Best Study Material for NEET Exam
NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Physics Class 11 > Mindmap: Gravitation
Mindmap: Gravitation | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
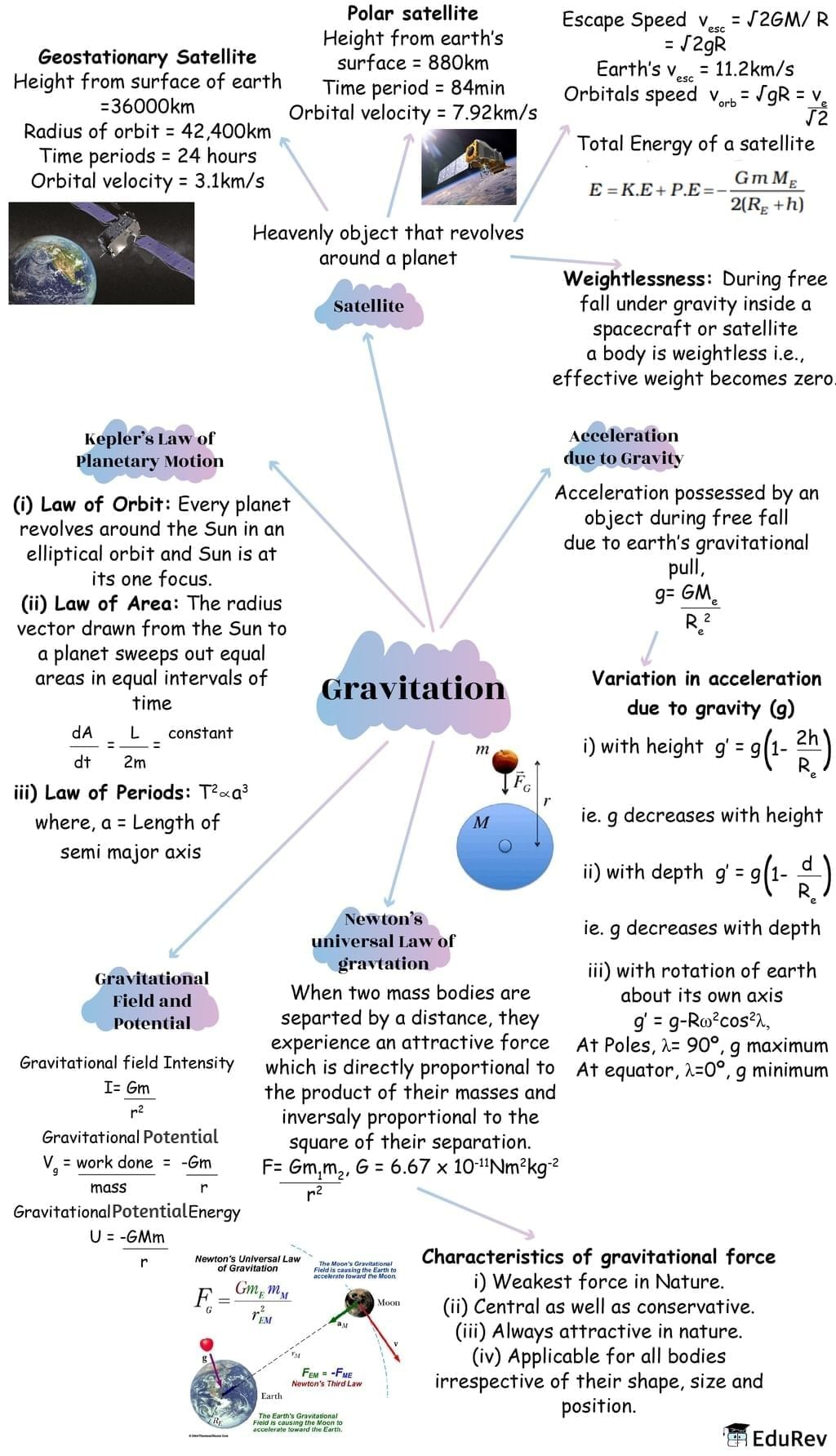
The document Mindmap: Gravitation | Physics Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Physics Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
97 videos|379 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on Mindmap: Gravitation - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the law of universal gravitation? |  |
| 2. How does gravity affect time? |  |
Ans. Gravity affects time through a phenomenon known as gravitational time dilation, which is a concept from Einstein's theory of general relativity. In stronger gravitational fields, time runs slower compared to weaker gravitational fields. This means that a clock closer to a massive object, like a planet or a star, will tick more slowly than a clock that is farther away. This effect, although very small in everyday scenarios, has been confirmed by experiments and is significant in the context of satellites and GPS technology.
| 3. What are the effects of gravity on Earth? |  |
Ans. Gravity on Earth has several effects, including keeping the atmosphere in place, causing objects to fall towards the ground, and influencing ocean tides through the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining the orbits of planets, moons, and artificial satellites around the Earth, ensuring stability in their paths.
| 4. What is the relationship between mass and weight? |  |
Ans. Mass and weight are related but distinct concepts. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, typically measured in kilograms, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass. Weight can be calculated using the formula W = m * g, where W is weight, m is mass, and g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s² on Earth). Thus, an object's weight can change depending on the gravitational pull acting on it, while its mass remains constant.
| 5. Can gravity be considered a force? |  |
Ans. Yes, gravity can be considered a force, particularly in the context of Newtonian physics. It is the attractive force that pulls objects toward one another based on their mass. However, in Einstein's general theory of relativity, gravity is described as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass. This means that rather than being a force in the traditional sense, gravity affects the motion of objects moving along the curved paths in spacetime.
Related Searches


























