Best Study Material for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam
Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Control Systems > Unit Impulse Response of 2nd Order System
Unit Impulse Response of 2nd Order System | Control Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Time Domain Characteristics
In specifying the Transient-Response characteristics of a control system to a unit step input, we usually specify the following: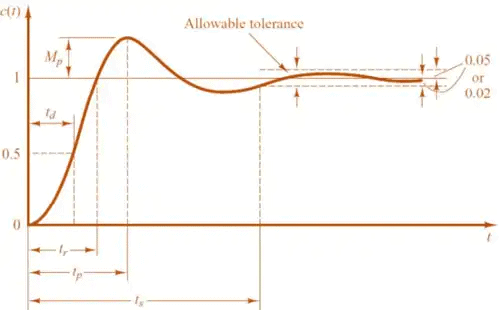
- Delay time (td): It is the time required for the response to reach 50% of the final value in first attempt.
The expression of delay time, td for second order system is: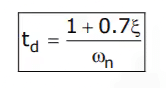
- Rise time, (tr): It is the time required for the response to rise from 0 to 100% of the final value for the under-damped system.
The expression of rise time, tr for second order system is: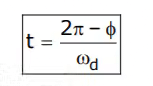
- Peak time, (tp): It is the time required for the response to reach the peak of time response or the peak overshoot.
The expression of peak time, tp for second order system is:
tP = nπ / ωd seconds
For first peak, n = 1 (maxima)
tP = π / ωd
For first minima, n = 2
tP = nπ / ωd
For second maxima, n = 3
tP = 3π / ωd - Settling time, (ts): It is the time required for the response to reach and stay within a specified tolerance band ( 2% or 5%) of its final value.
The expression of settling time, ts for second order system is:
For 2% tolerance band,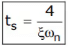
For 2% tolerance band,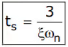
- Peak overshoot (Mp): It is the normalized difference between the time response peak and the steady output and is defined as
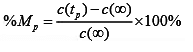
The expression of peak overshoot, Mp for second order system is: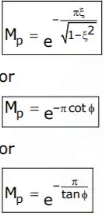
Where tanφ =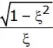
- Steady-state error (ess): It indicates the error between the actual output and desired output as ‘t’ tends to infinity.
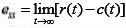
Effect of Adding a Zero to a System
If we add a zero at s = -z be added to a second order system. Then we have,
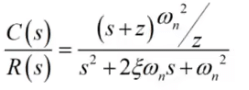
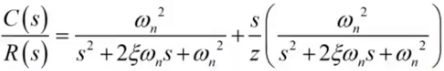
- The multiplication term is adjusted to make the steady-state gain of the system unity.
Manipulation of the above equation gives,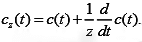
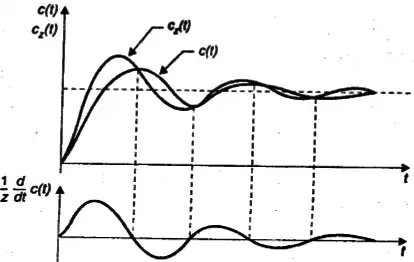
- The effect of added derivative term is to produce a pronounced early peak to the system response.
- Closer the zero to the origin, the more pronounce the peaking phenomenon.
- Due to this fact, the zeros on the real axis near the origin are generally avoided in design. However, in a sluggish system the artful introduction of a zero at the proper position can improve the transient response.
Types of Feedback Control System
The open-loop transfer function of a system can be written as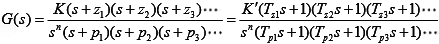
- If n = 0, the system is called type-0 system, if n = 1, the system is called type-1 system, if n = 2, the system is called type-2 system, etc.
Steady-State Error and Error Constants
The steady-state performance of a stable control system is generally judged by its steady-state error to step, ramp and parabolic inputs. For a unity feedback system,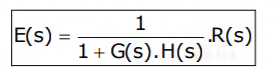
Where,
E(s) is error signal
R(s) is input signal
G(s) H(s) is the open loop transfer function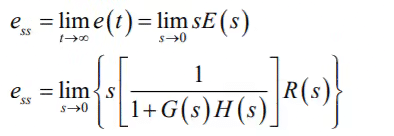
It is seen that steady-state error depends upon the input R(s) and the forward transfer function G(s).
- If input is unit step i.e R(t) = u(t)
R(s) = 1/s
Steady state error is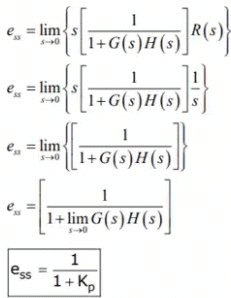
where,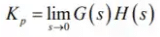
Kp is positional error constant. - If input is unit ramp i.e R(t) = tu(t)
R(s) = 1/s2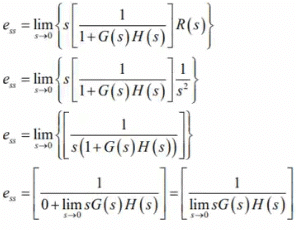
ess = 1/Kv
where,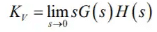
Kv is velocity error constant. - If input is unit parabolic i.e R(t) = 0.5tu(t)
R(s) = 1/s3
Steady state error,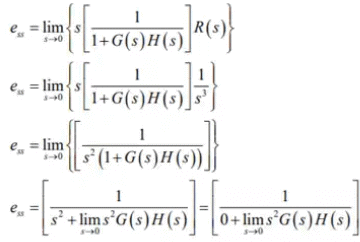
ess = 1/Ka
where,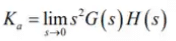
Ka is acceleration error constant.
The document Unit Impulse Response of 2nd Order System | Control Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Control Systems.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
54 videos|83 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Impulse Response of 2nd Order System - Control Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a unit impulse response? |  |
| 2. How is the unit impulse response of a 2nd order system calculated? |  |
Ans. The unit impulse response of a 2nd order system can be calculated by finding the inverse Laplace transform of the transfer function of the system. This involves manipulating the Laplace transform equation to isolate the impulse response and then applying the inverse Laplace transform to obtain the time-domain response.
| 3. What information can be obtained from the unit impulse response of a 2nd order system? |  |
Ans. The unit impulse response of a 2nd order system provides insights into the system's stability, damping ratio, natural frequency, and overall response characteristics. It allows us to analyze how the system will behave when subjected to different input signals or disturbances.
| 4. How does the damping ratio affect the unit impulse response of a 2nd order system? |  |
Ans. The damping ratio determines the shape and behavior of the unit impulse response of a 2nd order system. Higher damping ratios lead to overdamped responses, where the system takes longer to reach steady-state and exhibits less oscillation. Lower damping ratios result in underdamped responses, characterized by oscillations and a faster settling time.
| 5. Can the unit impulse response of a 2nd order system be used to determine the system's stability? |  |
Ans. Yes, the unit impulse response can provide information about the stability of a 2nd order system. If the unit impulse response decays to zero over time, the system is considered stable. However, if the response grows indefinitely or exhibits oscillations, the system is unstable. By analyzing the shape and behavior of the unit impulse response, one can assess the stability of the system.
Related Searches