Agro and Social-Forestry | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Social Forestry
Social forestry is the management and development of forests with afforestation on barren lands to achieve environmental benefit and rural development. The term was first used by National Commission on Agriculture, Government of India, in 1976. It was then that India embarked upon a social forestry project with the aim of taking the pressure off the forests and making use of all unused and fallow land.
Government forest areas that are close to human settlement and have been degraded over the years due to human activities needed to be afforested. Trees were to be planted in and around agricultural fields. Plantation of trees along railway lines and roadsides, and river and canal banks were carried out. They were planted in village common land, Government wasteland, and Panchayat land. The government also extended incentives so that the planted sapling would be cared for and maintained. Initially, the government encouraged the free distribution of USUFRUCT species. Programme was launched as a mass mobilization programme with the intention of involving the common population.
Benefits of Social Forestry Programme
- Social forestry is supposed to diversify non-farm options or non-crop income options for poor farmers & landless labourers.
- It was also designed to ensure better land use where wasteland encroached into a forestry plantations.
- The programme was supposed to be one of the initiatives under the afforestation scheme with the objective of increasing farming area of India to meet the total target of 33% forest area.
- This programme became part of a wasteland development programme to encourage forestry land use on slopes and upstream.
- With the introduction of this scheme, the government formally recognized the local communities’ rights to forest resources and is now encouraging rural participation in the management of natural resources. Through the social forestry scheme, the government has involved community participation, as part of a drive towards afforestation, and rehabilitating the degraded forest and common lands.
Shortcomings of Social Forestry Programme
- Although social forestry as a concept was revolutionary but in India, it was not too much success. Primarily because of the wrong implementation under the incentive given to farmers & villagers to encourage Social forestry. Many farmers opted for diverting agricultural land to forestry; this compromises Agricultural prospect & food security.
- Although Programme suggested USUFRUCT species but because of lack of ecological understanding & lack of specific directive most of the plantation opted for is eucalyptus which is not ecologically suitable in the Indian settings.
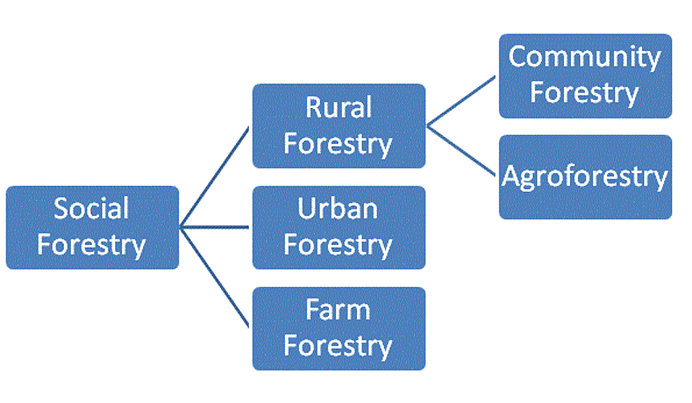
Types of Social Forestry
The various types of social forestry systems are shown in the chart below:
Farm Forestry
- At present, in almost all the countries where social forestry programs have been taken up both commercially and non-commercial farm forestry is being promoted in one form or the other.
- Individual farmers are being encouraged to plant trees on their own farmland to meet the domestic needs of the family. In many areas, this tradition of growing trees on the farmland already exists.
- Non-commercial farm forestry is the main thrust of most of the social forestry projects in the country today.
- It is not always necessary that the farmer grows trees for fuelwood, but very often they are interested in growing trees without any economic motive. They may want it to provide shade for the agricultural crops; as wind shelters; soil conservation or to use wasteland.

Urban Forestry
- It is raising and management of trees on private or publically owned lands in and around urban centers for the purpose of improving the urban environment.
- Urban forestry includes the management of individuals as well as groups of trees. Urban forestry is also not restricted to trees that have been planted.
- Many urban trees may have established naturally, although, in an environment in which competition for land is high, they are unlikely to survive long unless actively cultivated and managed.
- Urban forestry also includes the management of forests at the urban fringe.

Rural Forestry
Rural forestry can be divided into:
- Community forestry
- Agroforestry
1. Community Forestry
- It is the raising of trees on community land and not on private land as in farm forestry. All these programs aim to provide for the entire community and not for any individual.
- The government has the responsibility of providing seedlings, fertilizers but the community has to take responsibility for protecting the trees. Some communities manage the plantations sensibly and in a sustainable manner so that the village continues to benefit.
- Some others take advantage and sell the timber for a short-term individual profit. Common land being everyone’s land is very easy to exploit. Over the last 20 years, large-scale planting of Eucalyptus, as a fast-growing exotic, has occurred in India, making it a part of the drive to reforest the subcontinent, and create an adequate supply of timber for rural communities under the augur of ‘social forestry’.
2. Agro Forestry
- Agroforestry is defined as a land-use system that integrates trees and shrubs on farmlands and rural landscapes to enhance productivity, profitability, diversity, and ecosystem sustainability. It is a dynamic, ecologically-based natural resource management system that through the integration of woody perennials on farms and in the agricultural landscape diversifies and sustains production and builds social institutions. It combines forestry with:
- Production of multiple outputs with the protection of the resource base.
- Places emphasis on the use of multiple indigenous trees and shrubs.
- Particularly suitable for low-input conditions and fragile environments.
- It involves the interplay of socio-cultural values more than in most other land-use systems.
- It is structurally and functionally more complex than monoculture.
- Agroforestry systems include both traditional and modern land-use systems where trees are managed together with crops and or/ animal production systems in agricultural settings. Agroforestry is practiced in both irrigated and rain-fed conditions where it produces food, fuel, fodder, timber, fertilizer, and fiber, contributes to food, nutritional and ecological security, sustains livelihoods, alleviates poverty, and promotes productive and resilient cropping and farming environments.
- Agroforestry also has the potential to enhance ecosystem services through carbon storage, prevention of deforestation, biodiversity conservation, and soil and water conservation. In addition, when strategically applied on a large scale, with the appropriate mix of species, agroforestry enables agricultural land to withstand extreme weather events, such as floods and droughts, and climate change.

Benefits of Agroforestry System
1. Environmental Benefits
- Reduction of pressure on natural forests.
- More efficient recycling of nutrients by deep-rooted trees on the site.
- Better protection of ecological systems.
- Reduction of surface run-off, nutrient leaching, and soil erosion through the impeding effect of tree roots and stems on these processes.
- Improvement of microclimates, such as lowering of soil surface temperature and reduction of the evaporation of soil moisture through a combination of mulching and shading.
- Increment in soil nutrients through addition and decomposition of litterfall.
- Improvement of soil structure through the constant addition of organic matter from decomposed litter.
- It is also recognized that Agroforestry is perhaps the only alternative to meeting the target of increasing forest or tree cover to 33 percent from the present level of less than 25 percent, as envisaged in the National Forest Policy (1988).
- Agroforestry is known to have the potential to mitigate the climate change effects through microclimate moderation and natural resources conservation in the short run and through carbon sequestration in the long run. Agroforestry species are known to sequester as much carbon in below-ground biomass as the primary forests, and far greater than the crop and grass systems.
2. Economic Benefits
- Increment in outputs of food, fuelwood, fodder, fertilizer, and timber.
- Reduction in the incidence of total crop failure, which is common to single cropping or monoculture systems.
- Increase in levels of farm income due to improved and sustained productivity.
- Agroforestry has significant potential to provide employment to the rural and urban populations through production, industrial application, and value addition ventures. Current estimates show that about 65 % of the country’s timber requirement is met from the trees grown on farms. Agroforestry also generates significant employment opportunities.
3. Social Benefits
- Improvement in rural living standards from sustained employment and higher income.
- Improvement in nutrition and health due to increased quality and diversity of food outputs.
- Stabilization and improvement of communities through the elimination of the need to shift sites of farm activities.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Agro and Social-Forestry - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is social forestry? |  |
| 2. What is the role of social forestry in sustainable development? |  |
| 3. How does social forestry contribute to rural development? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of social forestry for local communities? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to social forestry? |  |





















