Human Development Index | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Human Development Approach
The Human Development Approach (HDA) was introduced in the late 1980s as a more comprehensive way to evaluate a country's well-being, moving beyond just economic growth or per capita gross domestic product (GDP). It was developed by Dr. Amartya Sen and Dr. Mahbub ul Haq, who emphasized the importance of people and their needs in the development process.
- Focus on People: The HDA places people at the center of development, viewing economic growth and wealth as means to an end, not the end itself. The goal is to enhance human life by improving various aspects such as health, nutrition, education, and community participation.
- Removing Obstacles: Development is seen as a way to remove barriers that prevent individuals from reaching their full potential. These barriers include poverty, illiteracy, poor health, limited access to resources, and a lack of civil and political freedoms.
- Human Development Report: The first Human Development Report described human development as a process that expands people's choices. The most important choices highlighted were living a long and healthy life, gaining an education, and achieving a decent standard of living. Other important choices include political freedom, human rights, and self-respect. This concept is central to the Human Development Index (HDI), which measures and promotes human development.
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a measurement published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) as part of their Human Development Report. It evaluates the average achievements in three primary areas of human development:
- A long and healthy life
- Knowledge and education
- A decent standard of living
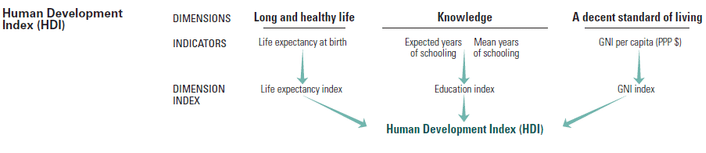
To calculate the HDI, the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of these three dimensions is used. Life expectancy at birth is used to assess the health dimension, with a minimum value of 20 years and a maximum value of 85 years. The education component is measured by the average years of schooling for adults aged 25 and older and the expected years of schooling for children at school-entry age. The standard of living dimension is evaluated using the gross national income per capita.
Countries are then classified into four categories based on their HDI score:
- Very high human development (HDI 0.900 and above)
- High human development (HDI 0.800 – 0.899)
- Medium human development (HDI 0.500 – 0.799)
- Low human development (HDI below 0.500)
India, for example, falls into the medium human development category.
The Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)
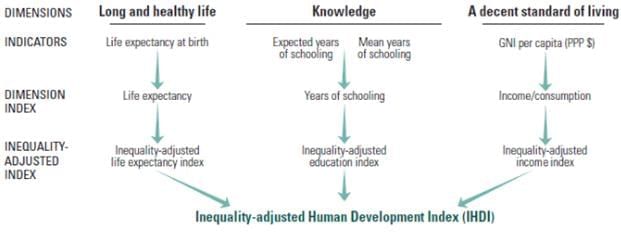
IHDI is a measurement that takes into account the average level of human development while also considering how these achievements are distributed amongst a population. This means that two countries with varying distributions of accomplishments can still have the same average HDI value. When there is perfect equality, the IHDI and HDI values are the same; however, the IHDI decreases as inequality increases. The gap between the IHDI and HDI represents the cost of inequality in terms of human development, or the overall loss to human development caused by inequality. By understanding the IHDI, we can better address inequalities in various aspects of life and work towards reducing them, thus improving overall human development.
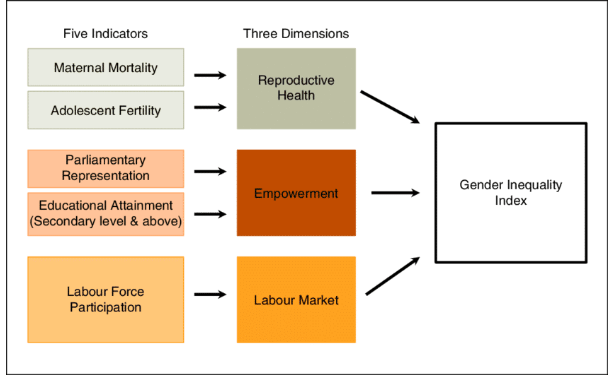
The Gender Inequality Index (GII)
It is another measurement that specifically assesses gender-based inequalities in human development. It evaluates disparities in three crucial areas:
- Reproductive health which is determined by the maternal mortality ratio and adolescent birth rates.
- Empowerment which is gauged by the percentage of women holding parliamentary seats and the proportion of adult women and men (aged 25 years and older) who have received at least some secondary education.
- Economic status which is reflected in the labor market participation and measured by the labor force participation rate of women and men aged 15 years and older.
In summary, both the IHDI and GII provide valuable insights into inequalities within societies, helping to inform policies and actions aimed at reducing these disparities and ultimately improving overall human development.
The GII sheds new light on the position of women in 162 countries as it yields insights in gender gaps in major areas of human development.
The component indicators highlight areas in need of critical policy intervention and it stimulates proactive thinking and public policy to overcome systematic disadvantages of women.
It measures the human development costs of gender inequality. Thus, the higher the GII value the more disparities between females and males.
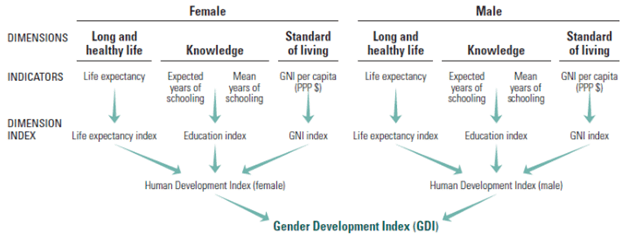
Gender Development Index (GDI)
- Gender Development Index (GDI) evaluates the differences in human development between men and women, focusing on health, education, and living standards. It uses the same indicators as the Human Development Index (HDI) but breaks them down by gender.
- For health, the GDI considers life expectancy at birth for both genders. For education, it looks at expected years of schooling for boys and girls, as well as the average years of schooling completed by individuals aged 25 and older, divided by gender. By comparing these indicators, the GDI highlights gender disparities in human development achievements and promotes gender equality.
Purpose and Importance of GII:
- Identifying Gender Gaps. The GII highlights disparities between females and males in key areas of human development, helping to identify where inequalities exist.
- Informing Policy Action. By pinpointing areas needing critical policy action, the GII guides governments and organizations in developing strategies to address gender-based disparities.
- Monitoring Progress. The GII can be used to monitor changes in gender inequality over time, assessing the effectiveness of policies aimed at improving women's status.
- Understanding Human Development Costs. The GII measures the human development costs of gender inequality, showing how much development is compromised due to disparities between genders.
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) is a comprehensive measure of poverty that was first introduced in 2010. It goes beyond traditional monetary measures of poverty by taking into account the overlapping deprivations that people in developing countries experience in their health, education, and standard of living.
- The MPI identifies deprivations across the same three dimensions as the Human Development Index (HDI) and calculates the number of people who are considered multidimensionally poor. This is determined by assessing the deprivations they face in 33% of weighted indicators. The Index also reveals the number of deprivations that each poor household typically deals with.
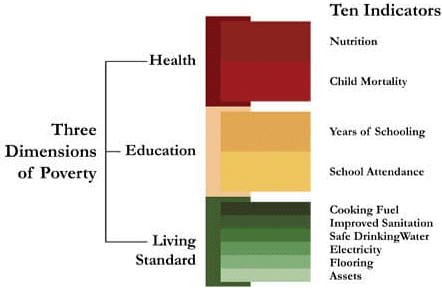
- The MPI is a valuable tool for policymakers as it can be broken down by region, ethnicity, and other groups, as well as by dimensions. This allows for the effective allocation of resources by targeting those with the highest intensity of poverty. The MPI helps address the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) strategically and enables the monitoring of the impacts of policy interventions.
- The MPI can be adapted to national levels using region or country-specific indicators and weights. This makes it suitable for adoption in national poverty eradication programs and allows for the analysis of changes over time.
- Developed by the Oxford Poverty & Human Development Initiative (OPHI) and the United Nations Development Programme, the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) uses various factors to determine poverty beyond income-based metrics. The global MPI replaced the previous Human Poverty Index and is released annually by OPHI, with results published on its website.
Conclusion
The Human Development Approach (HDA) offers a more comprehensive way to measure a country's welfare by focusing on improving various aspects of people's lives, such as health, education, and community involvement. The Human Development Index (HDI), Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI), Gender Inequality Index (GII), Gender Development Index (GDI), and Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) are important tools that help assess the progress of countries in these areas. By considering such indices, policymakers can work towards reducing disparities and improving overall human development for their citizens, ultimately ensuring a more equitable society.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Human Development Index
What is the Human Development Approach (HDA)?
The HDA is a comprehensive way to measure a country's welfare beyond just economic growth or per capita GDP. It places people at the heart of the development process, focusing on improving human lives through aspects such as health, nutrition, education, and community involvement.
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
The HDI is a measurement published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) that evaluates the average achievements in three primary areas of human development: a long and healthy life, knowledge and education, and a decent standard of living.
What is the Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)?
The IHDI is a measurement that takes into account both the average level of human development and how these achievements are distributed amongst a population. It calculates the percentage loss in HDI due to inequality, providing a more comprehensive understanding of a country's progress.
What is the difference between the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Inequality Index (GII)?
The GDI assesses the differences in human development between men and women, focusing on health, education, and living standards. The GII, on the other hand, specifically evaluates gender-based inequalities in three crucial areas: reproductive health, empowerment, and economic status.
How has India performed in the Human Development Report 2020?
India ranked 131 among 189 countries on the HDI for 2019, slipping two places from the previous year. However, if the Index were adjusted to assess the planetary pressures caused by each nation's development, India would move up eight places in the ranking.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Human Development Index - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the Human Development Approach? |  |
| 2. What is the Human Development Index (HDI)? |  |
| 3. How is the HDI calculated? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of the Human Development Index? |  |
| 5. How is the Human Development Index used in policymaking? |  |





















