Sustainable Development of Cities | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- Sustainable development is a holistic concept that goes beyond the realms of science, business, and trade, encompassing aspects of human development, cultural values, and diversity. Many organizations now use the term "sustainable human development" to emphasize the importance of gender equality, participation in decision-making processes, and access to education and healthcare.
- Cities have emerged as the central hubs for these elements, being the primary consumers and distributors of goods and services. However, cities often consume a significant amount of resources, leading to the depletion of resources from external regions they rely on. This increasing consumption and growing dependence on trade mean that the ecological impact of cities extends far beyond their geographical boundaries.
What is Sustainable Urban Planning?
- Sustainable Urban Planning is the process of designing and managing urban lands in a way that supports urban growth while ensuring long-term sustainability, efficiency, and equity. This approach to planning focuses on addressing concerns such as climate change, clean air and water, renewable energy, and land use to create self-sustaining communities that can thrive in the long term without burdening future generations.
- The United Nations defines sustainability as "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Sustainable urban planning, therefore, incorporates various disciplines, including architecture, engineering, biology, environmental science, materials science, law, transportation, technology, economic development, accounting and finance, and government.
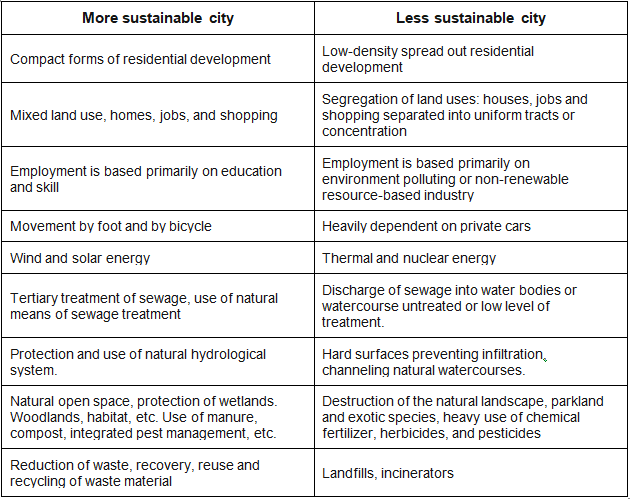
- Some innovative solutions to urban planning problems that promote sustainability include green buildings and housing, mixed-use developments, walkability, greenways and open spaces, alternative energy sources such as solar and wind, and diverse transportation options. Effective sustainable land use planning helps enhance the well-being of people and communities by turning urban areas and neighborhoods into healthier and more efficient spaces.
- In India, urban centers are defined by the Census of India, 2011, as areas that meet the following criteria: a minimum population of 5,000, at least 75% of the male population engaged in non-agricultural sectors, and a population density of at least 400 persons per square kilometer. Sustainable urban planning in these areas is crucial to support India's growing urban population while preserving the environment and resources for future generations.
What is a sustainable city?
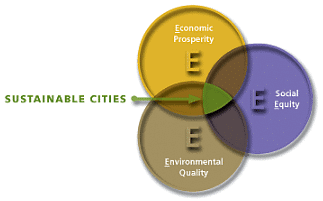
- A sustainable city refers to an urban area that effectively caters to the needs of its population, such as basic necessities, infrastructure, civic amenities, healthcare, housing, education, transportation, and employment, while prioritizing environmental conservation, social equity, and long-term stability.
- Sustainable urban development aims to enhance the quality of life for all residents, taking into account various ecological, cultural, political, institutional, social, and economic aspects, without creating a burden for future generations due to depleted natural resources and excessive debt. In essence, a sustainable city focuses on inclusivity and resource management to ensure a balanced and healthy environment for current and future inhabitants.
The Need for Sustainable Urban Planning in India
India is currently undergoing a transformation from being predominantly rural to becoming more urbanized. As per the 2011 Census, 31.2% of the Indian population resides in towns, and this number is expected to rise to over 50% by 2050. To ensure a sustainable future, this urban transition must be accompanied by green energy, clean water, mass mobility, proper nutrition, education, healthcare, and effective waste management.The rapid urbanization in India has led to several challenges:
- Rapid urban growth: The 2011 Census revealed a 185% increase in the number of census towns in India from 2001 to 2011, while the number of villages only increased by 0.36%.
- Unsustainable urban expansion: The population density of the National Capital Territory (NCT) is 11,297 people per sq. km (Census, 2011), much higher than the national average of 382 persons per sq. km. This indicates that the city's expansion is not keeping pace with the growing urban population.
- Migration: The lack of employment, healthcare, education, and other facilities in rural areas has led to excessive migration towards urban centers, resulting in the growth of slums in cities.
- Shift away from agriculture: Government policies and increased population pressure on agriculture have led to a sudden shift from agricultural activities to other economic sectors. This has caused a population explosion in urban centers as people search for employment opportunities.
- Unequal economic development: The uneven distribution of natural and economic resources has created a development divide in the country. The focus on a few economic centers and the legacy of colonialism have only widened this gap.
In conclusion, sustainable urban planning is crucial for India's future as the country continues to urbanize. Addressing the challenges posed by rapid urbanization, such as unsustainable growth, migration, and resource depletion, will play a critical role in ensuring a sustainable living environment for the country's growing urban population.
Characteristics of Sustainable cities
Sustainable cities are those that are aware of their consumption patterns and their impact on other regions and ecosystems. They should strive to reduce, reuse, and recycle consumer goods and may even implement user fees to control unsustainable consumption. Ensuring a healthy city is essential to contributing to a healthy nation.
Some key characteristics of sustainable urban development include:
- A controlled population with available, meaningful employment opportunities.
- Adequate governance services that address civic duty, community participation, identity, responsibilities, transparency, and equality in local institutions.
- Efficient basic amenities for a reasonably comfortable existence, such as power and water supply.
- Planned housing communities with essential infrastructure like schools, parks, drainage systems, and local healthcare establishments.
- Transportation planning that considers a wide range of options, including roads, parking lots, alternative transportation systems, and mass transit facilities, with the goal of reducing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Effective environmental infrastructure to address issues of untreated sewage and pollution in rivers, lakes, and coastal zones, thus preserving aquatic ecosystems.
- Empowerment and inclusion of women in political, social, and economic life within the city, as well as the adoption of urban policies that consider women's needs and initiatives.
- Development of an efficient urban private sector, both formal and informal, which reduces poverty through job creation and supports economic growth.
- A comprehensive healthcare system that addresses nutrition, family planning, and sanitation.
- Law-abiding citizens who actively contribute to the growth and development of the city.
According to the United Nations' World Economic and Social Survey 2013, sustainable cities should meet the developmental needs of their inhabitants without imposing unsustainable demands on local or global resources. They should not transfer risk spatially or temporally, and should integrate socio-economic development, environmental management, and urban governance. Additionally, sustainable cities should be inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
Advantages of sustainable cities
- Sustainable cities offer numerous benefits that contribute to the overall well-being of their citizens and the environment. By adopting sustainable urban planning and practices, cities can transform into thriving communities that provide a high quality of life for their residents while also preserving the ecosystems upon which they depend.
- One of the key advantages of sustainable cities is that they prioritize a balanced approach to development, ensuring the needs of the present generation are met without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This long-term perspective is essential for creating cities that are both economically and environmentally resilient.
- A significant benefit of sustainable cities is the focus on improving the quality of life for their inhabitants. This includes providing access to essential services, such as healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, as well as promoting social equity and reducing crime rates. By fostering a strong sense of community and prioritizing the well-being of all residents, sustainable cities can create a more inclusive and harmonious living environment.
- Another advantage of sustainable cities is their emphasis on preserving and enhancing natural open spaces. These green spaces offer numerous benefits, such as improving air and water quality, supporting biodiversity, and providing recreational opportunities for residents. By integrating nature into the urban fabric, sustainable cities can create healthier and more enjoyable living environments.
- Sustainable cities also prioritize waste reduction and resource efficiency. By adopting practices such as recycling, composting, and the use of renewable energy, these cities can minimize their environmental footprint and promote a more responsible use of resources. This not only has positive implications for the environment but can also lead to cost savings for both municipal governments and citizens.
In conclusion, sustainable cities offer a multitude of advantages that contribute to a higher quality of life, environmental preservation, and long-term resilience. By prioritizing balanced development, social equity, and environmental stewardship, sustainable cities can create thriving communities that support the well-being of both current and future generations.
Planned cities in India
A few of the planned cities in India include
- Delhi-NCR,
- Amravati (Andhra Pradesh),
- Gandhinagar (Gujarat),
- Navi Mumbai,
- Lavasa (Maharashtra),
- Chandigarh (Punjab),
- Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh), etc.
Challenges associated with Sustainable Urban Planning in India
Economic Challenges
- Balancing production and resource utilization: The rapid growth of urban populations and increasing per capita income have led to a higher demand for luxury goods. Ensuring a balanced supply and demand while also sustainably managing resources can be challenging.
- Addressing labor and welfare issues: A significant portion of migration to urban areas consists of laborers and daily wage earners. Monitoring their working and living conditions and guaranteeing their welfare presents a considerable challenge.
- Developing technology and infrastructure: A major concern is the lack of advanced, eco-friendly technology and sustainable infrastructure to support the growing urban population.
- Securing investments and efficient fund utilization: As a developing nation with around 35% of its urban population living below the poverty line, India faces challenges in acquiring the necessary funds and investments to provide basic facilities at affordable prices.
Political problems
- Governance Issues: The areas surrounding urban centers often face confusion and uncertainty when it comes to governance. With multiple governing bodies in place, there is often a lack of clarity regarding the delivery of services and the proper development of these regions.
- Law and Order Challenges: The unplanned and disorganized growth of urban areas, coupled with rapid development, can lead to increased crime rates, drug abuse, and other illicit activities. This creates a challenging environment for maintaining law and order in these regions.
- Safety Concerns: Women and children are particularly vulnerable in urban societies, with evolving social norms and a highly cosmopolitan population exacerbating safety concerns. Many Indian cities still lack adequate surveillance systems and police forces to ensure the safety and security of these vulnerable groups.
- Ethics and Accountability: Ensuring that governing bodies operate ethically and are held accountable for their actions is crucial for the sustainability of urban centers. This poses a significant challenge in creating thriving and well-functioning urban environments.
Social problems
- Slums and informal settlements: The rapid influx of people into urban areas has resulted in illegal land occupation and the growth of unplanned settlements, known as slums. Residents of these areas often lack representation and access to basic amenities, exacerbating the issue.
- Societal pollution: Urban societies with a diverse mix of cultures are more susceptible to social pollution and the degradation of societal norms. These areas are often prone to crime and other unlawful activities.
- Health and sanitation issues: Unplanned urbanization often lacks essential infrastructure, particularly in terms of sanitation and waste management, leading to various health concerns. Pollution and contaminated food supplies also contribute to health problems in urban areas. Mental health disorders are also on the rise in these regions.
- Gender disparities: Despite high literacy rates, the gender ratio in urban areas of India is poor. According to the 2011 Census, Delhi has a gender ratio of 832 females to 1000 males, while Mumbai's ratio is 852 females to 1000 males. High crime rates against women in these areas also raise significant concerns about their safety.
- Generational challenges: Changes in social structures have significantly impacted family values in urban settings. The increasing trend of nuclear families with both partners working has left children and elderly individuals more vulnerable in society.
Environmental problems
- Environmental degradation: The expansion of urban areas, along with excessive construction activities and emissions from vehicles and industries, has significantly impacted the urban micro-climate. This increased vulnerability to climate and environmental hazards is due to the degradation of the region's natural environment.
- Waste management: Ineffective waste management practices and the use of landfills contribute to the negative effects on the urban climate and the pollution of water sources. Proper waste disposal and recycling methods are essential to mitigate these impacts.
- Changing land use patterns: The rapid transformation of land use in the outskirts of urban areas, from agricultural and forested land to densely built environments, is a cause for concern. Unplanned expansion of urban centers leads to the depletion of natural resources and further environmental degradation.
- Deforestation and desertification: The growing population and increased construction activities contribute to the rapid loss of forests and the spread of deserts in the rural-urban fringe. This process, known as deforestation and desertification, must be addressed to preserve the environment and maintain ecological balance.
Government Initiatives for Sustainable Urban Planning in India
The Ministry of Housing & Urban Poverty Alleviation (MoHUPA) serves as the primary authority for the Government of India in developing housing policies and programs, managing plan schemes, and promoting the adoption of measures to reduce building costs. Several initiatives have been put in place to encourage sustainable urban planning.- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT): AMRUT aims to establish urban renewal projects that provide robust sewerage networks and water supply, ensuring proper infrastructure for urban transformation.
- Smart City Mission: This initiative strives to drive economic growth and improve citizens' quality of life through local development and the use of technology to create smart outcomes.
- Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY): HRIDAY focuses on the holistic development of heritage cities, with selected cities including Ajmer, Amritsar, Amravati, Badami, Dwarka, Gaya, Kanchipuram, Mathura, Puri, Varanasi, Velankanni, and Warangal.
- Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) (Urban): Launched in 2014, this initiative aims to make India clean by 2019. The INDO-SAN India Sanitation Conference 2016 involved all stakeholders, such as state governments, urban local bodies, NGOs, and citizens, to accelerate the Swachh Bharat Mission's progress.
- Housing for All by 2022 Mission: The National Mission for Urban Housing also contributes to sustainable urban planning. Its objectives include slum rehabilitation, promotion of affordable housing through credit-linked subsidies, affordable housing in partnership with public and private sectors, and subsidies for beneficiary-led individual house construction or enhancement.
Considering the various aspects of urban planning and the challenges involved, there is a clear need for sustainable urban planning to meet the growing urban population's needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sustainable urban planning is essential for India's future as it undergoes rapid urbanization. Addressing challenges such as unsustainable growth, migration, and resource depletion is crucial to ensuring a sustainable living environment for the growing urban population. By prioritizing balanced development, social equity, and environmental stewardship, sustainable cities can create thriving communities that support the well-being of both current and future generations. Government initiatives, such as AMRUT, Smart City Mission, HRIDAY, SBM, and Housing for All by 2022, play a significant role in promoting sustainable urban planning and transforming India's urban landscape for the better.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Sustainable Development of Cities
What is the main goal of sustainable urban planning?
The main goal of sustainable urban planning is to design and manage urban areas in a way that supports urban growth while ensuring long-term sustainability, efficiency, and equity. This includes addressing concerns such as climate change, clean air and water, renewable energy, and land use to create self-sustaining communities that can thrive in the long term without burdening future generations.
Why is sustainable urban planning important in India?
Sustainable urban planning is crucial for India's future as the country continues to urbanize. Rapid urbanization has led to several challenges, such as unsustainable growth, migration, and resource depletion. Addressing these challenges through sustainable urban planning can help ensure a sustainable living environment for India's growing urban population.
What are some key characteristics of sustainable urban development?
Key characteristics of sustainable urban development include controlled population growth, efficient basic amenities, planned housing communities, diverse transportation options, effective environmental infrastructure, and the empowerment and inclusion of women in political, social, and economic life within the city.
What are some advantages of sustainable cities?
Sustainable cities offer numerous benefits, including a higher quality of life for residents, environmental preservation, long-term resilience, improved social equity, and reduced crime rates. They also prioritize waste reduction and resource efficiency, leading to cost savings for both municipal governments and citizens.
What are some examples of planned cities in India?
Examples of planned cities in India include Delhi-NCR, Amravati (Andhra Pradesh), Gandhinagar (Gujarat), Navi Mumbai, Lavasa (Maharashtra), Chandigarh (Punjab), and Naya Raipur (Chhattisgarh). These cities have been designed with sustainable urban planning principles in mind to support their growing populations and preserve the environment for future generations.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|





















