Problems of deforestation and conservation measures | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Deforestation
Deforestation refers to the widespread practice of cutting down trees, which includes repeated lopping, felling, and removing forest litter, as well as browsing, grazing, and trampling of seedlings. This process can be defined as the destruction or degradation of forest vegetation to such an extent that the forest can no longer support its natural plant and animal life.
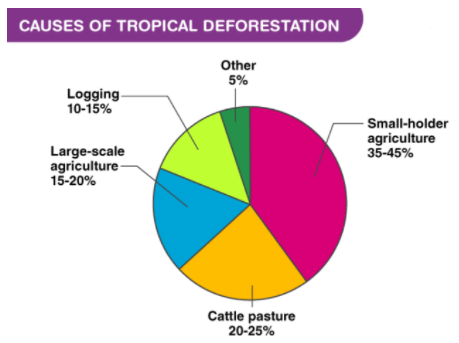
There are several factors that contribute to deforestation. The primary cause is the demand for wood, which is used as fuel, lumber, and paper. Another significant factor is the clearance of forest land for agricultural purposes, such as converting forests into cropland or pastures. The main causes of deforestation can be summarized as follows:
1. Agriculture
One of the primary drivers of deforestation is the growth of agriculture. As the demand for agricultural products increases, more land is needed for cultivation, leading to the clearance of forests, grasslands, and even marshes and underwater areas. This results in significant ecological damage, outweighing any potential benefits from increased crop yields. Furthermore, forest soils are not sustainable for long-term farming, as their nutrients become depleted over time. Once the soil is no longer suitable for cultivation, the area becomes prone to soil erosion and degradation.
2. Shifting cultivation
Shifting cultivation, also known as Jhoom farming or slash-and-burn agriculture, is a 12,000-year-old practice that marked a transition from food gathering to food production. Each year, approximately 500,000 hectares of forest are cleared for this type of farming. This cultivation method results in significant deforestation, as the land is only used for 2-3 years before being abandoned and left for natural recovery. Today, shifting cultivation continues to be practiced in Indian states such as Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, as well as the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
3. Demand for firewood
Firewood has long served as a source of energy for various purposes such as cooking and heating. In fact, approximately 44% of the world's total wood production is used to meet fuel demands. When examining the distribution of wood usage, it becomes apparent that developed countries allocate 16% of their wood production for fuel purposes. India, in particular, consumes a substantial amount of firewood, with an annual usage of around 135-170 million tons. This consumption leads to the deforestation of 10-15 hectares of forest land in order to satisfy the fuel requirements of both urban and rural low-income populations.
4. Wood for industry and commercial use
- Wood is an incredibly versatile material derived from forests and is utilized for various industrial applications, including the production of crates, packing cases, furniture, matchboxes, wooden boxes, paper, pulp, and plywood. The uncontrolled exploitation of timber and other wood resources for commercial purposes is a significant factor contributing to the deterioration of forests.
- One such example of this is the apple industry in the Himalayan region, which has led to the destruction of fir and other tree species due to the demand for wooden boxes to transport apples. Similarly, plywood crates have been widely used for packaging various products, such as tea, resulting in further deforestation and forest degradation.
5. Urbanization and developmental projects
Urbanization and development projects frequently contribute to deforestation. This typically starts with the construction of infrastructure, such as roads, railways, dams, residential areas, and electricity supply networks. The establishment of thermal power plants and the extraction of coal, metal ores, and minerals are also significant factors driving deforestation.
6. Overgrazing of forests of moderate cover by animals mainly in the tropical and subtropical and arid and semi-arid areas has resulted in large-scale degradation of natural vegetation if not the complete destruction of forests.
7. Other causes
In recent times, global developments have led to significant environmental damage, particularly in tropical forest regions. The vast resources – both living and nonliving (such as minerals, rivers, and land) – found within these forests have drawn the attention of various industries and development organizations, resulting in substantial deforestation. Forest fires, whether triggered naturally or by human activity, are also major contributors to the destruction of forest cover.
Consequences of Deforestation
Deforestation has significant consequences on both the physical and biological aspects of the environment.
- Soil erosion and flash floods: A decrease in forest cover, combined with overexploitation of groundwater, has led to accelerated erosion along the slopes of the lower Himalayas and Aravali hills, increasing the risk of landslides. The loss of forests has also altered rainfall patterns. The absence of forest cover allows water to flow off the ground more easily, washing away the topsoil and depositing it as silt in river beds. Forests help to prevent soil erosion, landslides, and reduce the severity of floods and droughts.
- Climate change: Forests play a crucial role in enhancing local precipitation, improving the water-holding capacity of soil, regulating the water cycle, and maintaining soil fertility by recycling nutrients through leaf fall and litter decomposition. Forests protect against soil erosion, landslides, and mitigate the impacts of floods and droughts. They also have a significant influence on the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and maintaining a balance between carbon dioxide and oxygen levels. Forests are essential for providing oxygen in the air we breathe, regulating the water cycle in the environment, and acting as environmental buffers that help control climate and atmospheric humidity.
The greenhouse effect, which is a major issue of this century, is partly caused by deforestation. The entire Himalayan ecosystem is under threat and facing severe imbalance as the snow-line has thinned, and perennial springs have dried up. Annual rainfall has declined by 3 to 4%, and chronic droughts have started occurring in areas like Tamilnadu and Himanchal Pradesh, where they were previously unknown. - Loss of wildlife: The destruction and modification of habitats due to deforestation lead to an ecological imbalance in the affected regions. The reduction of green cover negatively impacts the stability of the ecosystem. As habitats are destroyed, the wildlife that depends on these areas for survival also suffers, leading to a decline in biodiversity and the overall health of the ecosystem.
Conservation Measures
Protecting and conserving forest resources is crucial for a nation's economic development and maintaining environmental and ecological balance at local, regional, and global levels. Integrated Conservation Research (ICR), an ecological group from the U.S., has initiated extensive forest conservation programs in partnership with UNESCO's Man and Biosphere (MAB) program.
The primary objective in conserving forests is to safeguard existing forests from unchecked and indiscriminate deforestation by profit-driven individuals. This goal can be achieved through government legislation and by raising public awareness regarding the significance of forest resources. India's National Forest Policy has established fundamental principles for the proper management and conservation of the country's forest resources, such as:
- Categorizing forests based on their functions as protected forests, reserved forests, village forests, and so on.
- Expanding forest cover by planting trees to improve the physical and climatic conditions for the well-being of the population.
- Ensuring a steady increase in the supply of fodder for animals and timber for agricultural tools and firewood for local inhabitants near forests.
- Discouraging the unwarranted expansion of agricultural land at the expense of forest land.
- Extending forested areas through large-scale tree plantation projects to cover 33% of the country's geographical area.
An essential step in conserving natural forests effectively is to adopt a scientific and sensible method for tree cutting. This approach involves selectively cutting only mature and economically valuable trees while avoiding those with less value.
Another measure is to promote afforestation on wasteland and previously deforested areas. Forests should not be replaced with commercial fruit orchards, as these may cause further deforestation. For instance, apple cultivation in parts of the Himalayas, particularly in Himachal Pradesh (India), has significantly damaged natural forests. Deforestation occurs due to the need for land clearance for apple cultivation and the high demand for wood for apple packaging.
The Integrated Conservation Research group has proposed comprehensive programs to improve forests, including:
- Agroforestry: The integration of agriculture and forestry practices for sustainable land management.
- Ethnobotany: The study of the relationships between plants and people, focusing on traditional uses of plants in local cultures.
- Nature-based tourism: Promoting tourism activities that are oriented towards the appreciation and conservation of natural history and biodiversity.
By implementing these measures and programs, we can better protect and preserve our precious forest resources for the benefit of both people and the environment.
Remedial Measures
- To promote afforestation, comprehensive development plans should be implemented, including planting high-yielding varieties in appropriate areas. Utilizing modern techniques for seasoning and preservation can help prevent unnecessary losses.
- Implementing effective strategies to protect forests from fires and diseases can significantly contribute to addressing numerous issues. Conducting a detailed inventory of forest resources is crucial for accurately assessing our resources and planning their appropriate use.
- Discouraging shifting cultivation and providing alternative livelihood sources for tribes relying on this practice is essential. Additionally, ensuring proper training for those involved in forest protection can further enhance conservation efforts.
Government initiatives
- Government initiatives in India have been implemented to protect and conserve the country's natural resources. The Botanical Survey of India (BSI) and the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) conduct surveys and inventories of the country's plant and animal resources. The Forest Survey of India, meanwhile, is responsible for developing accurate databases for planning and monitoring purposes.
- The Biological Diversity Act 2002 and the Biological Diversity Rules 2004 were established to conserve the country's biological resources and regulate access to them, ensuring that benefits from their use are distributed equitably.
- Industries are required to obtain "Consent for Establishment" and "Consent to Operate" from the concerned State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) under the provisions of the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, before commencing operations.
- Environmental Impact Assessments are conducted for developmental projects, and Environmental Management Plans are prepared in accordance with the Environmental Impact Assessment notification of September 2006. Industries are encouraged to adopt cleaner technologies and use improved fuel quality. Regular monitoring is carried out to ensure environmental compliance.
- The Joint Forest Management (JFM) program was introduced by the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, in 1990 to involve village communities and voluntary agencies in the regeneration of degraded forest lands. The program involves the joint protection and management of forests by the Forest Department and local communities.
- Sacred groves are patches of forests or natural vegetation dedicated to local folk deities or tree spirits and protected by local communities due to their religious beliefs and traditional rituals.
- The National Mission for a Green India aims to enhance the quality of forest cover and improve ecosystem services from 4.9 million hectares (MHA) of predominantly forest lands. Additionally, eco-restoration and afforestation efforts are being made to increase forest cover and ecosystem services from 1.8 MHA of various forest and non-forest lands.
- Finally, urban and peri-urban areas, including institutional lands, are targeted for tree planting, with the aim of enhancing tree cover in 0.2 MHA of these areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, deforestation poses severe threats to the environment, including soil erosion, climate change, and loss of wildlife. The primary causes of deforestation include agriculture, shifting cultivation, demand for firewood, wood for industry and commercial use, urbanization, and developmental projects. To mitigate these consequences and preserve our valuable forest resources, it is essential to adopt conservation measures such as agroforestry, promoting ethnobotany, and nature-based tourism. Government initiatives, such as the Biological Diversity Act, the Joint Forest Management program, and the National Mission for a Green India, play a crucial role in addressing deforestation and ensuring the sustainable use of forest resources for future generations.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Problems of deforestation and conservation measures
What are the main causes of deforestation?
The main causes of deforestation include agriculture, shifting cultivation, demand for firewood, wood for industry and commercial use, urbanization and developmental projects, overgrazing, and other factors such as forest fires and global developments.
What are the consequences of deforestation on the environment?
Deforestation has significant consequences on both the physical and biological aspects of the environment. Some of these consequences include soil erosion, flash floods, climate change, loss of wildlife, and reduced biodiversity.
What conservation measures can be taken to protect forests?
Conservation measures include categorizing forests based on their functions, expanding forest cover through tree planting, discouraging the unwarranted expansion of agricultural land at the expense of forest land, and promoting afforestation on wasteland and previously deforested areas.
What are some government initiatives in India to protect and conserve forests?
Government initiatives in India include the Botanical Survey of India (BSI), Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), Forest Survey of India, the Biological Diversity Act 2002, the Biological Diversity Rules 2004, Environmental Impact Assessments, and the Joint Forest Management (JFM) program.
What is the role of local communities in forest conservation?
Local communities play a vital role in forest conservation through initiatives such as Joint Forest Management (JFM), which involves joint protection and management of forests by the Forest Department and local communities. Additionally, sacred groves, which are patches of forests dedicated to local folk deities or tree spirits, are protected by local communities due to their religious beliefs and traditional rituals.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Problems of deforestation and conservation measures - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is deforestation? |  |
| 2. What are the major causes of deforestation? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of deforestation? |  |
| 4. What are some conservation measures to address deforestation? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to the conservation of forests and combating deforestation? |  |





















