DRDO - A View | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
DRDO works under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India. It is dedicated to establishing a world-class science and technology base for India, equipping the Defence Services with internationally competitive systems and solutions. As of 2025, DRDO, led by Chairman Dr. Samir V. Kamat, focuses on futuristic technologies like quantum computing, artificial intelligence, and advanced materials to address emerging threats such as cyber warfare and space-based challenges, while strengthening India’s self-reliance in defence manufacturing through the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
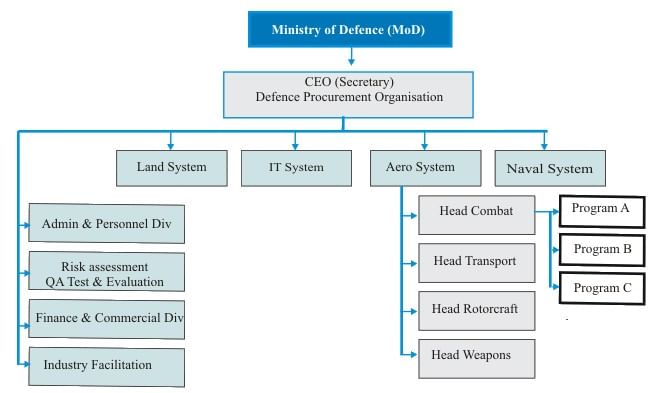 DRDO- Organisation Structure
DRDO- Organisation Structure
Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)
DRDO operates under the Ministry of Defence, Government of India, and is led by Dr. Samir V. Kamat as Chairman in 2025. It strives to provide the Defence Services with a decisive edge by developing advanced systems and solutions, contributing to India’s goal of achieving Rs 35,000 crore in defense exports by 2025.
1. Genesis & Growth
- DRDO was established in 1958 by combining the Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army, the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP), and the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- From 10 laboratories, DRDO has expanded to a network of 52 laboratories engaged in developing defense technologies across aeronautics, armaments, electronics, combat vehicles, engineering systems, instrumentation, missiles, advanced computing, special materials, naval systems, life sciences, training, information systems, and agriculture.
- The organization is supported by over 5,000 scientists and approximately 25,000 scientific, technical, and supporting personnel.
- Major projects include missiles, armaments, light combat aircraft, radars, and electronic warfare systems, with significant achievements in these areas.
- In 2025, DRDO established the Defence Space Research Agency (DSRO) to develop space warfare weapon systems, enhancing coordination with tri-services integrated Defence staff officers.
2. Mission
- Design, develop, and produce state-of-the-art sensors, weapon systems, platforms, and allied equipment for the Defence Services.
- Provide technological solutions to optimize combat effectiveness and promote troop well-being.
- Develop infrastructure, quality manpower, and a strong indigenous technology base, supporting India’s Rs 35,000 crore defense export target by 2025.
3. Recent Developments and Achievements
- In March 2025, DRDO and the Indian Navy successfully flight-tested an indigenously-developed Vertically-Launched Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile, enhancing naval defense capabilities.
- The tenth Ammunition Cum Torpedo Cum Missile (ACTCM) barge, LSAM 24 (Yard 134), was launched in March 2025, strengthening naval operations.
- DRDO conducted high-altitude trials of the Indigenous Integrated Life Support System for LCA Tejas in March 2025, improving pilot safety and performance.
- The Cabinet Committee on Security approved the acquisition of 307 Advanced Towed Artillery Gun Systems (ATAGS) worth nearly Rs 7,000 crore in March 2025, advancing self-reliance in defense manufacturing.
- A contract for High Mobility Vehicle 6x6 Gun Towing Vehicles was signed in March 2025 to enhance the Indian Army’s operational readiness.
- The Instruments Research and Development Establishment (IRDE) is developing a new electro-optical drone detection system to counter UAV threats, independent of other anti-drone projects like D-4 from LRDE.
- The Integrated Drone Detection and Interdiction System (IDD&IS) Mk2A, featuring a 360° EO/IR sensor and electronic warfare capabilities, entered production and deployment in 2025.
4. Defence Space Research Agency (DSRO)
The Cabinet Committee on Security, headed by the Prime Minister, established the Defence Space Research Agency (DSRO) to develop space warfare weapon systems and technologies. As of 2025, DSRO collaborates closely with tri-services integrated Defence staff officers, providing R&D support to the Defence Space Agency (DSA) in Bengaluru, led by an Air Vice Marshal-rank officer. DSA is integrating space-related capabilities, including the Defence Imagery Processing and Analysis Centre in New Delhi and the Defence Satellite Control Centre in Bhopal.
- DSRO employs a team of scientists working with tri-services officers.
- It supports the DSA, which comprises members of the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- DSA aims to enhance India’s capabilities to fight wars in space.
- DSA is gradually taking over space-related operations of the three forces.
- Existing military space agencies are being merged with DSA.
5. Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP)
The Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP), initiated in the early 1980s and completed in 2007, was a Ministry of Defence program led by Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam to achieve self-sufficiency in missile technology. It developed missiles like Prithvi, Trishul, Akash, Nag, and Agni. After its successful completion in 2008, DRDO continued advancing missile technology, with notable achievements like the March 2025 flight test of a Vertically-Launched Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile.
- IGMDP was launched to counter the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), which restricted India’s access to missile technology.
- A consortium of DRDO laboratories, industries, and academic institutions developed subsystems, components, and materials.
- Missiles developed include short-range surface-to-surface (Prithvi), short-range surface-to-air (Trishul), medium-range surface-to-air (Akash), and anti-tank (Nag).
- The Agni missile, initially a technology demonstrator, was upgraded to a ballistic missile with multiple ranges.
- Agni missiles are long-range, nuclear-capable ballistic missiles, with Agni-I first tested in 1989 and later separated from IGMDP for strategic importance.
6. Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)
The MTCR, established in 1987 by Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK, and the US, aims to limit missile and missile technology proliferation. It focuses on rockets and UAVs capable of delivering a 500 kg payload over 300 km. India joined the MTCR in 2016, enhancing its access to missile technology while adhering to non-proliferation norms. The MTCR is not a legally binding treaty.
7. Defence Acquisition Organization (DAO)
To enhance the procurement process and support the ‘Make in India’ initiative, the Ministry of Defence established the Defence Acquisition Organization (DAO), as recommended by the Pritam Singh Committee. As of 2025, DAO operates autonomously under the Ministry of Defence, formulating policy, planning, and executing weapons purchases for the Armed Forces. Funded with approximately Rs 400 crore initially, DAO ensures accountability and aligns with India’s self-reliance goals.
8. Principles and Organizational Structure
DRDO’s operations are guided by principles ensuring an autonomous, decentralized decision-making defense procurement organization with accountability and transparency, delivering within the PTCR (Performance, Cost, Time, and Risk) envelope based on annual acquisition plans:
- Risk management rather than risk avoidance.
- Individual rather than group accountability.
- Quarterly performance measures with internal customers (Army, Navy, Air Force).
- A process differentiated into three steps with autonomy and accountability.
- Technical requirements identification.
In 2025, DRDO has intensified collaboration with private industry, startups, and academia, with 25% of the 2022-23 defense R&D budget allocated to these sectors, fostering innovation and reducing import reliance under Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on DRDO - A View - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is DRDO? |  |
| 2. What are the main objectives of DRDO? |  |
| 3. How does DRDO contribute to national security? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of successful projects undertaken by DRDO? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to DRDO's efforts? |  |






















