India’s 3 Stage Nuclear Programme | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| India's 3-Stage Nuclear Programme |

|
| Understanding the 3-Stages of India’s Nuclear Program |

|
| Introduction to PFBR (Stage II) |

|
| Reasons Behind the Delay of PFBR (Stage II) |

|
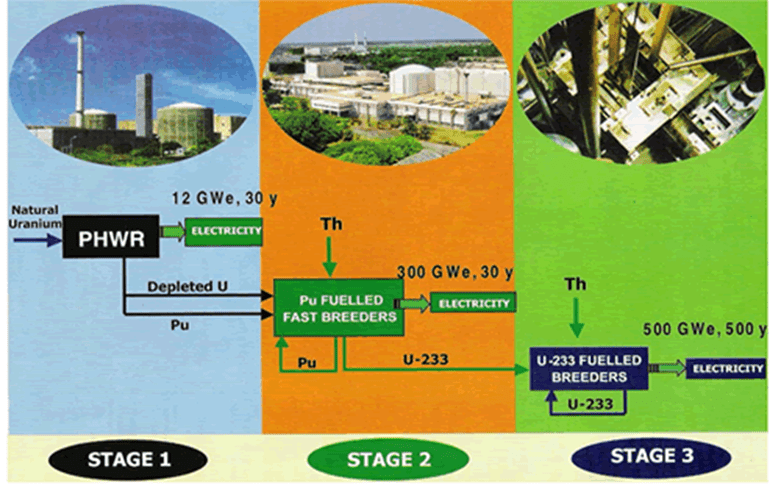
India's 3-Stage Nuclear Programme
India’s three-stage nuclear power programme, envisioned by Homi Bhabha in the 1950s, ensures long-term energy security by leveraging limited uranium and abundant thorium reserves. By 2025, it advances energy independence, supporting India’s net-zero carbon goal by 2070 through a sustainable nuclear fuel cycle.
- Stage 1: Employs natural uranium-fueled Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) to produce plutonium.
- Stage 2: Uses plutonium in Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) to breed uranium-233 from thorium.
- Stage 3: Deploys thorium-based Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs) for sustainable energy.
Thorium's Potential:
- India holds ~25% of global thorium reserves, making it a strategic asset, despite complex breeding requirements.
- Thorium’s conversion to fissile uranium-233 is costlier than uranium but ensures long-term sustainability.
Current Research and Development
The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) drives indigenous R&D for advanced nuclear systems, aligning with the three-stage programme. By 2025, India’s nuclear capacity is ~8,000 MW, with new 700 MW PHWRs at Kakrapar (Units 3 & 4) and Kudankulam (Units 3 & 4) operational. Nine reactors are under construction, and 10 more are approved for fleet-mode deployment by 2032. The 2025 Nuclear Energy Mission (₹20,000 crore) supports Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and thorium research, with BARC advancing AHWR designs and pilot projects.
 3 Stage Nuclear Programme
3 Stage Nuclear Programme
Understanding the 3-Stages of India’s Nuclear Program
The three-stage programme aims for nuclear self-sufficiency, utilizing India’s thorium reserves via a closed fuel cycle for sustainable energy. By 2025, it supports decarbonization and complements renewables, aligning with global nuclear resurgence.
Stage I: Employs Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) using natural uranium-238 (U-238), containing uranium-235 (U-235) for chain reactions.
- PHWRs use heavy water (deuterium) to moderate neutrons, enhancing fission efficiency under pressure.
- Fission produces plutonium-239 (Pu-239) and energy, consuming U-235 fully.
Stage II: Utilizes Pu-239 with U-238 in Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) to generate energy and breed more Pu-239 and uranium-233.
- The Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) at Kalpakkam achieved core loading in March 2024 and criticality in 2025, a major milestone.
- The Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam, Ltd. (BHAVINI), established in 2003, oversees Stage II, with plans for two additional FBRs by 2030.
Stage III: Employs Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs) using thorium-plutonium fuels to breed uranium-233 (U-233) from thorium-232 (Th-232), with pilot projects underway by 2025.
Introduction to PFBR (Stage II)
- A breeder reactor generates more fissile material than it consumes, key to Stage II.
- In ‘fast’ breeder reactors, unmoderated neutrons enable specific fission reactions.
Role of PHWRs in Breeding:
- PHWRs use natural uranium-238 (U-238) to produce plutonium-239 (Pu-239) as a byproduct.
- Pu-239 is mixed with U-238 to create mixed oxide fuel for FBR cores, with blanket material breeding more Pu-239.
- Blanket material reactions yield additional Pu-239, enhancing fuel efficiency.
Coolant System in PFBR:
- The PFBR uses liquid sodium coolant in two circuits for heat transfer.
- Primary coolant absorbs heat and radioactivity, transferring heat to the secondary circuit via exchangers.
- Secondary coolant powers generators, producing electricity safely.
Use of Thorium in PFBR:
- Thorium-232 (Th-232) serves as a blanket material in PFBRs.
- Th-232, non-fissile, transmutes into fissile uranium-233 (U-233).
- U-233 fuels Stage III, enabling thorium-based energy.
Transition to Third Stage
- The PFBR bridges Stages II and III, producing U-233 for thorium-based AHWRs, leveraging India’s vast thorium reserves.
Future Plans for PFBR:
- The PFBR (500 MWe) achieved criticality in 2025, with commercial operations imminent.
- DAE plans two additional FBRs by 2030, supported by the 2025 Nuclear Energy Mission’s funding.
Reasons Behind the Delay of PFBR (Stage II)
The Fast Breeder Test Reactor (FBTR) at Kalpakkam tested technologies for the Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR).- Post-1974 ‘Smiling Buddha’ sanctions forced FBTR to use mixed carbide fuel instead of enriched uranium, reducing output.
- Fuel changes altered FBTR’s operating conditions, complicating PFBR development.
- By 2003, PFBR’s start saw key FBTR team members retired, causing expertise gaps.
- A 2014 CAG audit criticized BHAVINI for over-relying on NPCIL for PFBR components.
- Technical issues with the sodium coolant system delayed progress.
- Costs escalated from ₹3,492 crore to over ₹6,800 crore, with criticality achieved in 2025.
- The Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) designed PFBR, overcoming delays with 2025 criticality.
Challenges Ahead for the Stage II of India’s Nuclear Program
- FBRs’ thorium fuel cycle produces radioactive isotopes (caesium-137, actinium-227, radium-224/228, thorium-230), complicating handling.
- The IAEA urged an independent regulator in 2015; the NSRA Bill remains under review in 2025, criticized for government control.
- The NSRA aims to replace the AERB, enhancing safety oversight.
- Nuclear power’s higher cost (~₹6/kWh) versus solar (~₹2.5/kWh) is offset by reliability and decarbonization benefits.
- The 2025 Nuclear Energy Mission promotes SMRs and PPPs to improve cost-efficiency and expand capacity, with NPCIL targeting one reactor commission annually.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on India’s 3 Stage Nuclear Programme - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key stages of India's Nuclear Programme? |  |
| 2. What is the purpose of the Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) in Stage II? |  |
| 3. What factors have contributed to the delays in the commissioning of the PFBR? |  |
| 4. How does India's 3-stage Nuclear Programme contribute to energy security? |  |
| 5. What are the expected benefits of the PFBR once it becomes operational? |  |















