Multiplication Class 2 Notes Maths
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication is a fast way to add the same number again and again.
Instead of writing 4 + 4 + 4, we can say “3 times 4.”
Think of it like this:
- You have 3 baskets.
- Each basket has 4 apples.

- To find the total, you could add: 4 + 4 + 4.
- Or you can multiply: 3 × 4 = 12.
So, 3 groups of 4 apples give 12 apples in all!
Multiplication helps us count groups quickly and easily.
Multiplication as Repeated Addition
Adding the same number again and again is called repeated addition.
Example: Aryan has 5 tricycles. Each tricycle has 3 wheels. What is the total number of wheels in all the tricycles?

There are 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15 wheels in all.
3 is repeatedly added 5 times.
We write it as 3 × 5 = 15.
We say, 5 times 3 is 15 or 5 threes are 15 or 3 into 5 is 15.
Repeated addition of the same number is called multiplication.
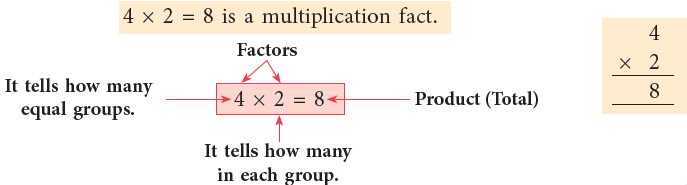
4 × 2 = 8 is a multiplication fact.
‘×’ is the sign of multiplication.
So, instead of adding the same number again and again, we can multiply to find out the answer.
Study the following.
Here are 4 baskets with 2 mangoes in each.
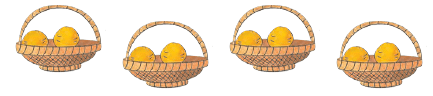
How many mangoes are there in all?
By adding repeatedly, we find that there are 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8 mangoes in all.
Using multiplication,
we write 4 × 2 = 8 and read as 4 times 2 are 8 or 4 multiplied by 2 is 8.
Multiplication on the Number Line
We already know that multiplication is repeated addition. We can represent multiplication on the number line by skip counting.
Let us find 3 × 5.
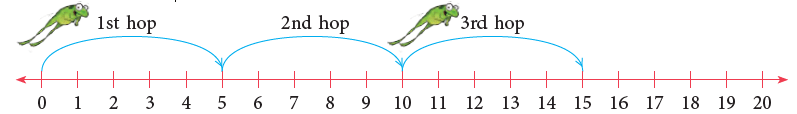
3 × 5 means take 3 skips of 5s starting from 0, as shown above.
We have reached 15 after 3 skips of 5s. So, 3 × 5 = 15.
Properties of Multiplication
Order Property of Multiplication

There are 2 rows of 5 pineapples each.
The multiplication fact becomes 2 × 5 = 10.
We can also think that there are 5 columns of 2 pineapples each.
Now, the multiplication fact becomes 5 × 2 = 10.
Since the product is the same in both cases,
we have 2 × 5 = 5 × 2 = 10.
We may multiply the numbers in any order, the product would be the same.
This basic property of multiplication is called the order property of multiplication.
Multiplicative Property of 1
5 groups of 1 = 5 × 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 5
1 group of 5 = 1 × 5 = 5
So, 5 × 1 = 1 × 5 = 5.
We can show the above results using a number line.
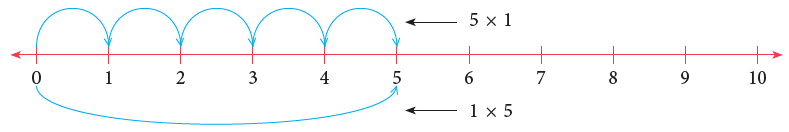
Any number multiplied by 1 equals that number. This is called the multiplicative property of 1.
Multiplicative Property of 0

There are 3 empty baskets, which means 3 groups of nothing.
So, 3 × 0 = 0.
Also, by order property 3 × 0 = 0 × 3 = 0.
Thus, we have
Any number multiplied by 0 equals 0. This is called the multiplicative property of 0.
Multiplication Tables
You have already learnt and memorised tables of 1 to 5 in Class 1. Let us revise the same.
Multiplication Table of 2
Count and build the table of 2.

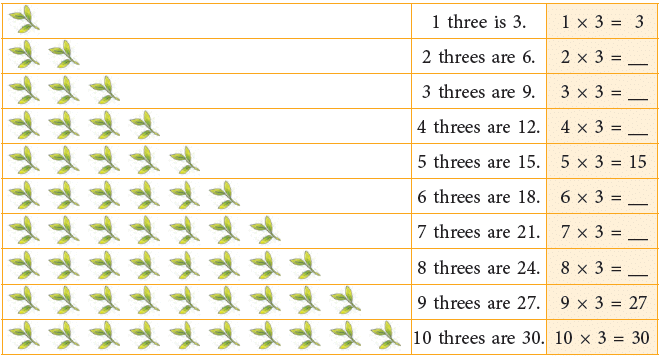
Multiplication Table of 3
Count and build the table of 3.
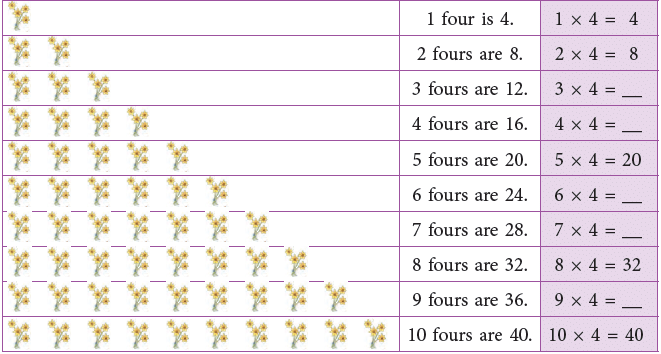
Multiplication Table of 4
Count and build the table of 4.
Multiplication Table of 5
Count and build the table of 5.

Multiplication Table of 6
Count and build the table of 6.

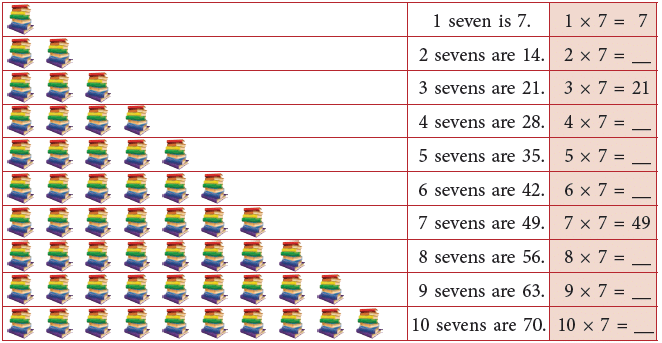
Multiplication Table of 7
Count and build the table of 7.
Multiplication Table of 8
Count and build the table of 8.

Multiplication Table of 9
Count and build the table of 9.
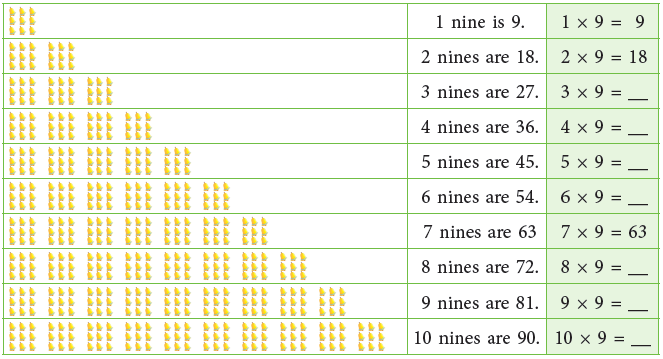
Multiplication Table of 10
Count and build the table of 10.

Problems Based on Real-Life Situations
Example 1: There are 6 bananas in a bunch. There are 9 bunches. How many bananas are there in all?
Sol:
Bananas in 1 bunch = 6
Bananas in 9 bunches = 9 × 6 = 54
Example 2: Reena has 5 pairs of gloves, 3 pairs of socks and 8 pairs of bangles. How many items are there in total?
Sol:
Number of gloves = 5 pairs = 5 × 2 = 10
Number of socks = 3 pairs = 3 × 2 = 6
Number of bangles = 8 pairs = 8 × 2 = 16
Total number of items = 10 + 6 + 16 = 32
Multiplication in Column Form
- Multiplication in Column Form is a way to multiply small and big numbers step by step by writing them neatly in columns.
- Let's understand with the help of an example.
Example 1: Multiply 6 x 3.
Sol: Let's learn multiplication step-by-step.
Step 1: Write the numbers in columns.
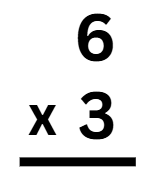
Step 2: Multiply 6 × 3 = 18.
Step 3: Write 8 in the one's place and carry over 1 (for 10) to the tens place.
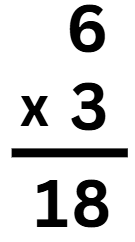
Example 2: Multiply 23 x 3.
Sol:
Step 1: Write the numbers in columns.
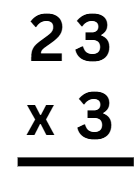
Step 2: Multiply the number in the ones place (3 × 3 = 9)
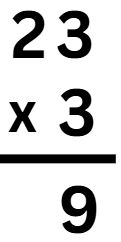
Step 3: Multiply the number in the tens place (2 × 3 = 6)
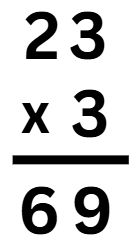
Column multiplication helps you multiply neatly and step by step!
|
32 videos|79 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Multiplication Class 2 Notes Maths
| 1. What is multiplication as repeated addition? |  |
| 2. How can I represent multiplication on a number line? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of multiplication? |  |
| 4. How can I memorize multiplication tables effectively? |  |
| 5. How can multiplication be applied to real-life situations? |  |





















