Bellman-Ford Algorithm | Algorithms - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Given a graph and a source vertex src in graph, find shortest paths from src to all vertices in the given graph. The graph may contain negative weight edges.
We have discussed Dijkstra’s algorithm for this problem. Dijkstra’s algorithm is a Greedy algorithm and time complexity is O(VLogV) (with the use of Fibonacci heap). Dijkstra doesn’t work for Graphs with negative weight edges, Bellman-Ford works for such graphs. Bellman-Ford is also simpler than Dijkstra and suites well for distributed systems. But time complexity of Bellman-Ford is O(VE), which is more than Dijkstra.
Algorithm
Following are the detailed steps.
Input: Graph and a source vertex src
Output: Shortest distance to all vertices from src. If there is a negative weight cycle, then shortest distances are not calculated, negative weight cycle is reported.
- This step initializes distances from the source to all vertices as infinite and distance to the source itself as 0. Create an array dist[] of size |V| with all values as infinite except dist[src] where src is source vertex.
- This step calculates shortest distances. Do following |V|-1 times where |V| is the number of vertices in given graph.
…..a) Do following for each edge u-v
………………If dist[v] > dist[u] + weight of edge uv, then update dist[v]
………………….dist[v] = dist[u] + weight of edge uv - This step reports if there is a negative weight cycle in graph. Do following for each edge u-v
……If dist[v] > dist[u] + weight of edge uv, then “Graph contains negative weight cycle”
The idea of step 3 is, step 2 guarantees the shortest distances if the graph doesn’t contain a negative weight cycle. If we iterate through all edges one more time and get a shorter path for any vertex, then there is a negative weight cycle
How does this work? Like other Dynamic Programming Problems, the algorithm calculates shortest paths in a bottom-up manner. It first calculates the shortest distances which have at-most one edge in the path. Then, it calculates the shortest paths with at-most 2 edges, and so on. After the i-th iteration of the outer loop, the shortest paths with at most i edges are calculated. There can be maximum |V| – 1 edges in any simple path, that is why the outer loop runs |v| – 1 times. The idea is, assuming that there is no negative weight cycle, if we have calculated shortest paths with at most i edges, then an iteration over all edges guarantees to give shortest path with at-most (i+1) edges.
Example:
Let us understand the algorithm with following example graph. The images are taken from this source.
Let the given source vertex be 0. Initialize all distances as infinite, except the distance to the source itself. Total number of vertices in the graph is 5, so all edges must be processed 4 times.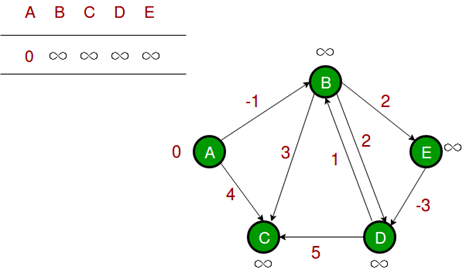 Let all edges are processed in the following order: (B, E), (D, B), (B, D), (A, B), (A, C), (D, C), (B, C), (E, D). We get the following distances when all edges are processed the first time. The first row shows initial distances. The second row shows distances when edges (B, E), (D, B), (B, D) and (A, B) are processed. The third row shows distances when (A, C) is processed. The fourth row shows when (D, C), (B, C) and (E, D) are processed.
Let all edges are processed in the following order: (B, E), (D, B), (B, D), (A, B), (A, C), (D, C), (B, C), (E, D). We get the following distances when all edges are processed the first time. The first row shows initial distances. The second row shows distances when edges (B, E), (D, B), (B, D) and (A, B) are processed. The third row shows distances when (A, C) is processed. The fourth row shows when (D, C), (B, C) and (E, D) are processed.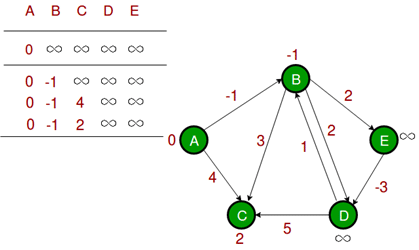 The first iteration guarantees to give all shortest paths which are at most 1 edge long. We get the following distances when all edges are processed second time (The last row shows final values).
The first iteration guarantees to give all shortest paths which are at most 1 edge long. We get the following distances when all edges are processed second time (The last row shows final values).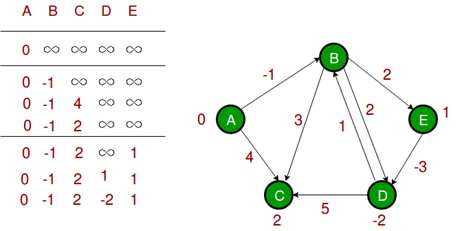 The second iteration guarantees to give all shortest paths which are at most 2 edges long.The algorithm processes all edges 2 more times. The distances are minimized after the second iteration, so third and fourth iterations don’t update the distances.
The second iteration guarantees to give all shortest paths which are at most 2 edges long.The algorithm processes all edges 2 more times. The distances are minimized after the second iteration, so third and fourth iterations don’t update the distances.
Implementation
- C++



} - Java



- Python3


- C#



Output: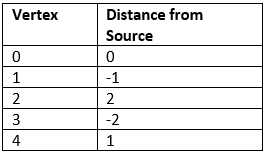
Notes:
- Negative weights are found in various applications of graphs. For example, instead of paying cost for a path, we may get some advantage if we follow the path.
- Bellman-Ford works better (better than Dijkstra’s) for distributed systems. Unlike Dijkstra’s where we need to find the minimum value of all vertices, in Bellman-Ford, edges are considered one by one.
- Bellman-Ford does not work with undirected graph with negative edges as it will declared as negative cycle.
|
81 videos|80 docs|33 tests
|





















