Adaptations in Plants Class 4 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Why Do Plants Need to Adapt? |

|
| Water or Aquatic Plants |

|
| Land or Terrestrial Plants |

|
| Important Tips |

|
Why Do Plants Need to Adapt?
Plants need to adapt in order to survive harsh climatic conditions and other unfavourable circumstances.
 Roses use thorns to scare off animals who intend to eat them up, which is a kind of Adaptation.
Roses use thorns to scare off animals who intend to eat them up, which is a kind of Adaptation.
- Plants grow in different places. They can be found in dry and sandy deserts, damp and wet plains, hilly areas, valleys, snow-covered high mountains, and even underwater.
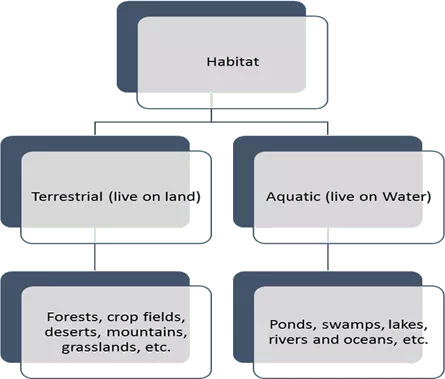
- Habitat: The place where an organism usually lives and grows in nature is called its habitat. A habitat contains everything that an organism needs. A habitat can be as small as a patch of a garden or as big as a forest.
- Adaptations: Some plants find it hard to live in certain climates, so they need to change or adapt to survive. Adaptations are special features that help a plant live in its habitat. For example, a plant might develop a thick skin to protect itself from harsh weather.
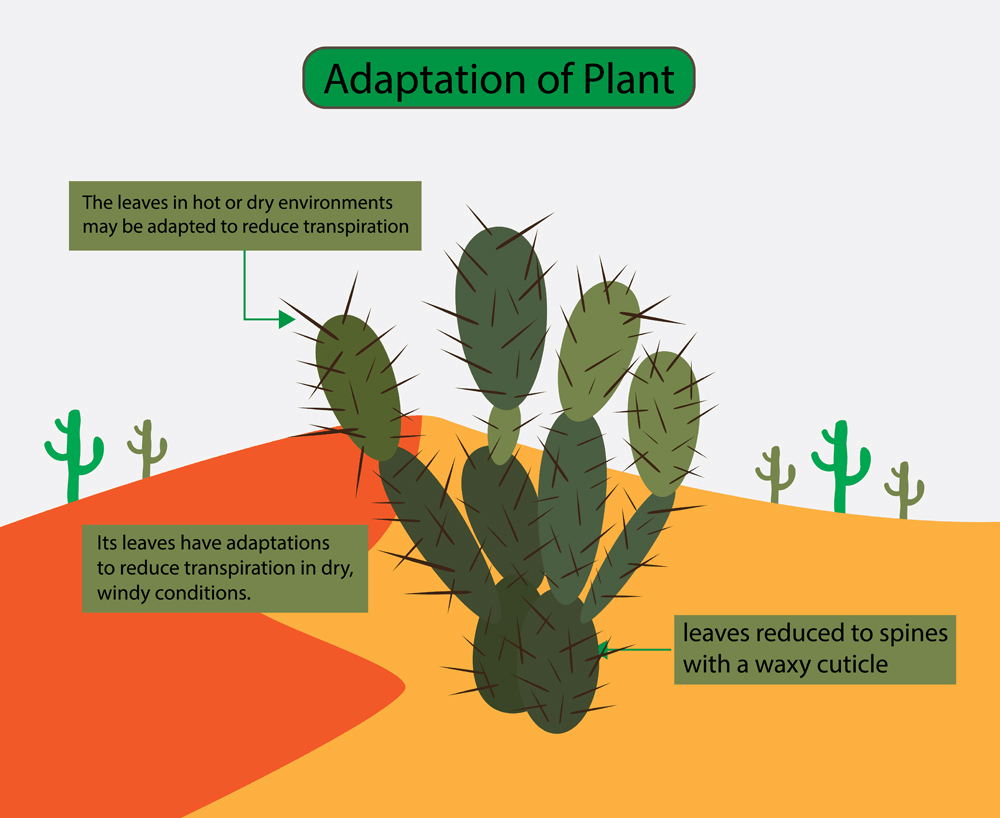 Leaves of Desert Plants have adapted to the Desert
Leaves of Desert Plants have adapted to the Desert
Depending on the habitat they live in, plants can be divided into two major groups:
- Water or aquatic plants
- Land or terrestrial plants
Water or Aquatic Plants
The plants that grow in water are called aquatic plants.
- Water covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface, making aquatic habitats more extensive than land habitats.
- Aquatic plants can thrive in both saltwater (found in oceans and seas) and freshwater (such as lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams).
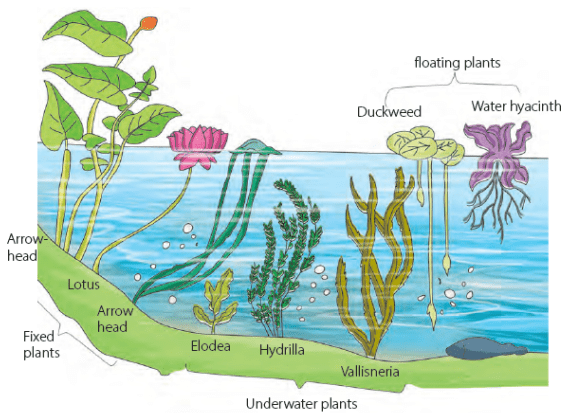
- Aquatic plants are categorized into three types: floating, fixed, and underwater plants.
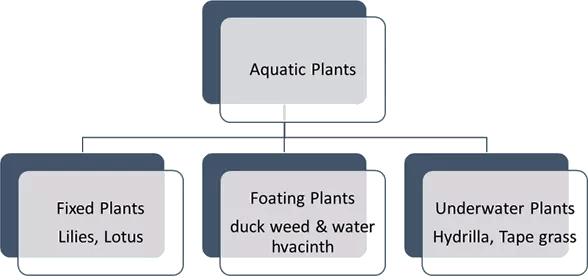
1. Floating Plants
- Floating plants, such as duckweed, Wolffia, Pistia, and water hyacinth, are lightweight and have a spongy texture. Their structure is filled with air pockets, making them highly buoyant.
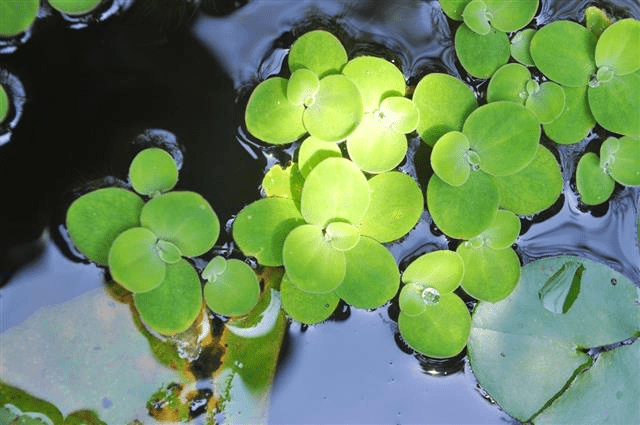 Duckweed Plants
Duckweed Plants
- These plants can easily float on the surface of the water due to their buoyancy.
- The upper surface of their leaves is often covered with a waxy layer, which helps to repel water.
- The roots of these plants hang freely in the water and are not anchored to the bottom.
2. Fixed Plants
- Fixed plants have their roots anchored at the bottom of water bodies, such as ponds, while their long stems extend to the surface of the water.
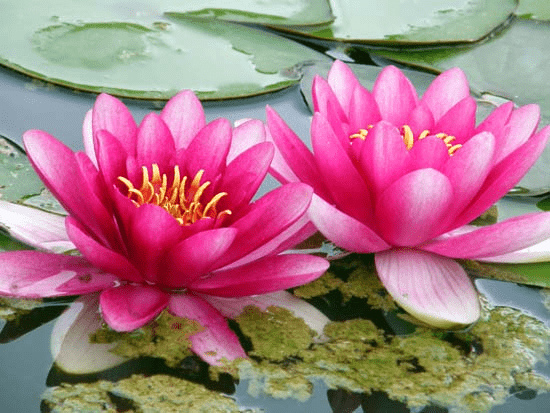 Water lilies bloom in the water. The plant's leaves float on top of the water.
Water lilies bloom in the water. The plant's leaves float on top of the water.
- These plants feature broad leaves that float on the water's surface. The leaves are coated with a waxy layer, which keeps them dry and prevents decomposition.
- Stomata, or tiny openings for gas exchange, are present on the upper side of the leaves.
- The stems of floating plants are thin, hollow, flexible, and lightweight, allowing the leaves to float. These stems can bend with the flow of water, helping to protect the plant from strong water currents.
- Examples of fixed plants include the lotus and the water lily.
Floating plants play a crucial role in providing habitat and oxygen within water bodies.
3. Underwater Plants
- Underwater plants are those that are firmly anchored to the bottom of water bodies and remain completely submerged.
- These plants possess stomata, which are essential for gas exchange. However, unlike land plants, the stomata in underwater plants are not located on the leaves that are submerged in water.
 Hydrilla: Underwater Plants
Hydrilla: Underwater Plants
- Underwater plants, such as Hydrilla, play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems by producing food through photosynthesis, using sunlight that penetrates the water's surface. During this process, they release oxygen, which is vital for the survival of aquatic animals.
- To adapt to the underwater environment, these plants have specific features:
- Hydrilla has slender leaves that allow water to flow through them, preventing damage from strong water currents.
- Vallisneria has ribbon-like leaves that can bend with the water's current, making it easier for the plant to withstand moving water.
- Examples of underwater plants include:
- Pondweed. This plant has broad leaves that provide habitats for small aquatic creatures, offering them shelter and protection.
- Eelgrass. Eelgrass is known for its long, ribbon-like leaves that thrive in deeper waters, providing food and habitat for various marine organisms.
- Water star grass. This plant features star-shaped leaves that float on the water's surface, contributing to the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem.
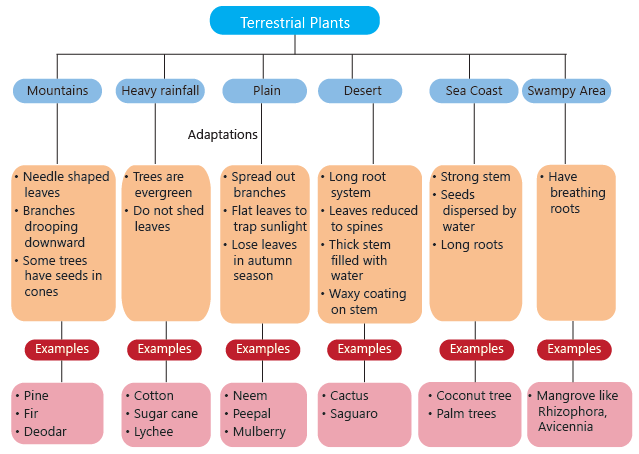
Land or Terrestrial Plants
Plants can be classified by where they grow, and those that thrive on land are called terrestrial plants.
There are different kinds of land areas. Plants growing in each of these areas need to adjust to the kind of weather, amount of rainfall, type of soil, and other such factors found in that place.
1. Plants in the Plains
- Some plants grow in the plains where the climate is hot in summer and cold in winter.
- Plants growing in plains have more space to spread out so they have several branches.
- They have flat leaves. These help water to evaporate and keep the tree cool when the climate gets hot. Flat leaves also help to trap a lot of sunlight.
- Mango, banyan, neem, peepal, mulberry, poplar, and Sheesham are some trees that grow in plains.
 Mango Tree
Mango Tree
- Some of these trees lose all their leaves at once generally during autumn in order to survive harsh weather conditions. As spring approaches, new leaves start growing. Such trees are called deciduous trees. Examples: cherry, maple tree, teak, and beech tree.
- Trees that do not lose their leaves at once are called evergreen trees. Examples: jack fruit tree, eucalyptus, and pine.
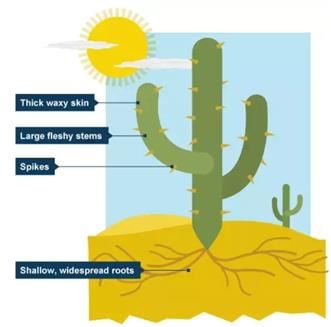
2. Plants in Deserts
- Deserts are dry and very hot places. There is a scarcity of rainfall and a lot of direct sunlight falls on the plants.
- The soil in the desert is sandy and unable to hold much water. Cactus (Plural: cacti), such as saguaro are some examples of desert plants.
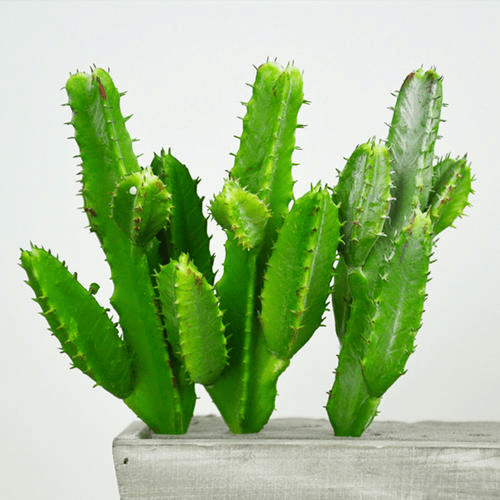 Cactus Plants
Cactus Plants
Adaptations found in desert plants include:
- Water Storage: Desert plants like cacti store water in their stems or leaves to survive the long dry periods.
- Deep Roots: Many desert plants have long root systems that reach deep into the ground to find and collect water.
- Reduced Leaves: To minimize water loss, some desert plants do not have leaves at all. In the case of cacti, the leaves have evolved into spines.
- Prickly Spines: The spines on cacti help protect the plant from animals that might eat them for water.
- Waxy Coating: A waxy layer on the stems of cacti helps to keep water inside the plant.
- Thick, Green Stems: The stems of cacti are thick, green, and filled with water. They also carry out photosynthesis, which is the process of making food using sunlight.
3. Plants in Mountains
Plants on mountains and hills are adapted to grow in very cold temperatures.
- Tall, straight, cone-shaped trees in mountains help snow slide off easily.
- Needle-like leaves on most mountain plants reduce water loss and help snow fall off.
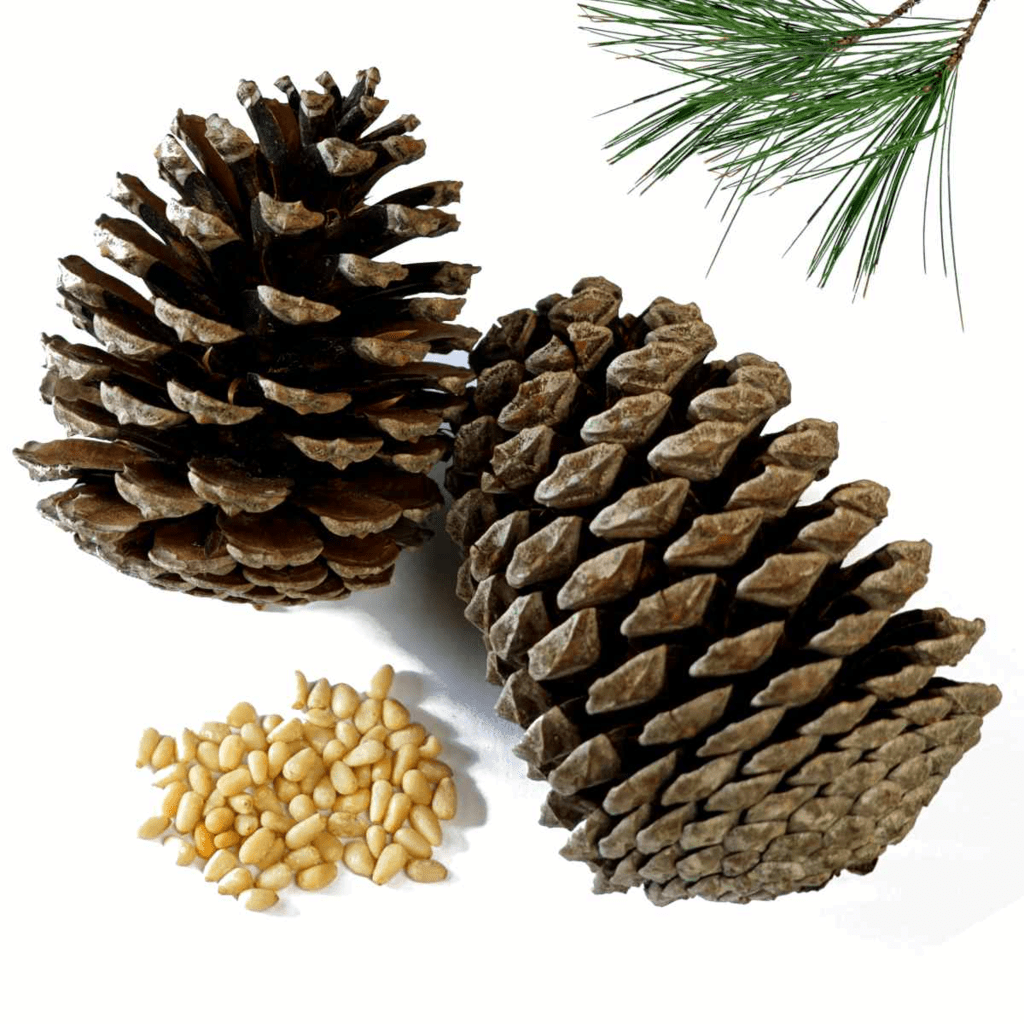 Pines
Pines
- Waxy coatings on leaves prevent evaporation and keep water inside. Dark green leaves absorb more sunlight.
- Many trees have branches that droop downwards to shed excess snow, preventing breakage.
- Conifers, like pine, fir, deodar, and spruce, are trees that bear seeds in cones instead of producing true flowers.
4. Plants in Heavy-rainfall Areas
- In areas with heavy rainfall, evergreen trees are found. They have plenty of sunlight and water throughout the year.
- The broad and abundant leaves capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Lychee, cashew, pineapple, sugar cane, cotton, rubber, and teak grow well in these areas.
 Cashew Plant
Cashew Plant
5. Plants along the Sea Coast
- Trees in the coastal areas are well-adapted to grow in sandy soil, salty water, and high rainfall.
- They have strong stems that can withstand strong winds.
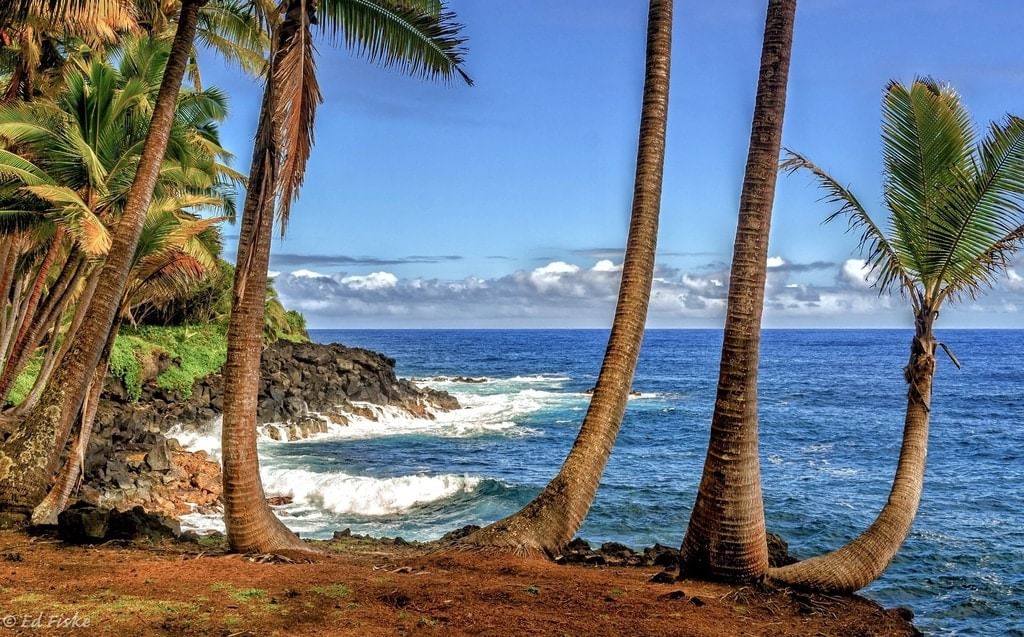 Palm Trees along the Sea Coast
Palm Trees along the Sea Coast
- They have long roots that grow deep into the sandy soil. These roots also firmly anchor the plant.
- Coconut and palm trees grow well in these areas.
6. Plants in Marshy or Swampy Areas
- Marshy areas are characterized by sticky and clayey soil, which creates a challenging environment for plant growth due to the lack of air reaching the roots.
- To adapt to this condition, the roots of these plants extend above the soil to access air. These above-ground roots are called aerial roots.
- Trees that thrive in marshy areas are known as mangroves. Examples of mangrove species include Rhizophora and Avicennia, which are adapted to live in saline water.
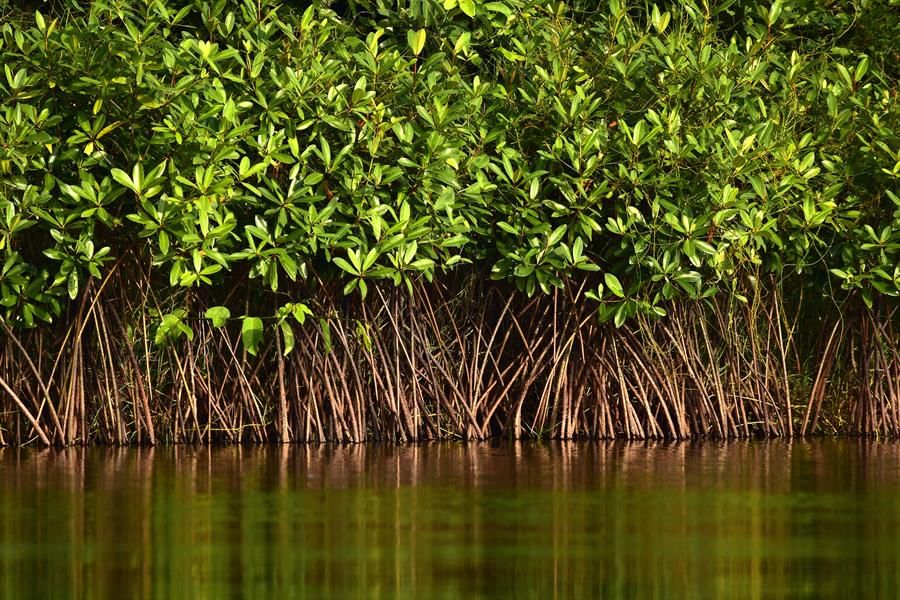 Mangroves
Mangroves
Important Tips
- Paper Conservation: Since paper is made from plants, it's crucial to avoid wasting it. We should strive to reuse paper whenever possible and always utilize both sides.
- Respecting Nature in Parks: When visiting a park, it's important not to pick leaves or flowers. Encourage others to do the same, as many plant leaves serve as homes for insects, birds, and small animals.
- Planting for Clean Air: Growing small herbs and shrubs around your home can contribute to providing cleaner air for us to breathe.
Scientist in Focus
Charles Darwin (1809–1882),
Charles Darwin
Early Life and Education
- Charles Darwin was born on February 12, 1809, into a prosperous family in England.
- From a young age, he showed a keen interest in nature and science.
- Darwin excelled in his studies, which paved the way for his future contributions to science.
Contribution to Science
- Darwin is best known for his groundbreaking book, "On the Origin of Species."
- In this book, he proposed the idea that all plants and animals have evolved and changed over time.
- His work laid the foundation for the field of evolutionary biology and changed the way we understand the development of life on Earth.
|
53 videos|70 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Adaptations in Plants Class 4 Notes Science
| 1. Why do water or aquatic plants need to adapt? |  |
| 2. How do land or terrestrial plants adapt to their environment? |  |
| 3. What are some common adaptations in plants? |  |
| 4. How do plants adapt to different climates? |  |
| 5. Can plants adapt to human-induced changes in the environment? |  |