UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Cabinet Committees
Cabinet Committees | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Cabinet Committees
- Recently the central government has reconstituted eight key cabinet committees including the creation of two new committees, one on investment and growth and another on employment and skill development.
- Cabinet Committees are extra-constitutional in emergence, which means, they are not mentioned in the Indian Constitution. But, the Rules of Business are provided for their formation.
- They are established by the PM as per the exigencies of the time and needs of the situation. Hence, their number, nomenclature, and composition vary from time to time. They are of two types—standing and ad hoc. The former is permanent, while the latter is temporary.
- The ad hoc committees are formed at times to deal with special problems. They are disbanded after their job is done.

Composition of Cabinet Committees
- Their membership varies from three to eight.
- They usually include only Cabinet Ministers.
- Non-cabinet ministers can also be included as members.
- Apart from the ministers in charge of the subjects covered, other senior ministers can also be included as members.
- Such Committees are usually chaired by the PM. At times, other Cabinet ministers like Home, Finance, etc. can also be the chairperson. But, if the Prime Minister is a member of the committee, then, he or she is the head of the committee.
Cabinet Committees Formed

- Appointments Committee of the Cabinet.
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs.
- Cabinet Committee on Political Affairs.
- Cabinet Committee on Investment and Growth.
- Cabinet Committee on Security.
- Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs.
- Cabinet Committee on Employment & Skill Development.
- Cabinet Committee on Accommodation.
All committees except Cabinet Committee on Accommodation and Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs are headed by Prime Minister.
Role of Cabinet Committees
- They are an organizational device to lessen the enormous workload of the Cabinet. They facilitate an in-depth examination of policy issues and effective coordination. They are based on the principles of division of labour and effective delegation.
- They not only resolve issues and frame proposals for the Cabinet’s consideration, but they also take decisions. The Cabinet can, of course, review their decisions.
Difference between Cabinet Committees and Council of Ministers (COMs)
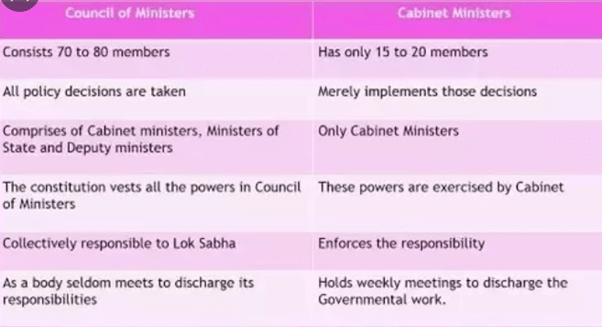
They are different from the Council of Ministers as COMs is a constitutional body, dealt in detail by the Articles 74 and 75 of the Constitution, unlike cabinet committees which are extra-constitutional in emergence.
- The Council of Ministers is a wider body comprising of 60 to 70 ministers including all 3 categories of ministers, namely, cabinet ministers, ministers of state, and deputy ministers.
- COMs are vested with all powers but only in theory. It implements the decisions taken by the cabinet while Cabinet Committees help the cabinet in decision making.
- COMs are collectively responsible to the Lower House of the Parliament while there is no such clause for cabinet committees.
- Although Cabinet Committees are not constitutional bodies their work can’t be under-estimated as they provide crucial guidance to the cabinet.
The document Cabinet Committees | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
170 videos|999 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Cabinet Committees - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are Cabinet Committees? |  |
Ans. Cabinet Committees are small groups of government ministers who are responsible for making decisions on specific policy areas. They are set up by the Prime Minister to discuss and coordinate government policies and provide recommendations to the full Cabinet.
| 2. How many Cabinet Committees are there? |  |
Ans. The number of Cabinet Committees can vary over time, but typically there are around 20 Cabinet Committees in the UK government. Each committee focuses on a specific policy area, such as economy, defense, or environment.
| 3. How are members of Cabinet Committees selected? |  |
Ans. The members of Cabinet Committees are selected by the Prime Minister and are usually senior ministers from the government. The Prime Minister considers their expertise and experience in the relevant policy area when appointing them to a committee.
| 4. What is the role of Cabinet Committees in decision-making? |  |
Ans. Cabinet Committees play a crucial role in the decision-making process of the government. They discuss and analyze policy issues, gather evidence, consult with relevant stakeholders, and make recommendations to the full Cabinet. The Cabinet then considers these recommendations before making final decisions.
| 5. How often do Cabinet Committees meet? |  |
Ans. The frequency of Cabinet Committee meetings can vary depending on the urgency and importance of the policy area. Some committees may meet regularly, while others meet on an ad-hoc basis when specific issues arise. The Prime Minister and the committee members determine the meeting schedule based on the needs of the policy area.
Related Searches





















