Geography of Africa- 1 | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
- Area: 3,03,35,000 sq. km (20.4% of total area Madagascar and other islands of Africa)
- Geography Population: 778.5 million
Latitude: 37031'N to 34052'S Longitude : 25011'W to 51024'E
Size: Second largest continent after Asia and nine times the size of India.

Africa is called the Dark Continent
- Situation: Situated to the south of Europe and southwest of Asia.
It is bound by the Mediterranean Sea in the north, the Atlantic Ocean in the west and southwest, the Indian Ocean in the east, and the Red Sea in the northeast.
Africa is sometimes nicknamed the “Mother Continent” as it’s the oldest inhabited continent on Earth.
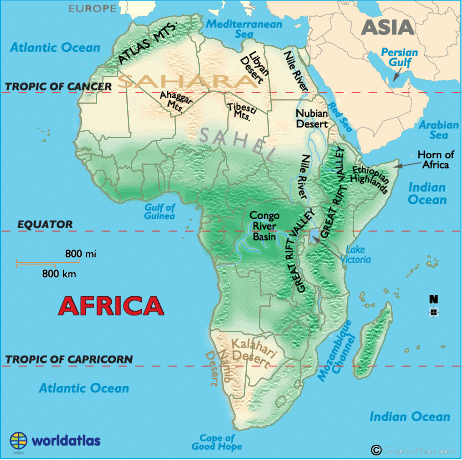
Africa belongs to all four hemispheres, and the bulk of the continent lies in the tropics.
It is joined to Asia by the narrow isthmus of Suez and separated from Eurasia at three different points (Strait of Gibraltar, Suez Canal, and Strait of Bab-el-Mandeb).
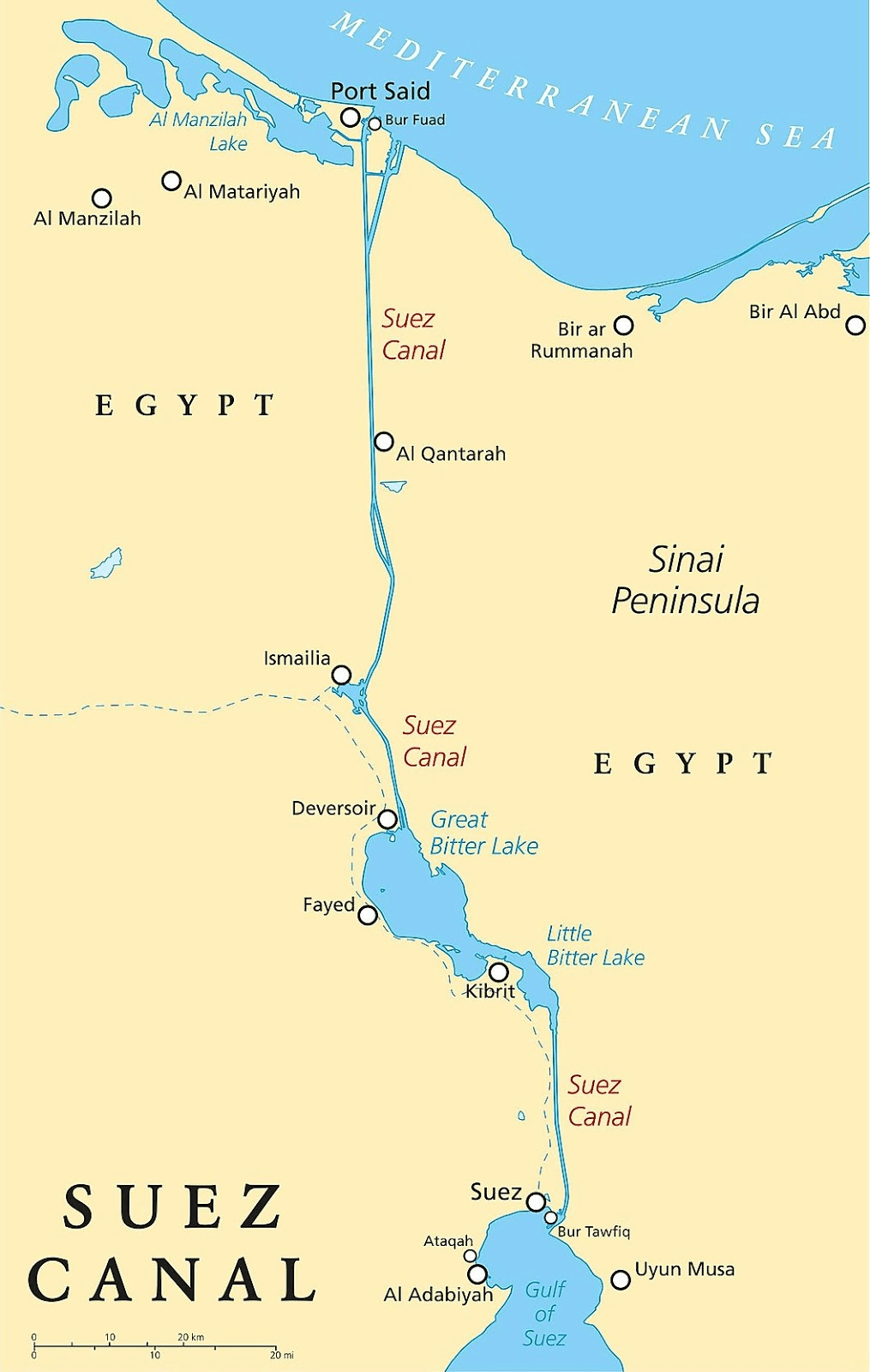
Africa is connected to Europe by the Strait of Gibraltar. It is connected to Asia by the Suez Canal. It is separated from Arabia by the Sinai Peninsula and the Strait of Bab-el Mandeb.
It is the only continent that is crossed by the Tropic of Cancer, Equator, and Tropic of Capricorn.
Greenwich Meridian passes through the western part of Africa. It is the only continent where the 0° latitude meets the 0° longitudes. These lines meet at the Gulf of Guiana.
Algeria is Africa’s largest country by area and Nigeria by population. Seychelles is the smallest country in Africa.
It is divided in half almost equally by the Equator. Africa has eight major physical regions: the Sahara, the Sahel, the Ethiopian Highlands, the savanna, the Swahili Coast, the rain forest, the African Great Lakes, and Southern Africa.
Africa is called the “Dark Continent’ because the greater part of its vast interior remained little known to the outside world until the last century.
Africa has 55 independent countries.
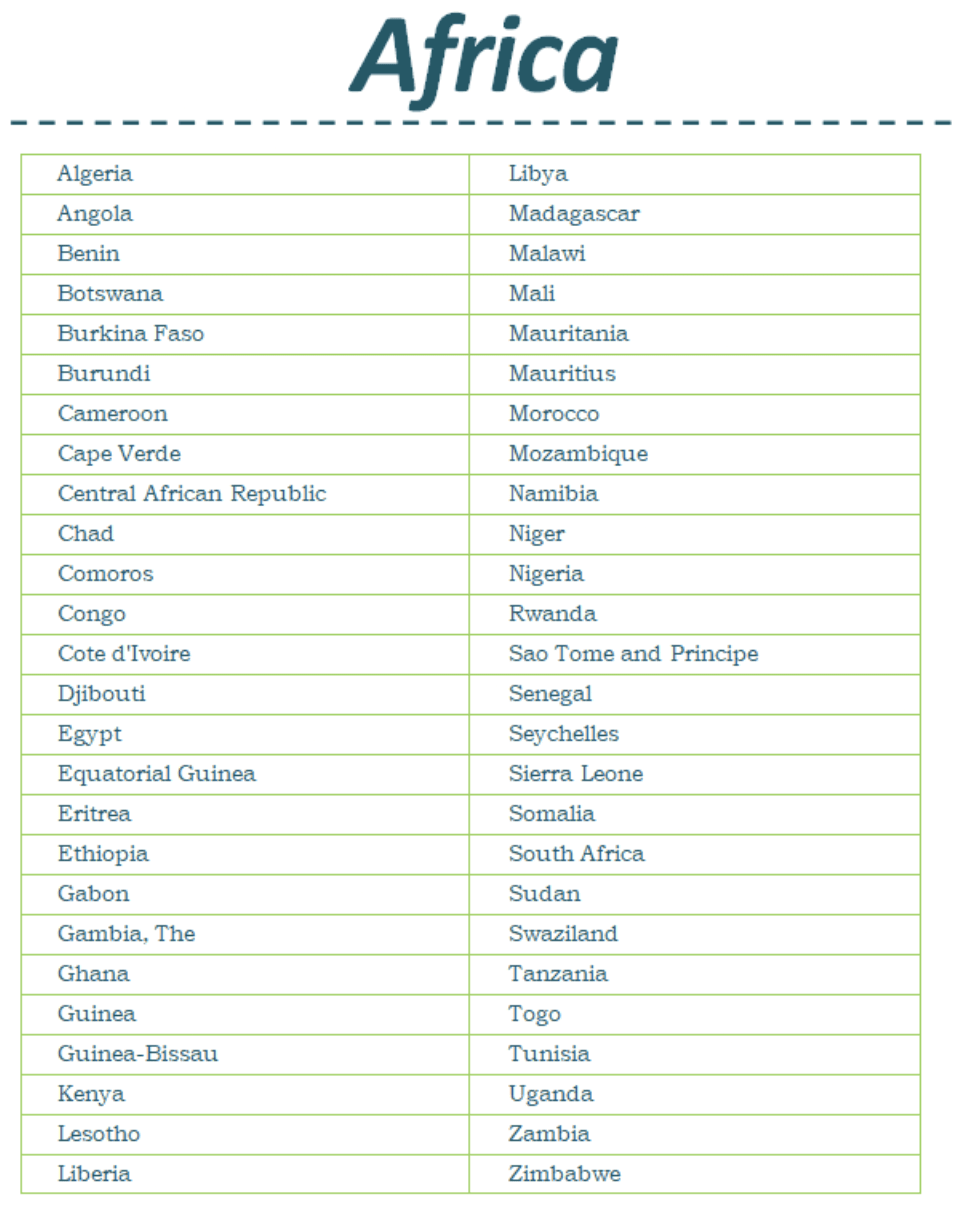
List of countries in Africa
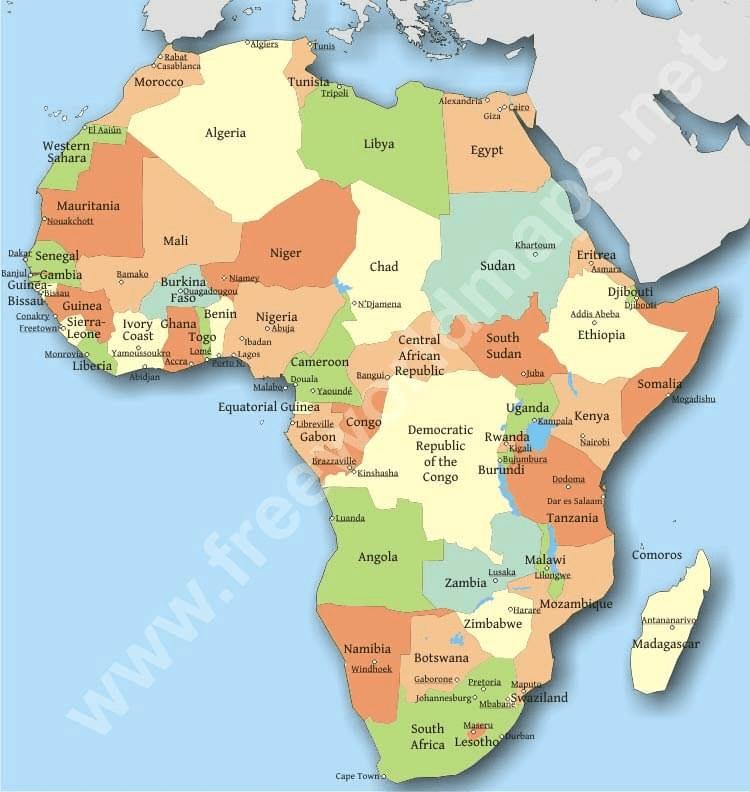
Regional divisions of Africa
The physiographic divisions of Africa are into the following six regions:
Northern Africa
Northeast Africa
Eastern Africa
Central Africa
Southern Africa
Western Africa
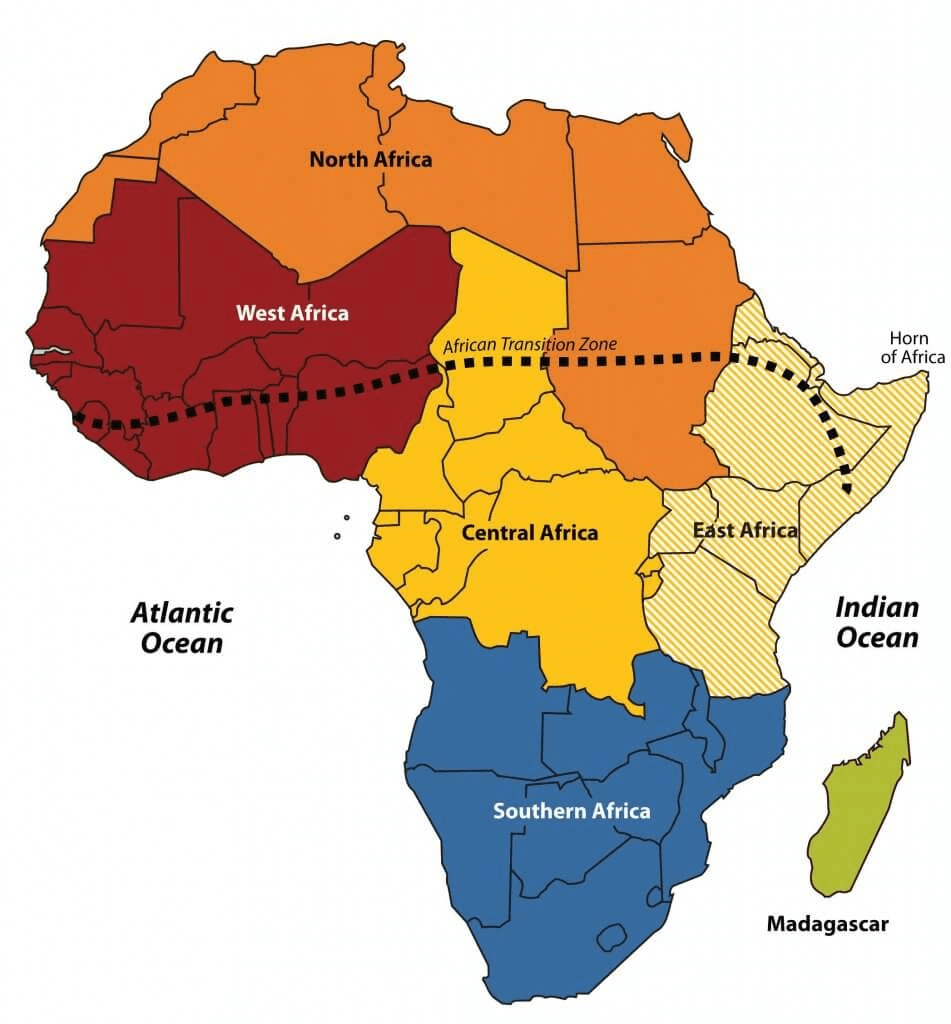 Northern Africa
Northern Africa
It extends from Algeria in the north, though, the Canary Islands, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Ceuta, Egypt, Libya, Madeira, Melilla, Morocco, Sudan, and Tunisia, It reaches up to Western Sahara.
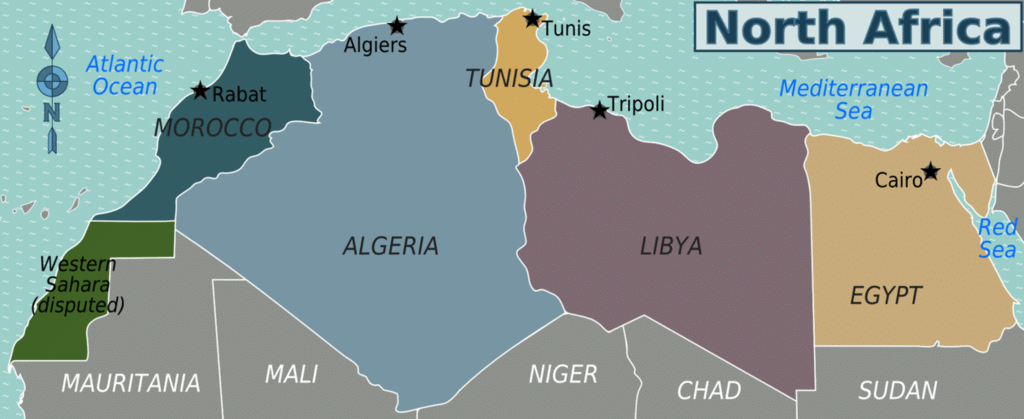
Northeast Africa
It is also called the horn of Africa, which extends several hundred kilometres into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It contains countries such as Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. 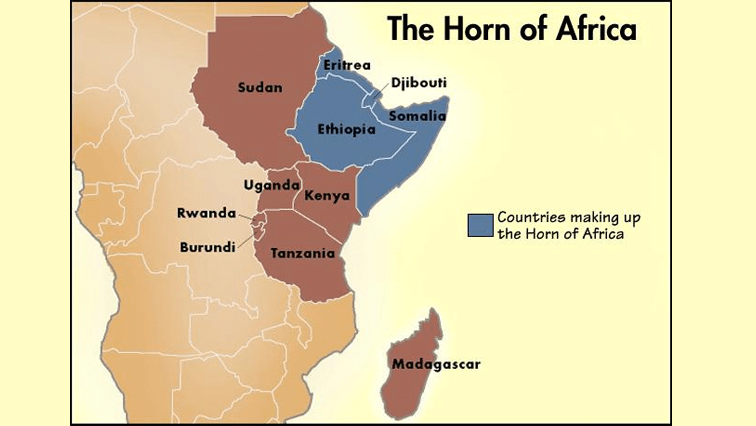
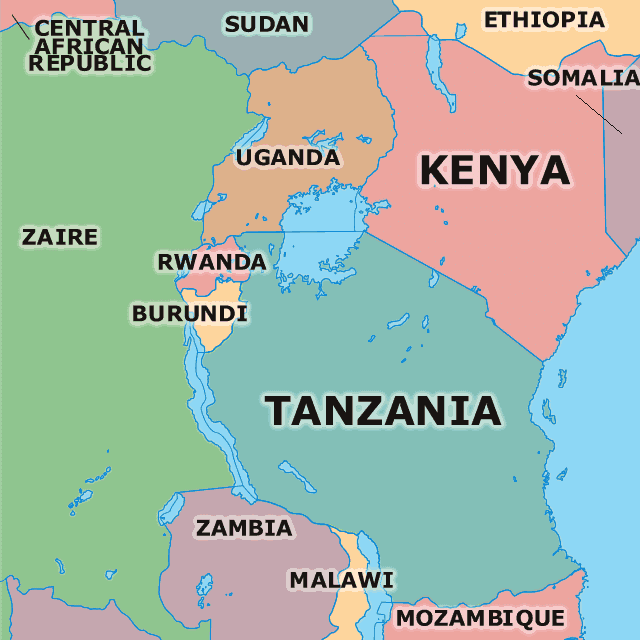
Eastern Africa
The extensive area stretches from the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa to Mozambique, including Burundi, Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mayotte, Mozambique, Réunion, Rwanda, Seychelles, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe.
Central Africa
It is a large landmass situated exactly in the middle of the continent covering Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, São Tomé, and Príncipe.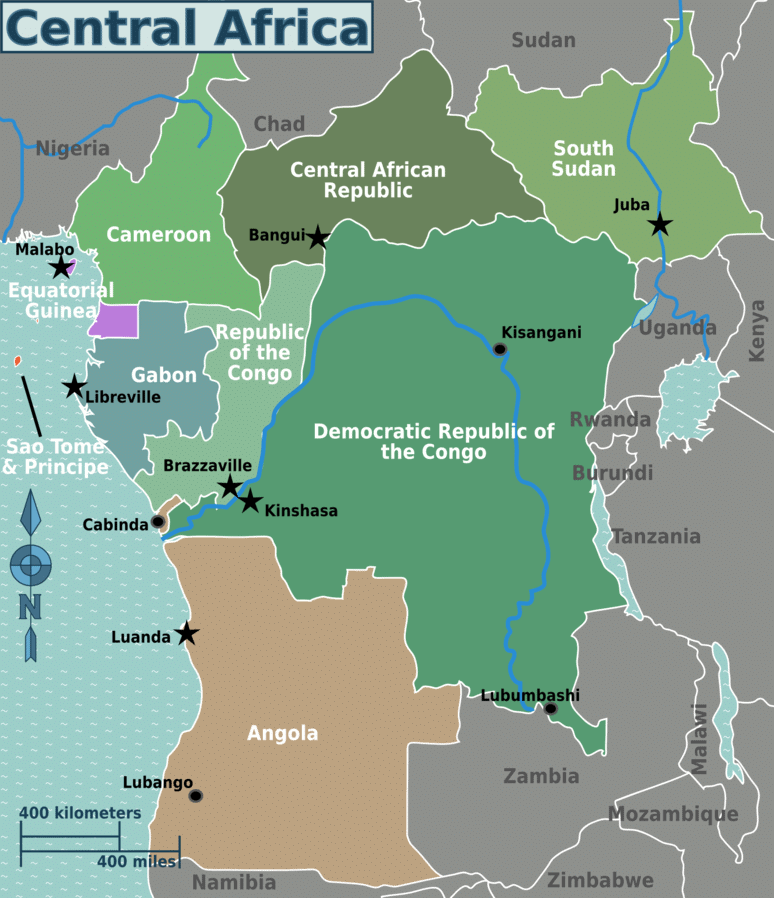
Southern Africa
It is the southernmost part of the continent and covers the countries such as Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, and Swaziland.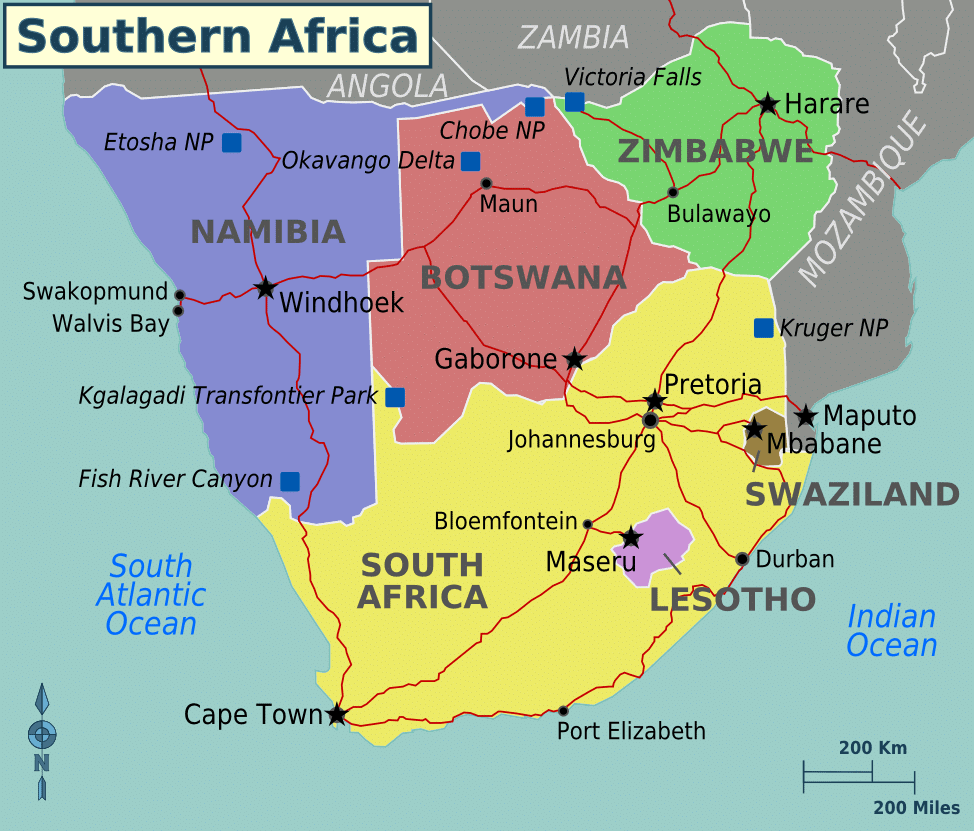
Western Africa
It is situated roughly at 100° E longitude covering countries like Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Saint Helena, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.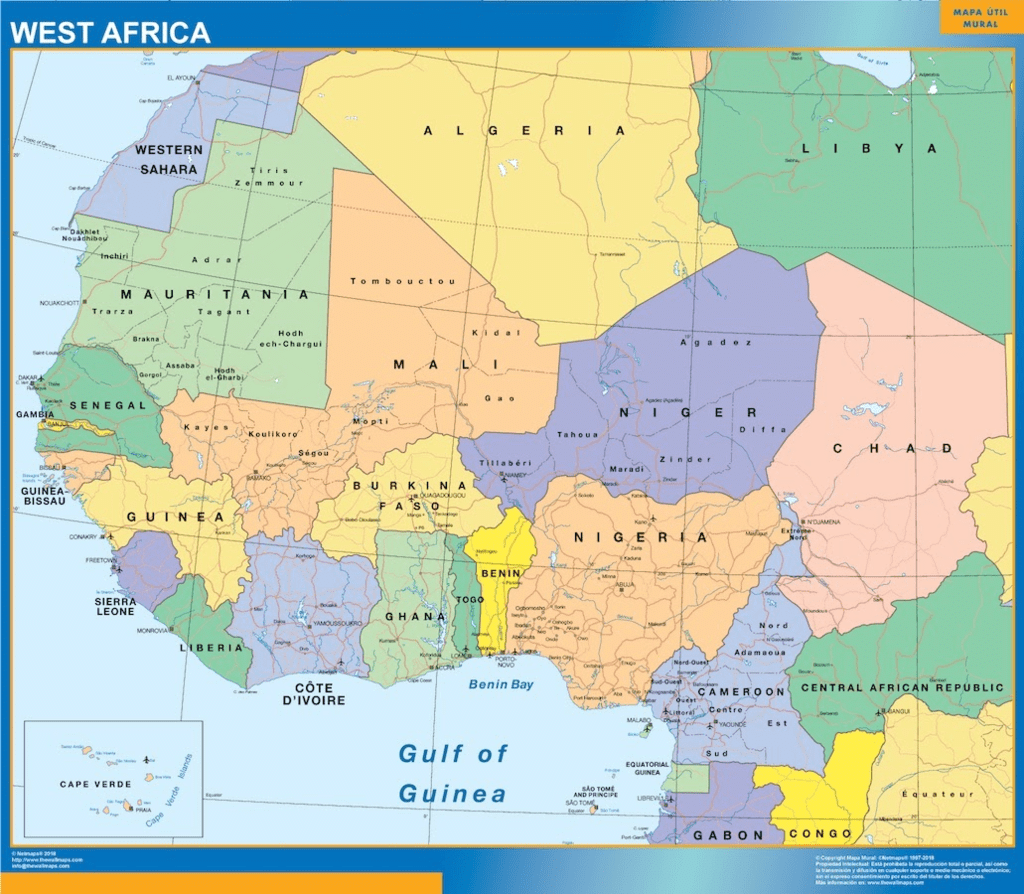
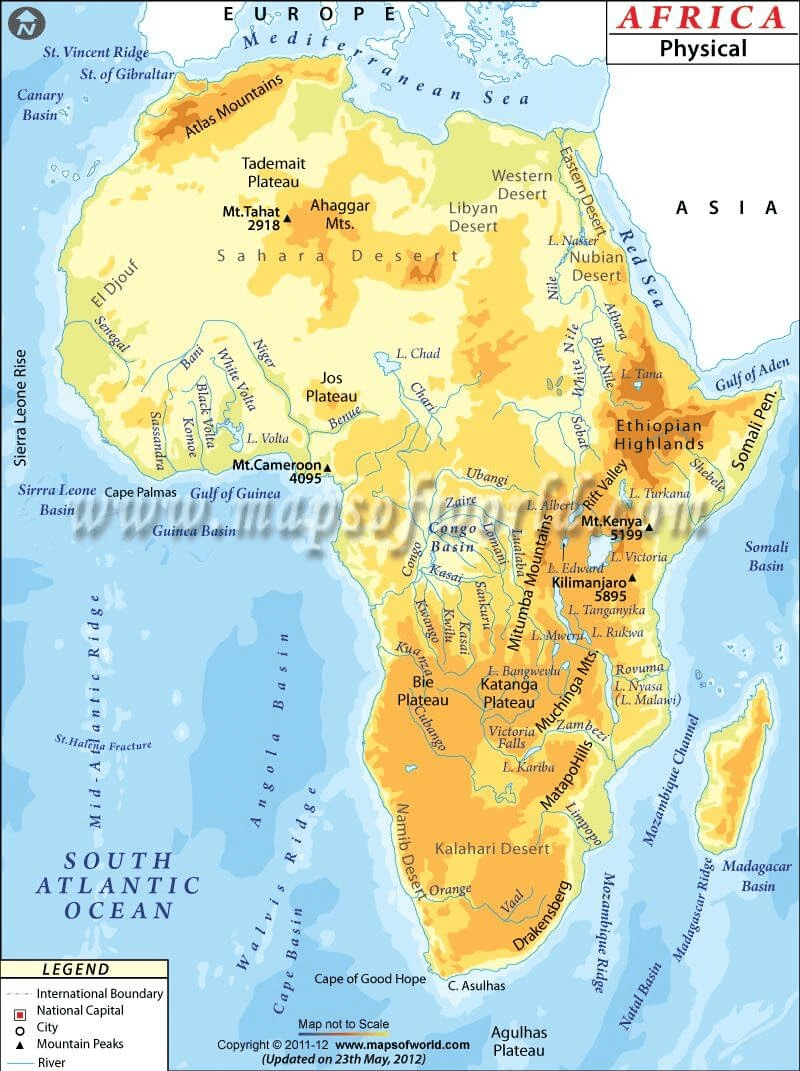
Major Physical Divisions of Africa
It is situated roughly at 100° E longitude, covering countries like Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Saint Helena, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
Major Physical Divisions of Africa
The major physical divisions of the African continent are:
The Plateau
The Fold Mountains
Deserts
Rivers
Islands
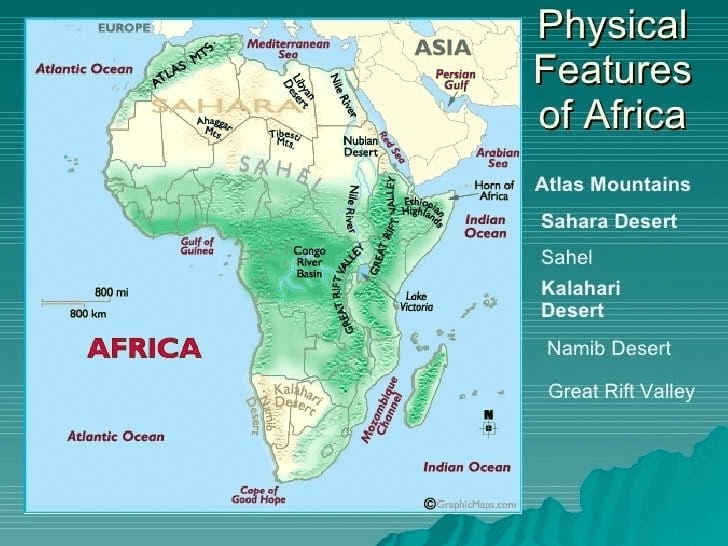
The Plateaus
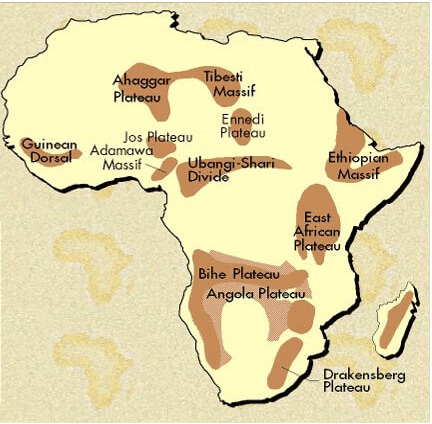
The vast African continents are famous for their saucer-shaped and steep-edged plateaus that are facing towards the coast and extending from Guinea coast to Somali Land and north Sahara to the Cape Province. These are divided into three groups:
South African plateau:
The South African plateau,,as far as about 12°S, bounded east, west, and south by bands of high ground which fall steeply to the coasts. The South African plateau is connected towards the northeast with the East African plateau.
East African plateau:
The East African plateau, with probably a slightly greater average elevation, and marked by some distinct features. It is formed by a widening out of the eastern axis of high ground, which becomes subdivided into a number of zones running north and south and consisting in turn of ranges, tablelands and depressions.
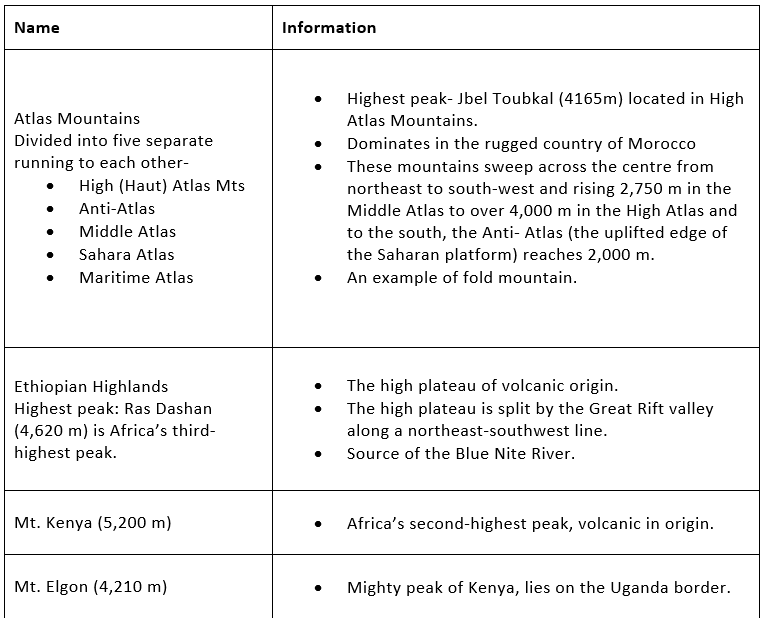
Ethiopian Highlands:
The third division of the higher region of Africa is formed by the Ethiopian Highlands, a rugged mass of mountains forming the largest continuous area of its altitude in the whole continent.
Plateaus
Katanga Plateau: Farming, ranching, resource-rich – copper and Uranium deposits
Ethiopian Plateau: Lake Tana (Source of Blue Nile), cooler despite close to the equator
Great Karoo: Semi-desert region
Bie Plateau: Important for copper, Agriculture, and cattle rearing
Adamawa Plateau: Savannah vegetation, Bauxite deposits
Mountains
Africa is famous for its newly formed folded mountains.
Prominent mountain ranges with some of the very high raised mountain peaks are the specialty of African Continents.
Some of the well-known mountain ranges are:
The Atlas Mountains:
It is situated on the northwestern part of the continent, stretching over an area of 2400 km towards the southwest direction across Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
The range is again subdivided into high, medium, and Anti – Atlas groups. The Jebel Toubkal is among such highlands or mountains whose height is 4165 m from sea level.
It is a physical separator between the extensive coasts of the Mediterranean and the Atlantic Sea and the Sahara Desert.
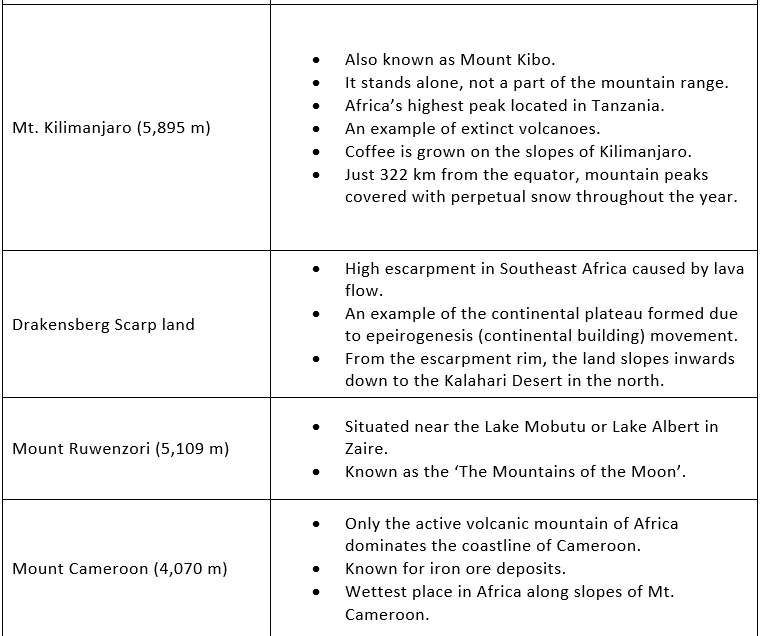
Ruwenzori Mountains:
Stretching over an area of 240 sq. miles, the range borders Uganda and Congo (Kinshasa) and is thought to be the “Mountains of the Moon.
Mount Stanley at Margherita Peak (5,119 m is the highest pick of this mountain system.
It is a gigantic horst of six separate glaciated masses that falls steeply westward to the Western Rift Valley.
Mount Elgon:
It is an extinct volcanic mountain situated in the northeast part of lake Victoria on the Uganda – Kenya border.
The height is about 4,321 km from the mean sea level.
As a volcanic mountain, it has a crater that is 610 m deep and 8 km across.
The Tibesti Mountains:
These are mostly situated in the northern part of Chad and spread west into northern Niger and the Southern border area of Libya.
They have a volcanic origin.
The highest peak is 3,415 m. from the mean sea level.
Ahaggar Mountains:
The Ahaggar Mountains, also known as the Hoggar, is a highland region in central Sahara, or southern Algeria near the Tropic of Cancer. They are located about 1,500 km south of the capital, Algiers. Mount Tahat is the highest peak (2, 918 m).
It has a volcanic formation.
The Drakensberg:
These mountains are the highest in Southern Africa, rising up at Thabana Ntlenyana at 3,482 m (11,422 ft) in height.
They are located in the eastern part of South Africa, running from some 1,000 km.
The highest peak is Thabana Ntlenyana at 3,482 m (11,422 ft). It is also the highest peak of Lesotho.
Mount Kenya:
Mount Kenya is the highest mountain in Kenya and the second-highest in Africa (after Mount Kilimanjaro). The highest peaks of the mountain are Batian (5,199m – 17,058 ft), Nelion (5, 188m – 17,022 ft), and Lenana (4,958 – 16,355 ft).
Mount Kenya is located in central Kenya, just south of the equator, around 150 km (95 miles) north-northeast of Nairobi.
Kilimanjaro:
Kilimanjaro, with its three volcanic cones, Kibo, Mawensi, and Shira, is an inactive stratovolcano in north-eastern Tanzania.
Kilimanjaro is the tallest free-standing mountain rise in the world, rising 4,600 m (15,100 ft) from its base and includes the highest peak in Africa at 5,895 meters (19,340 ft).
Important Mountains and Plateaus
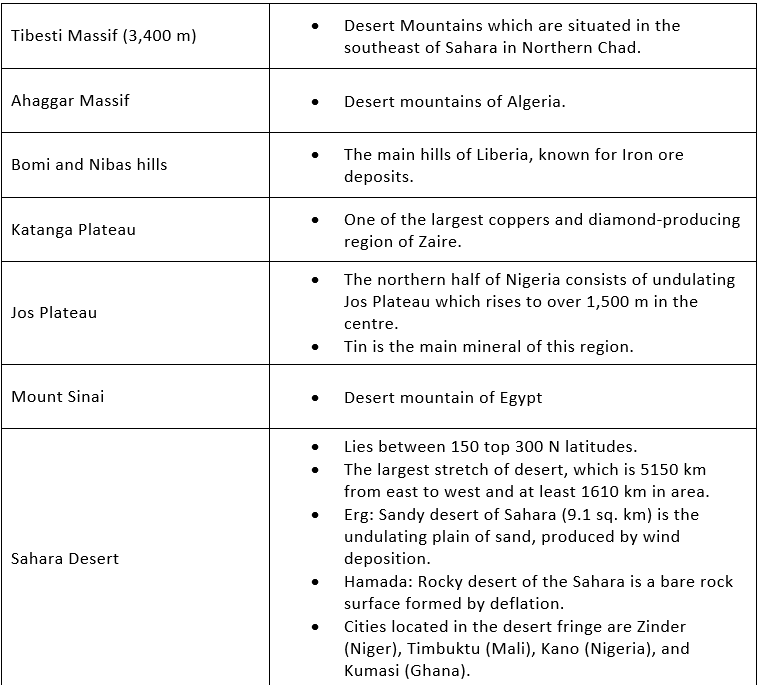

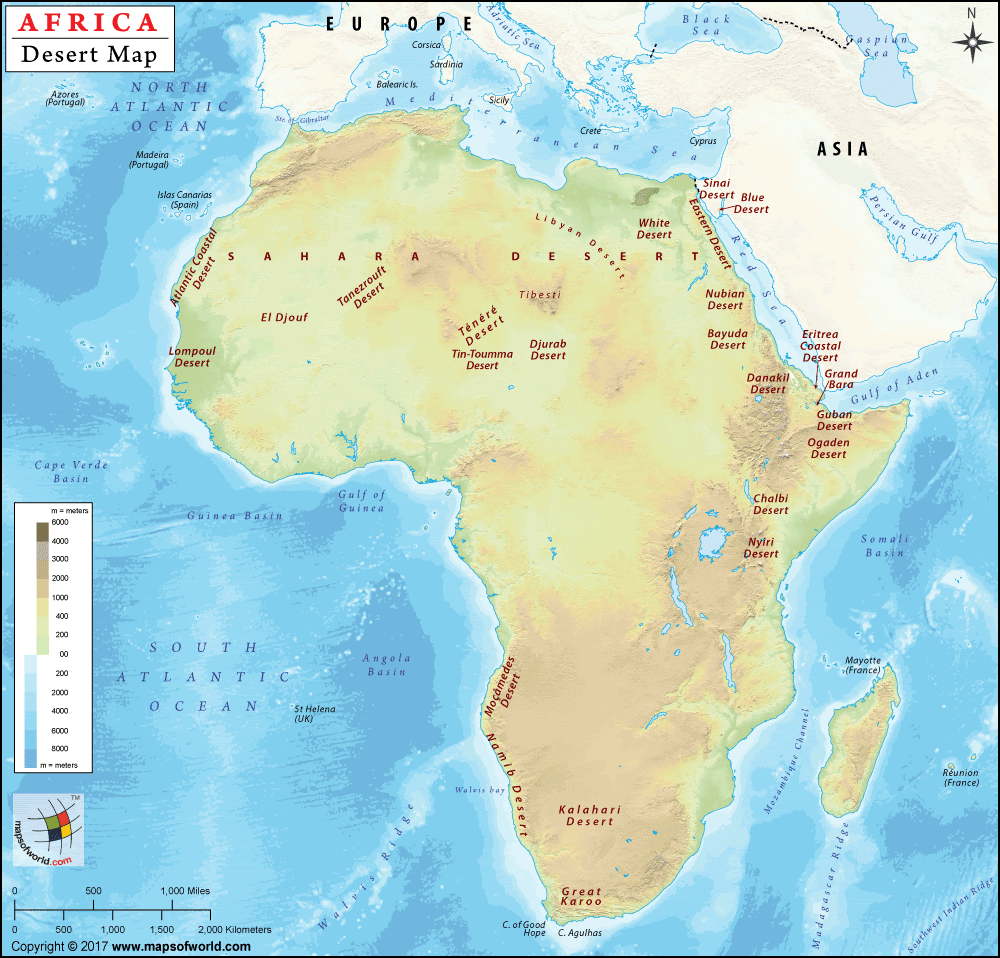
The Deserts
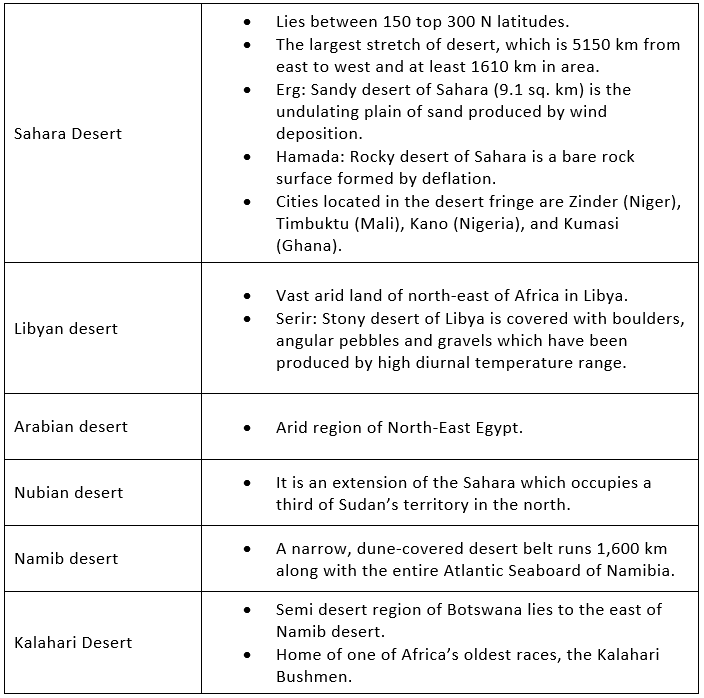
Sahara desert
The Sahara, the largest hot desert in the world, stretches across the entire width of North Africa. It covers an area of approx. 3,320,000 sq. miles.
The major countries contributing their land to Sahara deserts are Libya, Algeria, Egypt, Tunisia, Chad, Morocco, Eritrea, Niger, Mauritania, Mali, and Sudan.
The principal topographical features of the Sahara include shallow, seasonally inundated basins (chotts and dayas) and large oasis depressions; extensive gravel-covered plains (serirs or regs); rock-strewn plateaus (hammadas); abrupt mountains; and sand sheets, dunes, sand seas (ergs) and Oases( lush green area).
Desert greening
- Desert greening means exactly what it sounds like—the process of turning deserts into lush forests.
This isn’t only for deserts with vast never-ending seas of shifting sand dunes… semi-arid land is also included in desert greening.
The goal of the process is to reclaim parts of desert land, make them fertile, and use them for farming, forestry and other ecological reasons, such as preventing soil erosion and boosting biodiversity.
By converting tracts of desert into forests, some experts hope to help battle climate change and protect regions from its symptoms (like drought and famine).
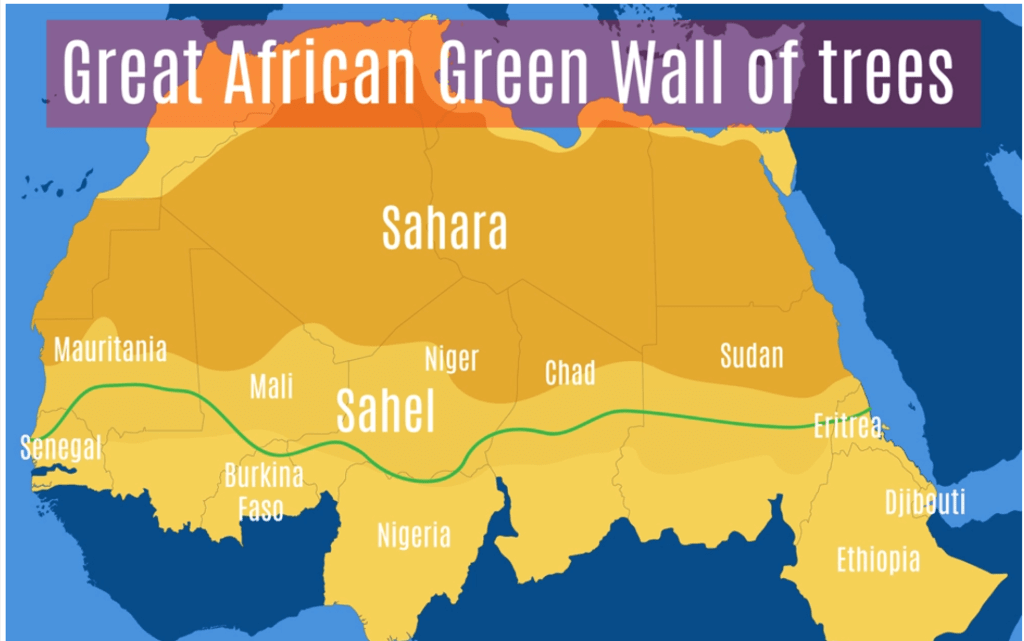
Nubian Desert
The Nubian Desert is the eastern region of the Sahara desert, between the Nile and the Red Sea. There is virtually no rainfall here, and there are no oases. It is in Egypt. It covers an area of 1,54,000 sq. miles approx.
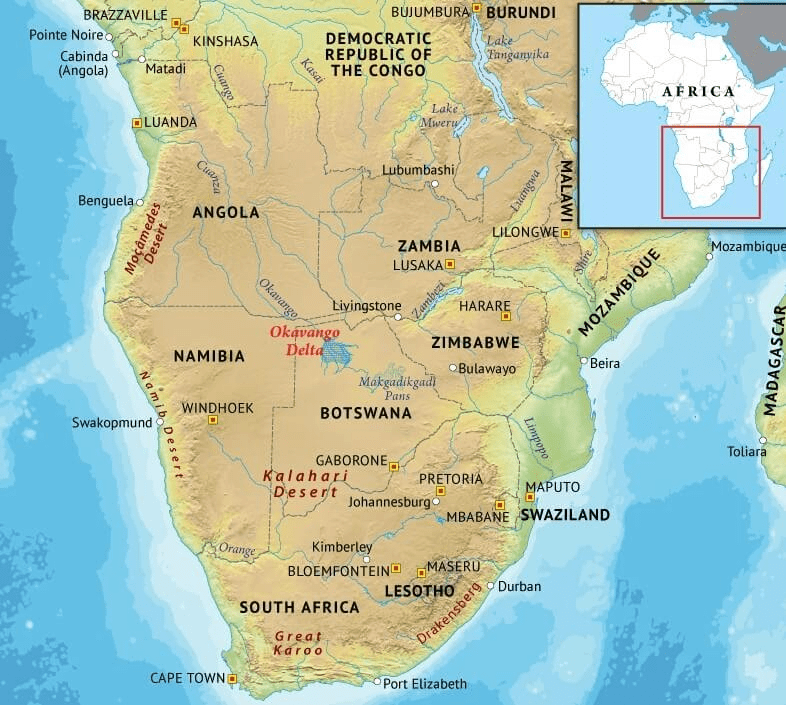
Namib desert
- Namib is a cool coastal desert in southern Africa. The Namib Desert is believed to be as old as 55 million years; thus, it is the oldest desert in the world.
The high sand dunes of the Namib Desert and the point where the desert meets the sea are the key attractions of this UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Kalahari Desert
- The Kalahari Desert lies in the south and the Namib Desert is along the southwest shore of Africa. It covers an area of 3,50,000 sq. miles and encroaching parts of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, Angola, and Zimbabwe.
San People have lived in the difficult terrain of the Kalahari Desert.
Famous for Dimond mining.
Okavango Delta
- It is one of the very few major interior delta systems that do not flow into a sea or ocean.
This delta comprises permanent marshlands and seasonally flooded plains.
The delta covers part of the Kalahari Desert and owes its existence to the Okavango (Kavango) River.
It is home to some of the world’s most endangered species of large mammal, such as the cheetah, white rhinoceros, black rhinoceros, African wild dog and lion.
Sahara Desert: Largest hot desert – subtropical HP zone, Tuareg tribes
Namib desert: Off-shore trade wind + cold Benguella current, sandy desert, Hottentots tribes
Kalahari Desert: Rain-shadow effect, stony-rocky desert. Bushmen tribe (the oldest surviving tribal group of Africa)
Nubian desert: Separated by Libyan desert by Nile river rocky desert
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of Africa- 1 - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the major geographical features of Africa? |  |
| 2. How does the Sahara Desert impact the geography of Africa? |  |
| 3. What role does the Nile River play in Africa's geography? |  |
| 4. How does the Great Rift Valley contribute to Africa's geography? |  |
| 5. What are the main challenges faced by Africa due to its geography? |  |