Strong & Weak Arguments | Logical Reasoning for CLAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Statement and Argument Reasoning? |

|
| Types of Statement and Argument |

|
| How to Solve Question Based on Statement and Argument Reasoning |

|
| Statement and Argument Questions |

|
What is Statement and Argument Reasoning?
An argument is a perspective on a specific issue, backed by supporting evidence. The task involves assessing the strength of the argument, and determining whether it is weak or strong. In technical terms, an argument consists of two or more statements, including a claim or conclusion, which is supported by one or more premises (statements that provide reasons for the conclusion). Some premises may not be explicitly stated but are implied, and these are called assumptions. The Statement and Argument reasoning section includes various types of questions, such as sequence arrangement, position tests, and time sequence tests. These kinds of logical reasoning problems are commonly found in government competitive exams.
Types of Statement and Argument
As now we know what consists of the questions related to the Statement and Argument reasoning section. Let us see the various types of questions that may come one by one from below. 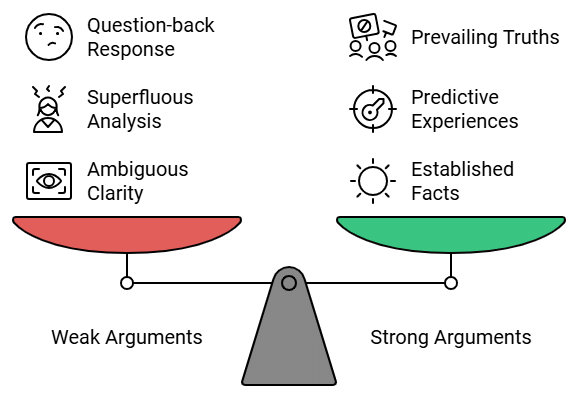
1. Weak Arguments
In weak argument reasoning, the provided arguments are either flimsy or illogical. Below are the types of weak arguments:
- Ambiguous Arguments:These arguments lack clarity on how they are related to the course of action, leaving the reader uncertain about the author’s intent. As a result, these arguments are weak.
- Superfluous Arguments:These arguments are unnecessary and fail to provide a deep analysis. They add little value, making them weak in nature.
- Irrelevant Arguments: Arguments that do not address the statement directly.
- Opinion-based Arguments: Arguments that rely on personal beliefs without evidence.
- Emotion-based Arguments: Arguments that appeal to emotions rather than logic or facts.
2. Strong Arguments
In strong argument reasoning, the provided arguments are solid and persuasive. Below are the types of strong arguments:
- Established Facts: These arguments are based on facts that are widely accepted as true, making them strong and reliable.
- Experiences predict that the result will follow: These arguments rely on past experiences, suggesting that a similar result will likely occur again, thus making them strong.
- Prevailing notion of truth: These arguments are based on beliefs or ideas that are universally acknowledged or accepted as true, ensuring their strength.
How to Solve Question Based on Statement and Argument Reasoning
Candidates can find various tips and tricks from below for solving the questions related to the Statement and Argument reasoning section. 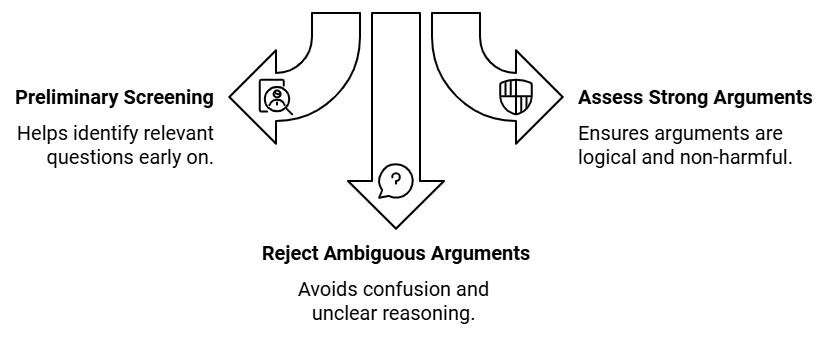
- Tip #1: Read the statement carefully to understand its main issue, then evaluate each argument for relevance and logical strength.
- Tip #2: Ensure strong arguments are supported by facts, past experiences, or widely accepted principles, and avoid those that are absurd, harmful, or irrelevant.
- Tip #3: Reject arguments that are ambiguous, irrelevant, or lack evidence.
Statement and Argument Questions
Q1: Statement: Should teachers be permitted to cane unruly children?
Argument:No, this will teach them that physical violence is an acceptable means of social behavior.
Solution: The argument is strong because it directly addresses the statement by highlighting a negative consequence of caning—promoting physical violence as acceptable behavior—which is a widely accepted social concern
Q2: Statement: Import of foreign items should be banned.
Arguments:Yes. Importing foreign books is of no use.
Solution: The argument is weak because it is too narrow, focusing only on books without addressing the broader implications of banning all foreign items. It also lacks evidence to support the claim that importing books is useless
Q3:Statement:Is privatizing all the schools in India the best solution to attain 100% liter- acy rate?
Argument:No, education will become unaffordable for poor people.
Solution: The argument states that education will become unaffordable for poor people if all the schools are privatized. Illiteracy is a huge problem amongst the poor sections of society. Privatization of education will make it expensive. Hence, it will not aid in attaining a 100% literacy rate, but on the contrary, work against it. Hence, this argument is strong.
Q4: Statement:Should India declare itself as a Hindu country?
Arguments:Yes, Because Hinduism is the largest religion in India, with 79.8% of the population identifying themselves as Hindu.
Solution: The argument is weak because, while it provides a factual statistic (79.8% of the population is Hindu), it does not logically justify declaring India a Hindu country, as it ignores the principles of secularism and the rights of minority groups.
Q5: Statement:Should learning self-defense be made compulsory for girl students?
Argument:Yes, in an environment where cases of assault on women are increasing, self-defense training becomes one essential part of women safety.
Solution: The argument is strong because it directly supports the statement by citing the increasing cases of assault on women, a verifiable trend, and logically connects self-defense training to improved safety for women
|
38 videos|128 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Strong & Weak Arguments - Logical Reasoning for CLAT
| 1. What is the difference between a statement and an argument in reasoning? |  |
| 2. How can I identify strong and weak arguments in reasoning? |  |
| 3. What are some common logical fallacies to watch out for in arguments? |  |
| 4. How can I practice statement and argument reasoning for exams? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to differentiate between strong and weak arguments? |  |
















