Geography of North America- 2 | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Islands |

|
| Drainage Pattern |

|
| Seas in North America |

|
| Important Industrial Centers of North America |

|
Islands
The world-famous islands of North America are:
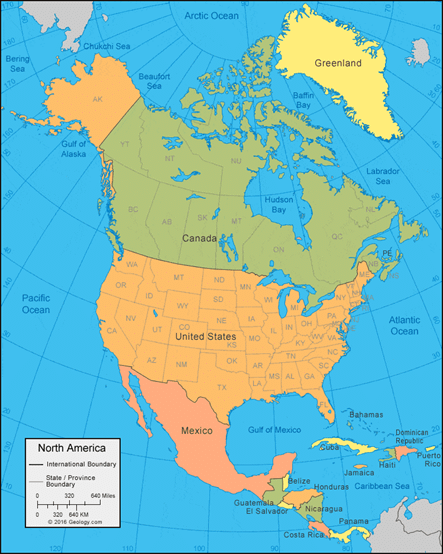
Vancouver Island
- It is situated on Canada’s Pacific Coast, is known for its mild climate and thriving arts community.
- It is separated from the British Columbia mainland by the Strait of Georgia and Queen Charlotte Strait and from Washington by the Juan De Fuca Strait.
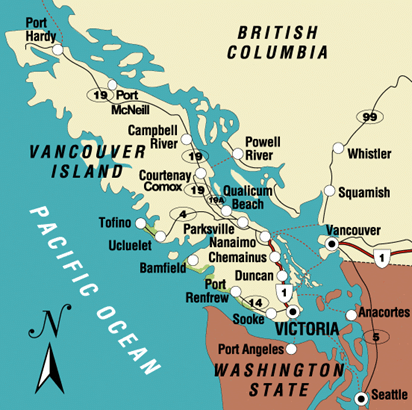
Greenland
- It is a massive island situated between the Atlantic and Arctic oceans and 80% of its land is covered by ice.
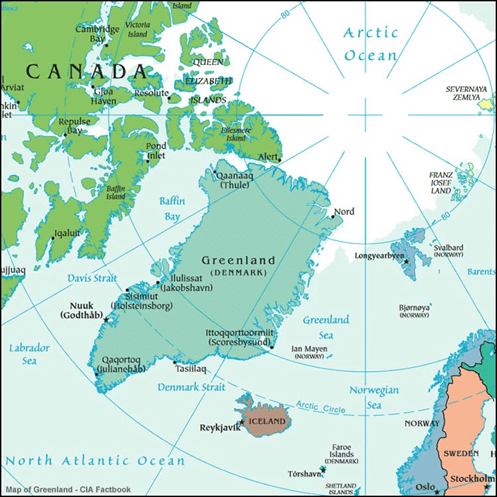
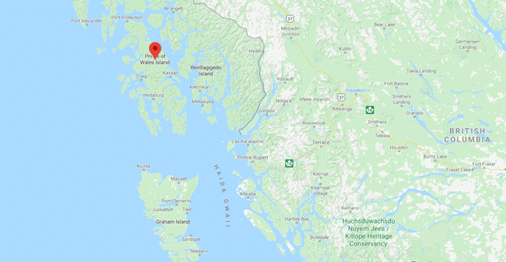
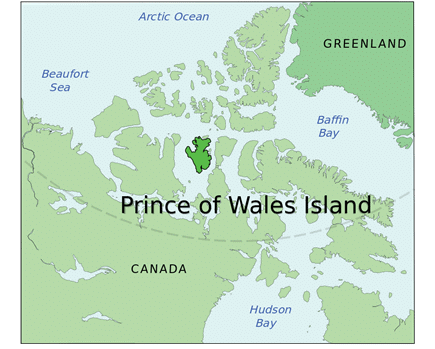
➤ Prince of Wales Island
- It is one of the islands of the Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle.
- This ranks four among the island in size.
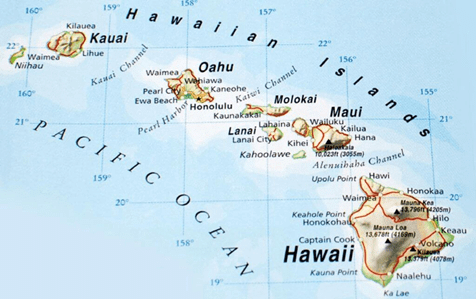
➤ Hawaii Island
- It is otherwise known as the Big Island provides a vast canvas of natural environment and it is the largest island of the Hawaiian archipelago in the Central Pacific.
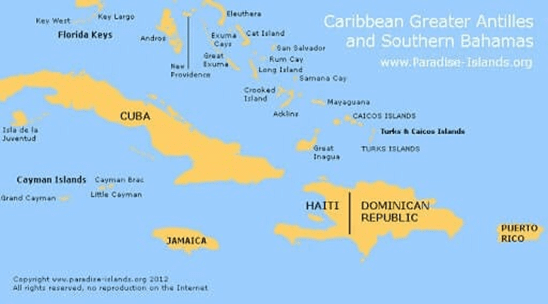
➤ Cuba Islands of Antilles
- It is known as the sugar bowl of the World and its vast source of metallic resources include cobalt, nickel, iron ore, chromium, and copper.
- Other resources include timber, petroleum, silica, salt, and arable land.
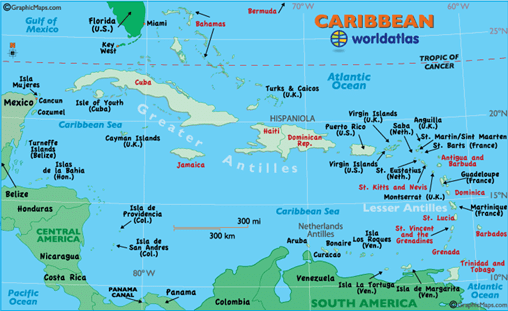
➤ Bermuda Island
- It is the territory of the British Islands in the North Atlantic and famous for its pink sand beaches such as Elbow and Horseshoe Bay.
Drainage Pattern
There are many rivers in North America. River of North America can be grouped according to the seas they drain into, like
- Rivers draining into the Gulf of Mexico
- Rivers draining into the Atlantic Ocean
- Arctic Ocean drainage
- Pacific Ocean Drainage
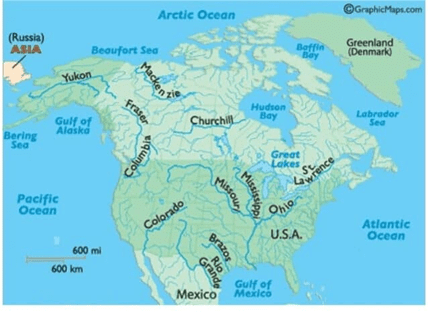
➤ The rivers draining into the Gulf of Mexico
- These are the Mississippi, Missouri and their tributaries drain the whole of the lower Central Lowlands.
- They start from the Western Cordilleras.
- The Ohio and Tennesse.
- Rivers which are also tributaries of the Mississippi but have their source in the Appalachians are exceptions.
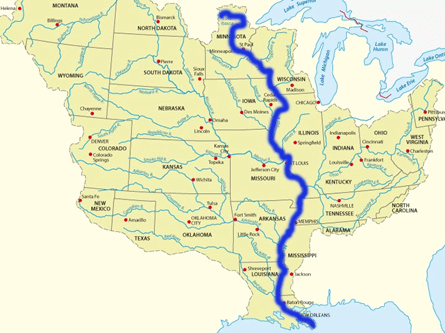 Mississippi River
Mississippi River
➤ Rivers draining into the Atlantic Ocean
- River St. Lawrence is the large river of this group.
- In this group, the smaller rivers of the Fall Line can also be included.
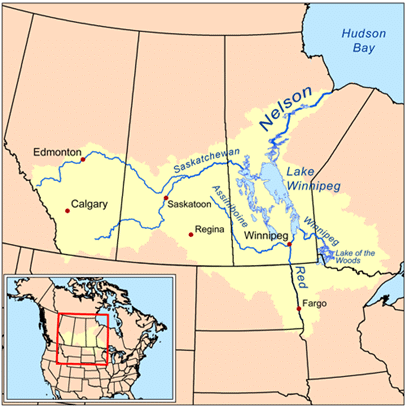
➤ Arctic Ocean drainage
- River Mackenzie has many shallow lakes on the Canadian Shield.
- River Nelson flows into the Hudson Bay.
➤ Pacific Ocean Drainage
- River Yukon in Alaska, Columbia, Fraser, and Colorado along the west coast.
- The Colorado River cuts across the Colorado plateau and forms the world’s most famous and attractive deep gorges, known as grand canons having nearly one km depth.
- Among the other rivers, the Yukon, the Fraser, the Snake, the Humboldt, the Sacramento, the San Joaquin, etc. are well known.
Seas in North America
➤ Caribbean Sea
- It is a sub-oceanic basin bordered by coasts of Venezuela, Colombia, and Panama; to the west by Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Guatemala, Belize, and the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico; to the north by the Greater Antilles islands of Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico; and to the east by the north-south chain of the Lesser Antilles, consisting of the island arc that extends from the Virgin Islands in the northeast to Trinidad.
➤ Beaufort Sea
- It is situated in the north of Canada and Alaska is known to be the marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean covering an area of 184,000 sq. miles and an average depth of 3,239 ft (1,004 m).
➤ Hudson Bay
- It is known as the second-largest bay in the world which encompasses an area of 1,230,000 square kilometers (470,000mi) and a large body of Saltwater.
➤ Labrador Sea
- It is bordered by continental shelves and separates Canada from Green Land.
➤ Bering Sea
- It is situated in the extreme North of North America separating the continents of Asia and North America.
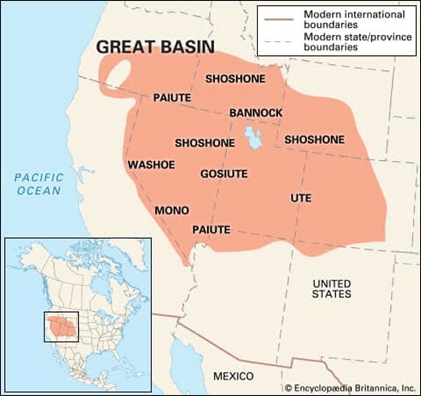
➤ Inland Drainage System
- The Great Basin area in the Rocky Mountains (Middle) has rivers that do not reach the coast but terminate in the land. This is the Inland Drainage System.
- The rivers are small, seasonal, and end up in saline lakes.
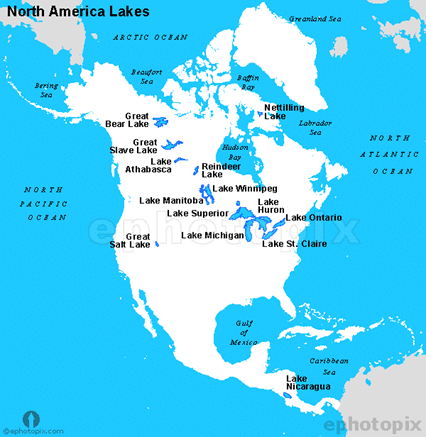
Lakes in North America
- The Lakes of the Canadian Shield are freshwater bodies.
- The Great Salt Lake between the Rockies and the Sierra Nevada has a high salt content and is an area of ‘Inland drainage’.
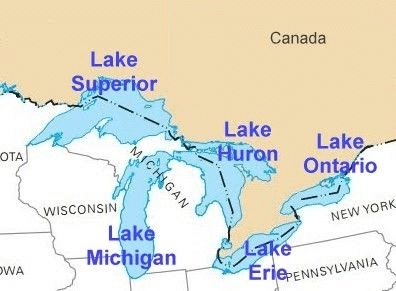
- Lake Erie in Ontario, Canada, and Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania in the USA.
- Lake Huron in Ontario, Canada, and Michigan in the USA.
- Lake Ontario in Ontario, and New York in the USA.
- Lake St Clair in Ontario, and Michigan in the USA.
- Lake Superior in Michigan, Minnesota, Wisconsin in the USA.
Resources
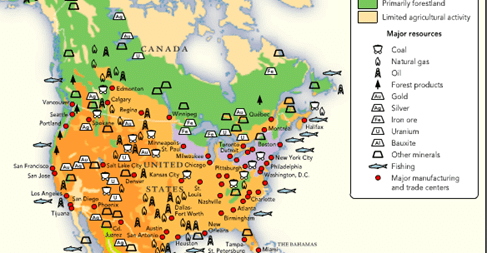
Agriculture
(i) From the freezing Arctic to the tropical jungles of Central America, North America enjoys more climate variation than any other continent.
(ii) Almost every type of ecosystem is represented somewhere on the continent, from coral reefs in the Caribbean to the ice sheet in Greenland.
(iii) These differences contribute to North America’s variety of agricultural industries, which are often divided by climate zone:
- tropical zone,
- subtropical zone,
- The cool temperate zone,
- dry zone
➤ Tropical Zone
- Farmer’s harvest oranges, sugar cane, coffee, cocoa, and bananas.
- These crops grow on coastal plains and humid mountain slopes. Cotton and hemp are cultivated in the warmer and drier intermediate climate zone.
- These crops are important exports for Central American countries.
➤ Subtropical Zone
- Fruits, vegetables, cotton, and tobacco are predominant in the warm, subtropical zones of northern Mexico and the United States.
- Important agricultural areas in this zone include the Rio Grande Valley (citrus fruits) in the U.S. state of Texas and Mexico, California’s Central Valley (fruits and vegetables), the Gulf Coastal Plain (vegetables), and the sandy valleys of the Appalachians (cotton and tobacco).
- These areas benefit from ample rain and warm air currents.
➤ Cool Temperate Zone
- Important agricultural areas in this climate include the Finger Lakes region of New York in the U.S.; the Niagara Peninsula in the Canadian province of Ontario; the Columbia River basin in the U.S. state of Washington and the Canadian province of British Columbia; and the valleys of the Appalachians.
- These areas benefit from excellent drainage and predictable, established frosts.
- The Dairy Belt, Corn Belt, and Wheat Belt are three agricultural areas in the continent’s cool temperate zones.
- Dairy animals, including cows, goats, and sheep, feed on the hay and hardy small grains that thrive in New England and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence region along the Atlantic coast. This is the Dairy Belt.
- The Corn Belt, located between the Ohio River and the lower Missouri River, receives ample water and strong summer sun, ideal for corn and soybeans.
- West of the Corn Belt, the Wheat Belt stretches from the U.S. state of Kansas through the Canadian Prairie Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. This vast area of the Great Plains allows wheat to be cultivated in both winter and spring.
➤ Dry Zone
- Dry zones, common in the southwestern U.S. and northern Mexico, are ideally suited for livestock ranching.
- Ranches with thousands of cattle are common in this region. Traditionally, livestock fed on locally grown fodder such as prairie grasses. However, irrigation for fruit and cotton farming has drained water supplies in the region.
- Native grasses cannot nourish the huge herds of livestock kept by ranchers. Cattle, sheep, hogs, and other livestock are less likely to graze than to eat corn-based feed.
- In fact, most of the corn grown in the Corn Belt is feeder corn used for livestock feed.
Forestry
- Forestry is the management, cultivation, and harvesting of trees and other vegetation in forests.
- In the Pacific Northwest, for instance, logging companies harvest cedar, fir, and spruce trees.
- Lumber from these trees is exported around the world for construction.
- Some of the continent’s largest paper mills are found in these temperate rain forests.
- In addition to paper, paper mills produce cardboard and fiberboard.
- Forestry is a major economic activity for much of North America.
- In the United States, the timber industry is strong in the Pacific Northwest, the Gulf states, and South Atlantic coastal plains.
- In Canada, forestry is a major industry in the provinces of Quebec, Ontario, and British Columbia.
 |
Download the notes
Geography of North America- 2
|
Download as PDF |
Mining
- North America is a leading producer of coal, used in energy production; bauxite used to create aluminum; iron and copper, both used in construction; and nickel, used to create steel, which North American companies export around the world.
- Gold and silver mines operate in the western part of the continent. Visitors to Crater of Diamonds State Park, a mine in the U.S. state of Arkansas, can search for their own diamonds.
Coal
- Coal remains a primary industry for the U.S. and is often linked with states near the Appalachians.
- Coal can be mined underground or in large, open pits. Around 20% of the World’s Coal is mined in Pennsylvania, USA.
Metallic minerals
- Large deposits of iron ore are found in the areas around Lake Superior and the Eastern part of the Canadian shield. Iron is also found in the southern Appalachians.
- The USA is one of the largest producers of copper in the world. It is mined extensively around the great lakes and the Rocky Mountains.
- Mexico is the world’s largest producer of silver. Large deposits of silver are found in the USA and Canada too. It is a byproduct of the Zinc industry as well. Chihuahua is the largest silver mine in the World. It is in Mexico.
- Canada and the US produce a substantial amount of Gold which is mined in the Rocky Mountains. California and Alaska saw the Gold rush in the early 1900s.
- Canada produces about 90% of the world’s Nickle.
- Canada is also the largest producer of Asbestos, Zinc, and platinum and the second-largest producer of cobalt, Uranium, and radium. Note that China is also one of the World’s largest producer of Asbestos.
- The USA is one of the world’s largest producer of Uranium and Sulphur.
Drilling
- North America is home to vast deposits of oil and natural gas, which are drilled for energy and fuel.
- Oil and gas extraction are key elements of North America’s economy. The United States, Canada, and Mexico are among the world’s top oil producers.
- The Athabasca tar sands, in the Canadian province of Alberta, are the world’s largest reservoir of heavy crude oil.
- More than 20 national and international extraction projects are established in the Athabasca tar sands.
- Large reserves of Petroleum are found in North America in a great arc from Alaska to Texas in the USA.
- The United States is the top oil-producing country in the world, with an average of 17.87 million b/d, which accounts for 18% of the world’s production.
- The U.S. overtook Russia in 2012 for the No. 2 spots and surpassed former leader Saudi Arabia in 2013 to become the world’s top oil producer.
- Much of the increased U.S. production is attributable to fracking in the shale formations in Texas and North Dakota.
- The U.S. has been a net exporter of oil (i.e., exports exceed imports) since early 2011.
- Mexico leads other North American countries as one of the top oil exporters in the world, largely because of its reserves in and around the Gulf. (Although both the United States and Canada produce more oil than Mexico, they also consume far more.
- Both countries are mostly importers, not exporters, of oil and natural gas.)
Important Industrial Centers of North America
United States of America
➤ West Coast Important Cities
- Seattle – world’s largest aircraft assembly center. Lumbering, fish canning, aluminum smelting electrical engineering are important industries.
- San Francisco – known as ‘The City of Golden Gate’. Famous for oil refining and ship building.
- Los Angeles – known for its film industry – Hollywood.
➤ Great Lake Region
- Famous for heavy industries and iron and steel.
- Important cities – Chicago, Pittsburg, Cleveland, Toledo, Detroit, etc.
- Detroit – greatest automobile region of USA
- Akron – world’s largest synthetic rubber and tyre making center.
- Pittsburg – highest production of Iron and steel
➤ Texas
- Houston – Oil refinery, shipbuilding, chemical, and machinery are important industries located here.
➤ Canada
- Hamilton – located at the head of Lake Ontario. It is known as the Birmingham of Canada. Center for iron and steelworks and engineering.
- Sudbury – Located on the shore of Lake Huron. It is one of the most productive mining areas of Canada which yields nickel, Platinum, copper, etc.
- Arvida – Situated on Saguenay River. It has the largest aluminum smelter in the world.
- Sarnia – Located on the shore of Lake Huron. It has the largest oil refinery in the world.
- Ottawa – Paper and pulp and sawmilling
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Geography of North America- 2 - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of drainage patterns in the geography of North America? |  |
| 2. Which seas are located in North America? |  |
| 3. What are some of the important industrial centers in North America? |  |
| 4. How do islands contribute to the geography of North America? |  |
| 5. What are the key geographical features of North America? |  |






















