Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Science Class 6 > Mindmap: Electricity and Circuits
Mindmap: Electricity and Circuits | Science Class 6 PDF Download
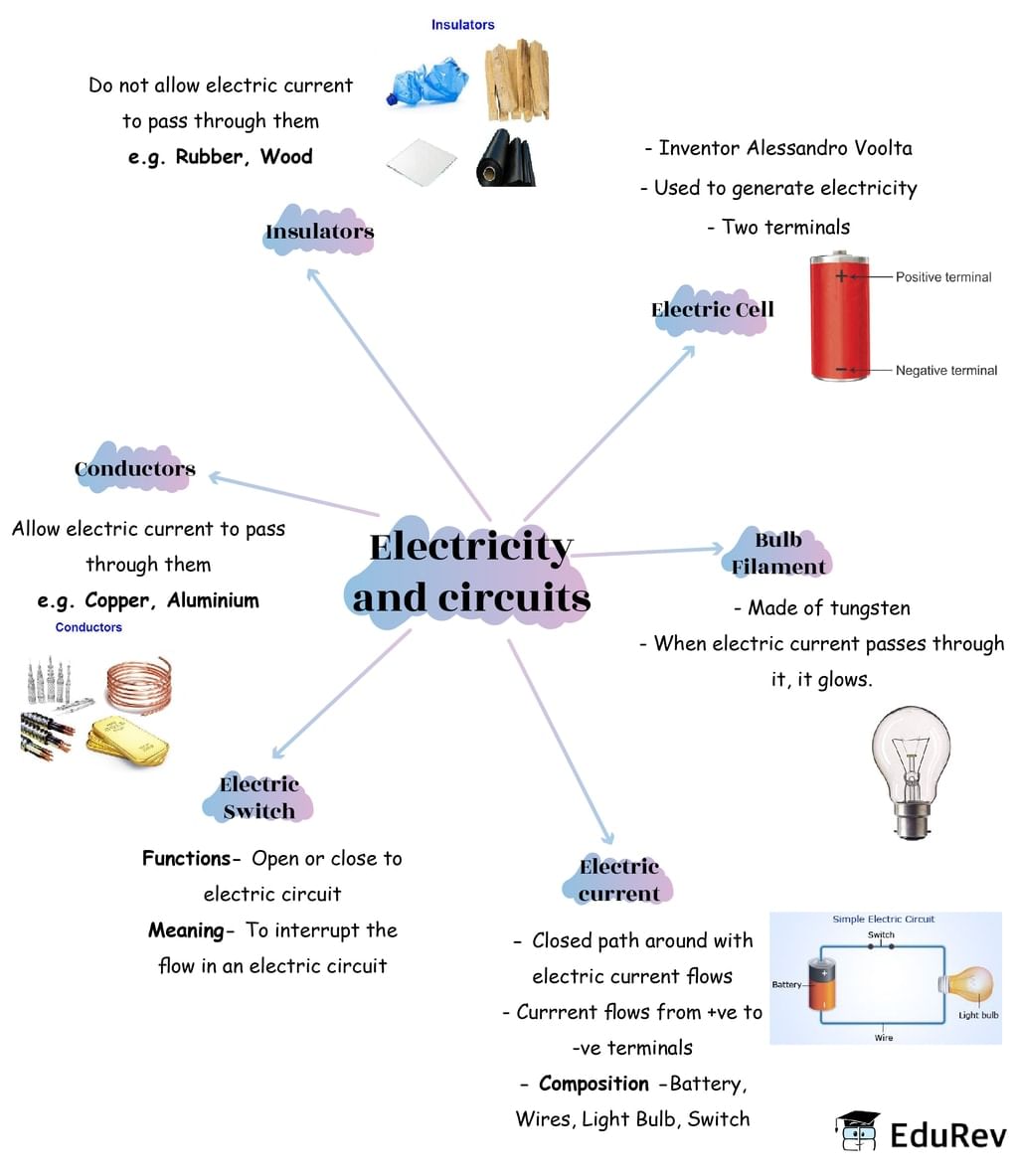
The document Mindmap: Electricity and Circuits | Science Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Science Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: Electricity and Circuits - Science Class 6
| 1. What is electricity and how is it generated? |  |
Ans. Electricity is the flow of electric charge. It is generated through various methods such as burning fossil fuels, nuclear reactions, or harnessing renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. In most cases, electricity is generated by rotating turbines that are connected to generators.
| 2. What is a circuit and how does it work? |  |
Ans. A circuit is a closed loop that allows electric current to flow. It consists of a power source, such as a battery or a generator, wires to conduct the current, and various components like resistors, capacitors, and switches. When the circuit is complete, the current can flow from the power source through the components and back, enabling them to perform their intended functions.
| 3. What is the difference between AC and DC circuits? |  |
Ans. AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) are two types of electric circuits. AC circuits have a constantly changing direction of current flow, as seen in household power outlets, while DC circuits have a steady, unidirectional flow of current, like in batteries. AC circuits are more suitable for long-distance power transmission, while DC circuits are commonly used in electronic devices and automotive applications.
| 4. How does a circuit breaker work? |  |
Ans. A circuit breaker is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by excess current. It detects when the current exceeds a safe level and automatically interrupts the flow of electricity. When the current reaches an unsafe point, the circuit breaker's internal mechanism trips, opening the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This prevents overheating, fires, and other potential hazards.
| 5. What is the purpose of grounding in an electrical circuit? |  |
Ans. Grounding is a safety measure in electrical circuits that involves connecting a conductor to the earth or a large conducting body like a metal water pipe. It provides a path of least resistance for electric current in case of a fault, such as a short circuit. Grounding helps to protect people and equipment by redirecting excess current away from them and facilitating the proper functioning of circuit protection devices like fuses and circuit breakers.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















