Factors Influencing World Distribution of Plants and Animals | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Cosmopolitan distribution refers to the widespread presence of certain species across the globe, while endemic distribution refers to the occurrence of species in a specific geographic location and nowhere else. For example, giraffes are endemic to Africa, and marmoset monkeys are endemic to South America. On the other hand, some plants and animals have a very narrow endemic range, such as the California redwoods, which are found only in California. In contrast, plants like coconuts (Cocos nucifera) have a wide endemic range, as they are found throughout the tropics and are considered pan-tropical in their distribution.
- In some instances, the distribution pattern of plants and animals can be discontinuous or disjointed, meaning that a species might be found in two widely separated areas, such as Central America and Indonesia, with no presence in the regions between them. One example of such a distribution is the Tapiran animal, found in South America and Malaysia. Biogeographers seek to understand the reasons behind these distribution patterns, which may be influenced by abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) factors.
Several theories have been proposed to explain the discontinuous or disjointed distribution of certain species, including:
- The theory of continental drift (also known as Wegener's theory or Jigsaw theory) suggests that the continents were once connected and have gradually drifted apart, resulting in the current distribution patterns.
- Darwin's theory of evolution proposes that species have evolved and adapted to their environments over time, which could explain the distribution of certain plants and animals.
- The theory of plate tectonics posits that the movement of Earth's tectonic plates has influenced the distribution of species.
- The theory of climate suggests that changes in climate have played a role in determining the global distribution of plants and animals.
In summary, understanding the global distribution of plants and animals is essential for studying biodiversity and making informed decisions about conservation efforts. Various theories, such as continental drift, evolution, plate tectonics, and climate, have been proposed to explain the distribution patterns of species, and both abiotic and biotic factors play a role in determining these patterns.
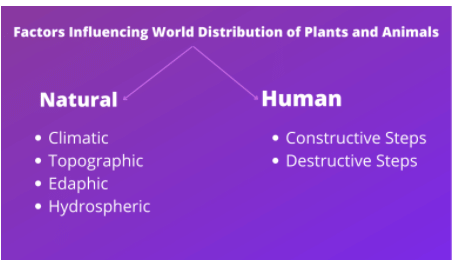
Abiotic factors affecting distribution of plants and animals
- Geological composition: The composition of rocks in the lithosphere is crucial for the formation of soil, which directly impacts plant growth. Soil characteristics largely depend on the parent rock, and certain rocks provide a more suitable environment for specific plants, including various species of lichens and mosses.
- Availability of food: All living organisms require food for survival, which is a fundamental factor determining the distribution of plants and animals across different regions.
- Atmospheric conditions: Plants and animals need air, specifically oxygen and carbon dioxide, for respiration and various growth processes. The availability of these gases can be affected by altitude, with lower air pressure at higher altitudes causing difficulties in breathing for some organisms.
- Water availability: Precipitation, in the form of snow, drizzle, sleet, rain, or hail, plays a significant role in determining the distribution of biomes worldwide. Aquatic animals depend on water for survival, while some desert-dwelling animals, such as desert rats and reptiles, have adapted to conserve water and survive in arid environments. Similarly, desert plants like xerophytes and phreatophytes have developed specialized features for storing and conserving water.
- Nutrient availability: Essential nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus are required for the formation of proteins, enzymes, nucleotides, and vitamins in organisms, affecting their distribution.
- Soil type: The type of soil in an area greatly influences the variety of plant species that can grow there, as it affects water content, mineral availability, and the presence of microorganisms. Different soil types have varying water retention capacities, fertility levels, and mineral contents, which impact plant growth and distribution.
- Temperature variations: The ability to withstand extreme temperatures varies among plants and animals. While endothermic animals like birds and mammals maintain constant body temperatures, ectothermic animals like insects, reptiles, and fish regulate their body temperatures using external sources. Plants, too, have developed adaptations to cope with high or low temperatures, such as hairy stems, increased solute concentration in cytoplasm to reduce freezing point, and growing in clusters to resist cold temperatures and wind.
- Light availability: Light is a crucial climatic factor that influences the production of chlorophyll and photosynthesis, which in turn affects the distribution of plants and animals. It serves as the primary source of energy in most ecosystems, with energy entering the ecosystem through sunlight.
Biotic factors affecting distribution of plants and animals
- Competition: Competition is a significant factor influencing the distribution of plants and animals in their habitats. They vie for space, which is essential for reproduction, movement, and feeding. Additionally, competition for resources such as food, water, and mates can impact species distribution. For example, in forest habitats, competition for sunlight results in an even distribution of trees to minimize competition.
- Predation: Predation plays a crucial role in determining the global distribution and abundance of plant and animal species, energy flow within ecosystems, and community diversity and composition. Predators also have a significant impact on the evolutionary process. For instance, some species develop specific traits to avoid predation, which, in turn, affects their distribution.
- Diseases: Disease outbreaks can have a profound impact on the distribution of plants and animals. Various diseases affect food crops, causing substantial losses to farmers and posing threats to food security. Examples include banana diseases, locusts, fruit flies, armyworm, cassava mosaic, and wheat rusts. These diseases can lead to reduced plant populations in affected areas, forcing them to thrive in disease-free zones. Similarly, animal populations may shift due to disease outbreaks brought about by factors such as global warming, which can disrupt the balance of ecosystems and alter the behavior and distribution of various species.
- Human Activities: Human activities can influence plant and animal populations, causing them to migrate away from their natural habitats. Land development for housing and infrastructure often involves deforestation, which alters plant and animal habitats. Some species, like skunks and raccoons, can adapt to these changes, while others cannot, leading to population declines or even extinction. Pollution from human activities can also negatively affect plant and animal populations. Overhunting has led to decreased populations of certain species, such as whales. Urbanization and agricultural activities have displaced numerous plant and animal species, forcing them to adapt to new environments or face extinction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the global distribution of plants and animals is crucial for studying biodiversity and informing conservation efforts. Various theories, including continental drift, evolution, plate tectonics, and climate, have been proposed to explain distribution patterns, while both abiotic and biotic factors play a role in determining these patterns. Factors such as geological composition, nutrient availability, water availability, and temperature variations, as well as competition, predation, diseases, and human activities, all impact the distribution of plants and animals. As the world continues to change, it is vital for researchers and conservationists to consider these factors when making decisions to preserve and protect our planet's diverse ecosystems.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Factors Influencing World Distribution of Plants and Animals
What is the difference between cosmopolitan and endemic distribution?
Cosmopolitan distribution refers to the widespread presence of certain species across the globe, while endemic distribution refers to the occurrence of species in a specific geographic location and nowhere else.
What are some theories that explain the discontinuous or disjointed distribution of certain species?
Some theories include the theory of continental drift, Darwin's theory of evolution, the theory of plate tectonics, and the theory of climate.
How do abiotic factors like geological composition and atmospheric conditions affect the distribution of plants and animals?
Geological composition affects the formation of soil, which directly impacts plant growth. Atmospheric conditions can influence the availability of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, which are essential for respiration and growth processes in plants and animals.
What are some examples of biotic factors that influence the distribution of plants and animals?
Biotic factors include competition, predation, diseases, and human activities. These factors can affect the population and movement of plant and animal species, leading to changes in their distribution patterns.
How do human activities impact the distribution of plants and animals?
Human activities such as land development, pollution, overhunting, urbanization, and agriculture can alter plant and animal habitats, forcing species to adapt to new environments or face population declines and even extinction.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Factors Influencing World Distribution of Plants and Animals - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the main factors influencing the world distribution of plants and animals? |  |
| 2. How does climate influence the distribution of plants and animals? |  |
| 3. How do geographical barriers affect the distribution of plants and animals? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact the distribution of plants and animals? |  |
| 5. How do ecological interactions influence the distribution of plants and animals? |  |
















