Motional Electromotive Force | Physics for JAMB PDF Download
Motional Electromotive Force
An emf induced by the motion of the conductor across the magnetic field is a motional electromotive force. The equation is given by E = -vLB. This equation is true as long as the velocity, field, and length are mutually perpendicular. The minus sign associated with the Lenz’s law.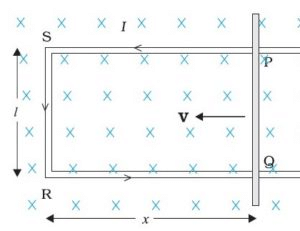
For us to understand the motional electromotive force, let us make a particular setup. Let us take a rectangular coil, a metal rod of length L, moving with velocity V, through a magnetic field B. There is a magnetic field at some location.
Length, velocity and magnetic field should always be at a right angle with each other. The direction of the magnetic field is going inside. Assume the metal rod is frictionless that means there is no loss of energy due to friction and we apply a uniform magnetic field. The conductor rod is moved with a constant velocity and placed in the magnetic field.
Browse more Topics under Electromagnetic Induction
ΦB = Blx
- AC Generator
- Eddy Currents
- Energy Consideration: A Quantitative Study
- Faraday’s and Lenz’s Law
- Inductance
But ‘x’ changes with time,
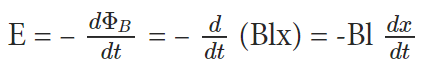 E = Blv
E = Blv
The induced emf Blv is motion electromotive force. So we produce emf by moving a conductor inside the uniform magnetic field. The power required to move a conductor rod in a magnetic field is,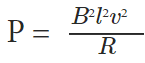
Where,
- B is the magnetic field,
- l is the length of the conductor
- v is the velocity of the conductor
- R is the resistance
The magnetic flux associated with the coil is given by Φ = BA cos θ. We know that cos θ = 0, so Φ = BA. The motion of electromotive force can be further explained by Lorentz force which acts on free charge carriers. The Lorentz force on charge is:
F = qVB
Solved Questions
Q.1. A coil having n turns and area A is initially placed with its plane normal to the magnetic field B. It is then rotated through 180º in 0.2 sec. The emf induced at the ends of the coils is
(a) 0.1 nAB
(b) nAB
(c) 5 nAB
(d) 10 nAB
Ans: (d)
Solution: Total change in flux = ΔΦ = 2 nAB
Total time of change = Δt = 0.2s
Emf induced = ΔΦ/Δt = 10nAB
Q.2. A straight line conductor of length 0. 4m is moved with a speed of 7ms-1 perpendicular to a magnetic field of an intensity of 0.9wbm-2 The induced emf across the conductor is:
(a) 25.2 V
(b) 5.24 V
(c) 2.52 V
(d) 1.26 V
Ans: (c)
Solution: The induced emf across the conductor E= Blv
= 0.98 × 0.4 × 7 = 2.52V
Q.3. Two conducting rings of radii r and 2r move in opposite directions with velocities 2v and v respectively on a conducting surface S. There is a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B perpendicular to the plane of the rings. The potential difference between the highest points of the two rings is:
(a) Zero
(b) 2rvB
(c) 4rvB
(d) 8rvB
Ans: (d)
Solution: Replace the emf in the rings by the cells.
E1= B2r(2V) = 4Brv
E2 = B(4r)v = 4Brv
V2 – V1 = 8Brv
|
260 videos|253 docs|230 tests
|
FAQs on Motional Electromotive Force - Physics for JAMB
| 1. What is motional electromotive force? |  |
| 2. How is motional electromotive force calculated? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of motional electromotive force? |  |
| 4. How does motional electromotive force impact electric generators? |  |
| 5. What factors affect the magnitude of motional electromotive force? |  |
















