Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Spherical Mirrors
Spherical Mirrors | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
A spherical mirror is a mirror that has the shape of a piece cut out of a spherical surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors: concave and convex mirror.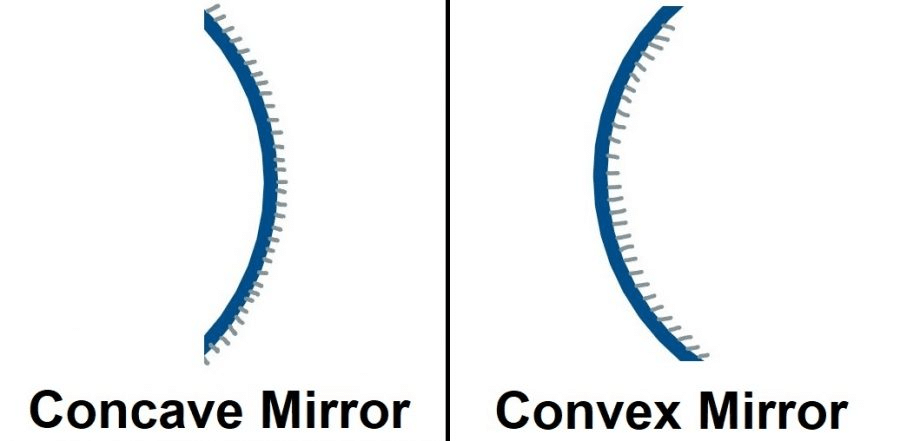
- A spherical mirror, whose reflecting surface is curved inwards, that is, faces towards the centre of the sphere, is called a concave mirror.
- A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards, is called a convex mirror.
Terminologies
There are a few basic terminologies that one needs to know while studying spherical mirrors, and they are: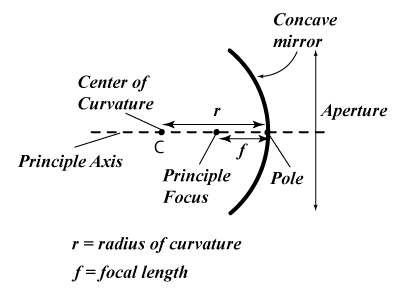
- Center of Curvature: The point in the centre of the mirror that passes through the curve of the mirror and has the same tangent and curvature at that point.
- Radius of Curvature: It’s the linear distance between pole and the center of curvature.
- Principal axis: The imaginary line passing through the optical center and the center of curvature of any lens or a spherical mirror.
- Pole: The midpoint of the spherical mirror.
- Aperture: An aperture of a mirror or lens is a point from which the reflection of light actually happens. It also gives the size of the mirror.
- Principal Focus: Principal Focus can also be called Focal Point. It’s on the axis of a mirror or lens wherein rays of light parallel to the axis converge or appear to converge after reflection or refraction.
- Focus: It’s any given point, where light rays parallel to the principal axis, will converge after getting reflected from the mirror.
- Focal length:The distance between the pole (P) and the focus (F) is called focal length (f) and
- Focal plane: An imaginary plane passing through the focus and at right angles to the principal axis.
- Real Image: When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror (or after getting refracted from a lens) actually meet at a point, a real image is formed. A real image can be obtained on a screen.
- Virtual image: When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror (or after getting refracted from a lens) appear to meet at a point, a virtual image is formed. Such an image can only be seen through a mirror (or a lens) but cannot be obtained on a screen.
Types of Spherical Mirrors
Spherical mirrors are of two types, and they are classified as follows:
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
1. Concave Mirror
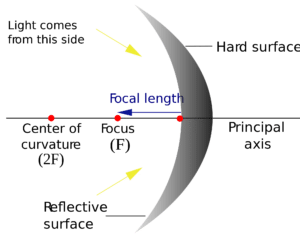 Concave Mirror
Concave Mirror- We know that a cut out of a reflective sphere is a spherical mirror. If the reflective surface is on the side curved inwards, it is a concave mirror.
- Concave mirrors are commonly used as shaving mirrors or by dentists and even in telescopes. The reflected image is magnified but the field of view is limited.
Characteristics of Concave Mirror
- Light converges at a point when it strikes and reflects back from the reflecting surface of the concave mirror. Hence, it is also known as a converging mirror.
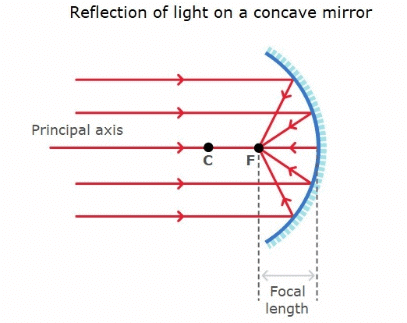
- When the concave mirror is placed very close to the object, a magnified and virtual image is obtained.
- However, if we increase the distance between the object and the mirror then the size of the image reduces and a real image is formed.
- The image formed by the concave mirror can be small or large or can be real or virtual.
Uses of Concave Mirror
- Satellite Dishes: One of the most important uses of a concave mirror is satellite dishes. These are used to receive the weaker signals sent from the communication satellites and then amplify it. These signals strike the concave mirror in parallel rays and get reflected back. These reflected rays are concentrated at the focus of the mirror. The main purpose of this mirror is to gather weaker signals coming from large areas and concentrate them at one point.
- Headlights in a car: A powerful source of light is kept at the focus point of the concave mirror in a smaller space at the back of the headlight. Any light striking the mirror from the focus will get reflected parallel to the axis of the concave mirror.
- Shaving mirror: Another use of concave mirror is a shaving mirror. The image formed after the reflections of the concave mirrors is helpful for people while shaving.
- Dentist’s mirror: The concave mirrors helps the dentist to focus light on the tooth to be examined.
2. Convex Mirror
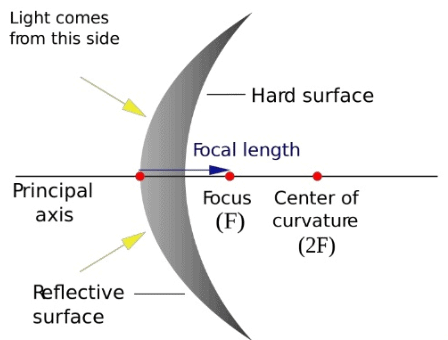 Convex Mirror
Convex Mirror- If the reflective surface is curved outwards, it is a convex mirror.
- Convex mirrors are used extensively as part of car mirrors. Depending on the focal length, the reflected image is reduced in size but the field of view is more. This is very useful for drivers as the blind spots are drastically reduced.
Characteristics of Convex Mirrors
- A convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as this mirror diverges light when they strike on its reflecting surface.
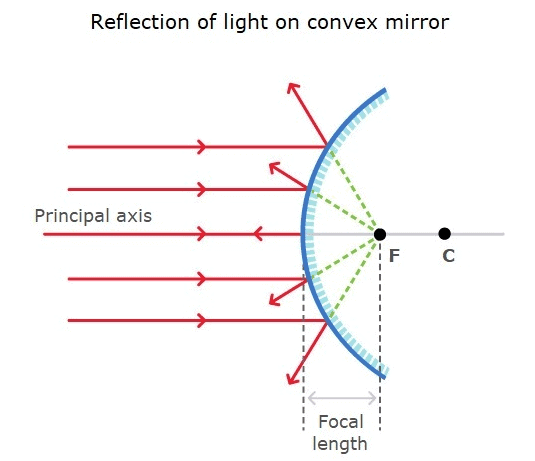
- Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror.
Uses of Convex Mirror
- Rearview mirror: The side view mirror of the car forms a small and erect image with the help of convex mirrors which helps to see the way behind the car.
- Security mirrors in ATM: Security mirrors are kept near the ATM’s so that the bank customer can check that somebody is behind them or not.
The document Spherical Mirrors | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Spherical Mirrors - Science Class 10
| 1. What are spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. Spherical mirrors are mirrors with a curved surface, either convex or concave, that can reflect light and form images. They are commonly used in various optical devices such as telescopes, cameras, and car rear-view mirrors.
| 2. What are the terminologies associated with spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. The terminologies associated with spherical mirrors include the center of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis, focal point, focal length, and mirror equation. These terms describe the different properties and characteristics of spherical mirrors.
| 3. What are the types of spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. There are two types of spherical mirrors: convex mirrors and concave mirrors. Convex mirrors bulge outwards and have a wider field of view but produce smaller and virtual images. Concave mirrors, on the other hand, curve inwards and can produce both real and virtual images depending on the object's position.
| 4. How do convex mirrors differ from concave mirrors? |  |
Ans. Convex mirrors differ from concave mirrors in their shape and the type of images they produce. Convex mirrors bulge outwards and have a wider field of view, making them ideal for use in car rear-view mirrors. They always produce virtual, erect, and diminished images. Concave mirrors, on the other hand, curve inwards and can produce both real and virtual images depending on the object's position.
| 5. What is the mirror equation for spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. The mirror equation for spherical mirrors is given by:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
where f is the focal length of the mirror, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance. This equation relates the distances of the object, image, and the focal length of the spherical mirror.
Related Searches

















