UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > UPSC Mains: International Relations > India & Organizations: BIMSTEC
India & Organizations: BIMSTEC | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
What is BIMSTEC?
- The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) is a regional multilateral organisation.
- Its members lie in the littoral and adjacent areas of the Bay of Bengal constituting a contiguous regional unity.
- Out of the 7 members,
- Five are from South Asia –
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- India
- Nepal
- Sri Lanka
- Two are from Southeast Asia –
- Myanmar
- Thailand
- Five are from South Asia –
- BIMSTEC not only connects South and Southeast Asia, but also the ecologies of the Great Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal.
- It mainly aims to create an enabling environment for rapid economic development; accelerate social progress; and promote collaboration on matters of common interest in the region.
Genesis of BIMSTEC
- This sub-regional organization came into being in 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- Initially, it was formed with four Member States with the acronym ‘BIST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Sri-Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- It became renamed ‘BIMST-EC’ in 1997, following the inclusion of Myanmar.
- With the admission of Nepal and Bhutan in 2004, the name of the grouping was changed to ‘Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation’ (BIMSTEC).
Objectives
- Creating an enabling environment for the rapid economic development of the sub-region.
- Encouraging the spirit of equality and partnership.
- Promoting active collaboration and mutual assistance in the areas of common interests of the member countries
- Accelerating support for each other in the fields of education, science, and technology, etc.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Principles of BIMSTEC
- Sovereign Equality
- Territorial Integrity
- Political Independence
- No-interference in Internal Affairs
- Peaceful Co- existence
- Mutual Benefit
- Constitute an addition to and not be a substitute for bilateral, regional or multilateral cooperation involving the Member States.
Potential
- Bridge between South and South East Asia and represents a reinforcement of relations among these countries.
- Platform for intra-regional cooperation between SAARC and ASEAN members.
- Home to around 1.5 billion people that constitute around 22% of the global population.
- With a combined gross domestic product (GDP) of 2.7 trillion economy, BIMSTEC Member States have been able to sustain an average 6.5% economic growth trajectory in the last five years.
- A fourth of the world’s traded goods cross the bay every year.
- Important Connectivity Projects:
- Kaladan Multimodal Project – links India and Myanmar.
- Asian Trilateral Highway - connecting India and Thailand through Myanmar.
- Bangladesh-Bhutan-India- Nepal (BBIN) Motor Vehicles Agreement - for seamless flow of passenger and cargo traffic.
Significance for India
- Allows India to pursue three core policies:
- Neighborhood First - primacy to the country’s immediate periphery;
- Act East - connect India with Southeast Asia; and
- Economic development of India’s northeastern states – by linking them to the Bay of Bengal region via Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- Allows India to counter China’s creeping influence in countries around the Bay of Bengal due to the spread of its Belt and Road Initiative.
- A new platform for India to engage with its neighbors with South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) becoming dysfunctional because of differences between India and Pakistan.
Areas of Cooperation
- Trade and Investment
- Technology
- Energy
- Transportation and Communication
- Tourism
- Fisheries
- Agriculture
- Cultural Cooperation
- Environment and Disaster Management
- Public Health
- People-to-People Contact
- Poverty Alleviation
- Counter Terrorism and Transnational Crime
- Climate Change
 |
Download the notes
India & Organizations: BIMSTEC
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Institutional Mechanisms
- BIMSTEC Summit – highest policymaking body in BIMSTEC process and is comprised of heads of state/government of member states.
- Ministerial Meeting – second apex policy-making forum of BIMSTEC attended by the External/Foreign Ministers of Member States.
- Senior Officials’ Meeting – represented by Senior Officials of Foreign Ministries of the Member States.
- BIMSTEC Working Group – attended by Ambassadors of BIMSTEC Member Countries to Bangladesh or their representatives on a monthly basis at the BIMSTEC Secretariat in Dhaka.
- Business Forum & Economic Forum – the two important forums to ensure active participation of private sector.
Challenges
Though largely devoid of bilateral tensions, as is the case in SAARC, BIMSTEC does not seem to have made much progress.
- Inconsistency in Meetings: BIMSTEC planned to hold summits every two years, ministerial meetings every year, but only four summits have taken place in 20 years upto 2018.
- Neglect by member states: It seems that India has used BIMSTEC only when it fails to work through SAARC in the regional setting and other major members like Thailand and Myanmar are focused more towards ASEAN than BIMSTEC.
- Broad Focus Areas: The focus of BIMSTEC is very wide, including 14 areas of cooperation like connectivity, public health, agriculture etc. It is suggested that BIMSTEC should remain committed to small focus areas and cooperate in them efficiently.
- Bilateral Issues between Member Nations: Bangladesh is facing one of the worst refugee crisis of Rohingyas from Myanmar who are fleeing prosecution in the state of Rakhine in Myanmar. There is a border conflict between Myanmar and Thailand.
- No FTA: BIMSTEC FTA was negotiated in 2004, talks on it are yet to be concluded.
- BCIM: The formation of another sub-regional initiative, the Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar (BCIM) Forum, with the proactive membership of China, has created more doubts about the exclusive potential of BIMSTEC.
Utility SAARC vs BIMSTEC
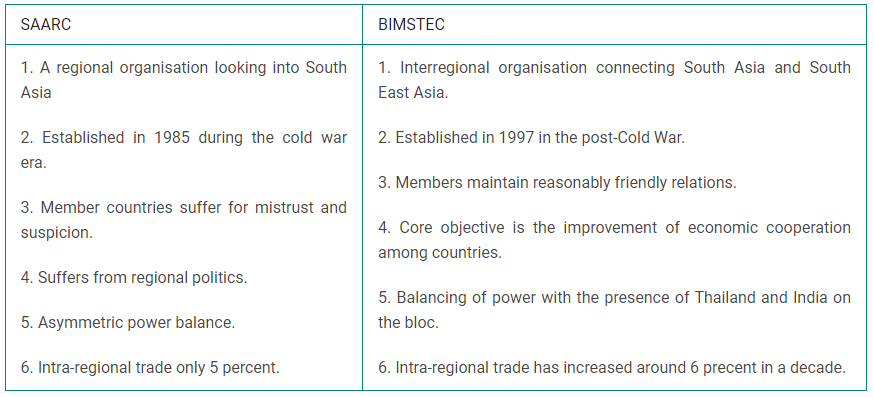
Way forward
- Since the BIMSTEC region is notable for its diversity, the member states need to build on the regional synergies and work towards utilising the available resources in the most optimal manner.
- This would help build a stronger and a more dynamic BIMSTEC.
The document India & Organizations: BIMSTEC | UPSC Mains: International Relations is a part of the UPSC Course UPSC Mains: International Relations.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
88 videos|120 docs
|
FAQs on India & Organizations: BIMSTEC - UPSC Mains: International Relations
| 1. What does BIMSTEC stand for? |  |
| 2. Which countries are members of BIMSTEC? |  |
Ans. The member countries of BIMSTEC are India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Nepal, and Bhutan.
| 3. What is the main objective of BIMSTEC? |  |
Ans. The main objective of BIMSTEC is to promote regional cooperation and integration among member countries in sectors such as trade, investment, technology, tourism, agriculture, energy, and transportation.
| 4. What are the key areas of cooperation under BIMSTEC? |  |
Ans. The key areas of cooperation under BIMSTEC include trade and investment, transport and communication, energy, tourism, fisheries, agriculture, public health, poverty alleviation, counter-terrorism, and climate change.
| 5. How does India contribute to BIMSTEC? |  |
Ans. India plays a significant role in BIMSTEC as one of the founding members. It actively participates in various programs and initiatives under BIMSTEC, including hosting summits, providing technical assistance, and promoting economic cooperation among member countries.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches



















