Heat Budget of The Earth | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The Earth's heat budget refers to the equilibrium between the incoming solar energy, known as solar insolation, and the outgoing heat emitted by the planet, called terrestrial radiation. This balance is crucial for maintaining the Earth's average annual temperature at around 15 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit). In simpler terms, the heat budget ensures that the Earth does not become too hot or too cold by regulating the amount of solar energy it receives and the heat it releases back into space.
Heat Budget of the Earth and Atmosphere
- The Earth's heat budget refers to the balance between the total solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface and the heat energy that is emitted back into the atmosphere. This solar radiation, known as global radiation, consists of both direct shortwave radiation from the Sun and diffuse radiation that has been scattered by the atmosphere.
- When this solar radiation reaches the Earth's surface, it is transformed into heat energy, which in turn warms the planet's outer surface. As a result, the Earth also emits energy back into the atmosphere in the form of long-wave radiation. This process involves two main types of radiation: incoming shortwave solar radiation from the Sun toward the Earth, and outgoing longwave terrestrial radiation from the Earth back into the atmosphere.
- The balance of these two forms of radiation is crucial for maintaining the Earth's overall temperature and climate.
How it is calculated?
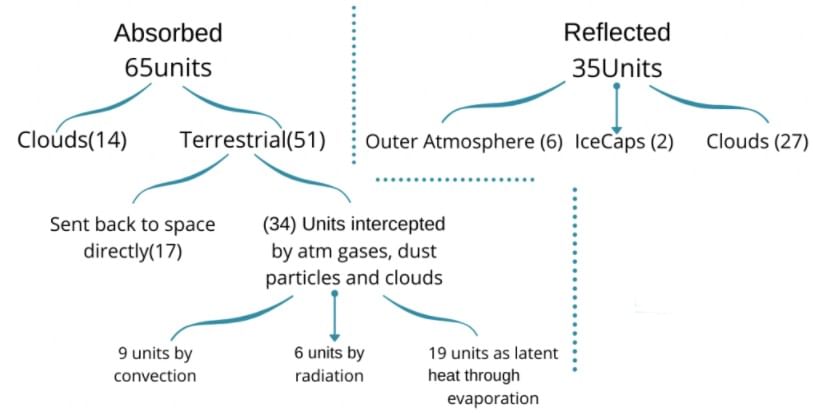
Suppose incoming solar insolation is = 100 units Amount lost through scattering and reflection.
a) Through Clouds- 27units
b) By dust particles – 6units
c) By Ice Caps and Glaciers- 2units
Total 35 units are reflected back into space. (known as albedo of the earth) Now, the units received by earth and its atmosphere = 100 – 35 = 65units.
Heat budget of the Earth
The Earth's heat budget consists of the balance between the incoming solar radiation and the outgoing terrestrial radiation. A total of 51 units of solar insolation are received by the Earth, which can be divided into two categories:
- Direct Radiation: 34 units
- Diffused Daylight: 17 units
Together, this amounts to 51 units of solar radiation.
The heat budget of the atmosphere involves the absorption of solar radiation by atmospheric gases in different vertical zones, which accounts for 14 units. Combining this with the initial 51 units, the total solar insolation received by the Earth and its atmosphere amounts to 65 units. Out of the 51 units of solar radiation received directly by the Earth, 17 units are re-radiated back into outer space, while the remaining 34 units are absorbed by the atmosphere in the form of outgoing terrestrial radiation. This results in a total of 48 units (14 + 34 = 48) of atmospheric heat.
- Albedo refers to the measure of how much light that strikes a surface is reflected back without being absorbed. It is represented as a reflection coefficient with a value of less than one. As solar radiation passes through the atmosphere, a portion of it is reflected, scattered, and absorbed. The amount of radiation that is reflected is known as the Earth's albedo.
- The effect of albedo can lead to higher average temperatures in highly developed areas, such as urban cities, compared to surrounding suburban or rural areas. This phenomenon is known as the Urban Heat Island Effect. Factors contributing to this effect include a lack of vegetation, higher population densities, and the presence of dark surfaces, such as asphalt roads and brick buildings, which absorb more heat.
Conclusion
The Earth's heat budget is a critical equilibrium between incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation, which maintains the planet's average temperature and climate. The balance of these radiations is influenced by various factors such as albedo, which plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's temperature. Understanding the heat budget and its components is essential for addressing climate change and preserving our planet's delicate balance.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Heat Budget of The Earth
What is the Earth's heat budget?
The Earth's heat budget refers to the equilibrium between the incoming solar energy (solar insolation) and the outgoing heat emitted by the planet (terrestrial radiation). This balance is essential for maintaining the Earth's average annual temperature and overall climate.
What is solar insolation?
Solar insolation refers to the total amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface. It consists of direct shortwave radiation from the Sun and diffuse radiation that has been scattered by the atmosphere.
What is terrestrial radiation?
Terrestrial radiation refers to the long-wave radiation emitted by the Earth's surface back into the atmosphere. This process helps maintain the Earth's heat budget by balancing the incoming solar radiation with the outgoing heat emitted by the planet.
What is albedo, and how does it affect the Earth's heat budget?
Albedo refers to the measure of how much light that strikes a surface is reflected back without being absorbed. The Earth's albedo is the portion of solar radiation that is reflected, scattered, and absorbed as it passes through the atmosphere. Albedo plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth's heat budget by regulating the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface.
What is the Urban Heat Island Effect?
The Urban Heat Island Effect is a phenomenon where highly developed areas, such as urban cities, have higher average temperatures compared to surrounding suburban or rural areas. This effect is attributed to factors such as a lack of vegetation, higher population densities, and the presence of dark surfaces like asphalt roads and brick buildings that absorb more heat.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Heat Budget of The Earth - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the heat budget of the Earth? |  |
| 2. How is the heat budget of the Earth maintained? |  |
| 3. What role does greenhouse effect play in the heat budget of the Earth? |  |
| 4. How does the heat budget of the Earth impact climate change? |  |
| 5. How can we measure and monitor the heat budget of the Earth? |  |





















