Noise in Digital Communication | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
In digital communication for better SNR, a matched filter is used whose impulse response h(t) is.
h(t) = S* (Tb – t)
where, * is represent complex conjugate
Tb = Bit duration
S(t) = Input signal to filter
Probability of error Pe is
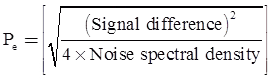
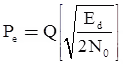
where,
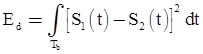
Note: N/2 is two sided noise power spectral density.
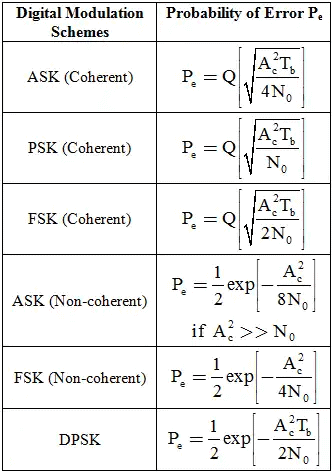
Probability of Error: The Probability of error for different digital modulation schemes is given below
Probability of Error Different Types of Digital Modulation Schemes
- In case of FSK f1 and f2 are choose such that f1 = mfs and f2 = kfs′ where m and are integers.
- Bandwidth efficiency for PSK is:

Noise
In electrical-terms, noise may be defined as an unwanted form of energy which tend to interfere with the proper reception and reproduction of transmitted signals. Conveniently noise can be classified as:
- External noise
- Internal noise
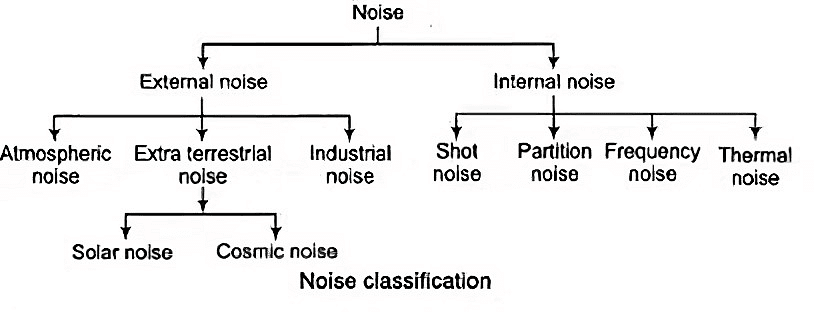 Classification of Noise
Classification of Noise
Noise Analysis in Communication System
The noise analysis can be done in communication system by calculating the following terms
Figure of Merit
Noise analysis in Continuous Wave (CW) modulation is carried out in the form of a parameter known as figure of merit denoted by γ. This parameter figure of merit γ is the ratio of output signal-to-noise ratio to the input signal-to-noise ratio of the receiver.
 |
Test: Noise
|
Start Test |
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
It is defined as ratio of signal power to noise power.
In-phase noise component:
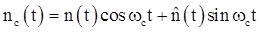
Where 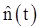 is the Hilbert transform of n(t)
is the Hilbert transform of n(t)
Quadrature noise component
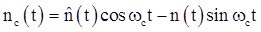
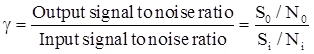
where, n (t) represents the filtered noise
Total noise power (N) = White noise power spectrum density x Bandwidth
OR
N= (n/2) x Bandwidth
Thus, the noise has a gaussian distribution.
- The effect of channel noise may be obtained by simple addition of signal x(t) and noise n (t).
- The noise performance depends on the relative magnitudes of the signal and noise.
Effect of Noise on a Baseband System
SNR is given by
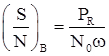
Where, PR = is received signal phase, No = two sided noise spectral density, and ω = Message signal bandwidth.
SNR of baseband system: 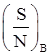
Effect of Noise on DSBSC AM
For coherent receiver, SNR at the output is:
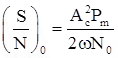
where, Pm = Message signal power, Pc = Carrier signal amplitude, and
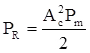
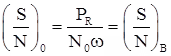
In DSBSC, the output SNR is the same as the SNR for a baseband system. Therefore DSBSC does not provide any SNR improvement over a baseband communication system.
Effect of Noise on SSB AM
For coherent receiver, SNR at the output is
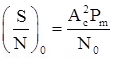
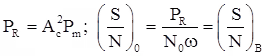
SNR in case of SSB is same as that of DSBSC and baseband system.
 |
Download the notes
Noise in Digital Communication
|
Download as PDF |
Effect of Noise on Conventional AM
For coherent receiver, SNR at the output is
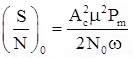
where, Ac = Amplitude of carrier wave, μ = Modulation index, and Pmn = Normalized message signal power.
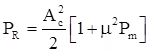

SNR of conventional AM is always less than the SNR of a baseband system.
Effect of Noise on Angle Modulation
Noise spectral density at the output of angle modulation receiver is
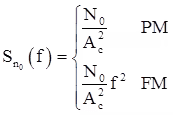
where, N0/2 is two sided power spectral density of noise.
- Effect of noise is independent of frequency for PM systems.
- Effect of noise is more at higher frequencies and less at small frequencies for FM systems.
For angle modulation system, SNR at output is
for PM:
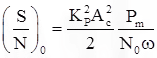
where, Pm = message signal power
For FM :
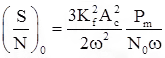
where, (A2c /2) received signal power Pr.
For PM :
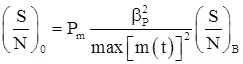
where, βP = modulation index of PM system.
For FM:
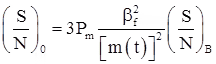
where, βf = modulation index of FM system.
With increase in β without increasing the transmitter power we can increase SNR at output. Increasing β will increasing the bandwidth requirement for transmission so we can increase SNR by increasing bandwidth.
Note: In both PM and FM systems, output SNR is proportional to the square of modulation index.
PYQs: Competitive Exams
Q1: A sinusoidal message signal is converted to a PCM signal using a uniform quantizer. The required signal-to-quantization noise ratio (SQNR) at the output of the quantizer is 40 dB. The minimum number of bits per sample needed to achieve the desired SQNR is __________ . (GATE 2017)
Ans: 7
Sol:
SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) for a sinusoidal message signal Quantized uniformly with ‘n’ bits in given by; SNRAB = 6n + 1.8
Calculation: Given, SNR = 40 dB, required at the output;
So, 40 ≤ 6n + 1.8
6n ≥ 40 – 1.8
n ≥ 6.366
So, the minimum number of bits per sample needed to achieve the derived SQNR is 7 bits
Q2: A sinusoidal signal of amplitude A is quantized by a uniform quantizer. Assume that the signal utilizes all the representation levels of the quantizer. If the signal to quantization noise ratio is 31.8 dB, the number of levels in the quantizer is ________. (GATE 2015)
Ans: 32
Sol:
In a PCM system with sinusoidal input, The SNR is given by 6n+1.8 dB. where n is a number of bits used for encoding the samples.
the number of quantization levels = L = 2n
Application: The SNR is given by 6n+1.8 = 31.8dB
⇒ n = 5 bits
Thus, the number of quantization levels L = 2n = 25=32
|
13 videos|39 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Noise in Digital Communication - Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is noise analysis in communication systems? |  |
| 2. What is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)? |  |
| 3. How does noise affect a baseband system? |  |
| 4. What is the effect of noise on DSBSC AM? |  |
| 5. How does noise impact angle modulation? |  |