Soil Class 3 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Soil? |

|
| Types of Soil |

|
| Importance of Soil |

|
| Soil and Crops |

|
Introduction
One day, Meera and her little brother Rohan were playing in the garden. Meera was planting a small flower when Rohan asked, "Why do we put plants in the soil?" Meera smiled and said, "Because soil gives food and water to plants. Without soil, plants cannot grow!" Just then, their grandfather came and said, "Soil is not just for plants. It also gives homes to insects, worms, and even some small animals!" Rohan looked at the ground and saw an earthworm crawling. "Wow! Soil is so important!" he said excitedly. Let’s learn more about soil and why it is so useful!
What is Soil?
Soil is the thin layer of material covering the Earth's surface where plants grow. It is made of tiny pieces of rocks, dead plants and animals, air, water, and small living things like insects and bacteria. Soil helps plants grow by giving them the nutrients they need. Soil
Soil
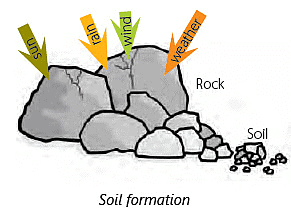
Formation of Soil
Soil takes a very long time to form. It does not happen in one day but over many, many years.
- Weathering of Rocks: Soil formation starts when rocks are exposed to elements like sunlight, rain, and wind. These forces break down the rocks into smaller and smaller pieces over time.
- Moving of Soil Particles: Wind and water carry these small rock pieces, called sediments, to different places. As they're transported, they rub against each other, further breaking down into tiny particles.
- Mixing with Dead Plants and Animals: Over time, these tiny particles mix with organic matter like fallen leaves and animal remains. This mixture, along with some water, forms what we call soil.
- Continual Process: Soil formation is an ongoing process in nature, but it happens very slowly. It can take millions of years for just an inch of soil to form.
What Does Soil Contain?
Soil is made up of different things that help plants grow.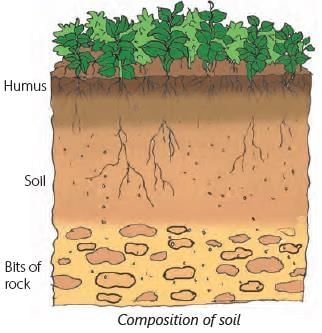
- Small Rock Pieces – Big rocks break into tiny pieces over time and mix with the soil.
- Humus – This comes from dead plants and animals. It makes the soil rich and helps plants grow. Dark soil has more humus.
- Water – Water fills small spaces in the soil. Plants need this water to grow.
- Air – Tiny air spaces in the soil help plant roots breathe.
All these things together make soil important for life!
Types of Soil
On the basis of the quantity of sand, clay, and humus present in the soil, we can divide soil into three main types:
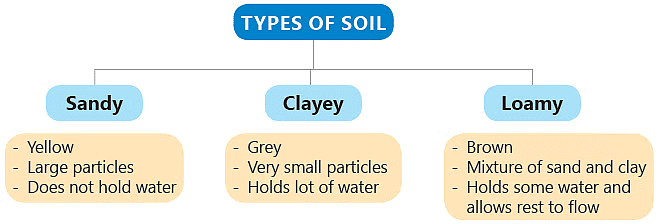
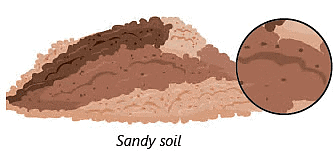
- Sandy Soil: This soil has lots of sand. It is dry and does not hold water well. However, it allows water to drain quickly, which can be good for some plants. Sandy soil warms up quickly in the spring, making it suitable for early planting.
- Clayey Soil: Clayey soil has a high proportion of clay particles. It's sticky when wet and hard when dry. Clayey soil holds water well but drains slowly, which can lead to waterlogging. It's nutrient-rich but can be difficult to work with, especially when wet, and may need amendments to improve drainage and aeration.
- Loamy Soil: Loamy soil is a mix of sand, clay, and humus(organic matter). It holds water but also drains extra water. It's often considered the ideal soil for gardening because it has good drainage, holds moisture well, and is nutrient-rich. Loamy soil is easy to work with and provides an excellent environment for plant roots to grow.
Importance of Soil
- Helps Plants Grow: Soil holds plant roots, gives them nutrients, and stores water.
- Keeps Water Clean: Healthy soil helps keep water fresh and safe.
- Controls Climate: Soil stores and releases carbon, which affects the air and weather.
- Home for Small Creatures: Earthworms, bacteria, and fungi live in the soil and help nature.
- Supports Buildings and Roads: Soil gives a strong base for houses, roads, and other structures.
- Used for Fun Activities: Soil is used for gardening, farming, and outdoor fun.
Overall, soil is essential for sustaining life, supporting ecosystems, and providing resources.
Soil and Crops
Soil is very important for growing crops. Farmers depend on soil to grow the food that we eat every day. Different types of soil are suitable for different crops:
- Sandy Soil – This soil is light and drains water quickly. It is good for crops like groundnut, watermelon, and coconut, which do not need too much water.
- Clayey Soil – This soil is heavy and can hold a lot of water. It is good for crops like rice and paddy, which need plenty of water to grow.
- Loamy Soil – This is the best soil for farming because it has the right balance of sand, clay, and humus. It is good for crops like wheat, sugarcane, cotton, and vegetables.
Healthy soil helps crops grow strong by giving them water and nutrients. At the same time, crops also help the soil. When leaves, stems, and old plants fall to the ground, they mix with the soil and make it richer and more fertile.
That is why farmers always say, “Healthy soil means healthy crops."
|
20 videos|121 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Soil Class 3 Notes Science
| 1. What is soil and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of soil? |  |
| 3. How does soil affect crop growth? |  |
| 4. What are crops and their significance? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between crops and soil? |  |
















