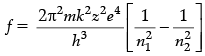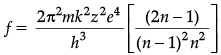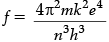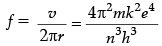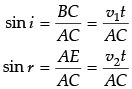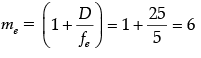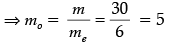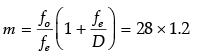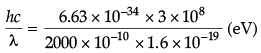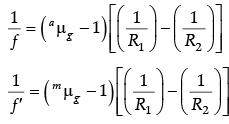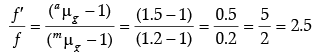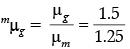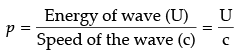Class 12 Physics: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 5 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- There are 12 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A contains three questions of two marks each, Section B contains eight questions of three marks each, Section C contains one case study-based question of five marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks and two questions of three marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- You may use log tables if necessary but use of calculator is not allowed.
Section - A
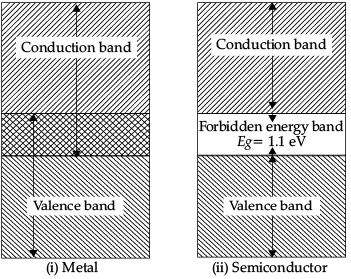
Q.1. (a) Explain the formation of energy bands in crystalline solids.
(b) Draw the energy band diagrams of (i) a metal and (ii) a semiconductor.
(a) Formation of energy bands in solid: An isolated atom possesses discrete energies of different electrons. When two isolated atoms are brought very close to each other, the electrons in the orbits of two atoms interact with each other and the energies of electrons do not remain in same level but changes from its original value. So, at the place of each energy level, a closely spaced two energy levels are created.
When large number of atoms are brought together to form a solid by interaction of electrons, a large number of closely spaced energy levels is created. These are known as bands of allowed energies. Between the bands of allowed energies, there are empty energy regions also, known as forbidden band of energies.
(b)
Q.2. Write the shortcomings of Rutherford atomic model. Explain how these were overcome by the postulates of Bohr’s atomic model.
OR
If the frequency of light incident on the cathode of a photocell is increased, how will following be affected ? Justify your answer.
(a) Energy of the photo electrons
(b) Photo current
Shortcomings of Rutherford atomic model: Rutherford proposed planetary model of atom in which electrons revolve round the nucleus. An electron revolving around the nucleus has an acceleration directed towards the nucleus.
Such accelerated electron must radiate electromagnetic radiation.
But, if an revolving electron radiates energy, the total energy of the system must decrease. In such situation, the electron must come closer to the nucleus and hit the nucleus. Also, the radiation spectrum of emitted electromagnetic waves should be continuous.
However, this does not happen in an atom. Atom is not unstable and the spectrum is not continuous. Rutherford atomic model cannot explain these two observations.
To overcome this discrepancy, Niels Bohr put forward three postulates combining classical Physics and Planck’s quantum hypothesis.
Bohr’s 1st postulate provides stability to the atomic model.
Bohr’s 2nd postulate provides justification that electrons may revolve in stationary orbit.
Bohr’s 3rd postulate provides the explanation of line spectrum.
OR
If the frequency of light incident on the cathode of a photocell is increased, then
(a) Energy of the photo electron increases as the energy of photon is directly proportional to the frequency.
(b) rate of electron emission remains same. Hence, the current remains same.
Q.3. (a) State the level of doping and biasing condition used in light emitting diode (LED).
(b) Write any two advantages of LED over the conventional low power lamps.
(a) LED is normally a heavily doped p-n junction diode. The doping level in LED determines the colour of light emitted.
LED is always operated in forward bias condition.
(b) Advantages of LED:
(i) LED has longer life span as compared to conventional lamps.
(ii) LED is extremely energy efficient device and may consume up to 90% less power than incandescent bulbs.
 |
Download the notes
Class 12 Physics: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 5
|
Download as PDF |
Section - B
Q.4. Derive an expression for the frequency of radiation emitted when a hydrogen atom de-excites from level n to level (n – 1). Also show that for large values of n, this frequency equals to classical frequency of revolution of an electron.
From Bohr ’s theory, the frequency f of the radiation emitted when an electron de – excites from level n2 to level n1 is given as
Given n1 = n − 1 , n2 = n , derivation of it
For large n, 2n − 1 = 2n , n − 1 = n and z = 1
Thus,
which is same as orbital frequency of electron in nth orbit.
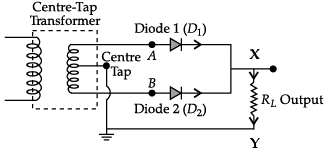
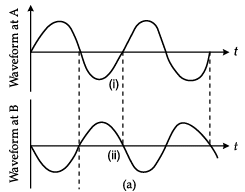
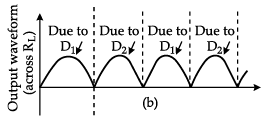
Q.5. Explain with a proper diagram how an ac signal can be converted into dc (pulsating) signal with output frequency as double than the input frequency using p-n junction diode. Give its input and output waveforms.
A junction diode allows current to pass only when it is forward biased. So, if an alternating voltage is applied across a diode the current flows only in that part of the cycle when the diode is forward biased. This property is used to rectify alternating voltages and the circuit used for this purpose is called a rectifier.
Circuit Diagram
Waveform in figure (a) in the input.
Output waveform shown in figure (b).
Q.6. How long can an electric lamp of 100 W be kept glowing by fusion of 2 kg of deuterium?
Take the fusion reaction as 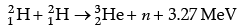
Number of atoms present in 2 g of deuterium = 6 × 1023
Number of atoms present in 2.0 kg of deuterium = 6 × 1026
Energy released in fusion of 2 deuterium atoms = 3.27 MeV
Energy released in fusion of 2.0 kg of deuterium atoms = (3.27/2) x 6 x 1026 MeV
= 9.81 x 1026 Me V
= 15.696 × 1013 J [∵ 1 MeV = 1.6 × 10–13 J]
Energy consumed by bulb per sec = 100 J
Time for which bulb will glow =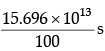
= 4.97 × 104 years
[∵ 1S = 3.169 × 10-8 years]
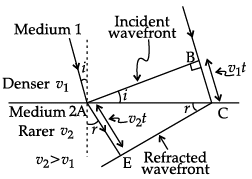
Q.7. Define wavefront. Draw the shape of refracted wavefront when the plane incident wave undergoes refraction from optically denser medium to rarer medium. Hence prove Snell’s law of refraction.
A locus of points, which oscillate in phase is called a wavefront.
OR
A wavefront is defined as a surface of constant phase.Derivation: AC is the surface separating the denser and rarer medium.
v1= speed of light wave in denser medium.
v2 = speed of light wave in rarer medium.
A plane wavefront AB is incident at an angle i with the normal to the interface.
Let t be the time taken by the wavefront to travel distance BC in the denser medium.
∴ BC = v1t
To determine the shape of the wavefront, a sphere of radius v2t is drawn in rarer medium with centre A. CE is the tangent drawn from point C on the sphere. CE represents the refracted wavefront.
AE makes an angle r with the normal to the interface.
AE = v2t
Considering the ∆ABC and ∆ AEC,...(i)
(i = Angle of incidence and r = Angle of refraction.)
If c be the speed of light in vacuum, then
μ1 = c/v1 and
μ2 = c/v2
Putting in equation (i)
μ1sin i = μ2 sin r
This is Snell’s law of refraction.
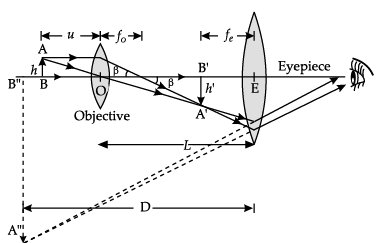
Q.8. (a) Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision?
(b) An angular magnification of 30X is desired using an objective of focal length 1.25 cm and an eye piece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound microscope for the final image formed at least distance of distinct vision?
OR
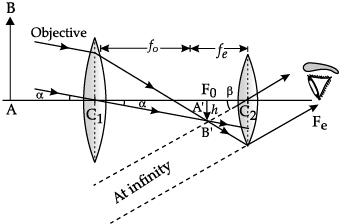
(a) Draw a ray diagram of Astronomical Telescope for the final image formed at infinity.
(b) A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5.0 cm. Find the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when
(i) the telescope is in normal adjustment,
(ii) the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision.
(a) Diagram of Compound Microscope for the final image formed at D:
(b) mo = 30, fo = 1.25 cm, fe = 5 cm
when image is formed at least distance of distinct vision, then D = 25 cm
Angular magnification of eyepiece
Total Angular magnification, m = mo me
As the objective lens forms the real image
m0 = v0/u0 = -5 ⇒ v0 = -5u0
using lens equation, uo = −1.5 cm,
vo = −5 × (−1.5) cm = +7.5 cm
Given ve = −D = −25 cm, fe = +5 cm, ue = ?
using again lens equation ue = 25/6
Thus, object is to be placed at 1.5 cm from the objective and separation between the two lenses should be L = |v0| + |ue| = 11.67 cm
OR
(a) Ray diagram of astronomical telescope when image is formed at infinity.
(b) (i) In normal adjustment : Magnifying power.
m = f0/fe = (140/5) = 28
(ii) When the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm) :
m = 33.6
Q.9. Light of wavelength 2000 Å falls on a metal surface of work function 4.2 eV.
(a) What is the kinetic energy (in eV) of the fastest electrons emitted from the surface?
(b) What will be the change in the energy of the emitted electrons if the intensity of light with same wavelength is doubled?
(c) If the same light falls on another surface of work function 6.5 eV, what will be the energy of emitted electrons?
λ = 2000 Å = (2000 × 10–10) m
Wo = 4.2eV
h = 6.63 × 10–34 (Js)
(a) Using Einstein's photoelectric equation
K.E. = hv – hv0
K.E. = hc/λ - W0
= 6.2 eV
K.E. = (6.2 – 4.2) eV = 2.0 eV
(b) The energy of the emitted electrons does not depend upon intensity of incident light; hence the energy remains unchanged.
(c) For this surface, electrons will not be emitted as the energy of incident light (6.2 eV) is less than the work function (6.5 eV) of the surface.
Q.10. The focal length of a convex lens made of glass of refractive index (1.5) is 20 cm.
What will be its new focal length when placed in a medium of refractive index 1.25 ? Is focal length positive or negative? What does it signify?
Given amg = 1.5
Focal length of the given convex lens when it is placed in air is f = + 20 cm
Refractive index of the given medium with respect to air is aμm = 1.25
New focal length of the given convex lens when placed in a medium is f'.
Dividing (A) by (B), we get
Here,
f ' = 2.5 f = (2.5 × 20) cm = + 50 cm
New focal length is positive.
The significance of the positive sign of the focal length is that given convex lens is still converging in the given medium.
Q.11. (a) Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
(b) If the Earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
(c) An e.m. wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident. Justify.
OR
(a) "If the slits in Young's double slit experiment are identical, then intensity at any point on the screen may vary between zero and four times to the intensity due to single slit".
Justify the above statement through a relevant mathematical expression.
(b) Draw the intensity distribution as function of phase angle when diffraction of light takes place through coherently illuminated single slit.
(a) Microwaves are suitable for the radar system used in aircraft navigation.
Range of frequency of microwaves is 108 Hz to 1011 Hz.
(b) If the Earth did not have atmosphere, then there would be absence of greenhouse effect of the atmosphere. Due to this reason, the temperature of the earth would be lower than what it is now,
(c) An e.m. wave carries momentum with itself and given by
when it is incident upon a surface, it exerts pressure on it.
OR
(a) The total intensity at a point where the phase difference is φ, is given by I = I1 + I2 +Here I1 and I2 are the intensities of two individual sources which are equal.
When φ is 0, I = 4I1.
When φ is 180°, I = 0
Thus intensity on the screen varies between 4I1 and 0.
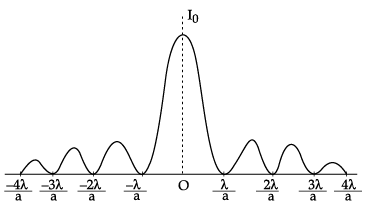
(b) Intensity distribution as function of phase angle, when diffraction of light takes place through coherently illuminated single slit.Width of central maximum = 2Dλ/a
Section - C
Q.12. Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Case Study : Photocell
A photocell is a technological application of the photoelectric effect. It is a device whose electrical properties are affected by light. It is also sometimes called an electric eye. A photocell consists of a semi-cylindrical photo-sensitive metal plate C (emitter) and a wire loop A (collector) supported in an evacuated glass or quartz bulb. It is connected to the external circuit having a high-tension battery B and micro ammeter (μA) as shown in the Figure.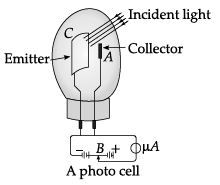
Sometimes, instead of the plate C, a thin layer of photosensitive material is pasted on the inside of the bulb. A part of the bulb is left clean for the light to enter it. When light of suitable wavelength falls on the emitter C, photoelectrons are emitted. These photoelectrons are drawn to the collector A. Photocurrent of the order of a few microampere can be normally obtained from a photo cell. A photocell converts a change in intensity of illumination into a change in photocurrent. This current can be used to operate control systems and in light measuring devices.
(a) Photocell is an application of
(i) thermoelectric effect.
(ii) photoelectric effect.
(iii) photoresistive effect.
(iv) None of these
(b) Photosensitive material should be connected to
(i) –ve terminal of the battery.
(ii) +ve terminal of the battery.
(iii) any one of (A) or (B).
(iv) connected to ground
(c) Which of the following statement is true?
(i) The photocell is totally painted black.
(ii) A part of the photocell is left clean.
(iii) The photocell is completely transparent.
(iv) A part of the photocell is made black.
(d) The photocurrent generated is in the order of
(i) ampere
(ii) milliampere
(iii) microampere
(iv) None of these
(e) A photocell converts a change in __________ of incident light into a change in __________.
(i) intensity, photovoltage
(ii) wavelength, photovoltage
(iii) frequency, photocurrent
(iv) intensity, photocurrent
(a) Option (ii) is correct.
Explanation: Photocell is a technological application of the photoelectric effect.
(b) Option (i) is correct.
Explanation: Photosensitive material used as emitter should be connected to -ve terminal of the battery so that the emitted electrons are repelled by emitter and collected by collector.
(c) Option (ii) is correct.
Explanation: A part of the bulb is left clean for the light to enter in it.(d) Option (iii) is correct.
Explanation: Photocurrent of the order of a few microampere can be normally obtained from a photocell.
(e) Option (iv) is correct.
Explanation: A photocell converts a change in intensity of illumination into a change in photocurrent. The magnitude of photocurrent depends on the number of photoelectrons which in turn depends on the intensity of the incident light. Hence any change in the light intensity can be converted to a change in photocurrent.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|