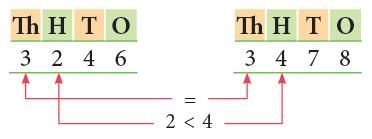4-Digit Numbers Class 3 Notes Maths
Why 4-Digit Numbers Matter
Imagine trying to tell someone how many chocolates you have, read the bus number, or check the odometer on a bike—without being able to write numbers! Four-digit numbers help us count thousands of things: money, days, scoreboards, and more.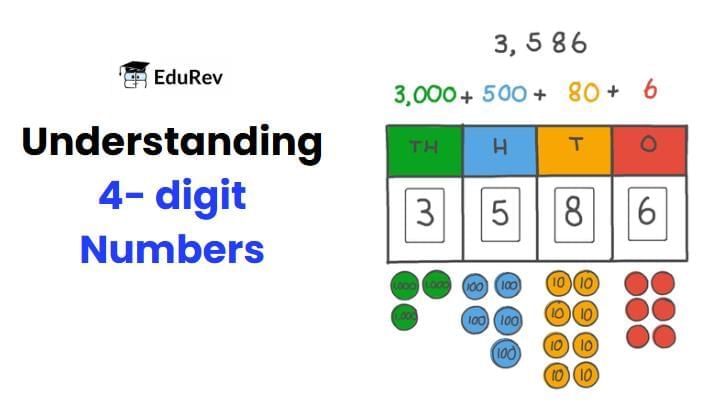
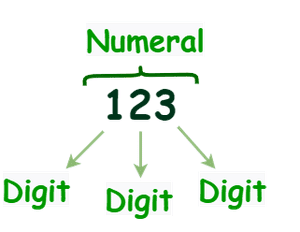
Difference between Digits and Numerals
- A digit is any one of the symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
 Difference between Numerals and Digits
Difference between Numerals and Digits
- A numeral is one or more digits written together to name a number (e.g. 5, 42, 589, 4 732).
- When digits are combined, they form numerals.
There are two types of numerals:
- Western Arabic Numerals: These are the everyday numbers we use, like 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
 Western Numerals
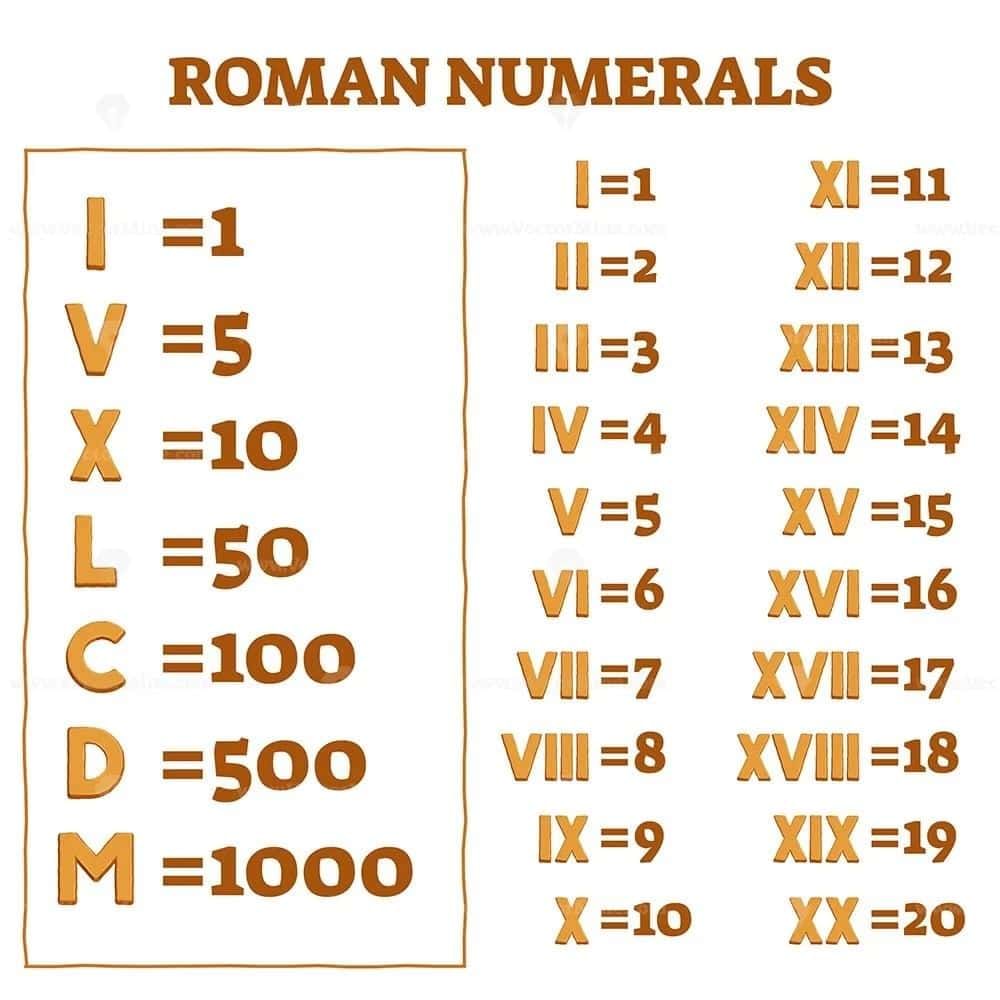
Western Numerals - Roman Numerals: These are special symbols that represent numbers, like I for 1, V for 5, X for 10, and so on.
What are 4-Digit Numbers ?
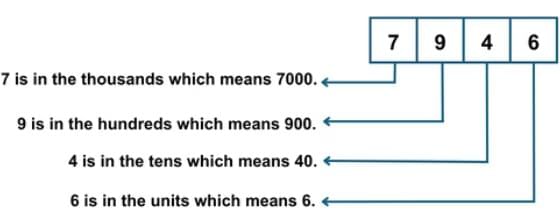
A numeral with four digits, like 7946, is called a four-digit number. To understand a number, we look at its place values, which go from Ones, Tens, Hundreds, to Thousands and beyond.
- We know that 999 is the greatest 3-digit number. Let us see which number comes just after 999.
- Recall, 9 + 1 = 10, 99 + 1 = 100. So, 999 + 1 = ?

- Let us understand how the number just after 999 can be formed pictorially.
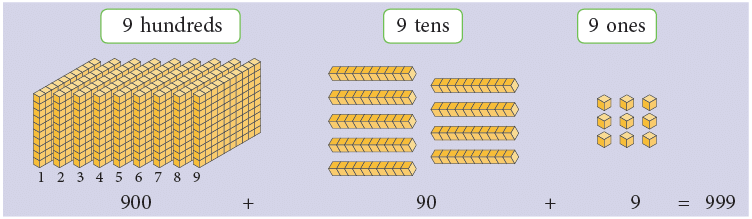 Add 1 (one) more to it and count the number of hundreds, tens, and ones.
Add 1 (one) more to it and count the number of hundreds, tens, and ones.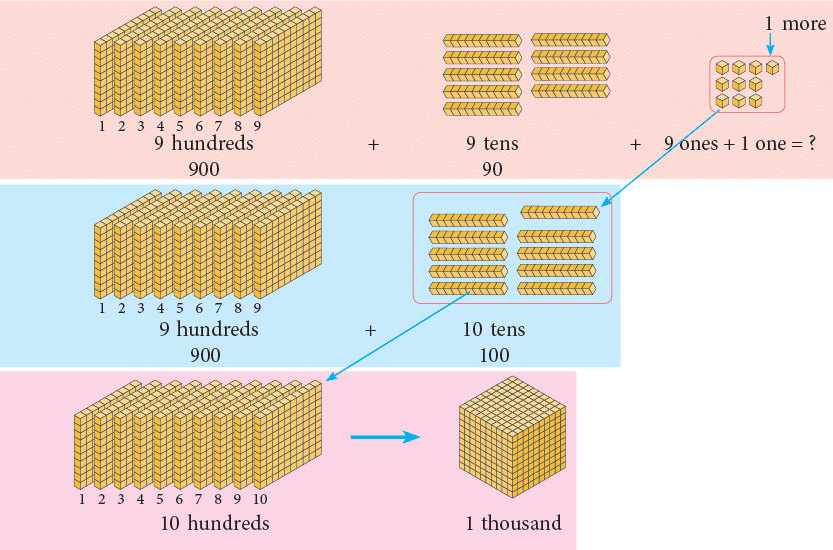
EduRev Tips:
- 10 ones = 1 ten. Change 10 ones to 1 stick of ten.
- 10 tens = 1 hundred. Change 10 tens to 1 block of hundred.
1 thousand is written as 1000.
1 thousand can be shown as:
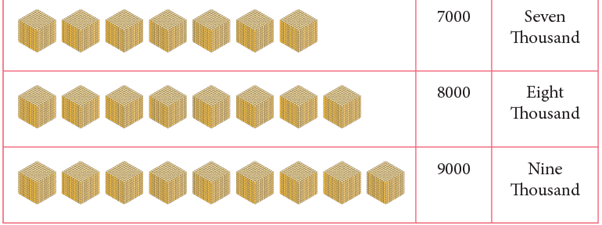
How to Count by Thousands?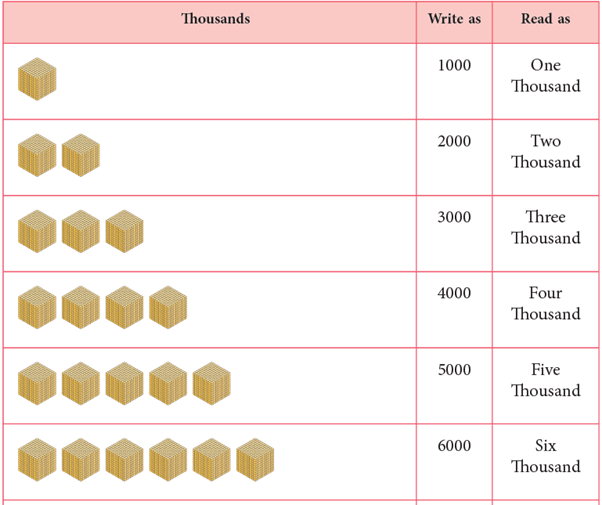
How to Form 4-Digit Numbers?
Have a look on: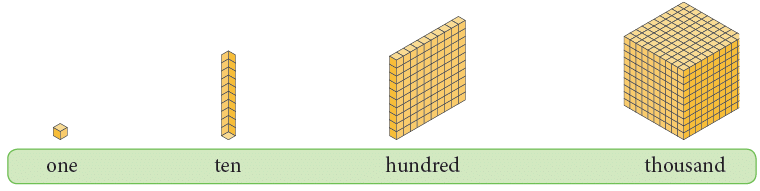 Now, observe the following.
Now, observe the following.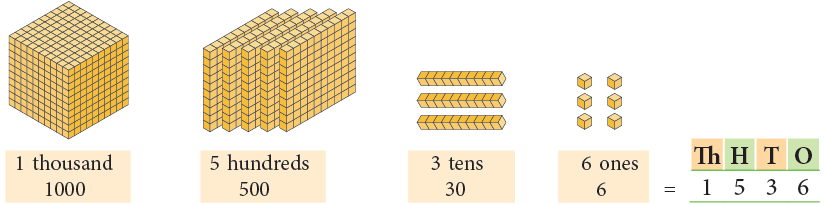 Number name for 1536 is ‘one thousand five hundred thirty-six.
Number name for 1536 is ‘one thousand five hundred thirty-six.We write the number 1536 in standard form as:

Likewise, we have
(a)
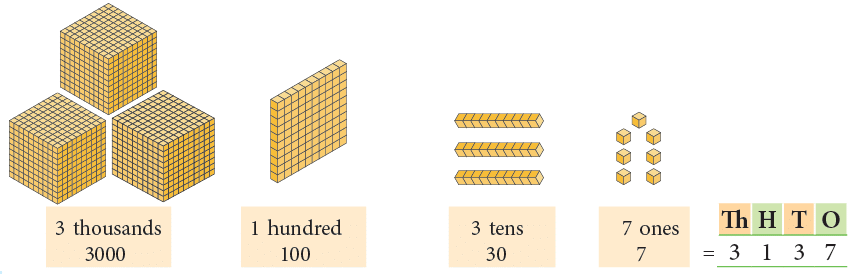
Number name: Three thousand one hundred thirty-seven
Standard form: 3,137
(b)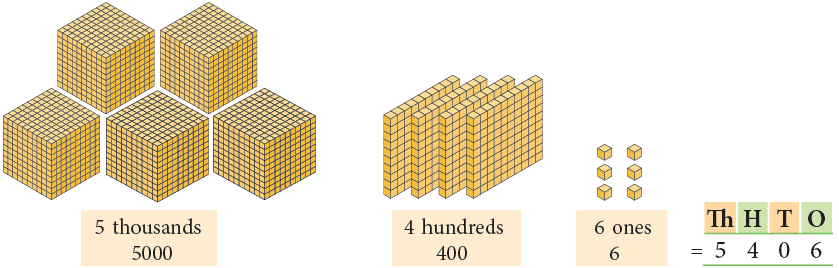
Number name: Five thousand four hundred six
Standard form: 5,406
(c)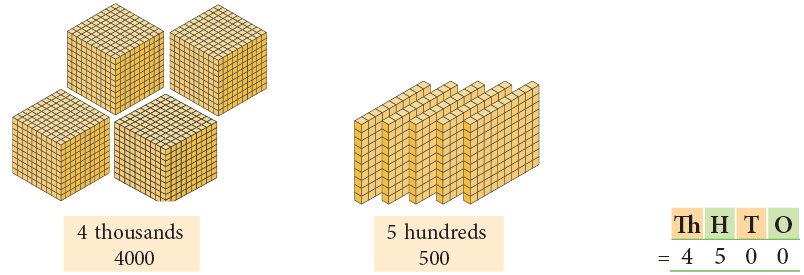
Number name: Four thousand five hundred
Standard form: 4,500
Similarly, we can form the numbers up to the largest 4-digit number, that is 9,999.
What are the different Ways to write a 4-digit Number?
A 4-digit number, say 5,789 can be written in three ways:
- Standard form: 5,789
- Expanded form: 5000 + 700 + 80 + 9
- Word form: Five thousand seven hundred eighty-nine
More Examples on Writing a 4-Digit Number:
Example1: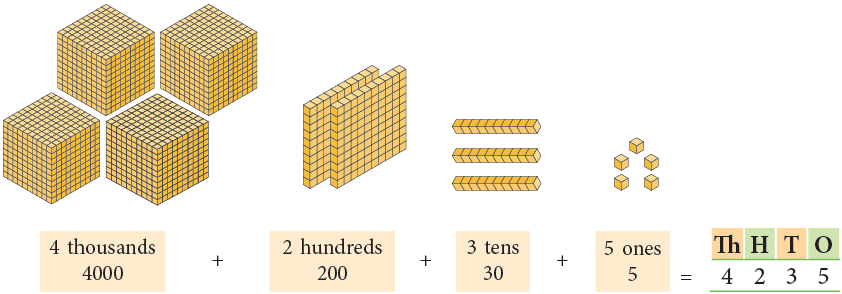
- Standard form: 4,235
- Expanded form: 4000 + 200 + 30 + 5
- Word form: Four thousand two hundred thirty-five
Example2: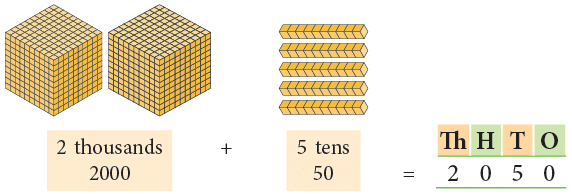
- Standard form: 2,050
- Expanded form: 2000 + 0 + 50 + 0
- Word form: Two thousand fifty
There are no hundreds, so put a ‘0’ at the hundreds place. There are no ones, so put a ‘0’ at the ones place.
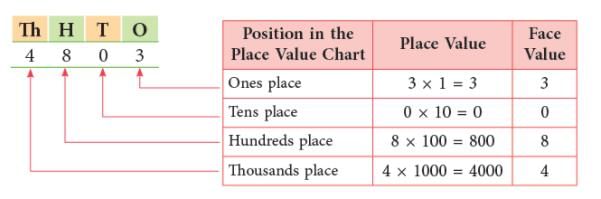
What are Place Value and Face Value?
You have already learned in the previous classes that place value of a digit in a number depends upon the place it occupies in the number.
The face value of a digit in a number is the digit itself. It does not depend on the place it occupies in the number. Consider the number 8435.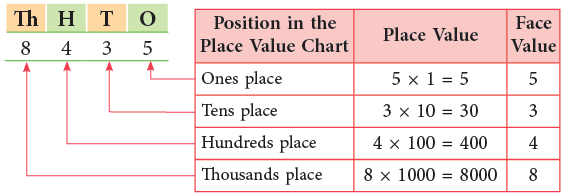
The face value and the place value of 0 is always 0.
What are Successors and Predecessors?
1. Successor
The number 18 comes just after 17. The number 18 is called the successor of 17.
The number that comes just after a particular number is called its successor.
You can get the successor by adding 1 to the number.
So, successor = given number + 1.
79 + 1 = 80, successor of 79; 460 + 1 = 461, successor of 460.
7652 + 1 = 7653, successor of 7652.
2. Predecessor
The number 16 comes just before 17. The number 16 is called the predecessor of 17.
The number that comes just before a particular number is called its predecessor.
You can get the predecessor by subtracting 1 from the number.
So, predecessor = given number – 1
88 – 1 = 87, predecessor of 88; 200 – 1 = 199, predecessor of 200.
9999 – 1 = 9998; predecessor of 9999.
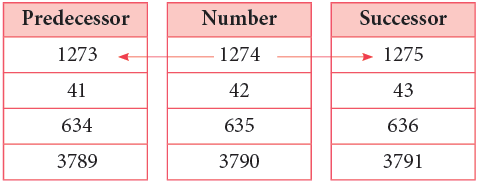
Observe the numbers in the middle column. Their predecessors are given in the first and the successors in the third column.
Comparing Numbers
1. Comparing Numbers with Different Digits
Rule: A number having more number of digits is greater than the number having lesser number of digits.
Example 1: Which is greater?
(a) 136 or 79
(b) 4386 or 896
(a) Do you notice that 79 is a 2-digit number while 136 is a 3-digit number? So, 136 > 79.
(b) 896 is a 3-digit number while 4386 is a 4-digit number. So, 4386 > 896.
2. Comparing Numbers with the Same Number of Digits
Rule: To compare two 4-digit numbers, first compare the digits at the thousands place. If they are equal, compare the digits at the hundreds place. If they are also equal, compare the digits at the tens place. If they are also equal, compare the digits at the ones place.
EduRev Tips: While comparing two numbers, always start comparing the digits from the leftmost place.
Ordering the Numbers
Ascending and Descending Orders
Ascending order means arranging the numbers from the smallest to the greatest.
Descending order means arranging the numbers from the greatest to the smallest.
 Ascending Order
Ascending Order  Descending Order
Descending Order
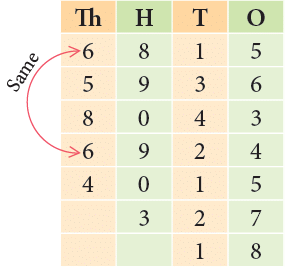
Example 1: Write the following numbers in descending and ascending order. 6815, 5936, 8043, 6924, 4015, 327, 18
Step 1: First, we arrange the given numbers in place value chart as shown.
Step 2: On comparing the digits at the thousands place, you would notice
8 > 6 > 5 > 4
There are two numbers with digit 6 at the thousands place.
Step 3: Comparing the digits at the hundreds place of 6815 and 6924, we notice that 9 > 8.
Therefore, 6924 > 6815.
Step 4: 327 has more digits than 18.
So, 327 > 18.
Thus, the given numbers arranged in descending order are:
8043 > 6924 > 6815 > 5936 > 4015 > 327 > 18
In ascending order the numbers would be arranged as:
18 < 327 < 4015 < 5936 < 6815 < 6924 < 8043
You may omit the symbol '<' and write them in simple form as under:
18, 327, 4015, 5936, 6815, 6924, 8043.
With some practice, it should be possible for you to write a given set of numbers in ascending or descending order without making a place value chart.
How to create the Smallest and Largest 4-Digit Numbers ?
1. When Digits are not Repeated
- The smallest 4-digit number using the digits 7, 3, 1, 9 can be formed by arranging the digits in ascending order, i.e., 1, 3, 7, 9. Thus, the required number is 1379.
- The largest 4-digit number using the digits 8, 6, 1, 2 can be formed by arranging the digits in descending order, i.e., 8, 6, 2, 1. Thus, the required number is 8621.
2. When One of the Digits is 0
If one of the digits is zero, as in 4, 7, 8, 0, then the largest number = 8740 and the smallest number = 4078 and not 0478 because 0478 becomes a 3-digit number.
3. When Digits are Repeated
Rule: To write the smallest 4-digit number, we arrange the digits in ascending order and repeat the smallest digit at the second highest place i.e, at the hundreds place.
Example 1: Write the smallest 4-digit number using the digits 1, 3, and 6. (Digits may be repeated)
Since we have to form the smallest 4-digit number using 3 given digits, we repeat the smallest digit, i.e., 1 at the hundreds place. Therefore, the required number is 1136.
Example 2: Write the greatest 4-digit number using the digits 3 and 7. The digits may be repeated.
Comparing the digits, we have 7 > 3. Since, we have to form the greatest 4-digit number using the two digits 3 and 7, we repeat the greater digit 7 at hundreds and tens place.
Therefore, the required greatest number is 7773.
|
45 videos|88 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on 4-Digit Numbers Class 3 Notes Maths
| 1. How can I form a 4-digit number using the digits 1, 2, 3, and 4? |  |
| 2. What are the definitions of successors and predecessors in terms of 4-digit numbers? |  |
| 3. How do I order a set of 4-digit numbers from smallest to largest? |  |
| 4. Can a 4-digit number start with zero? |  |
| 5. What is the range of 4-digit numbers? |  |