Dark Energy & Dark Matter | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Matter is anything that has mass and takes space. But apart from the ‘normal’ matter, there are different other forms of hypothesized matter. A few examples include Dark Matter, Anti Matter, and Negative Matter.
You by now know that matter and energy are interconvertible; so there is Dark Energy, Anti Energy, and Negative Energy too.
Now let’s see what each of these terms signify.
The term ‘dark’ is used to denote the unknown.
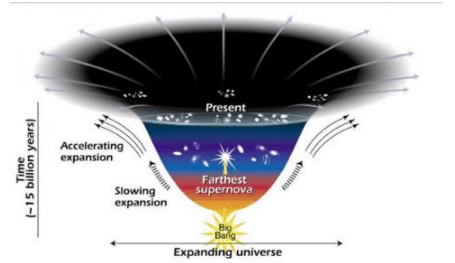
- Dark energy is an unknown form of energy hypothesized to permeate all of space, driving the accelerating expansion of the universe. Recent 2025 studies, such as those from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), suggest dark energy’s strength may evolve over time, challenging the traditional view of it as a constant force.
- Dark matter acts as an attractive force — a kind of cosmic cement that holds our universe together. It interacts gravitationally but does not reflect, absorb, or emit light. Emerging 2025 theories propose a complex ‘dark sector’ with multiple particles and forces, though some models suggest alternatives like singularities reducing the need for dark matter.
- Dark energy is a repulsive force — a sort of anti-gravity — that fuels the universe’s accelerating expansion. Its potential variability, as indicated by 2025 observations, is critical for understanding cosmic evolution.
- Dark energy is the dominant component, accounting for roughly 68 percent of the universe’s total mass and energy, though its evolving nature may affect this proportion over cosmic time.
- Dark matter constitutes approximately 27 percent, shaping galaxy formation through its gravitational influence.
- And the rest – a mere 5 percent is all the regular matter we see and interact with every day.
- The velocity of rotation for spiral galaxies depends on the amount of mass contained in them. However, the outer arms of the Milky Way rotate much faster than expected based on visible matter alone.
- This rapid rotation is possible only with additional mass, believed to come from dark matter, as confirmed by 2025 data from the Euclid telescope.
- Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter, likely composed of undiscovered subatomic particles, possibly within a complex dark sector, as explored in 2025 research.
- The name dark matter refers to the fact that it does not interact with observable electromagnetic radiation, such as light.
- It is thus invisible (or ‘dark’) to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, making it extremely difficult to detect.
- Dark matter interacts with the rest of the universe only through its gravity (that’s how we know it exists).
- The material is considered ‘matter’ due to its gravitational attraction and ‘dark’ because it does not interact with light or any part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Are Black Holes Dark Matter?
Black holes could be considered as a form of dark matter for the reasons mentioned below:
- Almost collision-less.
- They are stable (if sufficiently massive).
- They have non-relativistic velocities.
- They formed very early in the history of the universe.
In March 2016, three groups of researchers proposed that black holes had a primordial origin. Results from two groups suggested that primordial black holes could account for most dark matter. The third group concluded that black holes contributed less than 1% of total dark matter. By 2025, ongoing research, including Euclid telescope observations, continues to explore this hypothesis, though the dark sector model is gaining traction.
Anti-Matter and Anti Energy
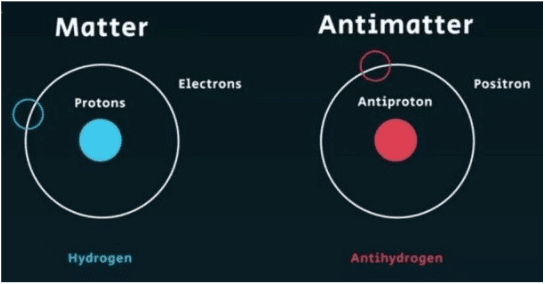
- ‘Anti’ means the opposite. So anti-matter has some properties opposite with respect to the usual matter.
- For example, the electron has as its antiparticle the antielectron. The electron and the antielectron have exactly the same masses, but they have exactly opposite electrical charges.
- It is hypothesized that every elementary particle in the Universe has a partner particle, known as an ‘antiparticle’.
- The particle and its antiparticle share many similar characteristics, but many other properties are the exact opposite.
- The electron, for example, has as its antiparticle the antielectron. They both have the same masses, but they have exactly opposite electrical charges.
- Most of the human understanding of anti-matter comes from high-energy accelerator experiments.
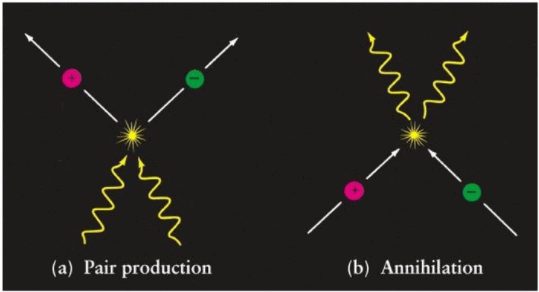
- When a matter particle meets its antimatter particle, they destroy each other completely (i.e. annihilation), releasing the energy equivalent of their rest masses (following Einstein’s E = mc2).
- For instance, when an electron meets an antielectron, the two annihilate and produce a burst of light which produces a corresponding energy level equivalent to the masses of the two particles.
Negative Matter and Negative Energy
- Negative matter is a hypothetical type of matter which, if it exists, will have negative mass and negative energy.
- It will in essence have a negative gravitational charge and repel normal matter. Yet it will interact just like any other matter in every other way.
- Hope you remember that matter and anti-matter will attract each other resulting in annihilation. But matter and negative matter will repel each other under gravity.
Neutrinos
- Proton, neutron, and electron are tiny particles that make up atoms. The neutrino is also a tiny elementary particle, but it is not part of the atom.
- A neutrino is a subatomic particle very similar to an electron but has no electrical charge and a very small mass, which might even be zero.
- There are actually three kinds of neutrinos: the electron neutrino, the muon neutrino, and the tau neutrino.
- Neutrinos are one of the most abundant particles in the universe. Because they have very little interaction with matter, they are incredibly difficult to detect.
- They interact very weakly with other matter particles. So weakly that every second, trillions of neutrinos pass through our bodies unnoticed.
- Neutrinos come from the sun (solar neutrinos), other stars, cosmic rays from beyond the solar system, and the Big Bang. They can also be produced in laboratories.
- The India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) will study atmospheric neutrinos, contributing to global particle physics research. Solar neutrinos have lower energy than INO’s detectors can measure.
Future Applications of Neutrino Science
Basic sciences research is essential to understand particle properties before practical applications emerge. A century ago, the electron’s discovery had no immediate uses; today, electronics are indispensable.
- Properties of the Sun: Visible light comes from the sun’s surface, but neutrinos, traveling near light speed, originate in its core. Studying neutrinos reveals insights into the sun’s interior, aiding solar physics.
- Constituents of the Universe: Light from distant stars helps detect new planets. Better understanding of neutrinos can enhance their use in astronomy to map the universe’s composition, complementing 2025 cosmological studies.
- Probing the Early Universe: Neutrinos, due to their weak interactions, travel vast distances undisturbed. Extragalactic neutrinos may carry clues from the universe’s infancy, post-Big Bang, informing cosmology research in 2025.
- Medical Imaging: Neutrino detector technologies, like those developed for INO, may lead to advances in medical imaging, similar to how particle physics research produced X-ray machines and MRI scans.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Dark Energy & Dark Matter - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is dark energy? |  |
| 2. What is dark matter? |  |
| 3. How do we know dark energy and dark matter exist if they are invisible? |  |
| 4. What are the current theories explaining the nature of dark energy and dark matter? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of dark energy and dark matter on the future of the universe? |  |

















