Motion in Magnetic Field & Combined Electric & Magnetic Field | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Magnetic Force |

|
| Lorentz Force |

|
| Motion of a charged particle in the electric and magnetic field |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
- We have read about the interaction of electric field and magnetic field and the motion of charged particles in the presence of both the electric and magnetic fields and also have derived the relation of the force acting on the charged particle, in this case, given by Lorentz force.
- We have also read about the magnetic force on a current-carrying conducting rod when placed in a magnetic field. But what happens when a charged particle moves in the presence of a magnetic field? How do we define the trajectory of such a particle? In this section, we will learn about this in detail.
Magnetic Force
- A force acting on a particle is said to perform work when there is a component of the force in the direction of motion of the particle. In the case under consideration where we have a charged particle carrying a charge q moving in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B, the magnetic force acts perpendicular to the velocity of the particle.
- Here we say that no work is done by the magnetic force on the particle and hence, no change in the velocity of the particle can be seen. Mathematically, when the velocity of the particle v is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, we can write,
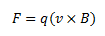 Here, the magnetic force is directed towards the center of circular motion undergone by the object and acts as a centripetal force. Thus, if v and B are perpendicular to each other, the particle describes a circle.
Here, the magnetic force is directed towards the center of circular motion undergone by the object and acts as a centripetal force. Thus, if v and B are perpendicular to each other, the particle describes a circle.- In other cases, when a component of velocity is present along the direction of the magnetic field B, then its magnitude remains unchanged throughout the motion, as no effect of a magnetic field is felt upon it. Also, the motion due to the perpendicular component of the velocity is circular in nature, as discussed above. The resulting motion due to the two components is a helical motion, as shown in the image below.
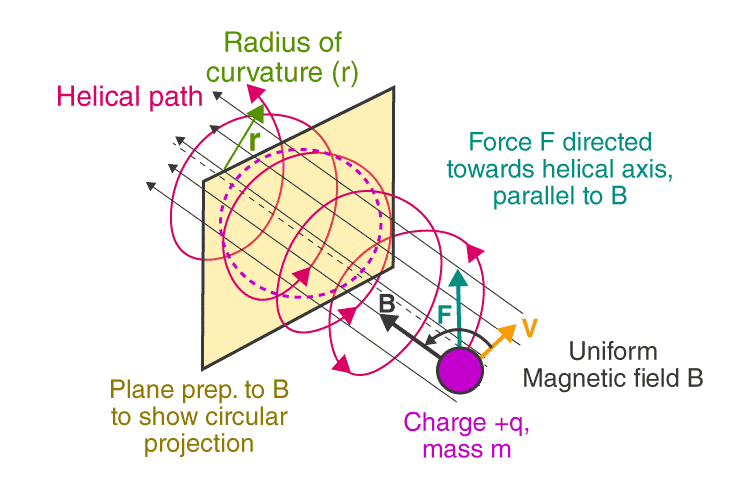
As the radius of the circular path of the particle is r, the centripetal force acting perpendicular to it towards the center can be given as,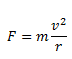
Also, the magnetic force acts perpendicular to both the velocity and the magnetic field and the magnitude can be given as,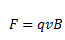
Equating the two, we get,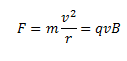
Or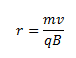
Here, r gives the radius of the circle described by the particle. Also, if we write the angular frequency of the particle as ω, then we can write,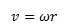
So,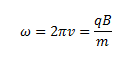
Here, v is the frequency of rotation of the particle. The time for one revolution can be given as,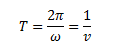
The distance moved by the particle along the direction of the magnetic field in one rotation is given by its pitch.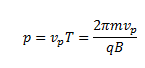 Where vp is the velocity parallel to the magnetic field.
Where vp is the velocity parallel to the magnetic field.
Lorentz Force
Lorentz force is the force exerted on a charged particle moving through both electric and magnetic field.
F = qE + qv × B ……….(1)
where,
F = Lorentz Force
q = Charge on the Particle
E = Electric Field
B = Magnetic Field
v = Velocity of the Particle
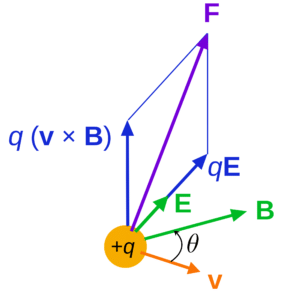 Lorentz Force
Lorentz Force
In a vacuum where collisions between particles are not very frequent, a particle with charge q, mass m, and velocity v perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B (no E) moves in a circular path with the radius
r = mv / qB ………..(2)
One can also deflect the trajectory of a charged particle with an electric field, although not into a circular path. If the electric force on the particle is both equal and opposite to the magnetic force, the net force on the particle will be zero. From Eq. (1), this will happen if
v=E / B ……….(3)
Motion of a charged particle in the electric and magnetic field
- In case of motion of a charge in a magnetic field, the magnetic force is perpendicular to the velocity of the particle. So no work is done and no change in the magnitude of the velocity is produced (though the direction of momentum may be changed). We shall consider the motion of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field. First, consider the case of v perpendicular to B.
- The perpendicular force, q v × B, acts as a centripetal force and produces a circular motion perpendicular to the magnetic field. If velocity has a component along B, this component remains unchanged as the motion along the magnetic field will not be affected by the magnetic field.
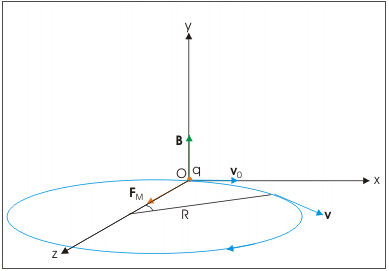 The circular motion of a charged particle in the magnetic field
The circular motion of a charged particle in the magnetic field
- The motion in a plane perpendicular to B is as before a circular one, thereby producing a helical motion. However, the electric field in y-direction imparts acceleration in that direction. The particle, therefore, acquires velocity in the y-direction and resulting motion is a helical motion.
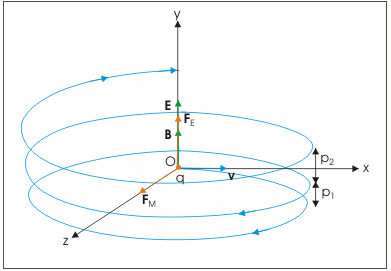 The motion of a charged particle in both electric and magnetic fields. Resulting motion is a helical motion with increasing pitch
The motion of a charged particle in both electric and magnetic fields. Resulting motion is a helical motion with increasing pitch
- The radius of each of the circular element and other periodic attributes like time period, frequency and angular frequency is same as for the case of circular motion of a charged particle in perpendicular to magnetic field.
R = ν / αB
T = 2π / αB
ν = αB / 2π
ω = αB
- If there is a component of the velocity parallel to the magnetic field (denoted by v2), it will make the particle move along both the field and the path of the particle would be a helical one. The distance moved along the magnetic field in one rotation is called pitch p.
p = v2T = 2πmv2 /qB
Applications
Some of the important applications associated with the presence of the two fields include:
- The motion of a charged particle in electric and magnetic fields
- Measurement of specific charge of an electron (J. J. Thomson experiment)
- Acceleration of charged particles (cyclotron)
Solved Examples
Ques: A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without the change in velocity. Which of the following is/are possible?
A) B = 0, E = 0
B) E = 0, B ≠ 0
C) E ≠ 0, B = 0
D) B ≠ 0, E ≠ 0
Ans: If A charged particle moves in a gravity-free space without a change in velocity, then
- Particle can move with constant velocity in any direction. So B =0, E = 0
- Particle can move in a circle with constant speed. Magnetic force will provide the centripetal force that causes particle to move in a circle.
- If qE = qvB and Magnetic & Electric force in opposite direction in this case also particle move with uniform speed.
|
320 videos|1000 docs|210 tests
|
FAQs on Motion in Magnetic Field & Combined Electric & Magnetic Field - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. How does a charged particle move in a magnetic field? |  |
| 2. What is the relationship between the magnetic force and the velocity of a charged particle? |  |
| 3. How does the motion of a charged particle differ in an electric field compared to a magnetic field? |  |
| 4. What happens when a charged particle moves in a combined electric and magnetic field? |  |
| 5. How can the motion of a charged particle in an electric and magnetic field be described mathematically? |  |




















