel – iron, nickel and chromium
(iii) Bronze – copper and tin.
Brass and bronze have lower electrical conductivity than their constituents. Stainless steel does not corrode easily as iron does.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Metals and Non-metals - 2 Class 10 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 4. What are some uses of metals and non-metals in everyday life? |  |
| 5. Are there any elements that exhibit properties of both metals and non-metals? |  |
















