Magnetic Properties of Materials | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Types of Magnetism
Magnetism in materials depends on how they respond to a magnetic field, which is influenced by their magnetic susceptibility (how much and in what way they can be magnetized). The three main types of magnetism are:
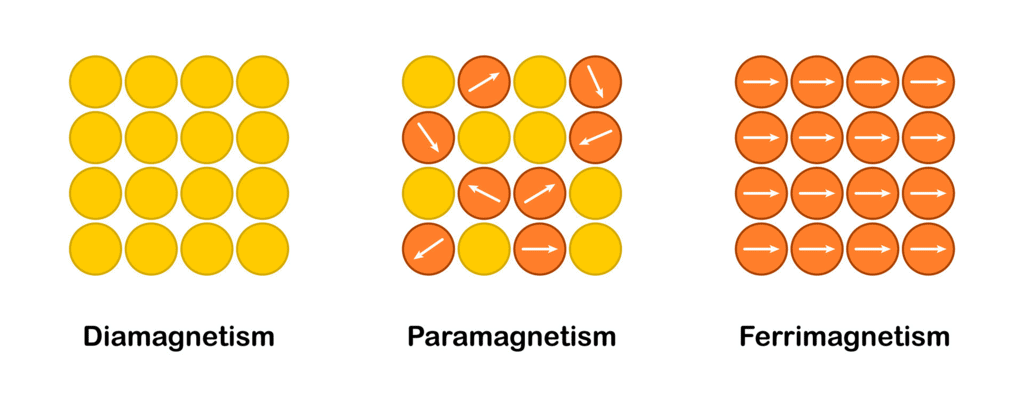 Three types of magnetism
Three types of magnetism
1. Dia-magnetism
- Characteristics: Extremely weak and only present when an external magnetic field is applied. This type of magnetism is not permanent.
- How it works: When an external magnetic field is applied, it slightly disturbs the electrons in the atoms of the material, causing tiny magnetic effects that oppose the field.
- Effect: The magnetic effect, known as diamagnetism, has a small magnetic moment that acts in the opposite direction to the applied magnetic field, resulting in a negative magnetic susceptibility.
- Examples: Materials like copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and silicon (Si) show diamagnetism at room temperature.
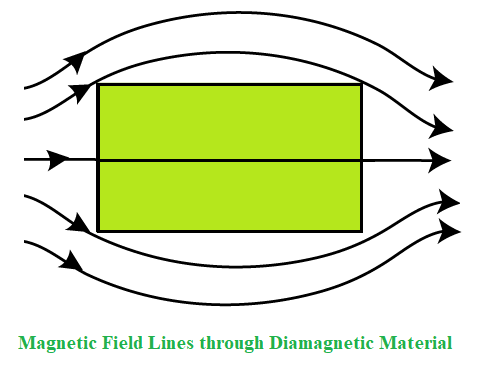
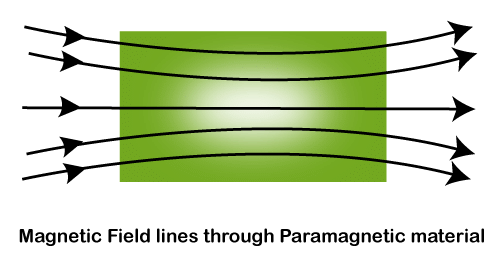
2. Para-magnetism
- Characteristics: Slightly stronger than diamagnetism, but still weak. The magnetic effect only exists when an external field is present and disappears once the field is removed.
- How it works: In para-magnetic materials, atomic dipoles (tiny magnetic orientations) align with the magnetic field when it is applied, creating a positive magnetization.
- Effect: This alignment is temporary and disrupted by thermal energy (heat) which causes the dipoles to move randomly again. The magnetic susceptibility of these materials is slightly positive.
- Examples: Aluminum, calcium, and titanium are examples of para-magnetic materials.
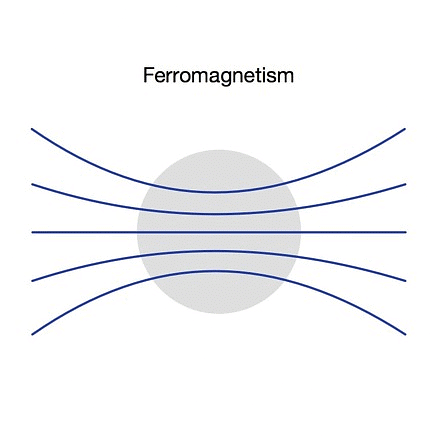
3. Ferro-magnetism
- Characteristics: Unlike dia- and para-magnetism, ferro-magnetism allows materials to be permanently magnetized even in the absence of an external magnetic field.
- How it works: Materials with ferro-magnetism have permanent magnetic moments due to unpaired electron spins that can strongly align with each other even without an external magnetic field.
- Effect: These materials can have a very high magnetic susceptibility, and their magnetism is strong and permanent up to a certain temperature (Curie temperature). Above this temperature, they behave like para-magnetic materials.
- Examples: Iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni) are typical ferro-magnetic materials.
In summary, the type of magnetism a material exhibits depends on its response to magnetic fields and its internal electronic structure. Dia-magnetism is very weak and temporary, para-magnetism is slightly stronger but also temporary, and ferro-magnetism is strong and permanent under normal conditions.
|
268 videos|732 docs|171 tests
|
FAQs on Magnetic Properties of Materials - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the different types of magnetism? |  |
| 2. How do magnetic properties of materials vary based on their composition? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of understanding magnetism in materials science? |  |
| 4. How can magnetism be utilized in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How can the magnetic properties of materials be manipulated for specific purposes? |  |





















