Geography of Africa- 3 | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
The Islands
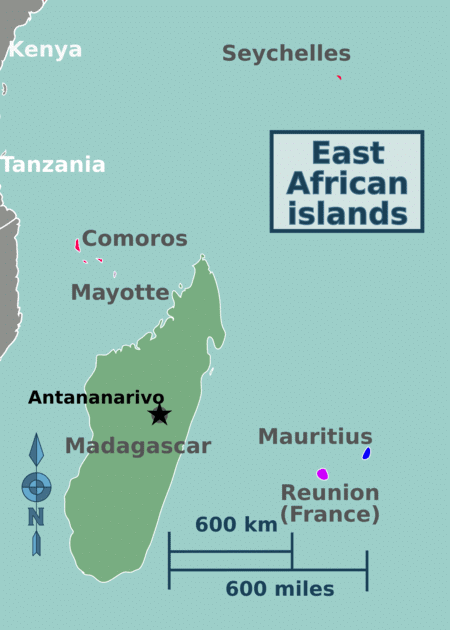
➤ There are very few islands near Africa
- Madagascar (Malagasy) in the Indian Ocean is the largest island in Africa.
- To the northwest, in the Atlantic Ocean, are the Canary Islands.
- West of Africa in the South Atlantic Ocean is the island of Saint Helena, where Napoleon died in exile.
- Zanzibar belongs to Tanzania and is closer to the Indian Ocean.
- Madeira – Portugal
- Canary – Spain
- Cape Verde
- Mauritius
- Reunion – France
- Comoros – France
- Seychelles
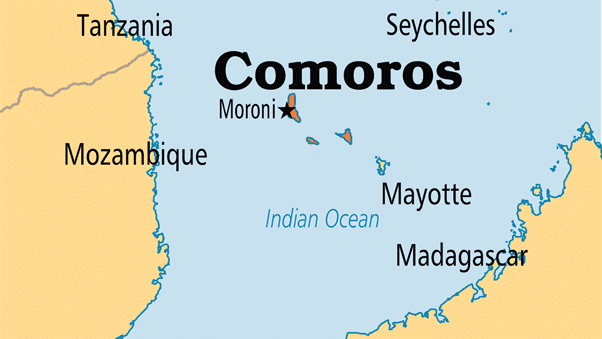
➤ Islands between Africa and Latin America
- All of them –British overseas territories
- Ascension Islands– UK military base
- St. Helena Islands – the exile of Napoleon
- Tristan De Cunha Island – the most remote island of the world
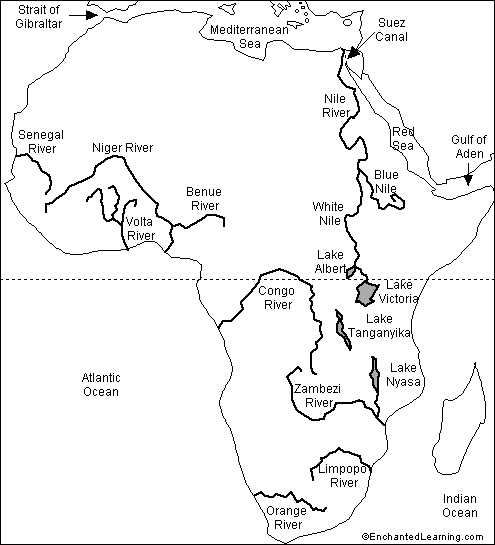
The Rivers of Africa
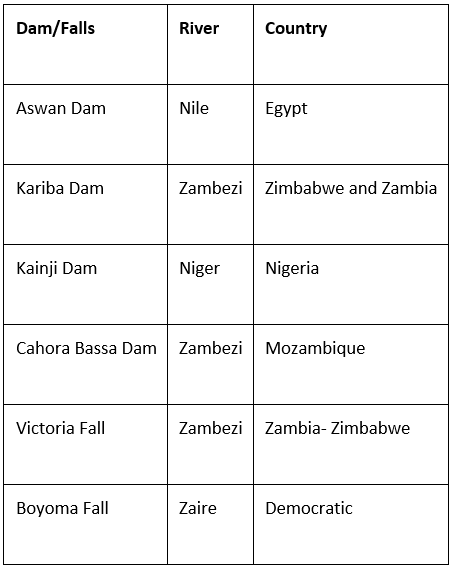
The most important ones are the Nile, the Congo, the Niger, and the Zambezi.
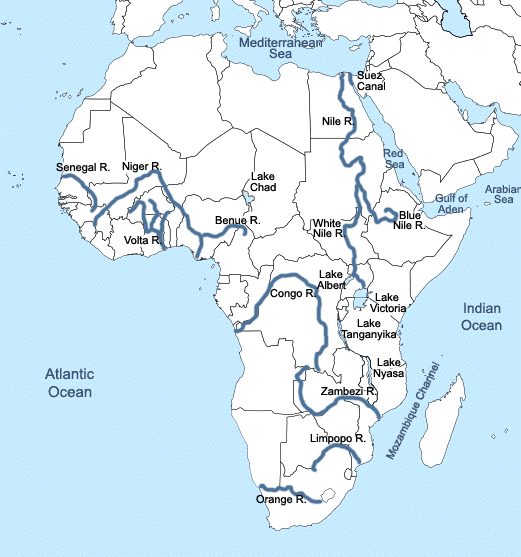
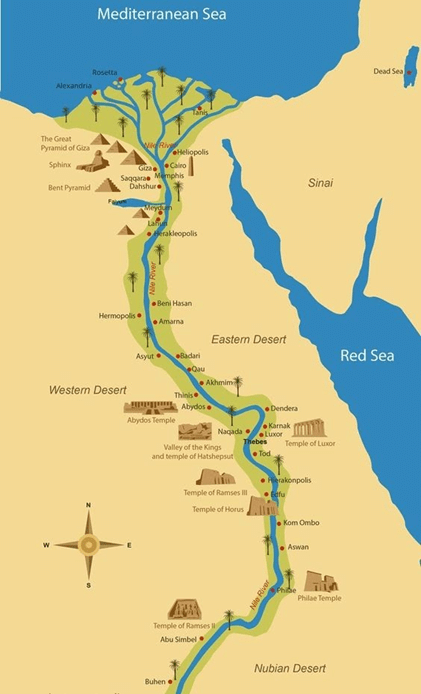
➤ River Nile
- This is the longest river in the world.
- It starts from many streams in the equatorial rainforest of the Lake Victoria and Ruwenzori Mountain (the mountains of the moon) region.
- From Lake Albert, it flows as the White Nile.
- At Khartoum, it is joined by the Blue Nile which starts from Lake Tana on the Ethiopian Highlands.
- The Nile flows from 3,000 kilometers through the dry Sahara Desert of Egypt and enters the Mediterranean Sea.
- Egypt is called the gift of the Nile because without the river it would have been a desert.
- Cotton cultivation,
- Petroleum at mouth, navigable, irrigation
- Aswan dam, lake Naseer
- Port Said and Alexandria at the mouth
- Cairo, Giza, Khartoum cities are on River Nile
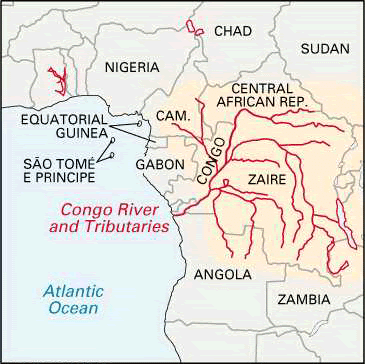
➤ River Congo or Zaire
- The Congo is the second-longest river in Africa.
- It starts from the south-west of Lake Tanganyika and flows into the Atlantic Ocean.
- The Zaire basin is one of the wettest regions of the Earth and is covered with dense impenetrable jungle.
- The river and its network of tributaries are not navigable because of rapids and waterfalls caused by the descent from the plateau to the coast.
- Origin: Katanga Plateau
- Boyoma waterfall
- Pigmy tribes
- Petroleum reserve at the mouth
- Crosses equator twice
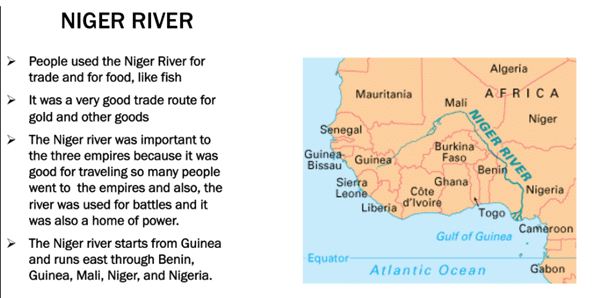
➤ River Niger
- This river is the chief river of West Africa. It rises from the Fout Djllon Mountain quite close to the sea but flows north and then turns south again to form a wide arc.
- Finally, it joins the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean.
➤ River Zambezi
- River Zambezi flows into the Indian Ocean.
- The famous Victoria Falls at the head of a long gorge is on this river.
➤ River Limpopo
- River Limpopo also flows into the Indian Oceans, which crosses the Tropic of Capricorn twice.
➤ River Orange
- This flows from the Drakensberg Mountains into the Atlantic Ocean.
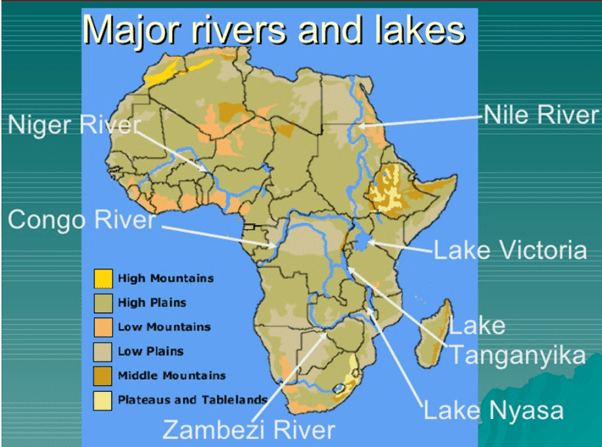
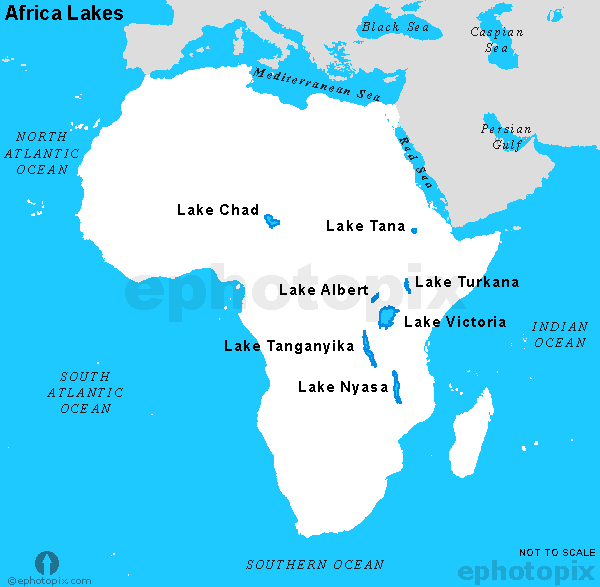
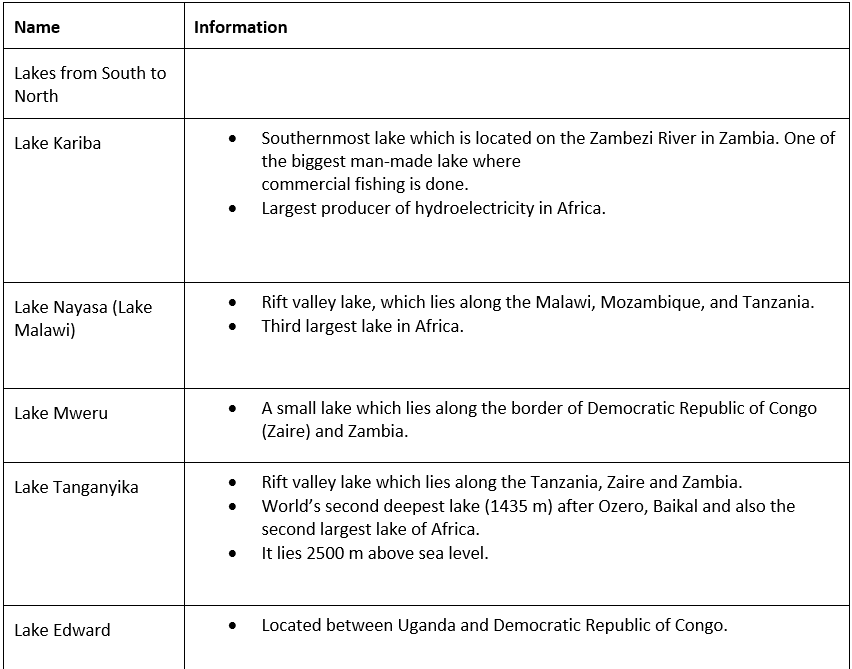
Lakes of Africa
- Lake Victoria is the second-largest freshwater lake in the world. It is the largest lake in Africa. It is situated on the block mountain between the two branches of the Great Rift Valley. The Equator passes through it. It is the source of the White Nile.
- The lakes of the rift valley. There is a string of lakes in the rift valley. Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa (Malawi) are the larger ones.
- Lake Tana is on the Ethiopian Plateau. It is the source of the Blue Nile.
- Lake Chad at the southern edge in the Sahara Desert is in a region of inland drainage. Streams start from the surrounding hills and flow into this lake instead of the sea. River Charl is the largest river in this area.
- Lake Nasser is on the river Nile. It is a man-made lake located between Egypt and Sudan.
- Lake Kariba is situated in the southernmost part of Africa, a Zambezi river. It is one of the biggest looks man-made like, and it is the largest producer of hydroelectricity in Africa.
- Lake Assal is situated in Djibouti and the lowest point in Africa
➤ Famous Lakes of Africa


Important Dams and Waterfalls
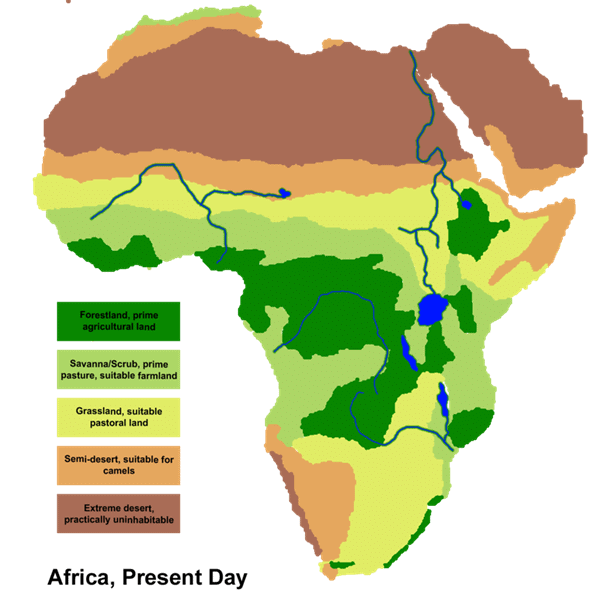
Climate
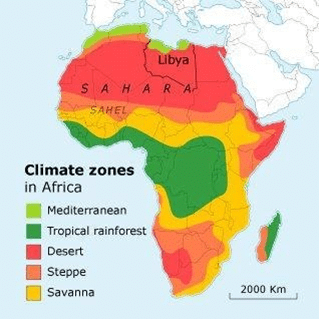
It is quite obvious that as a large continent Africa experiences a highly variable climate.
Keeping in view the prevailing weather conditions such as temperature, rainfall, humidity etc the climatic zones of Africa are:
- Equatorial rainforest climate
- Temperate grasslands
- Mediterranean Hot Summer
- Hot Desert Climate
- Tropical Wet/Dry (Savanna) Climate
Natural Vegetation
- There are extensive areas in Africa where few people live and where natural vegetation and wild animals have not been disrupted by such activities as farming or the raising of livestock.
- In some parts of the continent, large forest reserves have been established.
Tropical Rain Forests
- The large area of Africa is covered by tropical rain forests or selvas type of vegetation covering less than a tenth of the continent with heavy rain throughout the year. These forests contain several layers of vegetation.
- The top layer consists of the crowns of trees rising 125 to 250 feet (38 to 76 m) in height; the lower layers are arranged according to their height like shorter trees, shrubs, and vines respectively.
- They yield pulp, timber, and such cabinet woods as mahogany, ebony, and teak. Oil palms, rubber-producing trees and vines, orchids, and lilies are among the numerous kinds of plants found in these forests.
Tropical Savannas
- Savannas, covering perhaps one-third of the continent, consist of areas mainly growing grass.
- There are spots of woodlands, scattered trees, or shrubs, depending on the length of the dry season. Coarse grasses up to 12 feet (3.7 m) high and large woodlands of deciduous trees are found near the border of Tropical forest. They even include many evergreens found in tropical rain forests, such as oil palms, rubber trees, and African ebony trees.
- Away from the Equator to the north and south, rainfall decreases and there is a zone where there is a definite dry season unlike the equatorial region where it rains always.
- This is the Sudan type of climate and has tropical Grassland or Savanna vegetation.
- This region continues over the Eastern Highlands and forms a wide area around the equatorial forests.
- The grass is thick and coarse. In some places, there is the tall elephant grass.
Tropical Steppes and Deserts
- Increased aridity and longer dry seasons are the main features of tropical steppes.
- These are regions that grow short grasses only.
- Thorny acacias, dwarf palms, and jujube trees are found here. Steppes bordering on deserts no trees are spotted, rather widely scattered bunches of grasses grow.
- Vegetation at Oases includes date palms, fig-trees, willows, poplars, and tamarisks.
Mediterranean Forests
- Mediterranean type of vegetation in Africa is found along the northern and southern coast.
- Different variety of shrubs and small trees, both deciduous and evergreen are grown.
- The plants are able to withstand long, dry summers with waxy, leathery leaves and long taproots develop here.
- The northern region raises cork oak, olive trees, cedars, and pines; in the south, laurels, cedars, and ironwood.
- Grasses and low flowering plants grow only during the rainy months.
Montane Forests
- The Montane vegetation of highlands, particularly in Ethiopia and the mountains of the Great Rift Valley are such examples.
- Depending on elevation, latitude, and direction of the winds vegetation grows.
- The region under Montane forests yields valuable timber and cabinet woods along with bamboo and wild varieties of coffee and banana. The slopes of the mountain are covered with thick evergreen forests.
- The High Veld of southern Africa is temperate grassland between 3,500 and 11,000 feet (1,070 and 3,350 m) above sea level.
Mangrove Forests
- Mostly found along the African coast, but are most extensive along the Gulf of Guinea.
- A variety of other trees tailored to life in muddy estuaries and tidal flats are found other than Mangrove.
- Swamp and marsh also occur along the larger rivers and lakes of western and central Africa. Papyrus, tall grasses and lotus are the most common plants.
Mineral reserve of Africa
- Petroleum
- Coal
- Iron
- Diamonds
- Gold
- Uranium, Platinum
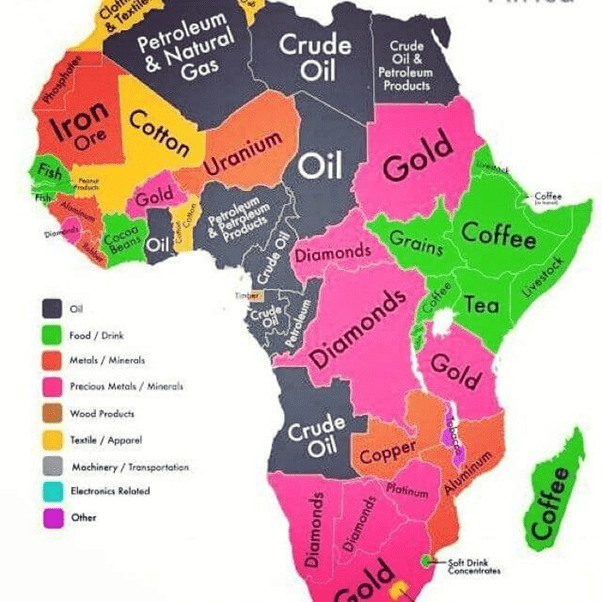
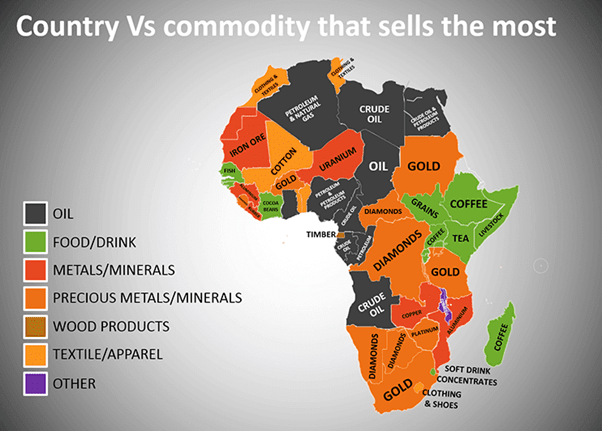
Agriculture
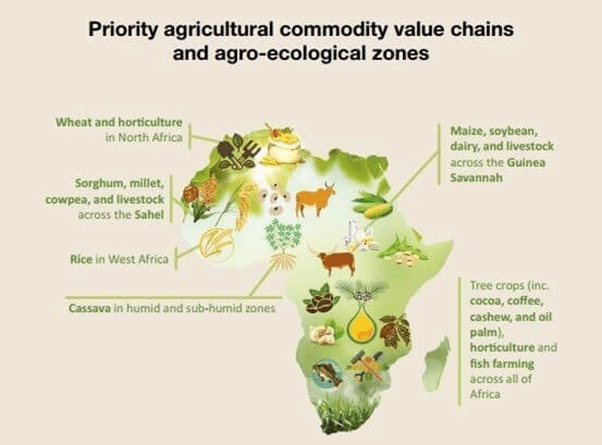
➤ Some of the most famous tribes in Africa
- Zulu, South Africa.
- Xhosa, South Africa
- Karo, Ethiopia.
- Hamar, Ethiopia
- Yoruba, Nigeria.
- Himba, Namibia.
- San Bushmen, Kenya
- Samburu, Kenya
- Maasai, Kenya, and Tanzania.
- Hadzabe, Tanzania
Sahel Region
Sahel region is an ecoclimatic and biogeographic zone of transition in Africa between the Sahara Desert to the north and Sudanian Savanna to the south. It stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea.
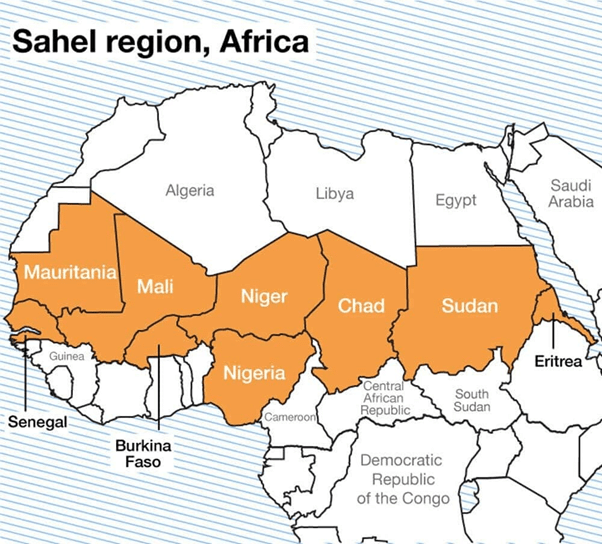
Geographic definitions of the Sahel region vary. Commonly, the Sahel stretches from Senegal on the Atlantic coast, through parts of Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and Sudan to Eritrea on the Red Sea coast.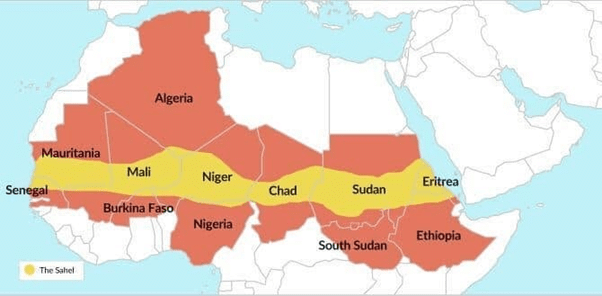
|
745 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of Africa- 3 - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What are the major islands in Africa? |  |
| 2. How did the islands in Africa form? |  |
| 3. What is the geographical significance of the islands in Africa? |  |
| 4. Are there any cultural differences between the islands in Africa and the mainland? |  |
| 5. How can one explore the islands of Africa? |  |





















